李宏毅 Tensorflow解决Fizz Buzz问题
提出问题
一个网友的博客,记录他在一次面试时,碰到面试官要求他在白板上用TensorFlow写一个简单的网络实现异或(XOR)功能。这个本身并不难,单层感知器不能解决异或问题是学习神经网络中的一个常识,而简单的两层神经网络却能将其轻易解决。但这个问题的难处在于,我们接触TensorFlow通常直接拿来写CNN,或者其他的深度学习相关的网络了,而实现这种简单网络,基本上从未做过;更何况,要求在白板上写出来,如果想bug free,并不是容易的事儿啊。
数据
李宏毅老师对数据进行了如下分析
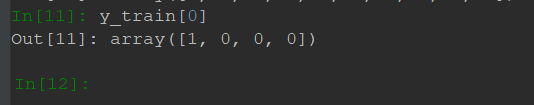
对数字101到1000做了labeling,即训练数据xtrain.shape=(900,10),每一个数字都是用二进位来表示,第一个数字是101,用二进位来表示即为[1,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0],每一位表示2^{n-1},n表示左数第几位。现在一共有四个case,[一般,Fizz,Buzz,Fizz Buzz],所以y_train.shape=(900,10),对应的维度用1表示,其他都为0
数据分析
900个样本,每个样本代表一个数字,并且有二进制值数值表示。观察样本,第一个数字是101,则二进制的表示为1010011000

然后观察label
如果不是被3,5或者同时被整出,则保留原数。所以一共有四种情况。“原数,fizz,buzz,fizz&buzz”
inputlayer是10维度,为中间隐藏层输出100维,最终输出4维。激活函数用的是ReLU函数,compile配置中,是做分类,学习率优化函数是adam,再设置batchsize和epoch即可。
源代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2019/9/13 11:12
# @Author : BaoBao
# @Mail : baobaotql@163.com
# @File : test6.py.py
# @Software: PyCharm
#fizz buzz问题
from keras.layers.normalization import BatchNormalization
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers.core import Dense,Dropout,Activation
from keras.optimizers import SGD,Adam
import numpy as np
def fizzbuzz(start,end):
x_train,y_train=[],[]
for i in range(start,end+1):
num = i
tmp=[0]*10
j=0
while num :
tmp[j] = num & 1
num = num>>1
j+=1
x_train.append(tmp)
if i % 3 == 0 and i % 5 ==0:
y_train.append([0,0,0,1])
elif i % 3 == 0:
y_train.append([0,1,0,0])
elif i % 5 == 0:
y_train.append([0,0,1,0])
else :
y_train.append([1,0,0,0])
return np.array(x_train),np.array(y_train)
x_train,y_train = fizzbuzz(101,1000) #打标记函数
x_test,y_test = fizzbuzz(1,100)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(input_dim=10,output_dim=10))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(Dense(output_dim=4))
model.add(Activation('softmax'))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',optimizer='adam',metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(x_train,y_train,batch_size=20,nb_epoch=100)
result = model.evaluate(x_test,y_test,batch_size=1000)
print('Acc:',result[1])
运行结果
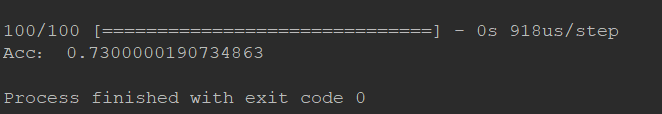
可以看到accuray的结果不是很好,那么我们考虑多种方案来解决,比如修改Activation function,或者将hidden neure修改为1000后 可以看到accuracy的明显提高
运行结果

----------------------------------华丽的分割线------------------------------------------
从别的博主看到的一个方法写的很简单QAQ我好菜啊
1.import 模块
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf
2.输入数据的placeholder
具体来说,一个data,一个label
data = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(4, 2))
label = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(4, 1))
由于本例比较特殊,异或只有四种输入和对应的四个输出,所以根据需求定义固定的shape
3.基于输入数据的placeholder构建model
异或需要两层神经网络,每层分别需要一个weights和一个bias,所以定义如下:
with tf.variable_scope('layer1') as scope: weight = tf.get_variable(name='weight', shape=(2, 2)) bias = tf.get_variable(name='bias', shape=(2,)) x = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(data, weight) + bias) with tf.variable_scope('layer2') as scope: weight = tf.get_variable(name='weight', shape=(2, 1)) bias = tf.get_variable(name='bias', shape=(1,)) x = tf.matmul(x, weight) + bias
这里为了方便变量管理,以及在tensorboard上的条理性,使用了variable_scope,当然,也可以不使用。
此外,因为我们后面的loss要使用sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits函数,所以这里第二层网络的输出没有过sigmoid函数。如果loss使用其他函数,则可以做相应处理。
4.定义loss
其实这里可以灵活选用各种loss函数,比如MSE,等等。但我们还是选用了在CNN中广泛使用的cross entropy
preds = tf.nn.sigmoid(x)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=label, logits=x))
我们这里把模型的输出x过了一下sigmoid函数,作为最终输出,以便在训练时对模型进行监视。
5.定义Optimizer
learning_rate = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss)
6.构建并输入数据,开始训练
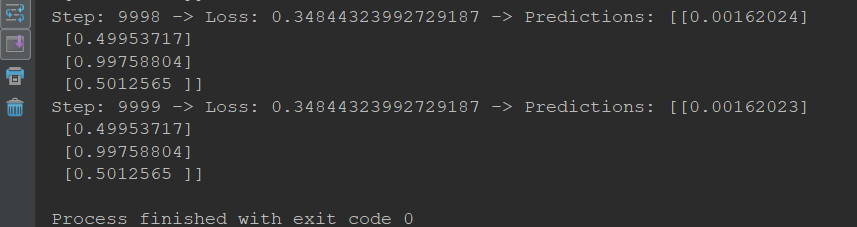
train_data = np.array([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]]) train_label = np.array([[0], [1], [1], [0]]) with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) for step in range(10000): if step < 3000: lr = 1 elif step < 6000: lr = 0.1 else: lr = 0.01 _, l, pred = sess.run([optimizer, loss, preds], feed_dict={data: train_data, label: train_label, learning_rate: lr}) if step % 500: print('Step: {} -> Loss: {} -> Predictions: {}'.format(step, l, pred)
完整代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2019/9/13 11:24 # @Author : BaoBao # @Mail : baobaotql@163.com # @File : test7.py # @Software: PyCharm #fizz buzz问题 import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf data = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(4, 2)) label = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(4, 1)) with tf.variable_scope('layer1') as scope: weight = tf.get_variable(name='weight', shape=(2, 2)) bias = tf.get_variable(name='bias', shape=(2,)) x = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(data, weight) + bias) with tf.variable_scope('layer2') as scope: weight = tf.get_variable(name='weight', shape=(2, 1)) bias = tf.get_variable(name='bias', shape=(1,)) x = tf.matmul(x, weight) + bias preds = tf.nn.sigmoid(x) loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=label, logits=x)) learning_rate = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss) train_data = np.array([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]]) train_label = np.array([[0], [1], [1], [0]]) with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) for step in range(10000): if step < 3000: lr = 1 elif step < 6000: lr = 0.1 else: lr = 0.01 _, l, pred = sess.run([optimizer, loss, preds], feed_dict={data: train_data, label: train_label, learning_rate: lr}) if step % 500: print('Step: {} -> Loss: {} -> Predictions: {}'.format(step, l, pred))
运行结果