java拓展----NIO
一、介绍java 中的IO
具体介绍请往这走http://blog.51cto.com/stevex/1284437
以前的
二、使用NIO
首先介绍一下
通道 和缓冲区 是
通道是对原
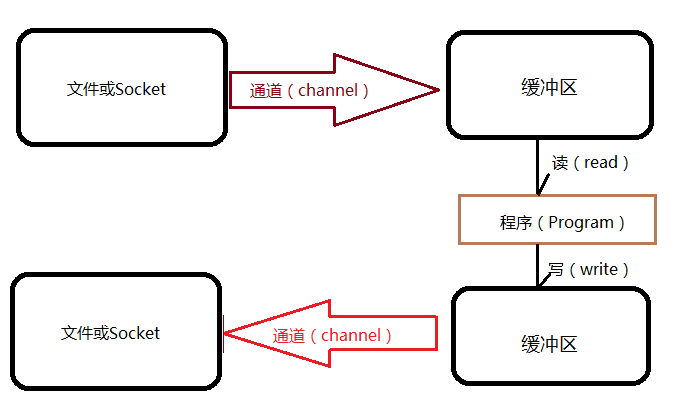
·
package com.demo.io.nio; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; public class FileChannelTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\Desktop\\test.jsp"); FileChannel foc = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\Desktop\\test.txt").getChannel(); FileChannel fic = fis.getChannel(); //创建一个缓冲区大小为48的ByteBuffer ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(2); int br = 0; while((br=fic.read(bb))!= -1) { //bb.flip() 的调用,首先读取数据到Buffer,然后反转Buffer,接着再从Buffer中读取数据 bb.flip(); //告诉当前位置和极限之间是否存在任何元素(此缓冲区中有元素) while(bb.hasRemaining()) { foc.write(bb); } System.out.println(); //缓存满了就会清理缓存 bb.clear(); } fic.close(); fis.close(); } }
三、简单的文件操作
操作流程图:
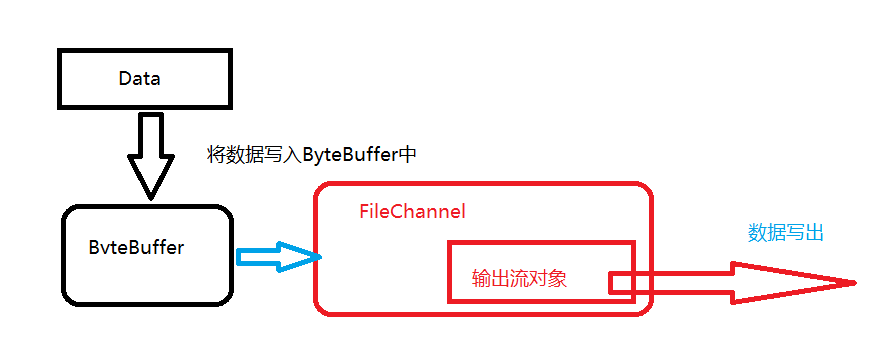
代码

public class NIOFileChannel { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String str = "hello world"; // 创建一个输出流 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("C:\\file\\file01.txt"); // 使用输出流获取到对应的FileChannel FileChannel fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel(); // 创建一个缓冲区 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // 将要写入的数据放入byteBuffer中 byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes()); // 反转ByteBuffer byteBuffer.flip(); // 将缓冲区的数据写入通道中 fileChannel.write(byteBuffer); fileChannel.close(); fileOutputStream.close(); } }

public class NIOFileChannelRead { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建文件输入流 FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("C:\\file\\file01.txt"); FileChannel fileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel(); // 创建缓冲区 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4); while (true) { // 将数据读取到fileChannel中 int read = fileChannel.read(byteBuffer); if (read == -1) { break; } // 这里如果缓冲区满了需要清空一下才能继续读 byteBuffer.clear(); // 输出数据内容 System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array())); } fileChannel.close(); fileInputStream.close(); } }

1 public class NIOFileChannelCopy { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 3 // 创建相关流 4 FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("C:\\file\\file01.txt"); 5 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("C:\\file\\file02.txt"); 6 // 获取相关管道 7 FileChannel sourceCh = fileInputStream.getChannel(); 8 FileChannel destCh = fileOutputStream.getChannel(); 9 10 // 使用transferForm完成拷贝 11 destCh.transferFrom(sourceCh, 0, sourceCh.size()); 12 sourceCh.close(); 13 destCh.close(); 14 } 15 }
四、零拷贝
大家都说
零拷贝(Zero-copy)技术指在计算机执行操作时,
简单点讲就是零拷贝就是没有
BIO 拷贝方式(经过4 次拷贝,三次态的切换)
mmap 拷贝方式(经过三次拷贝,三次态的切换)
sendFile(经过两次次拷贝,两次态的切换)
五、后记
个人觉得






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!