go ants源码分析
golang ants 源码分析
结构图
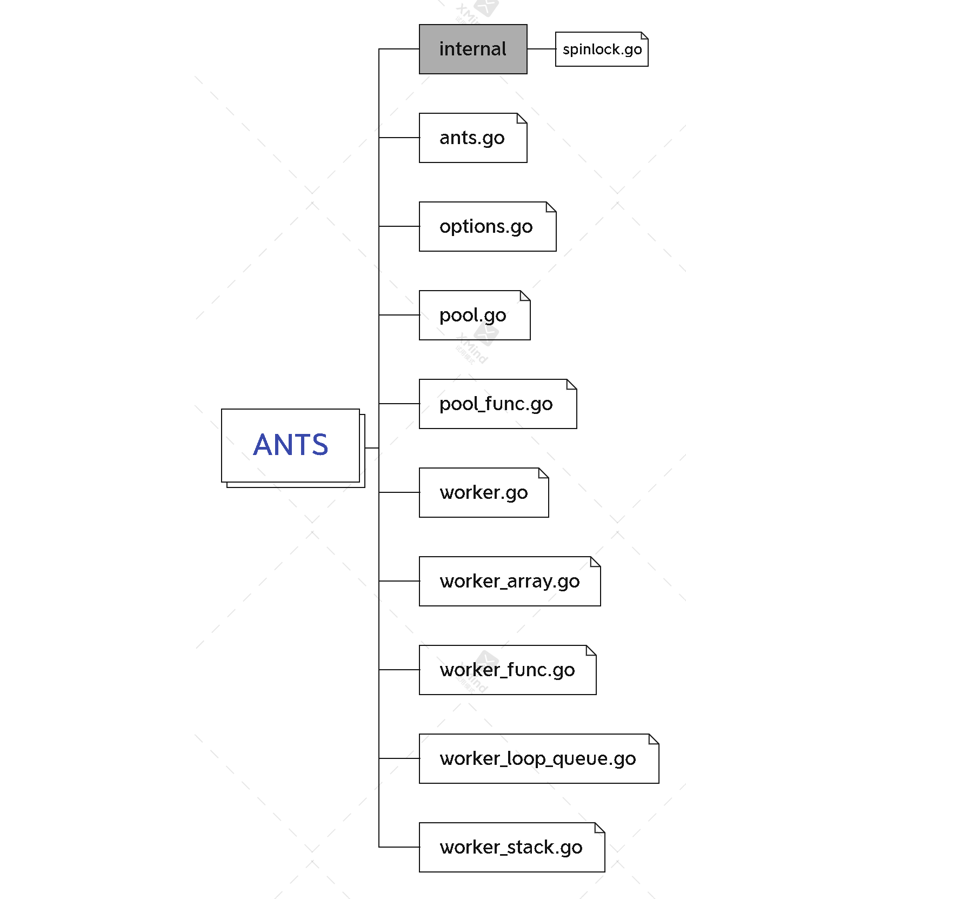
poolwithfunc与pool相差不大,这里我们只分析ants默认pool的流程
| 文件 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| ants.go | 定义常量、errors显示、默认建一个大小为2147483647的goroutine池、封装一些方便用户操作查看goroutine池的函数 |
| options.go | goroutine池的相关配置 |
| pool.go | 普通pool(不绑定特定函数)的创建以及对pool相关的操作 |
| pool_func.go | 创建绑定某个特定函数的pool以及对pool相关的操作 |
| worker.go | goworker的struct(其他语言中的类)、run(其他语言中的方法) |
| worker_array.go | 一个worker_array的接口和一个能返回实现该接口的函数 |
| worker_func.go | 略 |
| worker_loop_queue.go | 略 |
| worker_stack.go | workerStack(struct)实现worker_array中的所有接口 |
| spinlock.go | 锁相关 |
关键结构
type Pool struct
type Pool struct {
capacity int32 // 容量
running int32 // 正在运行的数量
lock sync.Locker //定义一个锁 用以支持 Pool 的同步操作
workers workerArray // workers 一个接口 存放可循环利用的Work(goroutine)的相关信息
// type workerArray interface {
// len() int
// isEmpty() bool
// insert(worker *goWorker) error
// detach() *goWorker
// retrieveExpiry(duration time.Duration) []*goWorker
// reset()
// }
state int32 //记录池子的状态(关闭,开启)
cond *sync.Cond // 条件变量
workerCache sync.Pool // golang原始池子 使用sync.Pool对象池管理和创建worker对象,提升性能
blockingNum int // 阻塞等待的任务数量;
stopHeartbeat chan struct{} //一个空结构体的通道,仅用于接收标志
options *Options // 用于配置pool的options指针
}
- func (p *Pool) purgePeriodically() //定期清理过期worker任务
- func (p *Pool) Submit(task func()) error //提交func任务与worker绑定进行运行
- func (p *Pool) Running() int //有多少个运行的worker
- func (p *Pool) Free() int //返回空闲的worker数量
- func (p *Pool) Cap() int // 返回pool的容量
- ......
- func (p *Pool) retrieveWorker() (w *goWorker) //返回一个worker
workerArray
type workerArray interface {
len() int // worker的数量
isEmpty() bool // worker是否为0
insert(worker *goWorker) error //将执行完的worker(goroutine)放回
detach() *goWorker // 获取worker
retrieveExpiry(duration time.Duration) []*goWorker //取出所有的过期 worker;
reset() // 重置
}
workerStack
type workerStack struct {
items []*goWorker //空闲的worker
expiry []*goWorker //过期的worker
size int
}
下面是对接口workerArray的实现
func (wq *workerStack) len() int {
return len(wq.items)
}
func (wq *workerStack) isEmpty() bool {
return len(wq.items) == 0
}
func (wq *workerStack) insert(worker *goWorker) error {
wq.items = append(wq.items, worker)
return nil
}
//返回items中最后一个worker
func (wq *workerStack) detach() *goWorker {
l := wq.len()
if l == 0 {
return nil
}
w := wq.items[l-1]
wq.items[l-1] = nil // avoid memory leaks
wq.items = wq.items[:l-1]
return w
}
func (wq *workerStack) retrieveExpiry(duration time.Duration) []*goWorker {
n := wq.len()
if n == 0 {
return nil
}
expiryTime := time.Now().Add(-duration) //过期时间=现在的时间-1s
index := wq.binarySearch(0, n-1, expiryTime)
wq.expiry = wq.expiry[:0]
if index != -1 {
wq.expiry = append(wq.expiry, wq.items[:index+1]...) //因为以后进先出的模式去worker 所有过期的woker这样wq.items[:index+1]取
m := copy(wq.items, wq.items[index+1:])
for i := m; i < n; i++ { //m是存活的数量 下标为m之后的元素全部置为nil
wq.items[i] = nil
}
wq.items = wq.items[:m] //抹除后面多余的内容
}
return wq.expiry
}
// 二分法查询过期的worker
func (wq *workerStack) binarySearch(l, r int, expiryTime time.Time) int {
var mid int
for l <= r {
mid = (l + r) / 2
if expiryTime.Before(wq.items[mid].recycleTime) {
r = mid - 1
} else {
l = mid + 1
}
}
return r
}
func (wq *workerStack) reset() {
for i := 0; i < wq.len(); i++ {
wq.items[i].task <- nil //worker的任务置为nil
wq.items[i] = nil //worker置为nil
}
wq.items = wq.items[:0] //items置0
}
流程分析
创建pool
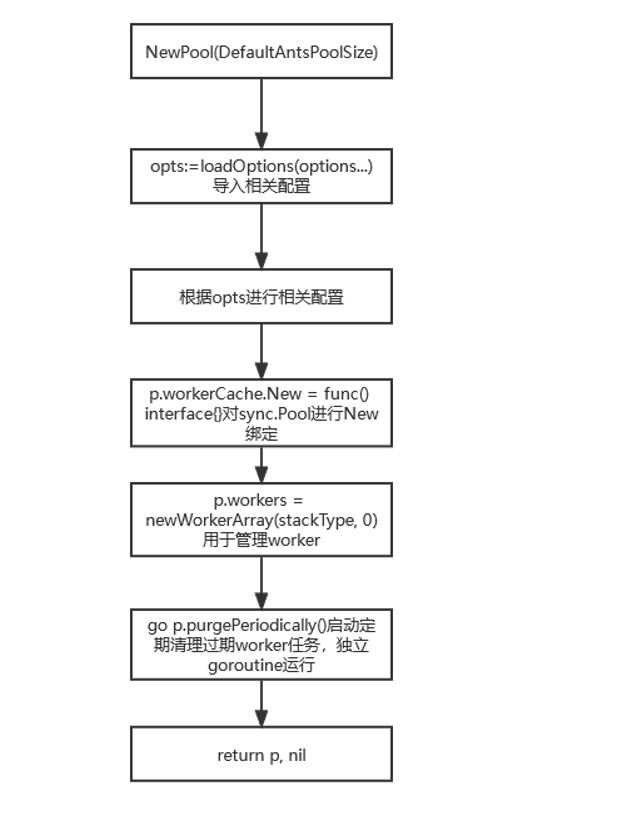
func NewPool(size int, options ...Option) (*Pool, error) {
opts := loadOptions(options...) // 导入配置
根据不同项进行配置此处省略
p := &Pool{
capacity: int32(size),
lock: internal.NewSpinLock(),
stopHeartbeat: make(chan struct{}, 1), //开一个通道用于接收一个停止标志
options: opts,
}
p.workerCache.New = func() interface{} {
return &goWorker{
pool: p,
task: make(chan func(), workerChanCap),
}
}
p.workers = newWorkerArray(stackType, 0)
p.cond = sync.NewCond(p.lock)
go p.purgePeriodically()
return p, nil
}
提交任务(将worker于func绑定)
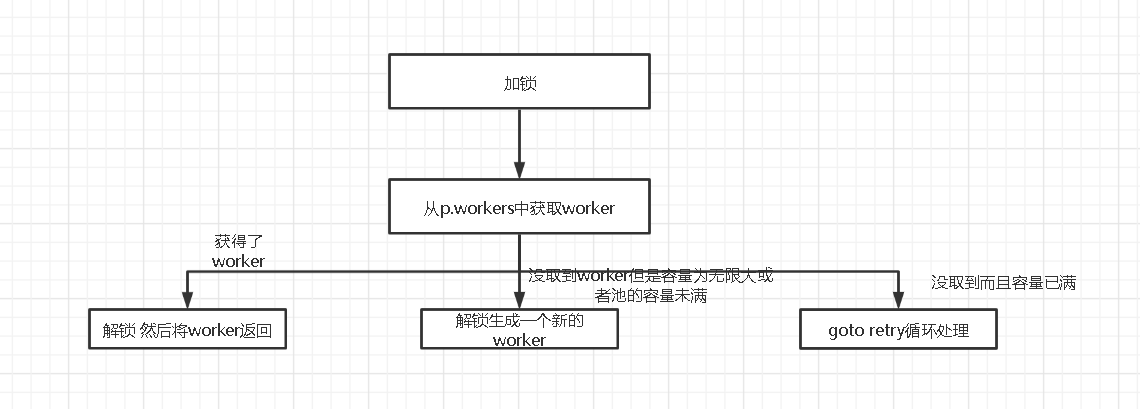
func (p *Pool) retrieveWorker() (w *goWorker) {
spawnWorker := func() {
w = p.workerCache.Get().(*goWorker)
w.run()
}
p.lock.Lock()
w = p.workers.detach() // 获取列表中最后一个worker
if w != nil { // 取出来的话直接解锁
p.lock.Unlock()
} else if capacity := p.Cap(); capacity == -1 || capacity > p.Running() { //没取到但是容量为无限大或者容量未满
p.lock.Unlock()
spawnWorker() //开一个新的worker
} else { // 没取到 而且容量已经满了
if p.options.Nonblocking { //默认为False
p.lock.Unlock()
return
}
retry:
xxxx
goto retry
xxxx
p.lock.Unlock()
}
return
}
goworker的运行
func (w *goWorker) run() {
w.pool.incRunning() //增加正在运行的worker数量
go func() {
defer func() {
w.pool.decRunning()
w.pool.workerCache.Put(w)
if p := recover(); p != nil {
if ph := w.pool.options.PanicHandler; ph != nil {
ph(p)
} else {
w.pool.options.Logger.Printf("worker exits from a panic: %v\n", p)
var buf [4096]byte
n := runtime.Stack(buf[:], false)
w.pool.options.Logger.Printf("worker exits from panic: %s\n", string(buf[:n]))
}
}
// Call Signal() here in case there are goroutines waiting for available workers.
w.pool.cond.Signal()
}()
for f := range w.task { //阻塞接受task
if f == nil {
return
}
f() //执行函数
if ok := w.pool.revertWorker(w); !ok { // 将goworker放回items中
return
}
}
}()
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号