【ML】之 线性回归(实战) 研读
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/fanfan4569/article/details/81263499
Topic:
- 最小二乘法代数求解 实战
- 最小二乘法矩阵求解 实战
- 使用 scikit-learn 进行线性回归预测
本文为实战篇,理论篇:线性回归理论
一、最小二乘法代数求解 实战
步骤:
- 导入数据集(使用
numpy模拟) - 绘制图形, 使用
matplotlib - 定义拟合直线函数,平方损失函数
- 计算求解
- 绘制图像
- 测试用例,预测结果
# 1. 导入数据集
#import inline as inline
import matplotlib
import numpy as np
x = np.array([56, 72, 69, 88, 102, 86, 76, 79, 94, 74])
y = np.array([92, 102, 86, 110, 130, 99, 96, 102, 105, 92])
# 2. 显示数据集在坐标上
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# %matplotlib inline
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.xlabel("Area")
plt.ylabel("Price")
plt.show()
# 3. 定义拟合直线
def f(x, b, w1):
y = b + w1 * x
return y
# 3.2 平方损失函数
def square_loss(x, y, w0, w1):
loss = sum(np.square(y - (w0 + w1*x)))
return loss
# 3.4 代入计算
b,w = w_calculator(x, y)
square_loss(x, y, b, w)
# 4. 绘制图像
x_temp = np.linspace(50,120,100) # 绘制直线生成的临时点
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(x_temp, x_temp*w + b, 'r')
plt.show() # 5. 如果手中有一套 150 平米的房产想售卖,二、最小二乘法矩阵求解 实战
步骤:
- 导入数据集
- 定义 拟合直线,平方损失函数
- 代入计算
- 绘图
# 1. 导入数据集
import inline as inline
import matplotlib
import numpy as np
x = np.array([56, 72, 69, 88, 102, 86, 76, 79, 94, 74])
y = np.array([92, 102, 86, 110, 130, 99, 96, 102, 105, 92])
# 2. 显示数据集在坐标上
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# %matplotlib inline
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.xlabel("Area")
plt.ylabel("Price")
plt.show()
# 3. 定义拟合直线
def f(x, b, w1):
y = b + w1 * x
return y
# 3.2 平方损失函数
def square_loss(x, y, w0, w1):
loss = sum(np.square(y - (w0 + w1*x)))
return loss
# 3.3 平方损失函数最小时对应的w参数值 ,b
def w_calculator(x, y):
n = len(x)
w1 = (n*sum(x*y) - sum(x)*sum(y))/(n*sum(x*x) - sum(x)*sum(x))
w0 = (sum(x*x)*sum(y) - sum(x)*sum(x*y))/(n*sum(x*x)-sum(x)*sum(x))
return w0, w1
# 3.4 代入计算
b,w w_calculator(x, y)
square_loss(x, y, b, w)
# 4. 绘制图像
x_temp = np.linspace(50,120,100) # 绘制直线生成的临时点
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(x_temp, x_temp*w + b, 'r')
plt.show()
# 5. 如果手中有一套 150 平米的房产想售卖,获取预估报价:
f(150, b, w)
三、使用 scikit-learn 进行线性回归预测
scikit-learn 实现最小二乘线性回归方法
这要用到
LinearRegression(),sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True, normalize=False, copy_X=True, n_jobs=1)
fit_intercept: 默认为 True,计算截距项。
normalize: 默认为 False,不针对数据进行标准化处理。
copy_X: 默认为 True,即使用数据的副本进行操作,防止影响原数据。
n_jobs: 计算时的作业数量。默认为 1,若为 -1 则使用全部 CPU 参与运算。
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import numpy as np
import scipy # 要导入scipy包,不然报错
# 1. 定义数据集
x = np.array([56, 72, 69, 88, 102, 86, 76, 79, 94, 74])
y = np.array([92, 102, 86, 110, 130, 99, 96, 102, 105, 92])
# 2. 定义线性回归模型
model = LinearRegression()
# 训练, reshape 操作把数据处理成 fit 能接受的形状
model.fit(x.reshape(len(x), 1), y)
# 3.得到模型拟合参数
model.intercept_, model.coef_
# 4. 预测
model.predict([[150]])
实战1:https://blog.csdn.net/txbsw/article/details/79046362
实战2:https://blog.csdn.net/kyriehe/article/details/77507473
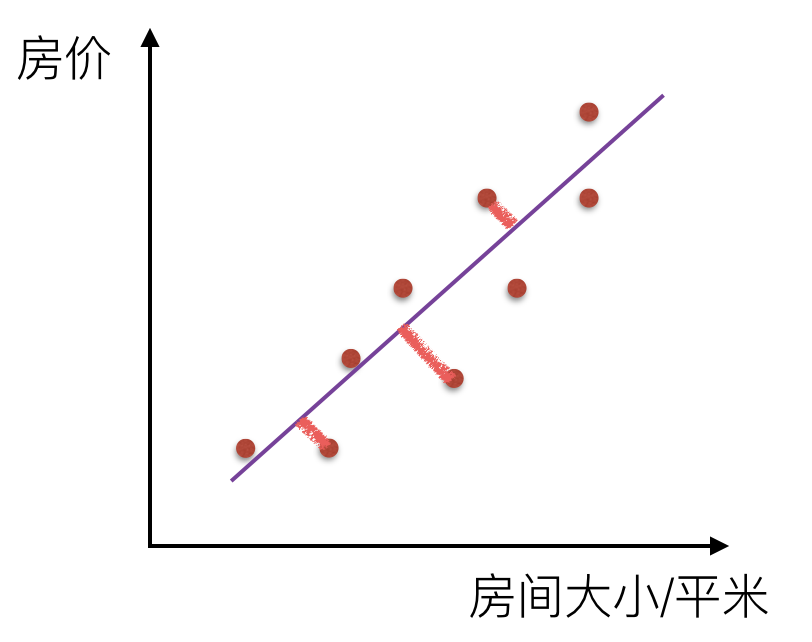
一元线性回归:
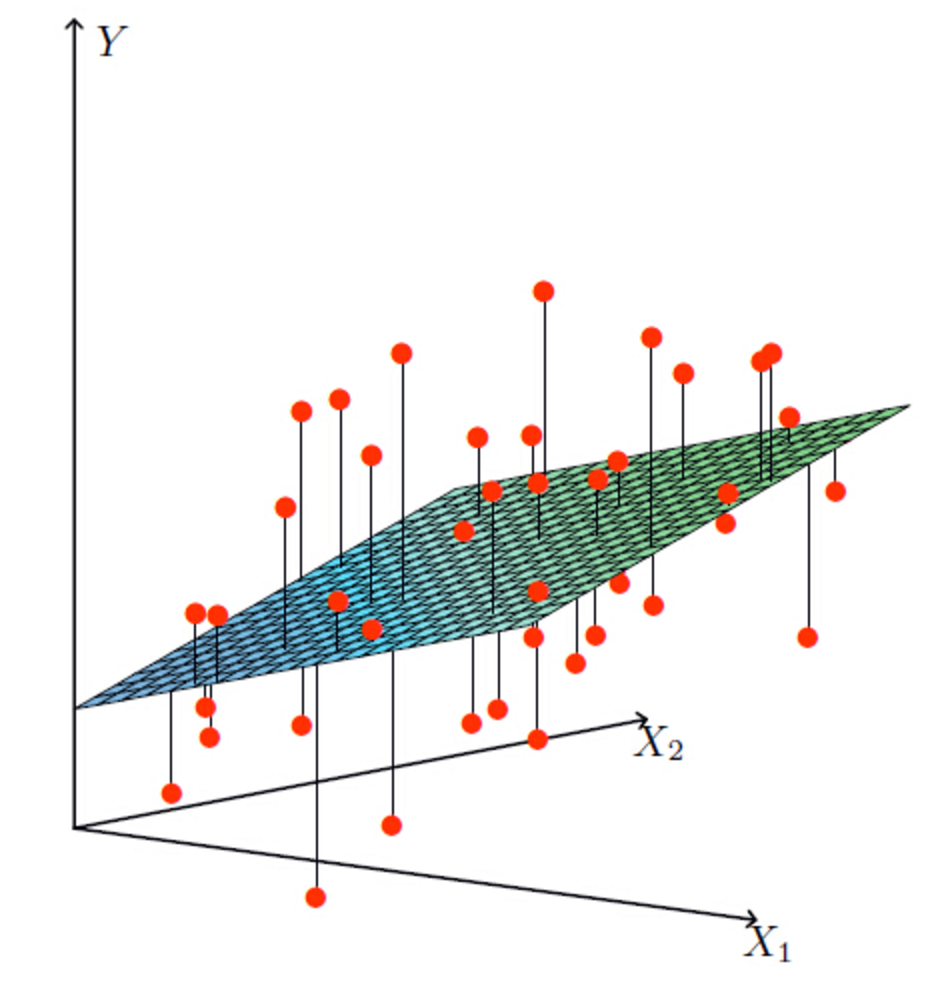
多元线性回归:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号