flex布局
概述
此前我们制作的所有网页都是基于盒子模型和浮动布局完成的
今天学习flex布局,又叫弹性布局(或者叫弹性盒子布局)
这是一种更先进的布局方式,可以让网页布局更简洁,更易于维护。
将元素设置成display:flex;元素会变成一个flex容器,容器内部的元素称为flex元素或flex项目(flex-item)。
基本概念
主轴、交叉轴

flex容器的默认效果
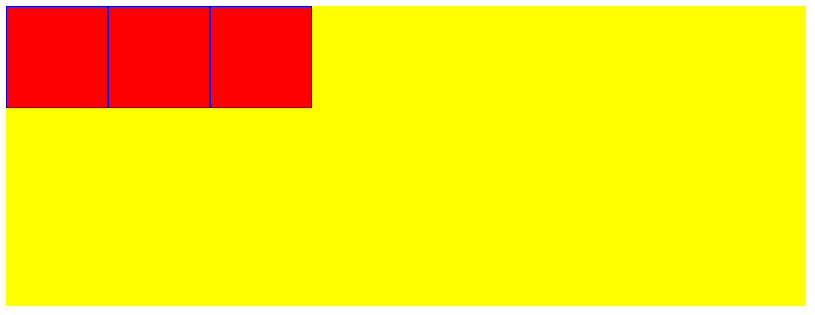
- flex项目在flex容器中延主轴排列
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.container{
display: flex;
width: 800px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.item{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid blue;
/*默认情况下flex容器内的元素是横向显示的*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="item"></div>
<div class="item"></div>
<div class="item"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
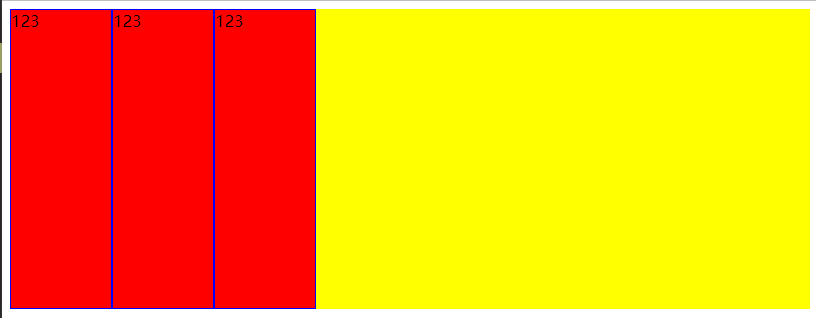
如果不是flex布局,则item会垂直分布

- flex项目高度适应flex容器高度(同行内元素)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.container{
/* display: flex; */
width: 800px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.item{
width: 100px;
/* height: 100px; */
/*没有设置高度的话,其高度取决于内容的高度,这里是文本123的高度*/
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="item">123</div>
<div class="item">123</div>
<div class="item">123</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

如果是flex布局,则没有设置高度的情况下默认高度是flex布局的高度
设置flex容器
flex-direction
flex-direction:设置flex项目的排列方向

- row
- row-reverse
- column
column和column-reverse主轴就会变成垂直方向,交叉轴变成水平方向

- column-reverse

一般用的最多的还是默认值row
justify-content
justify-content:flex项目主轴排列方式

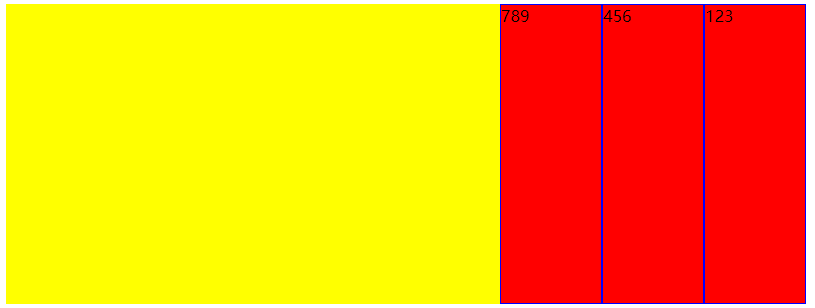
- flex-start:左对齐,默认值
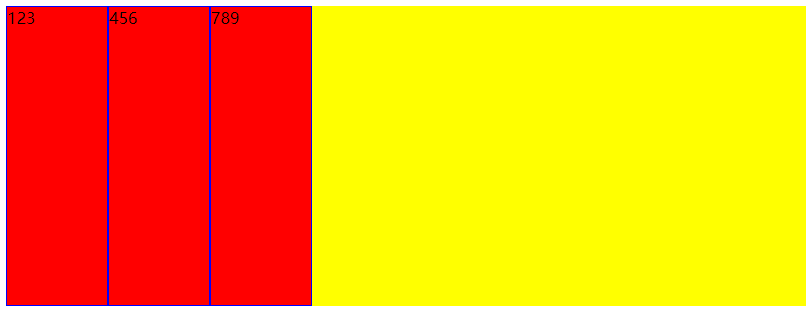
- flex-end:右对齐
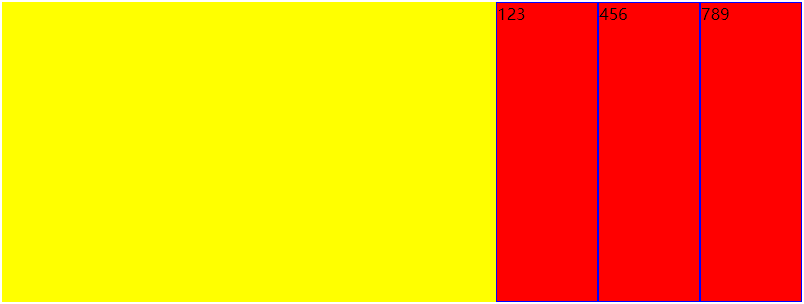
- center:居中

- space-between:两端对齐,项目间的间隔相同
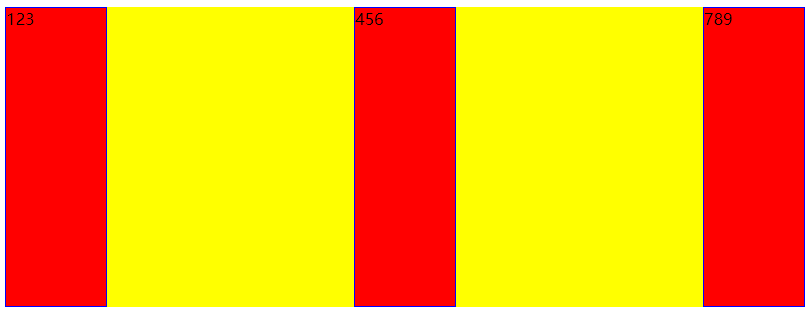
- space-around:每个项目两端的间隔相同
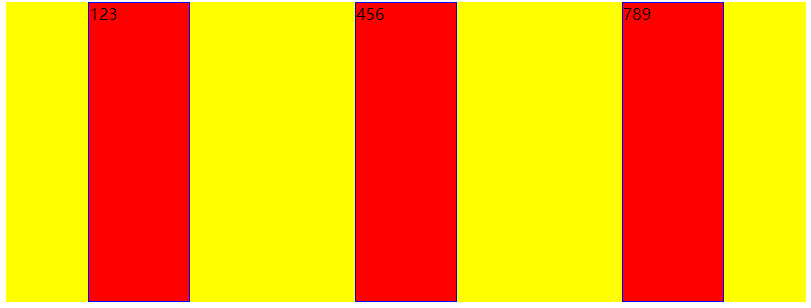
一般最常用的是居中center
align-items
align-items:flex项目在交叉轴的排列方式

- stretch:默认值,自适应占满flex容器的高度
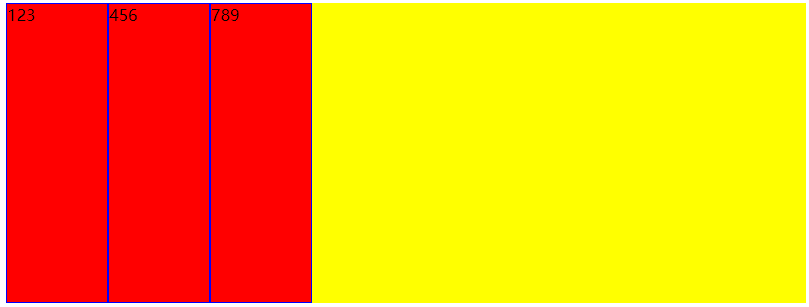
- flex-start:交叉轴的起点对齐

- flex-end:交叉轴的终点对齐

- center:交叉轴居中对齐
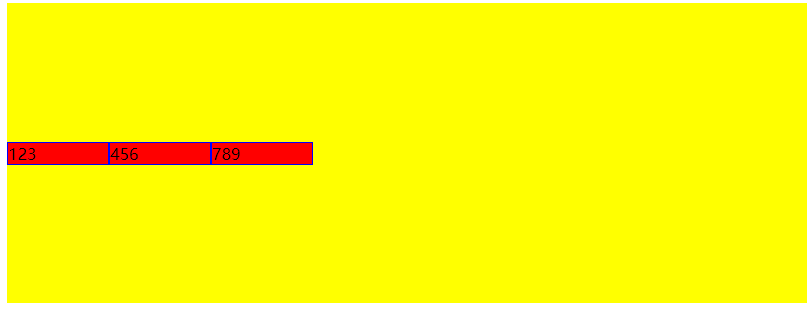
一般最常用的是居中center
设置flex项目

flow-grow:按照比例放大flex项目
初始状态
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.container{
display: flex;
/* justify-content: space-around;
align-items: center; */
width: 800px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.item{
/* width: 100px; */
/* height: 100px; */
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="item1">123</div>
<div class="item2">456</div>
<div class="item3">789</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

设置flex-grow
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.container{
display: flex;
/* justify-content: space-around;
align-items: center; */
width: 800px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.item1,.item3{
/* width: 100px; */
/* height: 100px; */
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid blue;
flex-grow: 1;
}
.item2{
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid blue;
flex-grow: 3;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="item1">123</div>
<div class="item2">456</div>
<div class="item3">789</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

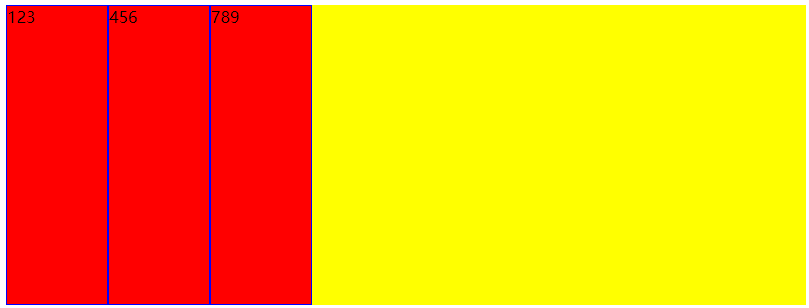
flex-shrink:按照比例缩小flex项目,用的很少
首先flex项目是不会超出flex容器的,当宽度设置超过了flex容器的大小,页面上显示还是占满整个容器而非超过,而实际宽度会按照1的比例缩小
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.container{
display: flex;
width: 800px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.item1,.item2,.item3{
width: 300px;/*总共是900px,超过了容器的800px*/
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="item1">123</div>
<div class="item2">456</div>
<div class="item3">789</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

每一个宽度是264.672px,并不是300px,说明默认下会被缩小
如果设置flex-shrink,就是按照shrink的数值为比例缩小
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.container{
display: flex;
width: 800px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.item1,.item2,.item3{
width: 300px;/*总共是900px,超过了容器的800px*/
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid blue;
}
.item2{
flex-shrink: 5;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="item1">123</div>
<div class="item2">456</div>
<div class="item3">789</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
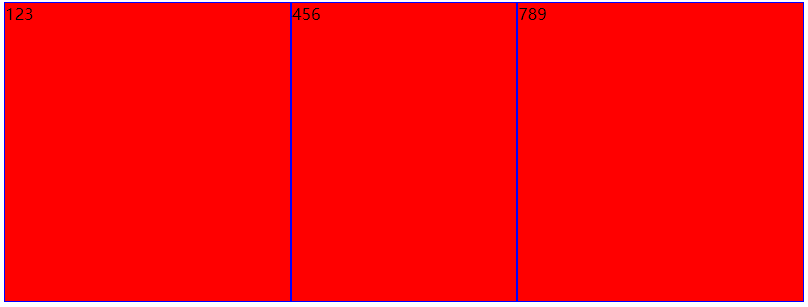
flex-basis
表示在flex项目被放入flex容器之前的大小,也就是items的理想或者假设大小,但是并不是其真实大小,其真实大小取决于flex容器的宽度
flex-basis不常用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.container{
display: flex;
width: 800px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.item1,.item2,.item3{
width: 300px;
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid blue;
}
.item2{
flex-basis: 600px;/*当flex-basis和width属性同时存在时,width属性不生效,flex item的宽度为flex-basis设置的宽度*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="item1">123</div>
<div class="item2">456</div>
<div class="item3">789</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

flex:上述三个属性的综合写法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.container{
display: flex;
width: 800px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.item1,.item2,.item3{
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid blue;
flex: 1 2 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="item1">123</div>
<div class="item2">456</div>
<div class="item3">789</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
不过flex后两个属性用的很少,所以更常见的写法是flex:1;
align-self:单独给flex项目设置的对齐方式
默认是auto
- center:居中
初始状态
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.container{
display: flex;
width: 800px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.item1,.item2,.item3{
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid blue;
flex: 1;
}
.item2{
height: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="item1">123</div>
<div class="item2">456</div>
<div class="item3">789</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
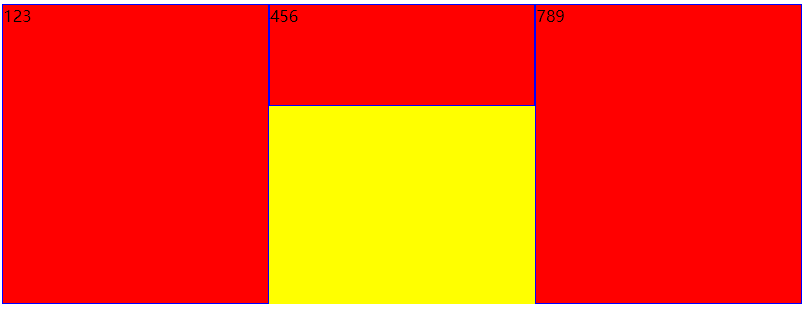
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.container{
display: flex;
width: 800px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.item1,.item2,.item3{
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid blue;
flex: 1;
}
.item2{
height: 100px;
align-self: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="item1">123</div>
<div class="item2">456</div>
<div class="item3">789</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
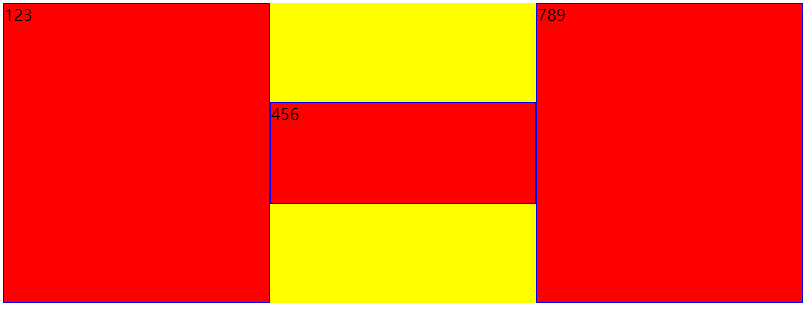
其他的与align-items类似
使用思路
用flex布局时,先想主轴交叉轴怎么排列,再想单独的flex项目怎么排列,属性用到就查笔记
练习
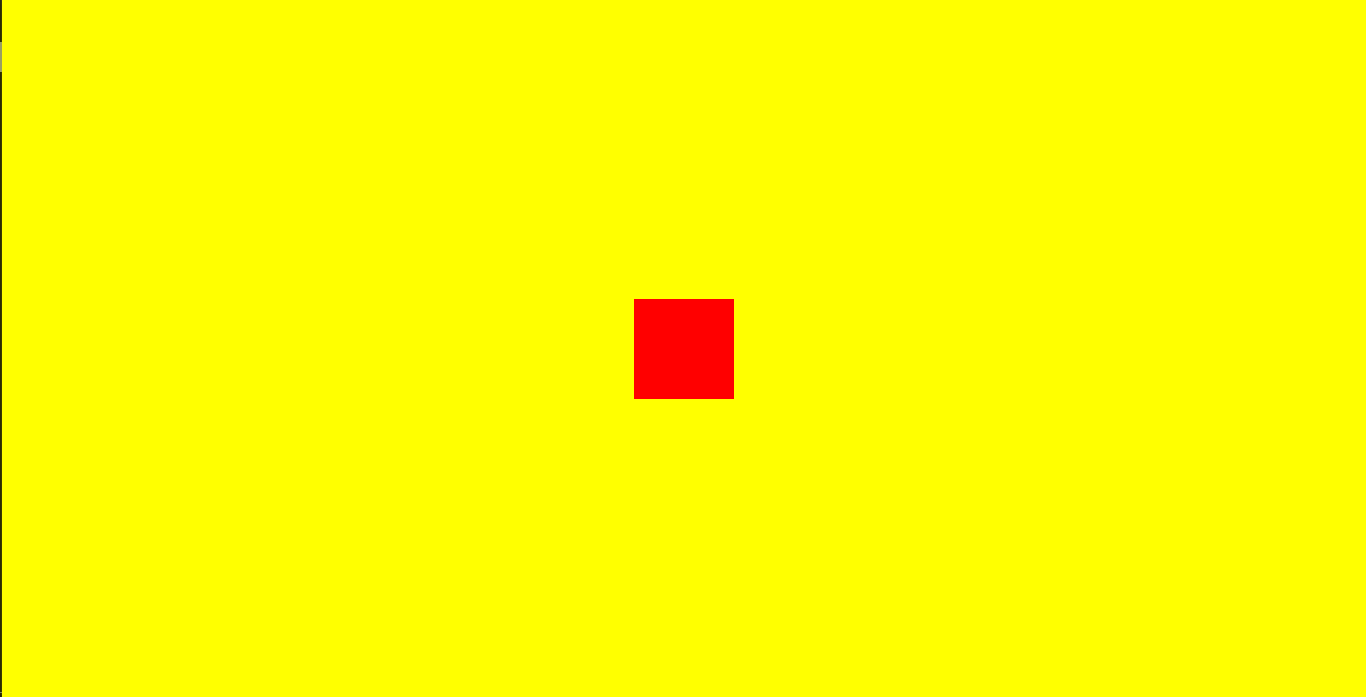
设置一个元素在容器中水平垂直居中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.container{
background-color: yellow;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100%;
}
body,html{
height: 100%;
/*如果需要一个元素占浏览器的100%显示,就需要将它所有的父级高度都设置成100%
这里要将container设置成页面的100%,它的父级是body和html
*/
}
.box{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
/* align-self: center; */
/*单独给项目设置垂直居中用这个,给整个容器设置垂直居中用align-items*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="box">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
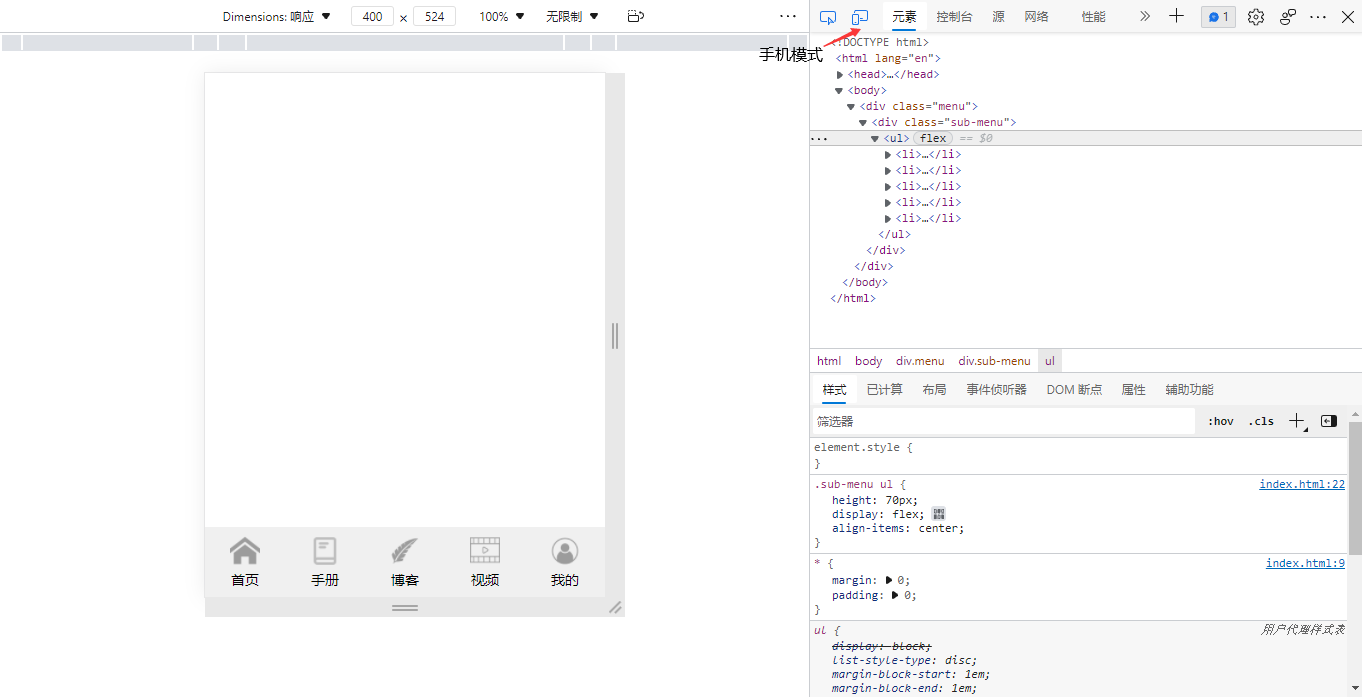
制作右侧网页的底部菜单
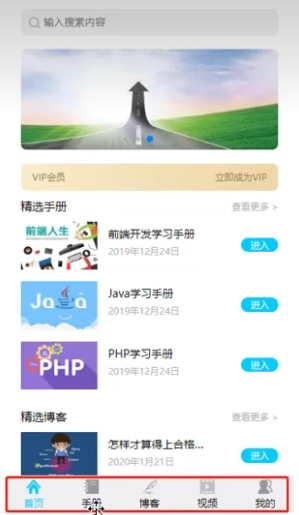
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.menu{
background-color: rgb(240,240,240);
width: 100%;
height: 70px;
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
}
.sub-menu ul{
height: 70px;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.sub-menu ul li{
flex: 1;
list-style: none;
text-align: center;
}
.sub-menu li a{
text-decoration: none;
color: black;
display: block;
font-size: 14px;
}
.sub-menu img{
width: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="menu">
<div class="sub-menu">
<ul>
<li>
<a href="#">
<img src="img/home.png" alt="">
<p>首页</p>
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">
<img src="img/book.png" alt="">
<p>手册</p>
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">
<img src="img/blog.png" alt="">
<p>博客</p>
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">
<img src="img/video.png" alt="">
<p>视频</p>
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">
<img src="img/mine.png" alt="">
<p>我的</p>
</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>