Leetcode solution 124: Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
Problem Statement
Given a non-empty binary tree, find the maximum path sum.
For this problem, a path is defined as any sequence of nodes from some starting node to any node in the tree along the parent-child connections. The path must contain at least one node and does not need to go through the root.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3]
1
/ \
2 3
Output: 6
Example 2:
Input: [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
-10
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
Output: 42
Problem link
Video Tutorial
You can find the detailed video tutorial here
Thought Process
When dealing with binary tree related problem, traversals using recursion is our friend. It seems we can perform a post-order traversal, and keep track of the maximum sums.
If the path has to go through root, then in each post-order step, we will have the max_sum_of_the_left_path, max_sum_of_the_right_path, the current_node_value, we simply return and record
single_path_max = max(the current_node_value, max(max_sum_of_the_left_path, max_sum_of_the_right_path) + current_node_value)
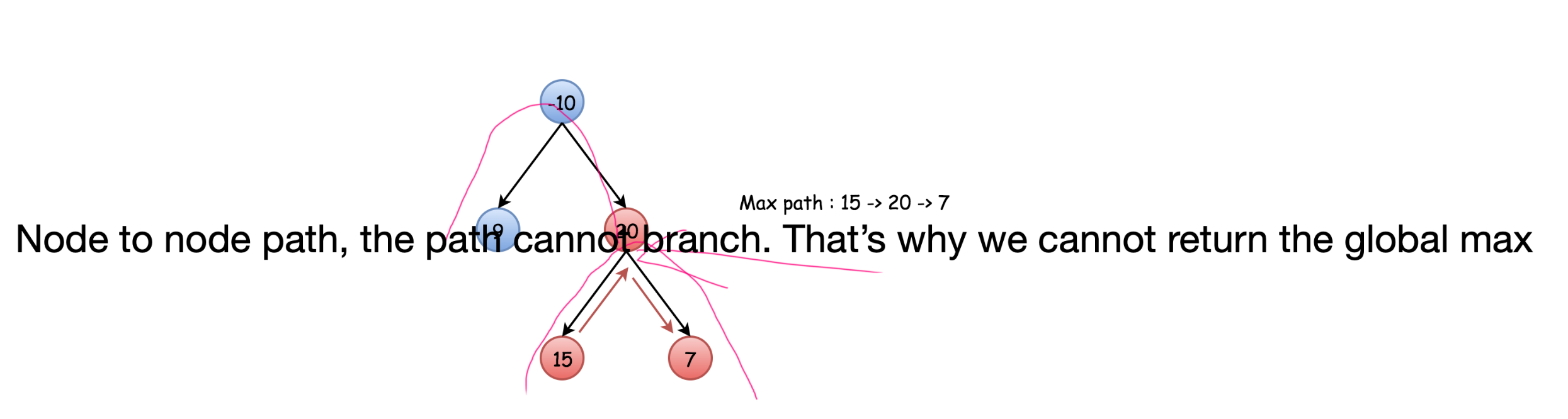
However, the problem allows a path that not goes through the root, therefore, we need to also record a max between left + current node value + right, i.e.,
global_max = max(single_path_max, max_sum_of_the_left_path + current_node_value + max_sum_of_the_right_path)
One caveat is in your recursion, we should still return the single_path_max. The reason we should not return the global_max is in that case, it will not be a single node to single node path.
Solutions
Post-order recursion
1 private int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; 2 3 public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) { 4 maxPathSumHelper(root); 5 return this.max; 6 } 7 8 public int maxPathSumHelper(TreeNode root) { 9 if (root == null) { 10 return 0; 11 } 12 13 int left = maxPathSumHelper(root.left); 14 int right = maxPathSumHelper(root.right); 15 16 // the max on a single path 17 int singlePath = Math.max(root.val, Math.max(left, right) + root.val); 18 // max across the current node on two sides 19 int acrossPath = Math.max(singlePath, left + right + root.val); 20 if (acrossPath > this.max) { 21 this.max = acrossPath; 22 } 23 24 // Note: always want to return the single path for recursion, because you cannot include both path, else, 25 // it will not be a path 26 return singlePath; 27 }
Time Complexity: O(N), each node is visited once
Space Complexity:No extra space is needed other than the recursion function stack


