ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
该类用来扫描 classpath(类路径)上的类,并注册为 BeanDefinition。默认会扫描 Spring 中的 @Component、@Repository、@Service 或 @Controlle 注释的类;还有 Java EE 6's javax.annotation.ManagedBean 和 JSR-330's javax.inject.Named 注解的类。
因为 @Repository、@Service 和 @Controlle 注解都被 @Component 注解了,所以能被扫描到;也就是说,其它注解只要使用了 @Component 注解都会被扫描到。
该类没有无参构造方法,最少传入一个 BeanDefinitionRegistry 实例,并且所有的构造方法最终都会调用:
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean useDefaultFilters,
Environment environment, @Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.registry = registry;
// useDefaultFilters 默认为 true;
if (useDefaultFilters) {
// 初始化包含过滤集合,这个集合就是一个白名单;在扫描 classpath 下所有类的时候,某个类只有满足白名单才会注册为 BeanDefinition。
// private final List<TypeFilter> includeFilters = new ArrayList<>();
// 会向集合中添加 Component、ManagedBean 和 Named 注解类型的包含过滤。
registerDefaultFilters();
}
// 就是将 environment 实例设置到当前扫描器
setEnvironment(environment);
// 该方法最主要的一件事情就是读取 META-INF/spring.components 文件,并封装成 CandidateComponentsIndex 实例。
setResourceLoader(resourceLoader);
}
doScan
此方法是这个类中最主要的方法,用来扫描类路径并将满足条件的类注册为 BeanDefinition。
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
// findCandidateComponents 方法具体看下面。
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
// 1.将 BeanDefinitionDefaults 的值设置到 BeanDefinition,这是当作默认值使用。
// 2.autowireCandidatePatterns 做什么?
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
// 将 Lazy、Primary、DependsOn、Role、Description 注解的值设到 BeanDefinition 中。
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder =
AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
// 向容器中注册 BeanDefinition 和 别名。
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
在扫描和注册完 BeanDefinition 后会设置基础容器的 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator、ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver,然后注册 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor、AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、EventListenerMethodProcessor、DefaultEventListenerFactory。
findCandidateComponents
这个方法就是用来扫描出满足条件的类,并封装为 BeanDefinition。
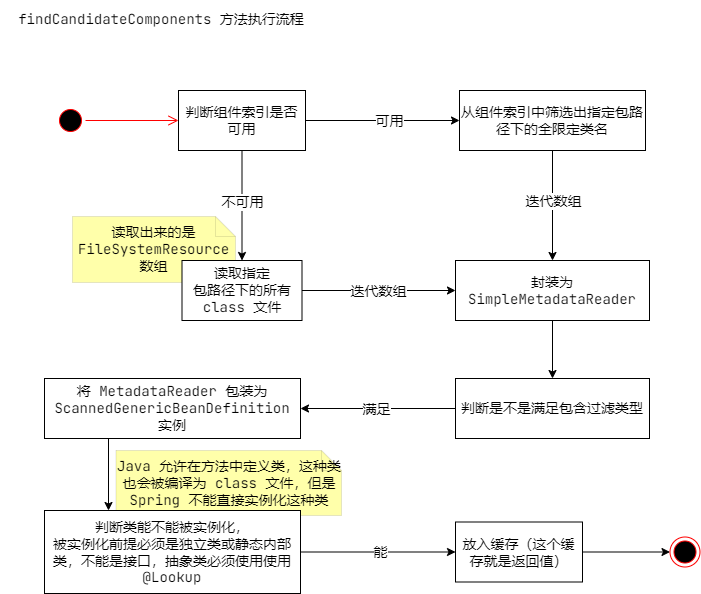
解释上图中的“判断组件索引是否可用”:
首先 CandidateComponentsIndex 实例必须存在,然后再判断包含过滤集合中的 AnnotationTypeFilter(注解) 和 AssignableTypeFilter(指定类) 过滤器是不是都使用了 @Indexed 注解,都使用了才会启用组件索引;如果包含过滤集合中存在其它类型过滤器则直接禁用组件索引。
值得注意的是:
判断包含过滤集合中的注解或指定类上有没有使用 @Indexed 注解;例如 @XXX 使用了 @Component 元注解,虽然 @Component 使用 @Indexed,但是判断是不会成立的,因为 @XXX 没有直接使用 @Indexed 元注解。
这样做是为了保证,@ComponentScan 指定的包和类能被扫描到,因为它可以指定第三方的包中的自定义注解、自定义类型或普通 Bean 能被扫描到,因为编译的时候只会将 @Indexed 注解和元注解的类保存到文件中,所以如果当前容器的包含过滤集合中有其它的过滤类型,就会导致禁用组件索引。
最后还有一点,上面图说的是 静态内部类,对于内部类这里也不会注册为 BeanDefinition。
ScopedProxyMode
MySingletonBean 依赖 MyPrototypeBean,你想要每次调用 getPrototypeBean 时都返回一个新的实例,这个时候就需要配置 ScopedProxyMode。
ScopedProxyMode 默认值为 No,它还有两个选项 INTERFACES 和 TARGET_CLASS;如果 MyPrototypeBean 实现了接口那么可以指定为 INTERFACES,它是使用 JDK 的动态代理来创建 MyPrototypeBean 的代理对象,否则就使用 TARGET_CLASS,它是使用 CGLIB 来创建 MyPrototypeBean 的代理对象。
也就是说 MySingletonBean 类中的 prototypeBean 属性被赋值为代理对象,当调用代理对象的方法时,会委托给真实对象。
注意:除了原型作用域,Request 或 Session 等作用域一样可以配置 ScopedProxyMode。
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class MyPrototypeBean {
private String dateTimeString = LocalDateTime.now().toString();
public String getDateTime() { return dateTimeString; }
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class MySingletonBean {
@Autowired
private MyPrototypeBean prototypeBean;
public void showMessage() { System.out.println("Hi, the time is "+prototypeBean.getDateTime()); }
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
@Scope(value = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE, proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS)
public MyPrototypeBean prototypeBean () { return new MyPrototypeBean(); }
@Bean
public MySingletonBean singletonBean () { return new MySingletonBean(); }
public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
MySingletonBean bean = context.getBean(MySingletonBean.class);
bean.showMessage();
Thread.sleep(1000);
bean.showMessage();
}
}
注意:在 Spring 的启动流程中,注册 BeanDefinition 之前会设置 ScopedProxyMode。
本文作者:不是很聪明
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/baoboshi/p/16381917.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步