筛选条件
【一】where公式
- 查询当前表中的全部数据
select * from 表名 where 筛选条件;
-- 查询当前表中的指定字段的数据
select 字段名,字段名 from 表名 where 筛选条件;
# 执行顺序
from
where
select
select * from * where *;
between ... and ...
a in (b,c)
【二】分组条件group by
(1)查询数据
select * from emp group by post;
# ERROR 1055 (42000): Expression #1 of SELECT list is not in GROUP BY clause and contains nonaggregated column 'day03.emp.id' which is not functionally dependent on columns in GROUP BY clause; this is incompatible with sql_mode=only_full_group_by
(2)严格模式
show variables like "%mode";
set session sql_mode='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION';
(3)替换严格模式
set global sql_mode = 'STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION';
SET GLOBAL sql_mode = 'STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER';
select * from emp group by post;

select * from * group by *;
select post,max(salary) from emp group by post;
select post,max(salary) as salary from emp group by post;
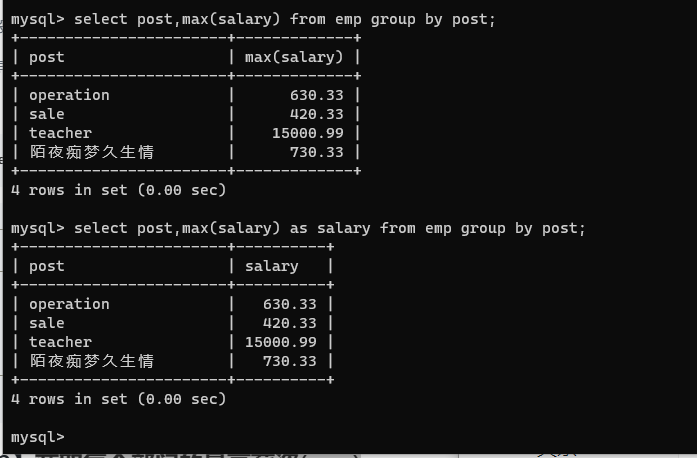
select * from * group by *;
select post,min(salary) from emp group by post;
select post,min(salary) as "最低薪资" from emp group by post;
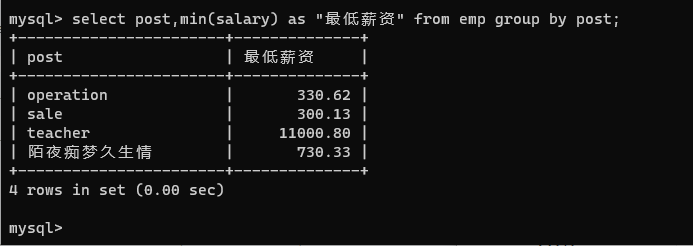
select * from * group by *;
select post,avg(salary) from emp group by post;
select post,avg(salary) as "平均薪资" from emp group by post;
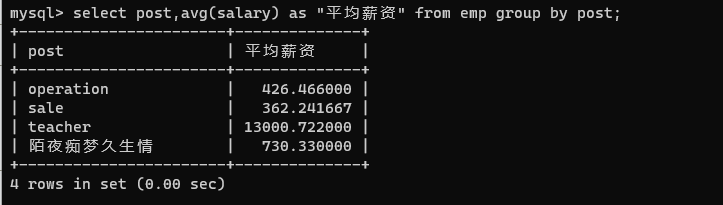
select * from * group by *;
select post,sum(salary) from emp group by post;
select post,sum(salary) as "薪资综合" from emp group by post;
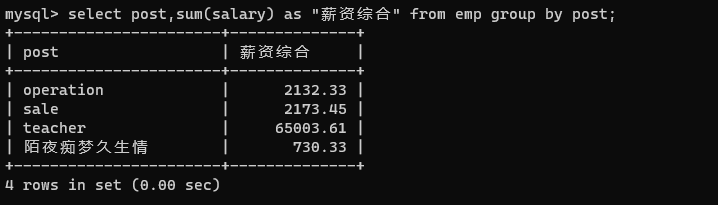
select * from * group by *;
select * from emp;
select post,count(salary) from emp group by post;
select post,count(id) as "部门总人数" from emp group by post;
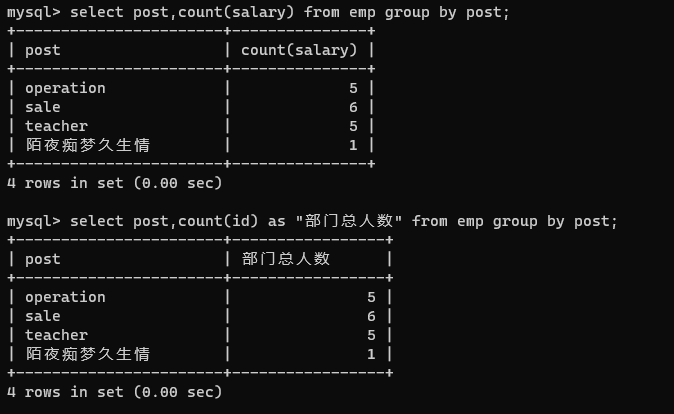
-- 不能对 null 计数
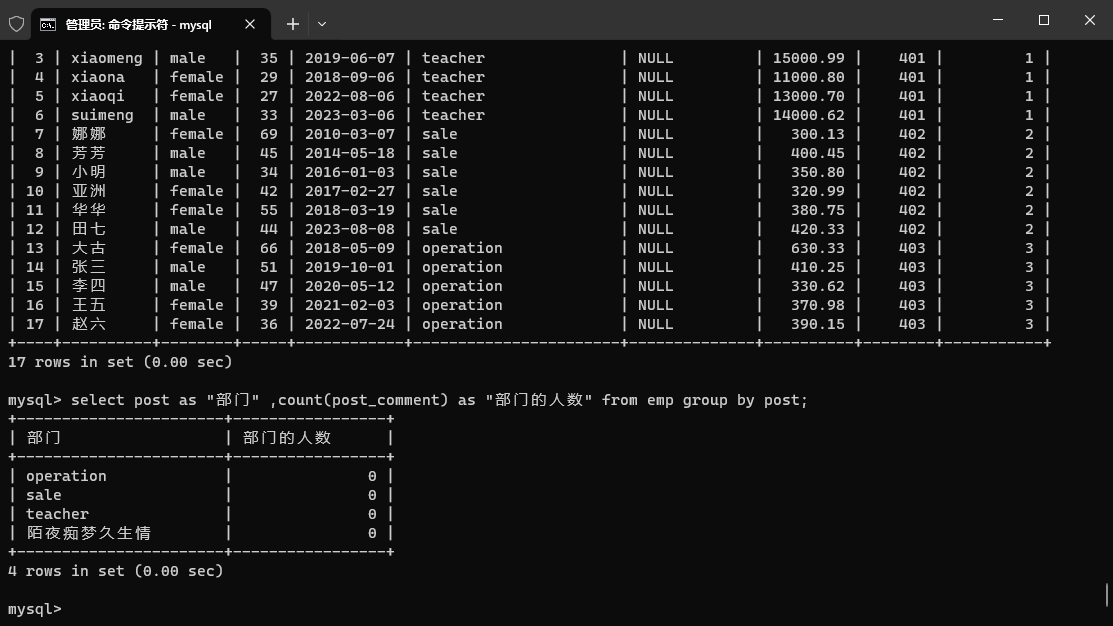
select post as "部门" ,count(post_comment) as "部门的人数" from emp group by post;
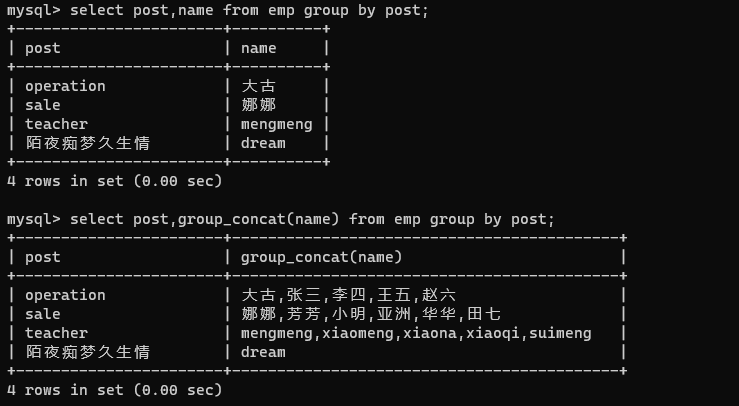
- 查询分组之后的部门名称和每个部门下所有的员工姓名(group_concat)
select post,group_concat(name) from emp group by post;
select post,name from emp group by post;
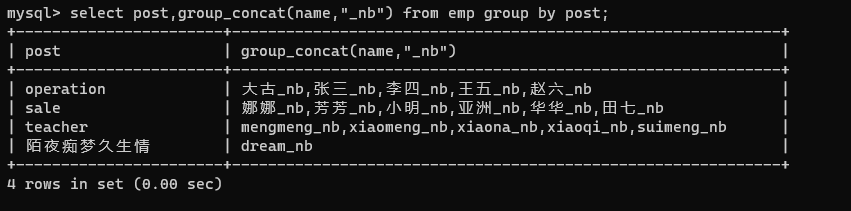
select post,group_concat(name,"_nb") from emp group by post;
select post,group_concat(name,':',salary) from emp group by post;
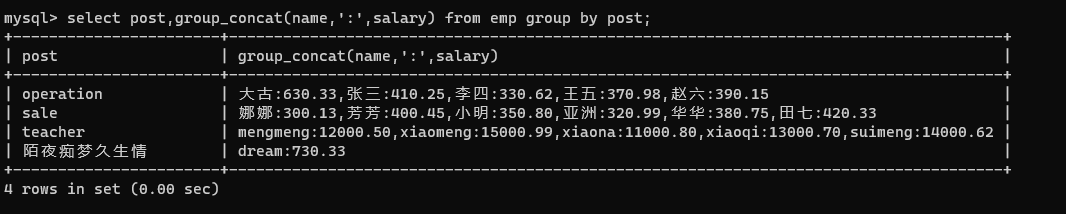
-- concat 不分组就可以使用
select concat("NAME:",name),concat("SALARY:",salary) from emp;
-- group_concat 必须分组之后才能使用
【4】分组注意事项
(1)关键字 where 和 group by 同时出现
- 关键字 where 和 group by 同时出现的时候,group by 必须在 where 后面
- where 先对整体数据进行过滤
- group by 再对数据进行分组
-- 同时出现要有先后顺序
-- where 先对整体过滤 group by 再对局部过滤
select * from * where * group by *;
(2)where 筛选条件不能使用聚合函数
- where 筛选条件不能使用聚合函数
- 不分组,默认整张表就是一组
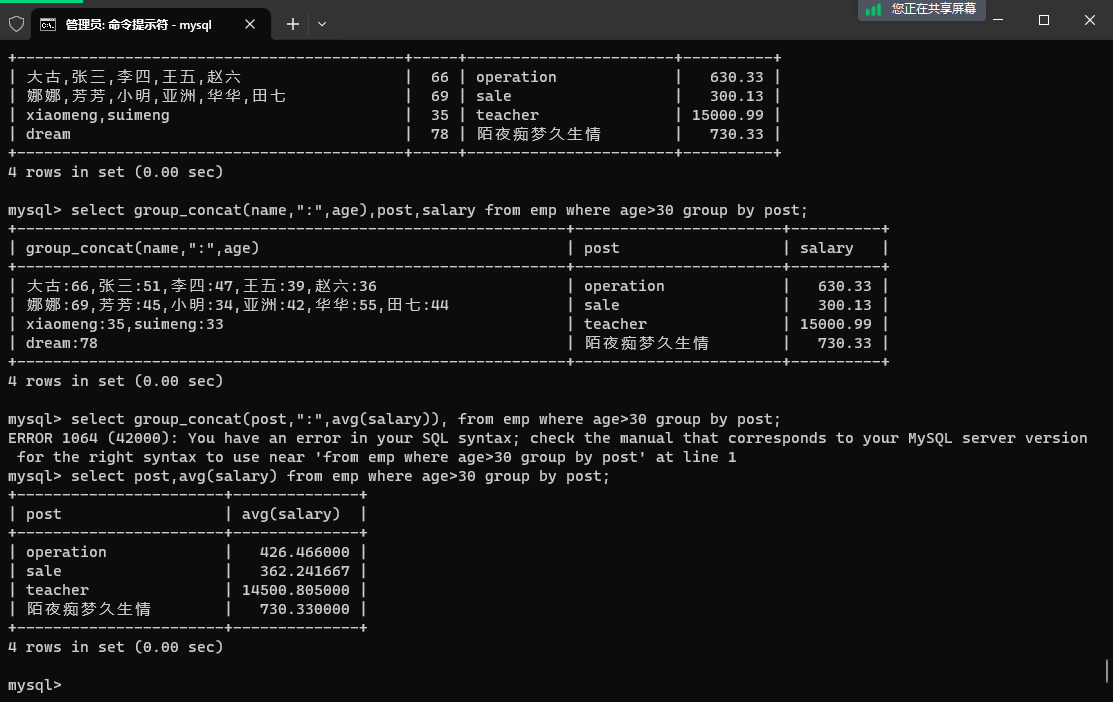
【5】统计各部门年龄在 30 岁以上的员工的平均薪资
-- 先筛选出大于30岁的员工
select name,age,post,salary from emp where age>30;
-- 再对大于30岁的员工进行部门分组
select group_concat(name,":",age),post,salary from emp where age>30 group by post;
-- 再对部门薪资使用聚合函数 avg
select post,avg(salary) from emp where age>30 group by post;
【三】筛选条件之having(分组之后筛选)
【1】引入
- having的语法和where是一致的
- 只不过having是在分组之后进行的过滤操作
- 即having是可以直接使用聚合函数的
select * from * where * group by * having *;
【2】练习
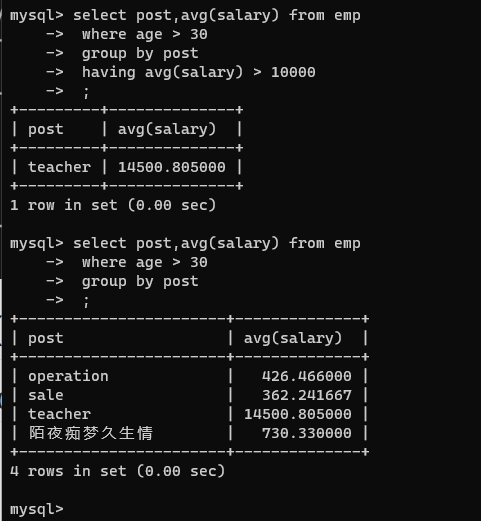
- 统计各部门年龄在 30 岁以上的员工的工资,并且保留平均薪资大于1w的部门
select post,avg(salary) from emp
where age > 30
group by post
;
select post,avg(salary) from emp
where age > 30
group by post
having avg(salary) > 10000
;
【四】筛选条件之distinct(去重)
【1】引用
- 必须是完全一样的数据才可以去重
- 一定要注意主键的问题
- 在主键存在的情况下是一定不可能去重的
select distinct id,age from emp;
insert into emp(name, sex, age, hire_date, post, salary, office, depart_id) values
("dream01", "male", 78, '20220306', "陌夜痴梦久生情", 730.33, 401, 1);
select * from emp;
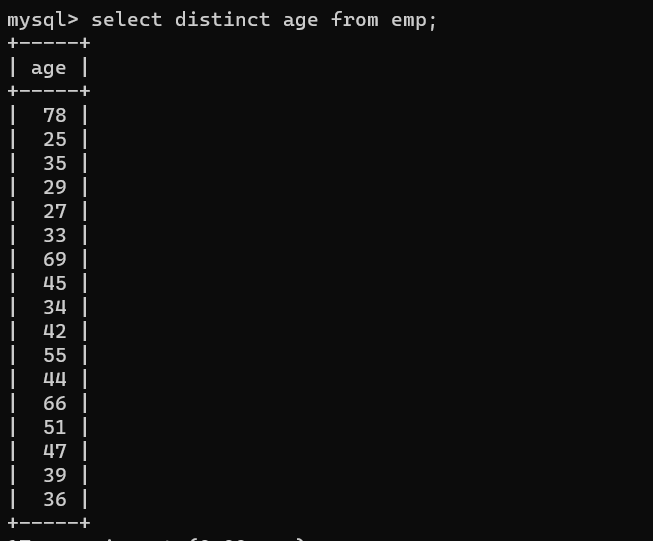
select distinct age from emp;
【五】筛选条件之排序
【1】引入:
- order by : 默认是升序
- asc 默认可以省略不写 ---> 修改降序
- desc : 降序
【2】order by语法
select * from * order by * asc;
select * from * order by * desc;
【3】例子
- 统计各部门年龄在 30 岁以上的员工的工资,并且保留平均薪资大于1000的部门,对平均工资进行排序
select * from * where * group by * having * order by * ;
select avg(salary) from emp
where age > 30
group by post
having avg(salary) > 400
order by avg(salary) desc
;
![image-20240126194513067]()
【五】筛选筛选条件之 limit(限制展示条数)
【1】引入:
- 针对数据太多的情况,我们大都是做分页处理
- limit x,y : 第一个参数是起始位置,第二个是条数
select * from * [where *] limit * ;
【2】查看员工表十条数据
select * from emp limit 10;
【3】按照区间取数据
select * from * [where *] limit x,y;
select * from emp limit 0,6
select * from emp limit 6,6;
start_page = 0 # 起始位置
step = 6 # 步长
while True:
sql = f"select * from emp limit {start_page},{step}"
start_page += step
select * from * [where *] group by * having * limit a,b order by * desc;
【六】正则语法
【1】语法
select * from * where 字段名 REGEXP 正则表达式;
【2】正则匹配语法
- “匹配方式”中有很多的模式匹配字符,它们分别表示不同的意思。
- 下表列出了 REGEXP 操作符中常用的匹配方式。
| 选项 |
说明 |
例子 |
匹配值示例 |
| ^ |
匹配文本的开始字符 |
‘^b’ 匹配以字母 b 开头的字符串 |
book、big、banana、bike |
| $ |
匹配文本的结束字符 |
‘st$’ 匹配以 st 结尾的字符串 |
test、resist、persist |
| . |
匹配任何单个字符 |
‘b.t’ 匹配任何 b 和 t 之间有一个字符 |
bit、bat、but、bite |
| * |
匹配前面的字符 0 次或多次 |
‘f*n’ 匹配字符 n 前面有任意个字符 f |
fn、fan、faan、abcn |
| + |
匹配前面的字符 1 次或多次 |
‘ba+’ 匹配以 b 开头,后面至少紧跟一个 a |
ba、bay、bare、battle |
| ? |
匹配前面的字符 0 次或1次 |
‘sa?’ 匹配0个或1个a字符 |
sa、s |
| 字符串 |
匹配包含指定字符的文本 |
‘fa’ 匹配包含‘fa’的文本 |
fan、afa、faad |
| [字符集合] |
匹配字符集合中的任何一个字符 |
‘[xz]’ 匹配 x 或者 z |
dizzy、zebra、x-ray、extra |
| [^] |
匹配不在括号中的任何字符 |
‘[^abc]’ 匹配任何不包含 a、b 或 c 的字符串 |
desk、fox、f8ke |
| 字符串 |
匹配前面的字符串至少 n 次 |
‘b{2}’ 匹配 2 个或更多的 b |
bbb、bbbb、bbbbbbb |
| 字符串 |
匹配前面的字符串至少 n 次, 至多 m 次 |
|
|
【3】案例
【1】创建表
CREATE TABLE `person` (
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(40) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`heigh` int(40) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`sex` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
【2】插入数据
INSERT INTO `person` VALUES ('Thomas ', 25, 168, '男');
INSERT INTO `person` VALUES ('Tom ', 20, 172, '男');
INSERT INTO `person` VALUES ('Dany', 29, 175, '男');
INSERT INTO `person` VALUES ('Jane', 27, 171, '男');
INSERT INTO `person` VALUES ('Susan', 24, 173, '女');
INSERT INTO `person` VALUES ('Green', 25, 168, '女');
INSERT INTO `person` VALUES ('Henry', 21, 160, '女');
INSERT INTO `person` VALUES ('Lily', 18, 190, '男');
INSERT INTO `person` VALUES ('LiMing', 19, 187, '男');
【3】案例
# 查询 name 字段以j开头的记录
select * from person where name REGEXP '^j';
select * from person where name REGEXP 'y$';
select * from person where name REGEXP 'Th*';
# SQL语句中的正则表达式并不完善,所以功能不全
select * from person where name REGEXP '....';
【七】多表查询
【1】语法
select * from * where (select * from * where * ;);
【八】联表查询
【1】拼表的四种情况
- inner join:内连接
- left join:左连接
- 左表所有的数据都展示出来,没有对应的项就用null表示
- right join:右连接
- 右表所有的数据都展示出来,没有对应的项就用null表示
- union:全连接
【2】拼表查寻
select * from dep,emp;
# 左边所有的部门名称都有四份
# 优化
select * from dep,emp where dep.id=emp.dep_id;
【九】四种连接方式
【1】内连接
select * from emp inner join dep on emp.dep_id=dep.id;
# 内连接 一定要在 on 后面加条件进行筛选
select * from emp inner join dep;
【2】左连接
- 左表所有的数据都展示出来,没有对应的项就用null表示
select * from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id=dep.id;
【3】右连接
- 右表所有的数据都展示出来,没有对应的项就用null表示
select * from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id=dep.id;
【4】全连接
select * from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id
union
select * from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id;
;
【十】链表查询案例
select * from emp inner join dep on dep.id=emp.dep_id ;
select dep.name from emp inner join dep on dep.id=emp.dep_id
group by dep.name
having avg(emp.age) > 25
;
select group_concat(dep.name,":",emp.name,":",emp.age) from emp inner join dep on dep.id=emp.dep_id
group by dep.name
having avg(emp.age) > 25
;
【五】练习
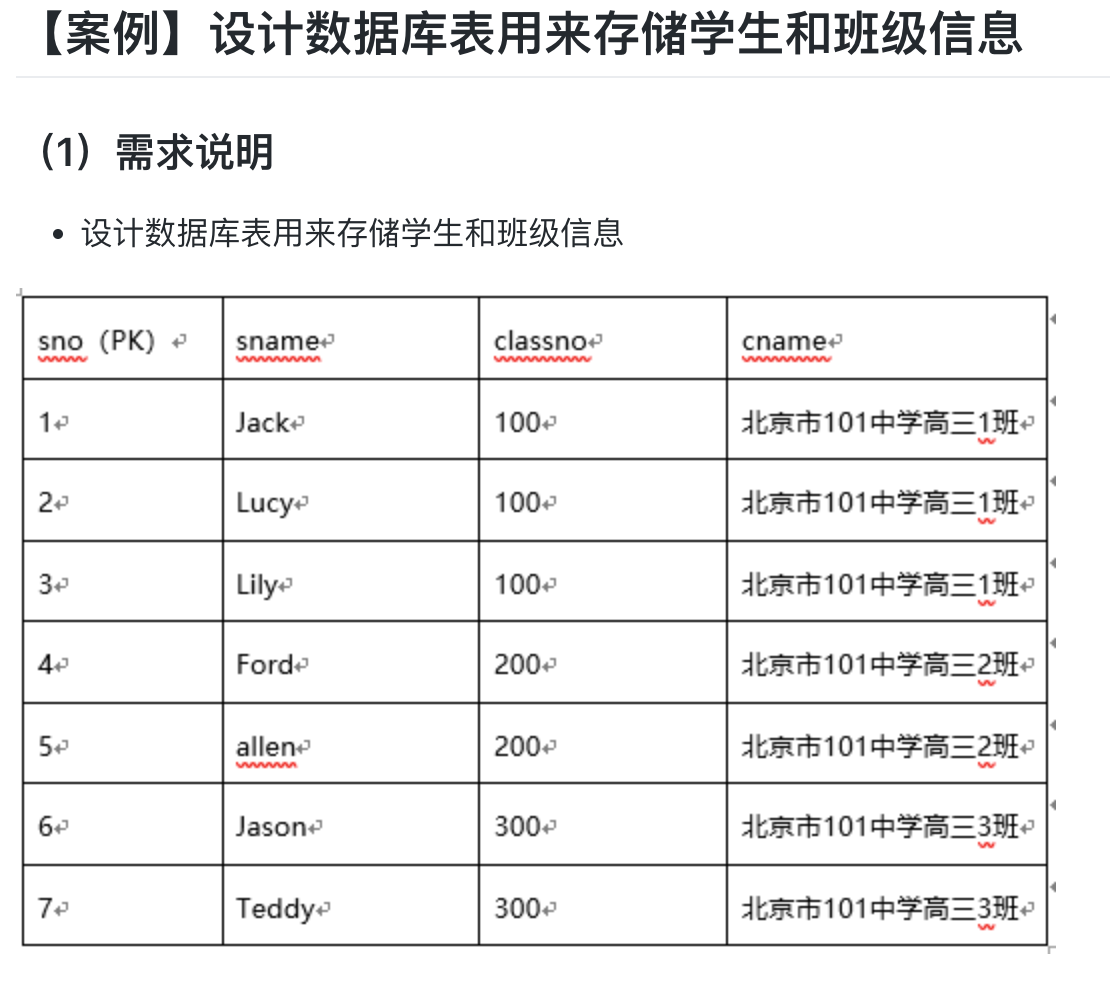
create table class(
cno int(10) primary key,
cname varchar(255) not null unique
);
create table student(
sno int(10) primary key ,
sname varchar(255) not null,
classno int(10),
constraint class_student foreign key(classno) references class(cno)
);
#插入数据
insert into class values(100,"北京市101中学高三1班");
insert into class values(200,"北京市101中学高三2班");
insert into class values(300,"北京市101中学高三3班");
insert into student values(1,"Jack",100),(2,"Lucy",100),(3,"Lily",100),(4,"Ford",200),(5,"allen",200),(6,"Jason",300),(7,"Teddy",300);
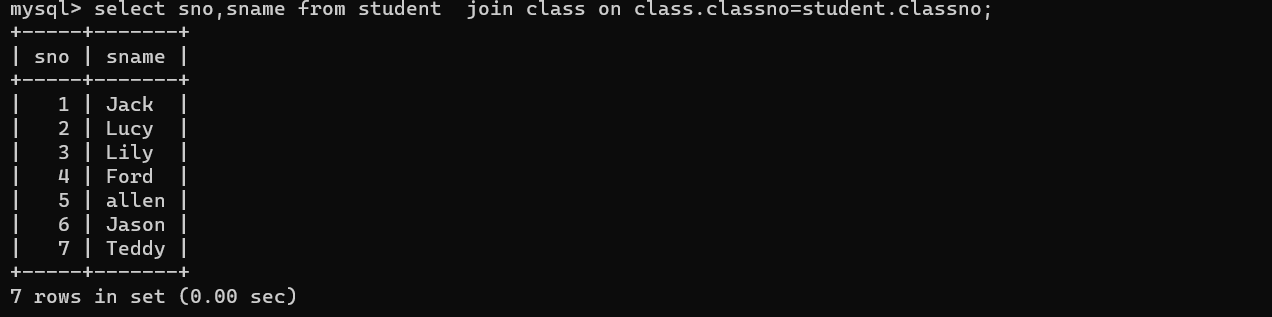
select sno,sname from student join class on class.cno=student.classno;
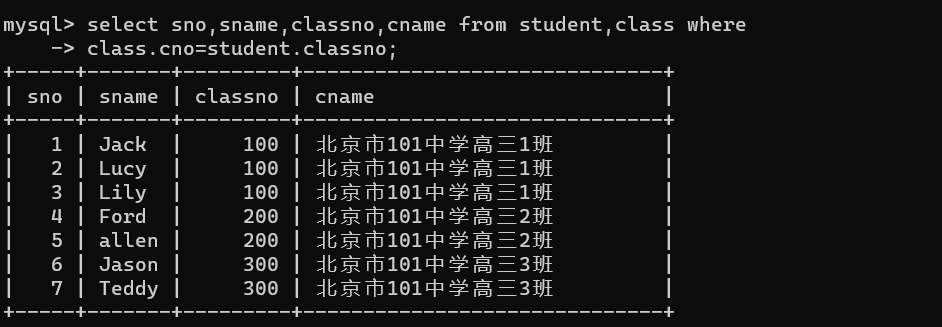
select sno,sname,classno,cname from student,class where
class.cno=student.classno;



















 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号