DOM
概念
DOM:文档对象模型,是一套标准的编程接口,可以通过DOM来操作html元素
js操作DOM元素
浏览器加载html的时候,会根据html的结构体形成一颗DOM树,dom树上有元素节点、属性节点。
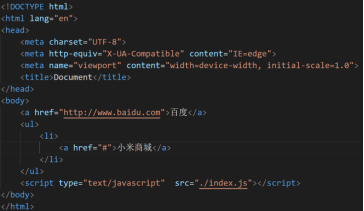
对应的DOM树
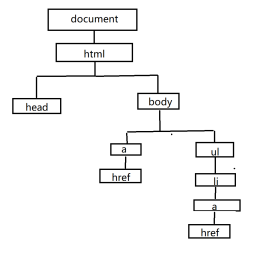
document对象
DOM通过document对象为开发者提供大量的接口来操作DOM树
获取节点

getElementById
<h1 id="title">hello h1</h1>
<script>
let h=document.getElementById("title");//返回值是一个dom节点
console.log(h);//<h1 id="title">hello h1</h1>
</script>
getElementByClassName
<body>
<button class="btn">1</button>
<button class="btn">2</button>
<button class="btn">3</button>
<script>
let btns = document.getElementsByClassName("btn");//返回值是dom节点的一个集合
console.log(btns);//HTMLCollection(3) [button.btn, button.btn, button.btn]
</script>
</body>
element.innerHTML/innerText
innerHTML和innerText都能获取和设置document对象的文本内容
innerHTML指的是从对象的起始位置到终止位置的全部内容,包括Html标签。
innerText指的是从起始位置到终止位置的内容,但它去除Html标签。
同时,innerHTML是所有浏览器都支持的,innerText是IE浏览器和chrome 浏览器支持的,Firefox浏览器不支持。
其实,innerHTML是W3C 组织规定的属性;而innerText属性是IE浏览器自己的属性,不过后来的浏览器部分实现这个属性罢了。
innerHTML是符合W3C标准的属性,而innerText只适用于IE浏览器(现在也适应chrome浏览器)
因此尽可能地去使用innerHTML,而少用innerText
如果要输出不含HTML标签的内容,可以使用innerHTML取得包含HTML标签的内容后,再用正则表达式去除HTML标签
- 获取内容
<h1 id="title">
hello h1
<p>hello p</p>
</h1>
<script>
let h=document.getElementById("title");
console.log(h.innerHTML);//带标签,如<p>
console.log(h.innerText);//不带标签
</script>
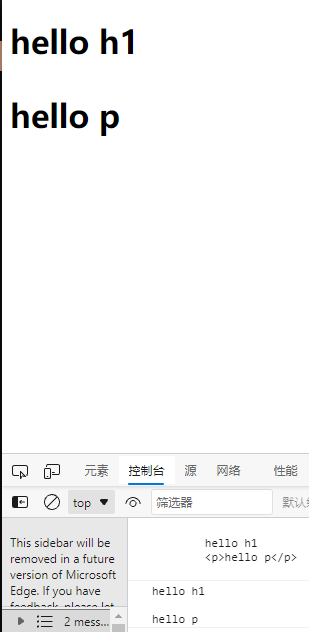
- 设置内容
<h1 id="title">
hello h1
<p>hello p</p>
</h1>
<script>
let h=document.getElementById("title");
console.log(h.innerHTML);
console.log(h.innerText);
h.innerHTML="hello hh1";
h.innerText="hello hhh1";//两者效果上一致,所以后面的会替换前者的效果
</script>

document.querySelector&querySelectorAll
getID和getClassName都是旧的方法,现在多采用效率更高的querySelector和querySelectorAll
通过选择器来获取节点
<h1 id="title">hello h1</h1>
<button class="btn">1</button>
<button class="btn">2</button>
<button class="btn">3</button>
<script>
let g1 = document.querySelector("#title");
let g2 = document.querySelector(".btn");//如果有多个相同的类名,只会选择第一个
console.log(g1);//<h1 id="title">hello h1</h1>
console.log(g2);//<button class="btn">1</button>
let g3 = document.querySelectorAll(".btn");//获取所有符合的节点
console.log(g3);//NodeList(3) [button.btn, button.btn, button.btn]
</script>
事件类型
触发某些事件,产生某些效果
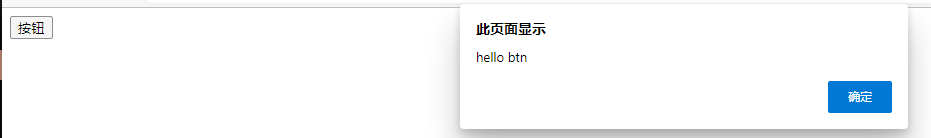
点击事件:onclick
点击按钮,弹出弹窗
<button class="btn">按钮</button>
<script>
let g = document.querySelector("button");
//事件监听函数
g.onclick = function(){
alert("hello btn");
}
</script>
鼠标移入元素:onmouseenter
<button class="btn">按钮</button>
<script>
let g = document.querySelector("button");
g.onmouseenter = function(){
console.log("enter");
}
</script>
移入鼠标打印enter

鼠标移出元素:onmouseleave
<button class="btn">按钮</button>
<script>
let g = document.querySelector("button");
g.onmouseleave = function(){
console.log("out");
}
</script>
移开鼠标打印out

事件设置样式
<style>
.box{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"></div>
<script>
let g = document.querySelector(".box");
g.onclick = function(){
this.style.backgroundColor = "blue";//this是g
}
g.onmouseenter = function(){
this.style.backgroundColor = "yellow";
}
g.onmouseleave = function(){
this.style.backgroundColor = "green";
}
</script>
</body>
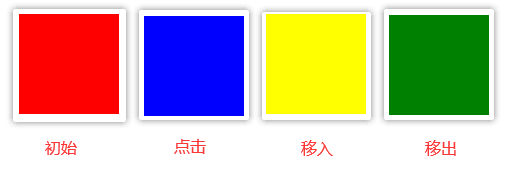
事件设置属性
- id、className
<button class="btn">1</button>
<script>
let g = document.querySelector("button");
g.onclick = function(){
g.id="btn1";//点击后设置id属性,有就覆盖,没有就添加
g.className="active";
}
</script>
- 利用className的变化实现样式
<style>
.active{
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button>1</button>
<button>2</button>
<button>3</button>
<script>
let btnArr = document.querySelectorAll("button");
for(let i of btnArr){
i.onclick=function(){
if(this.className==="active"){
this.className="";
}else{
this.className="active";
}
}
}
</script>
点击对应按钮就会加上类名active(前提是原类名没有active)背景色也会变成红色

如果本来的类名是active,点击后类名就会变为空,背景色变回原样

- img
<style>
img{
height: 500px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<img src="img/keli.jpg" alt="">
</div>
<button>1</button>
<button>2</button>
<button>3</button>
<script>
let img = document.querySelector("img");
let imgArr = ["img/keli.jpg","img/yae.png","img/jay.jpg"];
let btns = document.querySelectorAll("button");
for(let i in btns){//i=0,1,2 遍历按钮数组
btns[i].onclick=function(){//点击对应按钮切换相应图片
img.src=imgArr[i];
}
}
</script>
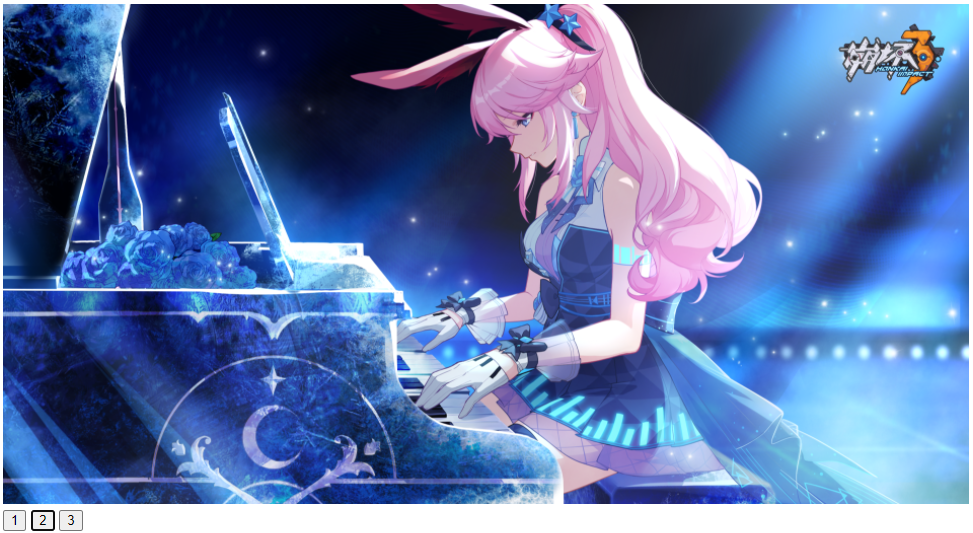
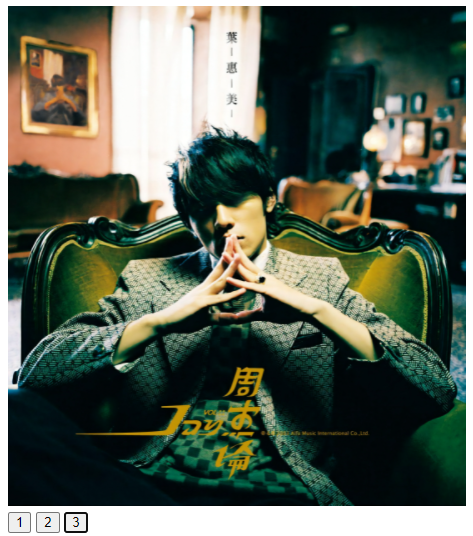


轮播图
3张图,flex布局横向排列,通过hidden隐藏掉超出的图片,通过向左平移实现图片的切换
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.swiper{
width: 640px;
height: 320px;
overflow: hidden;
position: relative;
}
.img-container{
width: 1920px;/*容纳3张图片以实现横向排列*/
height: 320px;
transition: transform 0.3s;/*切换图片*/
display: flex;/*消除幽灵空白*/
}
.img-container img{
width: 640px;
height: 320px;
}
.btn-list{
position: absolute;/*绝对定位抵消隐藏*/
bottom: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="swiper">
<div class="img-container">
<img src="img/keli.jpg" alt="">
<img src="img/yae.png" alt="">
<img src="img/jay.jpg" alt="">
</div>
<div class="btn-list">
<button>1</button>
<button>2</button>
<button>3</button>
</div>
</div>
<script>
let btn = document.querySelectorAll(".btn-list button");
let container = document.querySelector(".img-container");
for(let i in btn){
btn[i].onclick = function(){
/*
0 * 640 = 0
1 * 640 = 640
2 * 640 = 1280
*/
container.style.transform = `translate(${-640*i}px)`;//不同按钮有相应的偏移值
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
DOM节点分类

innerHtml
innerHtml不只能设置文本,还能设置标签、属性等内容
点击按钮显示列表
<button>按钮</button>
<ul></ul>
<script>
let btn = document.querySelector("button");
let u = document.querySelector("ul");
btn.onclick = function(){
u.innerHTML = `
<li>苹果</li>
<li>香蕉</li>
<li>雪梨</li>
`;
}
</script>

innerHtml是一个大刀阔斧的操作,一般用更细致的操作
节点操作

通过添加节点的方式
<input type="text">
<button>按钮</button>
<ul></ul>
<script>
let inp = document.querySelector("input");
let btn = document.querySelector("button");
let ul1 = document.querySelector("ul");
btn.onclick = function(){
let li1 = document.createElement("li");//创建li标签
let value1 = inp.value;//将文本框输入的内容赋值给value1
let txt = document.createTextNode(value1);//创建文本,内容是value1
ul1.appendChild(li1);//将li1即li标签添加到ul1即ul中
li1.appendChild(txt);//将txt即文本添加到li1即li标签中
}
</script>

点击列表,删除列表项
<input type="text">
<button>按钮</button>
<ul class="fruit">
<li>苹果</li>
<li>香蕉</li>
<li>雪梨</li>
</ul>
<script>
let inp = document.querySelector("input");
let btn = document.querySelector("button");
let ul1 = document.querySelector("ul");
let list = document.querySelectorAll(".fruit li");
btn.onclick = function(){
let li1 = document.createElement("li");
let value1 = inp.value;
let txt = document.createTextNode(value1);
ul1.appendChild(li1);
li1.appendChild(txt);
}
for(let i in list){
list[i].onclick = function(){//点击列表删除列表
ul1.removeChild(this);//removeChild删除节点
//this是list[i]调用的,指代一个li
}//这个删不了新添加的列表,因为list选中的li是加载时就确定的,新添加的不在其中
}
</script>
事件对象
<style>
.box{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"></div>
<script>
let b = document.querySelector(".box");
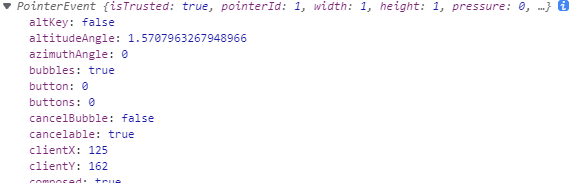
b.onclick = function(e){//e就是事件对象,可以取任何名字,就是个形参,建议e或者Event
console.log(e);//返回值是一个对象,里面包含一些关于事件对象的信息
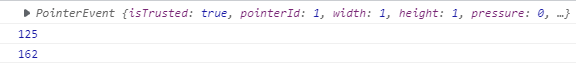
console.log(e.clientX);//鼠标点击位置的x坐标
console.log(e.clientY);//鼠标点击位置的y坐标
}
</script>
</body>
随鼠标移动显示大图
<style>
.pic-list img{
width: 320px;
height: 160px;
}
.pic-big img{
width: 640px;
height: 320px;
}
.pic-big{
position: absolute;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="pic-list">
<img src="img/1.jpg" alt="">
<img src="img/2.jpg" alt="">
<img src="img/3.jpg" alt="">
</div>
<div class="pic-big"></div>
<script>
let pics = document.querySelectorAll(".pic-list img");
let bigPic = document.querySelector(".pic-big");
let picList = document.querySelector(".pic-list");
for(let i in pics){
pics[i].onmouseenter = function(){
bigPic.innerHTML = `<img src="${this.src}">`;//this指向pics[i]
}
pics[i].onmouseleave = function(){
bigPic.innerHTML = ``;
}
}
picList.onmousemove = function(e){
let x = e.clientX;
let y = e.clientY;
bigPic.style.top = y + 10 + "px";//如果不加10,bigpic的图片会挡住picList,从而触发picList的移出js
bigPic.style.left = x + 10 + "px";
}
</script>
</body>




