Netty框架入门

一、概述
Netty是由JBOSS提供的一个java开源框架。
Netty提供异步的、事件驱动的网络应用程序框架和工具,用以快速开发高性能、高可靠性的网络服务器和客户端程序。
二、体系结构图
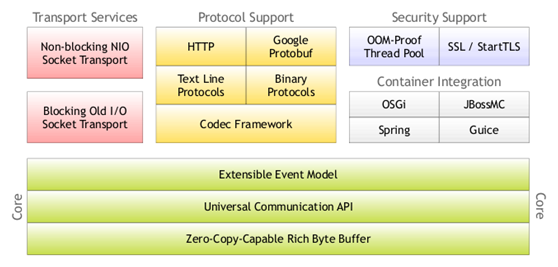
三、Netty的核心结构
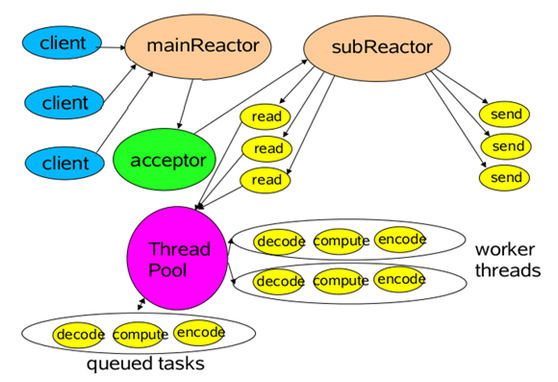
Netty是典型的Reactor模型结构,在实现上,Netty中的Boss类充当mainReactor,NioWorker类充当subReactor(默认NioWorker的个数是当前服务器的可用核数)。
在处理新来的请求时,NioWorker读完已收到的数据到ChannelBuffer中,之后触发ChannelPipeline中的ChannelHandler流。
Netty是事件驱动的,可以通过ChannelHandler链来控制执行流向。因为ChannelHandler链的执行过程是在subReactor中同步的,所以如果业务处理handler耗时长,将严重影响可支持的并发数。
四、客户端和服务器端通信Demo
Server-main:
ChannelFactory factory = new NioServerSocketChannelFactory(Executors.newCachedThreadPool(), Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(factory);
bootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new ChannelPipelineFactory(){
@Override
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() throws Exception {
return Channels.pipeline(new TimeServerHandler());
}
});
bootstrap.setOption("child.tcpNoDelay", true);
bootstrap.setOption("child.keepAlive", true);
bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(1989));
ChannelFactory 是一个创建和管理Channel通道及其相关资源的工厂接口,它处理所有的I/O请求并产生相应的I/O ChannelEvent通道事件。这个工厂并自己不负责创建I/O线程。应当在其构造器中指定该工厂使用的线程池,这样我们可以获得更高的控制力来管理应用环境中使用的线程。
ServerBootstrap 是一个设置服务的帮助类。设置了一个继承自ChannelPipelineFactory的匿名类,用来作为ChannelPipeline通道,当服务器接收到一个新的连接,一个新的ChannelPipeline管道对象将被创建,并且所有在这里添加的ChannelHandler对象将被添加至这个新的ChannelPipeline管道对象。
Server-Handler:
@Override
public void channelConnected(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelStateEvent e) throws Exception {
//TimeServer
Channel ch = e.getChannel();
ChannelBuffer time = ChannelBuffers.buffer(8);
time.writeLong(System.currentTimeMillis());
ChannelFuture future = ch.write(time);
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture arg0) throws Exception {
Channel ch = arg0.getChannel();
ch.close();
}
});
}
Handler中是我们的业务逻辑,在Server的Handler里重载了channelConnected方法,当收到连接请求时,将当前服务器时间写入到Channel,并且在写完后触发关闭Channel。
Client-main:
ChannelFactory factory = new NioClientSocketChannelFactory(Executors.newCachedThreadPool(), Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
ClientBootstrap bootstrap = new ClientBootstrap(factory);
bootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new ChannelPipelineFactory() {
@Override
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() throws Exception {
return Channels.pipeline(new TimeClientHandler());
}
});
bootstrap.setOption("tcpNoDelay",true);
bootstrap.setOption("keepAlive", true);
bootstrap.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 1989));
Client端初始化Netty的过程和Server类似,只是将使用到的类替换为Client端的。
Client-Handler:
Client-Handler:
@Override
public void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e) throws Exception {
ChannelBuffer buf = (ChannelBuffer)e.getMessage();
Long currentTimeMillis = buf.readLong();
System.out.println(new Date(currentTimeMillis));
e.getChannel().close();
}
Client端的Handler里,我们将从服务器端接收到的信息转换为时间打印到控制台。
五、基于HTTP协议的服务器端实现
//HttpServerPipelineFactory.java
public class HttpServerPipelineFactory implements ChannelPipelineFactory {
@Override
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = Channels.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new HttpRequestDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new HttpResponseEncoder());
pipeline.addLast("handler", new HttpServerHandler());
return pipeline;
}
}
新建一个HttpServerPipelineFactory类,在getPipeline()方法中添加了对Http协议的支持。
// HttpServer.java bootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new HttpServerPipelineFactory());
在Server里面使用我们新建的HttpServerPipelineFactory。
//HttpServerHandler.java
public void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e) throws Exception {
DefaultHttpRequest defaultHttpRequest = (DefaultHttpRequest)e.getMessage();
String uri = defaultHttpRequest.getUri();
byte[] data = defaultHttpRequest.getContent().array();
String content = URLDecoder.decode(new String(data),"utf-8").trim();
System.out.println(uri+"|"+content);
Channel ch = e.getChannel();
HttpResponse response = new DefaultHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, OK);
ChannelBuffer buffer = new DynamicChannelBuffer(2048);
buffer.writeBytes("200".getBytes("UTF-8"));
response.setContent(buffer);
response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=UTF-8");
response.setHeader("Content-Length", response.getContent().writerIndex());
if (ch.isOpen() && ch.isWritable()) {
ChannelFuture future = ch.write(response);
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture arg0) throws Exception {
Channel ch = arg0.getChannel();
ch.close();
}
});
}
}
在Handler里面我们可以直接拿到DefaultHttpRequest类型的对象,因为Netty已经用HttpRequestDecoder帮我们把接受到的数据都转换为HttpRequest类型了。
使用了多个Handler后,通过下图,Netty的事件驱动就可以被很好的理解了:

UpstreamEvent是被UpstreamHandler们自底向上逐个处理,DownstreamEvent是被DownstreamHandler们自顶向下逐个处理,这里的上下关系就是向ChannelPipeline里添加Handler的先后顺序关系。
六、总结
Netty是一个简单却不失强大的架构。这个架构由三部分组成——缓冲(Buffer)、通道(Channel)、事件模型(Event Model)——所有的高级特性都构建在这三个核心组件之上。
七、深入学习
http://netty.io/
https://github.com/netty/netty



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号