用man wait学习wait waitpid的使用
- wait()函数功能:wait()函数使父进程暂停执行,直到它的一个子进程结束为止,该函数的返回值是终止运行的子进程的PID. 参数status所指向的变量存放子进程的退出码,即从子进程的main函数返回的值或子进程中exit()函数的参数。如果status不是一个空指针,状态信息将被写入它指向的变量。
- waitpid函数功能:waitpid()的作用和wait()一样,但它并不一定要等待第一个终止的子进程,它还有若干选项,如可提供一个非阻塞版本的wait()功能等。实际上wait()函数只是waitpid()函数的一个特例。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
main()
{
int status;
pid_t pc,pr;
pc=fork();
if(pc<0) /* 如果出错 */
printf("error ocurred!\n");
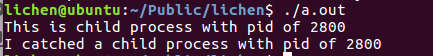
else if(pc==0){ /* 子进程 */
printf("This is child process with pid of %d.\n",getpid());
}
else{ /* 父进程 */
pr=wait(&status);
if(WIFEXITED(status)){ /* 如果WIFEXITED返回非零值 */
printf("the child process %d exit normally.\n",pr);
}else /* 如果WIFEXITED返回零 */
printf("the child process %d exit abnormally.\n",pr);
}
}
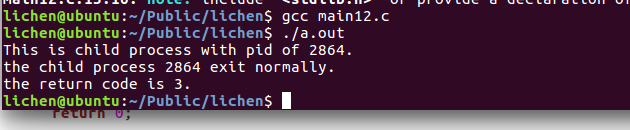
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
main()
{
int status;
pid_t pc,pr;
pc=fork();
if(pc<0) /* 如果出错 */
{printf("error ocurred!\n");
return -1;}
else if(pc==0){ /* 子进程 */
printf("This is child process with pid of %d.\n",getpid());
}
else{ /* 父进程 */
pr=wait(&status);
if(WIFEXITED(status)){ /* 如果WIFEXITED返回非零值 */
printf("the child process %d exit normally.\n",pr);
printf("the return code is %d.\n",WEXITSTATUS(status));
}else /* 如果WIFEXITED返回零 */
printf("the child process %d exit abnormally.\n",pr);
}
}