TensorFlow实战第五课(MNIST手写数据集识别)
Tensorflow实现softmax regression识别手写数字
MNIST手写数字识别可以形象的描述为机器学习领域中的hello world。
MNIST是一个非常简单的机器视觉数据集。它由几万张28*28像素的手写数字组成,这些图片只包含灰度值信息。我们的任务就是对这些手写数字进行分类。转换为0-9共十个分类。
首先在命令行中运行如下代码加载MNIST手写数据集:
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data #number 1 to 10 data #创建文件夹存放数据 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot=True)
数据集中包含55000个样本,测试集中有10000个样本,同时验证集有5000个样本。每一个样本都有他对应的标注信息,即label。
我们将在训练集上训练模型,在验证集上检验效果并决定何时完成训练,最后我们在测评及评测模型效果。
准备好数据后我们开始设计算法。我们采用的是softmax regression的算法训练手写数字识别的分类模型。数字分为0-9,所以一共有十个类别,当我们对一张图片进行预测时,softmax regression会对每一种类别估算一个概率,然后取估算概率最大的数字作为模型的输出结果。
注:当我们处理多分类模型时,通常需要使用softmax regression。例如卷积神经网络或者循环神经网络,如果是分类模型,那么最后一层同样是softmax regression。
loss函数选择的是交叉熵函数,交叉熵用来衡量预测值与真实值的相似程度,如果完全相同,他们的交叉熵等于零。
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(ys * tf.log(prediction), reduction_indices=[1])) # loss
train方法(最优化方法)采用梯度下降法。
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy) sess = tf.Session() # tf.initialize_all_variables() 这种写法马上就要被废弃 # 替换成下面的写法: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
完整代码:
#classification 分类学习 import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data #number 1 to 10 data #创建文件夹存放数据 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot=True) def add_layer(inputs,in_size,out_size,activation_function=None): #添加一个以上的层 并且返回这个层的输出 Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size,out_size])) biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size])+0.1) Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs,Weights)+biases if activation_function is None: outputs = Wx_plus_b else: outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) return outputs def compute_accuracy(v_xs,v_ys): global prediction y_pre = sess.run(prediction,feed_dict={xs:v_xs}) correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_pre,1),tf.argmax(v_ys,1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) result = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={xs: v_xs, ys: v_ys}) return result #define placeholder for inputs to network xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])#None就是不规定他有多少sample,但是规定大小为28*28 ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10]) #add output layer #激励函数采用softmax函数 prediction = add_layer(xs,784,10,activation_function=tf.nn.softmax) # the error between prediction and real data '''loss函数即最优化目标函数 选用交叉熵函数 交叉熵用来衡量预测值和真实值相似程度 如果完全相同 ,他们的交叉熵为零 ''' cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(ys * tf.log(prediction), reduction_indices=[1]))
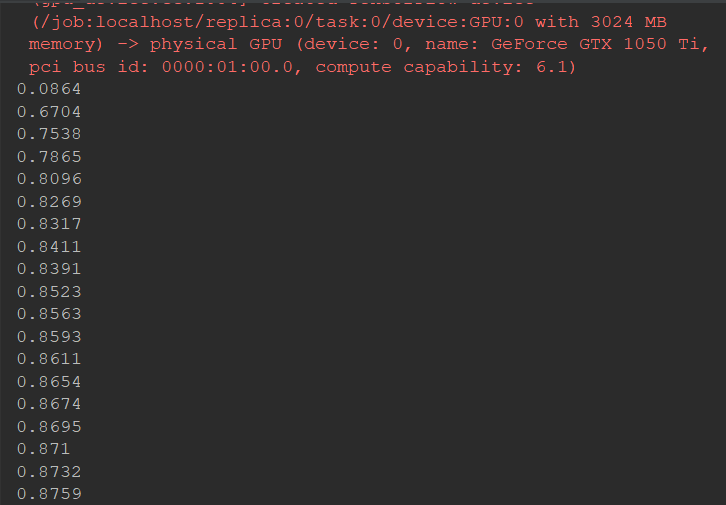
# loss #采用梯度下降法 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy) sess = tf.Session() init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) for i in range(2000): #每次只取100张图片 batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100) sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={xs:batch_xs,ys:batch_ys}) if i%50==0: print(compute_accuracy(mnist.test.images,mnist.test.labels))
输出结果: