986. Interval List Intersections
Given two lists of closed intervals, each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order.
Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
(Formally, a closed interval [a, b] (with a <= b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a <= x <= b. The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that is either empty, or can be represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].)
Example 1:
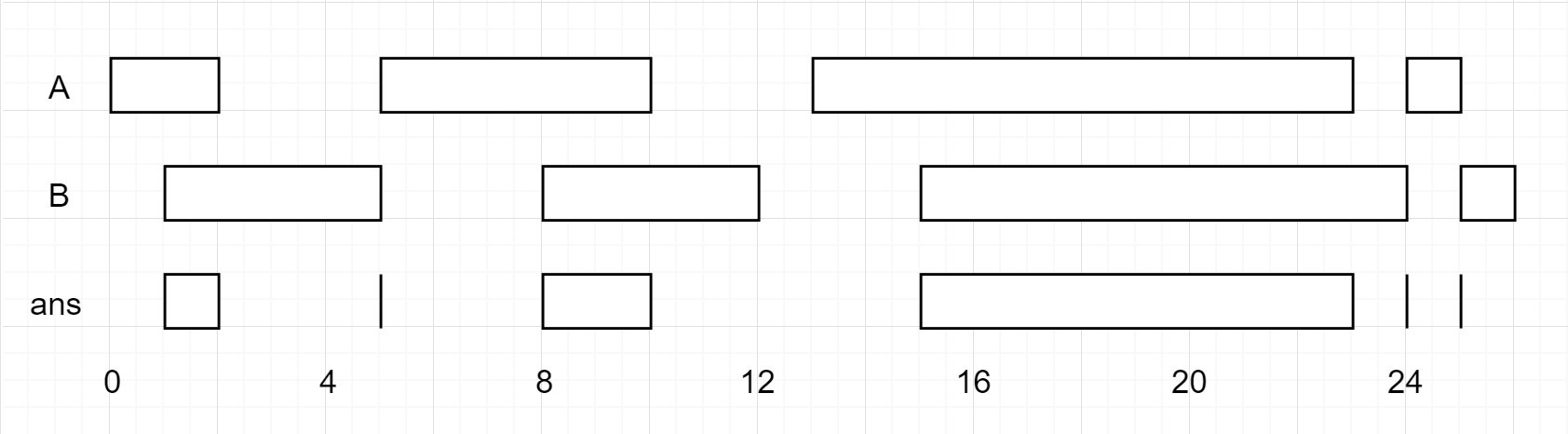
Input: A = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], B = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]] Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]] Reminder: The inputs and the desired output are lists of Interval objects, and not arrays or lists.
1 class Solution { 2 public int[][] intervalIntersection(int[][] A, int[][] B) { 3 if (A == null || A.length == 0 || B == null || B.length == 0) { 4 return new int[0][0]; 5 } 6 7 int m = A.length, n = B.length; 8 int i = 0, j = 0; 9 List<int[]> res = new ArrayList<>(); 10 while (i < m && j < n) { 11 int[] a = A[i]; 12 int[] b = B[j]; 13 14 // find the overlap... if there is any... 15 int startMax = Math.max(a[0], b[0]); 16 int endMin = Math.min(a[1], b[1]); 17 18 if (endMin >= startMax) { 19 res.add(new int[]{startMax, endMin}); 20 } 21 22 //update the pointer with smaller end value... 23 if (a[1] == endMin) { i++; } 24 if (b[1] == endMin) { j++; } 25 } 26 return res.toArray(new int[0][0]); 27 } 28 }

