es6 class解析
直入主题。源代码如下:
class A{
aName = 'A'
constructor(aAge){
this.aAge = aAge
}
static aStatic = 'aStatic'
}
class B extends A{
bName = 'b'
constructor(bAge){
super()
this.bAge = bAge
}
static bStatic = 'bStatic'
}
var b = new B;
使用babel转换后的代码如下:
"use strict";
// typeof
function _typeof(obj) {}
function _inherits(subClass, superClass) {
if (typeof superClass !== "function" && superClass !== null) {
throw new TypeError("Super expression must either be null or a function");
}
subClass.prototype = Object.create(superClass && superClass.prototype, {
constructor: { value: subClass, writable: true, configurable: true },
});
Object.defineProperty(subClass, "prototype", { writable: false });
if (superClass) _setPrototypeOf(subClass, superClass);
}
// 设置原型 setPrototypeOf
function _setPrototypeOf(o, p) {}
function _createSuper(Derived) {
var hasNativeReflectConstruct = _isNativeReflectConstruct();
return function _createSuperInternal() {
var Super = _getPrototypeOf(Derived),
result;
if (hasNativeReflectConstruct) {
var NewTarget = _getPrototypeOf(this).constructor;
result = Reflect.construct(Super, arguments, NewTarget);
} else {
result = Super.apply(this, arguments);
}
return _possibleConstructorReturn(this, result);
};
}
function _possibleConstructorReturn(self, call) {
if (call && (_typeof(call) === "object" || typeof call === "function")) {
return call;
} else if (call !== void 0) {
throw new TypeError(
"Derived constructors may only return object or undefined"
);
}
return _assertThisInitialized(self);
}
function _assertThisInitialized(self) {
if (self === void 0) {
throw new ReferenceError(
"this hasn't been initialised - super() hasn't been called"
);
}
return self;
}
// 是否支持 Reflect.construct
function _isNativeReflectConstruct() {}
// 获取原型 getPrototypeOf
function _getPrototypeOf(o) {}
// 定义属性
function _defineProperties(target, props) {
for (var i = 0; i < props.length; i++) {
var descriptor = props[i];
descriptor.enumerable = descriptor.enumerable || false;
descriptor.configurable = true;
if ("value" in descriptor) descriptor.writable = true;
Object.defineProperty(target, descriptor.key, descriptor);
}
}
// 给prototype设置属性 / 设置static属性 / 禁止修改prototype
function _createClass(Constructor, protoProps, staticProps) {
if (protoProps) _defineProperties(Constructor.prototype, protoProps);
if (staticProps) _defineProperties(Constructor, staticProps);
Object.defineProperty(Constructor, "prototype", { writable: false });
return Constructor;
}
// 检查 <不能将类作为函数调用>
function _classCallCheck(instance, Constructor) {}
// 设置属性
function _defineProperty(obj, key, value) {
if (key in obj) {
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
value: value,
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
writable: true,
});
} else {
obj[key] = value;
}
return obj;
}
var A = /*#__PURE__*/ _createClass(function A(aAge) {
_classCallCheck(this, A);
_defineProperty(this, "aName", "A");
this.aAge = aAge;
});
_defineProperty(A, "aStatic", "aStatic");
var B = /*#__PURE__*/ (function (_A) {
_inherits(B, _A);
var _super = _createSuper(B);
function B(bAge) {
var _this;
_classCallCheck(this, B);
_this = _super.call(this);
_defineProperty(_assertThisInitialized(_this), "bName", "b");
_this.bAge = bAge;
return _this;
}
return _createClass(B);
})(A);
_defineProperty(B, "bStatic", "bStatic");
var b = new B();
流程图如下:
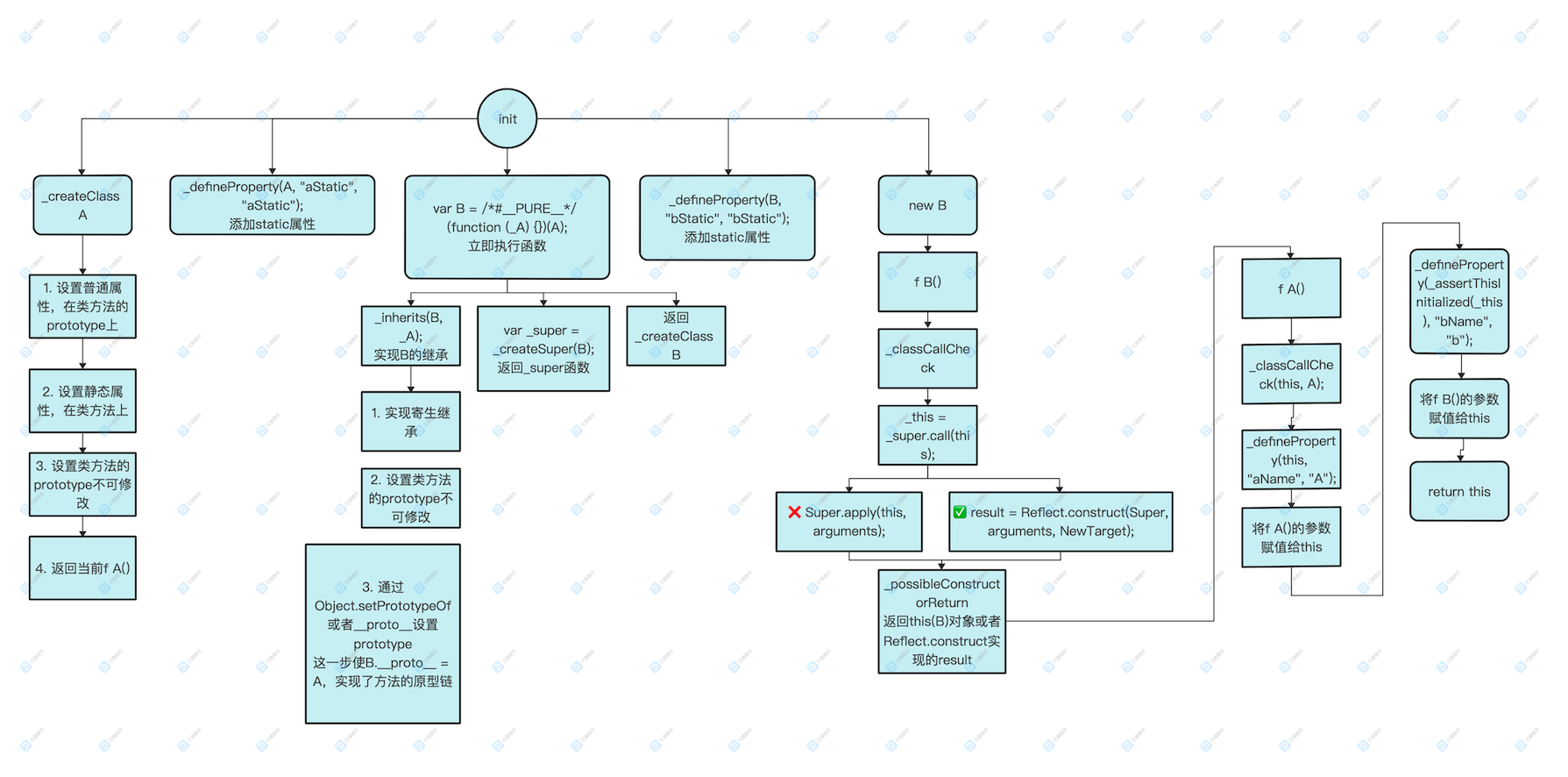
第一步会执行到这一行:
var A = /*#__PURE__*/ _createClass(function A(aAge) {
进入_createClass, 执行结束后返回处理过的 function A
- 给构造函数的原型设置属性(原型属性)
- 给构造函数本身设置属性(静态属性)
- 禁止修改 构造函数的prototype
- 最后返回构造函数本身
function _createClass(Constructor, protoProps, staticProps) {
if (protoProps) _defineProperties(Constructor.prototype, protoProps);
if (staticProps) _defineProperties(Constructor, staticProps);
Object.defineProperty(Constructor, "prototype", { writable: false });
return Constructor;
}
第二步执行:
_defineProperty(A, "aStatic", 'aStatic');
在这里给A设置aStatic=aStatic.
当key在obj中存在时,修改它的value,并且设置为可枚举,可删除,可修改
否则在obj中新增value.
// 设置属性
function _defineProperty(obj, key, value) {
if (key in obj) {
// 修改
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
value: value,
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
writable: true,
});
} else {
// 新增
obj[key] = value;
}
return obj;
}
第三部执行
var B = /*#__PURE__*/ (function (_A) {
这里实现了原型继承和方法继承
_inherits(B, _A);
subClass.prototype = Object.create(superClass && superClass.prototype, {
constructor: { value: subClass, writable: true, configurable: true },
});
这里可以拆分成3部分
- Object.create(superClass && superClass.prototype);
Object.create()方法创建一个新对象,使用现有的对象来提供新创建的对象的__proto__
也就是说这里生成了一个空对象{},空对象的__proto__是父类的.prototype.
也就是{}.__proto__ = { constructor: f A() }
- { constructor: { value: subClass, writable: true, configurable: true } }
如果该参数被指定且不为 undefined,将为新创建的对象添加指定的属性值和对应的属性描述符。
这里给上面创建的空对象添加constructor属性,值是f B(),并且设置constructor可修改/删除,不可被枚举
就变成了这样{ constructor: f B() }.__proto__ = { constructor: f A() }
- subClass.prototype =
这里给B设置原型
相当于B.prototype = { constructor: f B() }.__proto__ = { constructor: f A() }
到这里,原型继承就实现成功了.
Object.defineProperty(subClass, "prototype", { writable: false });
设置B的prototype不可写
if (superClass) _setPrototypeOf(subClass, superClass);
这里实现了方法的继承,B.__proto__ = A
function的寄生组合继承是没有上面一步的.只有class extends才有.
var _super = _createSuper(B);
判断了环境是否支持Reflect.construct,返回_createSuperInternal闭包给_super变量
return _createClass(B);
同上 _createClass A
_defineProperty(B, "bStatic", "bStatic");
同上
第四步执行 new
var b = new B();
先执行 function B(bAge) { 里面的内容
检查是否为function _classCallCheck(this, B);
调用上面的_super函数, _this = _super.call(this); ,执行 _createSuperInternal
var Super = _getPrototypeOf(Derived),
result;
if (hasNativeReflectConstruct) {
var NewTarget = _getPrototypeOf(this).constructor;
result = Reflect.construct(Super, arguments, NewTarget);
} else {
result = Super.apply(this, arguments);
}
return _possibleConstructorReturn(this, result);
通过 Reflect.construct 或者 Super.apply 得到实例对象.接下来将 this(也就是f B()) 和 result 传递给 _possibleConstructorReturn
function _possibleConstructorReturn(self, call) {
if (call && (_typeof(call) === "object" || typeof call === "function")) {
return call;
} else if (call !== void 0) {
throw new TypeError(
"Derived constructors may only return object or undefined"
);
}
return _assertThisInitialized(self);
}
function _assertThisInitialized(self) {
if (self === void 0) {
throw new ReferenceError(
"this hasn't been initialised - super() hasn't been called"
);
}
return self;
}
result有值,并且是object或者function时返回resultresult是基本类型时报错- 否则返回B对象
_defineProperty(_assertThisInitialized(_this), "bName", "b");
给B对象设置class中定义好的属性_this.bAge = bAge;
执行constructor中的this.bAge = bAge
返回B对象return _this;



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号