leetcode 算法整理
一 双指针
1.1 最大盛水量(No.11)
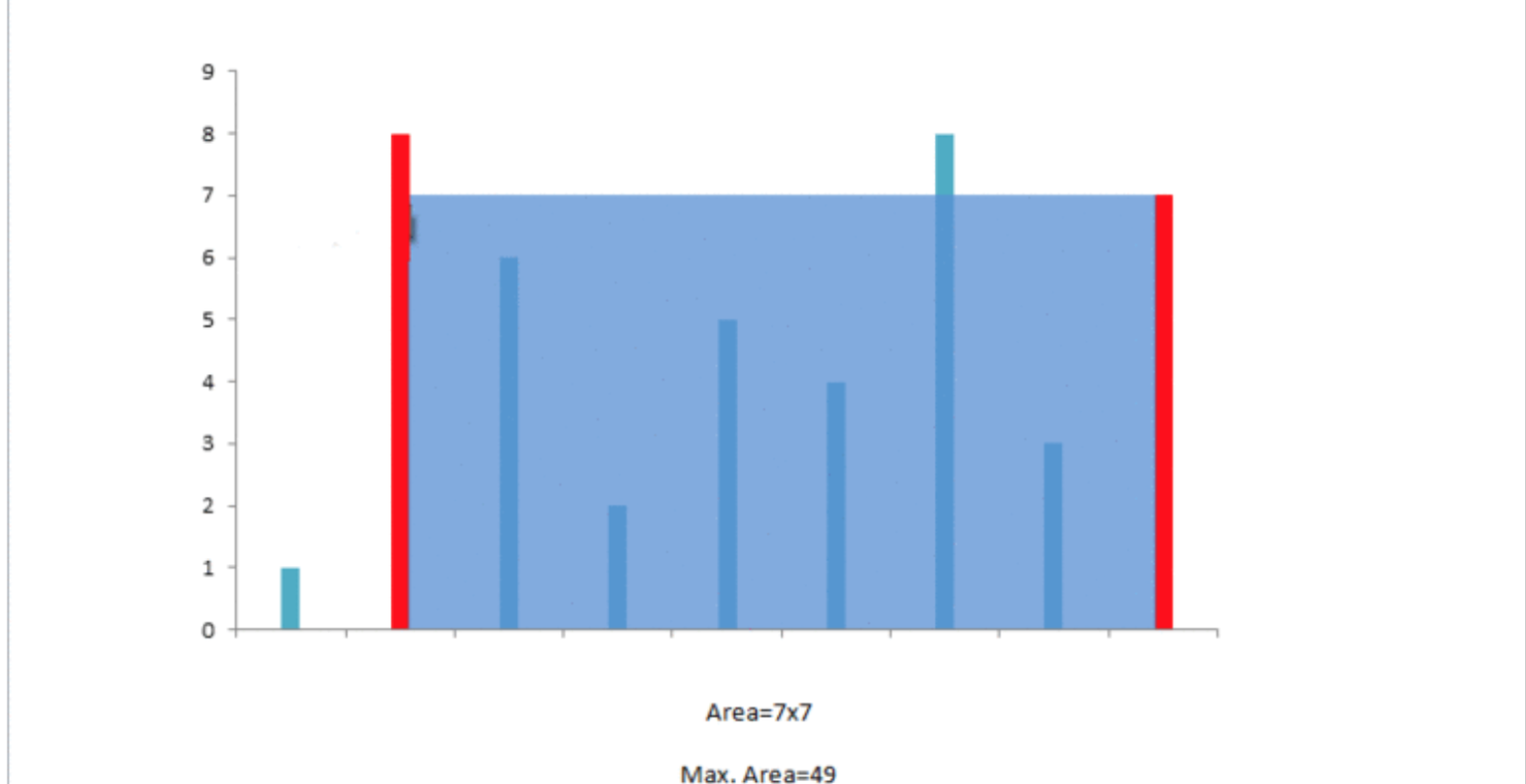
两个指针l和r,初始化为数组的两端,然后向中间移动找到最大的面积。如果l指向的数字小,则l需要右移才有可能获得更大容量,因为r左移,得到的容量肯定比r左移之前的容量小(高度已经被较小的l限制住了)。同理,r指向的数据小的话,则需要进行左移r。
public class Solution { public static int maxArea(int[] height) { int left = 0; int right = height.length - 1; int maxArea = 0; while (left < right) { maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, (right - left) * Math.min(height[left], height[right])); if (height[left] < height[right]) { left++; } else { right--; } } return maxArea; } }
1.2 接雨水(No.42)
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
示例 1:

输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 输出:6 解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
与最大承盛水量不同的是需要所有的雨水面积和,最快方法仍然是双指针
class Solution { public int trap(int[] height) { int ans = 0; int left = 0, right = height.length - 1; int leftMax = 0, rightMax = 0; while (left < right) { leftMax = Math.max(leftMax, height[left]); rightMax = Math.max(rightMax, height[right]); if (height[left] < height[right]) { ans += leftMax - height[left]; ++left; } else { ans += rightMax - height[right]; --right; } } return ans; } }
1.3 找出数组中三个数相加为0的不同组合(No.15)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] 满足 i != j、i != k 且 j != k ,同时还满足 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 。请
你返回所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4] 输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]] 解释: nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2] = (-1) + 0 + 1 = 0 。 nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[4] = 0 + 1 + (-1) = 0 。 nums[0] + nums[3] + nums[4] = (-1) + 2 + (-1) = 0 。 不同的三元组是 [-1,0,1] 和 [-1,-1,2] 。 注意,输出的顺序和三元组的顺序并不重要。
class Solution { public static List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>(); int length = nums.length; Arrays.sort(nums); for (int i = 0; i < length - 2; i++) { // 剪枝。已排序,整数作为最小的数,无法构造出三个数相加等于0 if (nums[i] > 0) { break; } // 剪枝。相等的数无需重复计算 if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) { continue; } int target = -nums[i]; int left = i + 1; int right = length - 1; while (left < right) { if (target == nums[left] + nums[right]) { ret.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right])); // 去重 while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) { left++; } while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) { right--; } left++; right--; } else if (target > nums[left] + nums[right]) { left++; } else { right--; } } } return ret; } }
1.4 移动0(No.283)
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
请注意 ,必须在不复制数组的情况下原地对数组进行操作。示例 1:
输入: nums = [0,1,0,3,12]
输出: [1,3,12,0,0]
class Solution { public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) { int n = nums.length, left = 0, right = 0; while (right < n) { if (nums[right] != 0) { if (left != right) { swap(nums, left, right); } left++; } right++; } } public void swap(int[] nums, int left, int right) { int temp = nums[left]; nums[left] = nums[right]; nums[right] = temp; } }
1.5 颜色分类(No.75)
给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色、共 n 个元素的数组 nums ,原地对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
我们使用整数 0、 1 和 2 分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。必须在不使用库内置的 sort 函数的情况下解决这个问题。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,0,2,1,1,0]
输出:[0,0,1,1,2,2]
class Solution { public void sortColors(int[] nums) { int n = nums.length; int p0 = 0, p1 = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (nums[i] == 1) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[p1]; nums[p1] = temp; ++p1; } else if (nums[i] == 0) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[p0]; nums[p0] = temp; if (p0 < p1) { temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[p1]; nums[p1] = temp; } ++p0; ++p1; } } } }
二 二分法
2.1 搜索插入位置(No.35)
给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。
请必须使用时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 5 输出: 2
示例 2:
输入: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 2 输出: 1
示例 3:
输入: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 7 输出: 4
class Solution { public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) { int left = 0; int right = nums.length - 1; int tmp = -1; while (left <= right) { int mid = (left + right) >> 1; if (nums[mid] == target) { return mid; } else if (nums[mid] < target) { left = mid + 1; tmp = left; } else { right = mid - 1; tmp = right + 1; } } return tmp; } }
2.2 D天内送达包裹的能力(No.1011)
同No.410
传送带上的包裹必须在 days 天内从一个港口运送到另一个港口。
传送带上的第 i 个包裹的重量为 weights[i]。每一天,我们都会按给出重量(weights)的顺序往传送带上装载包裹。我们装载的重量不会超过船的最大运载重量。
返回能在 days 天内将传送带上的所有包裹送达的船的最低运载能力。
示例 1:
输入:weights = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], days = 5 输出:15 解释: 船舶最低载重 15 就能够在 5 天内送达所有包裹,如下所示: 第 1 天:1, 2, 3, 4, 5 第 2 天:6, 7 第 3 天:8 第 4 天:9 第 5 天:10 请注意,货物必须按照给定的顺序装运,因此使用载重能力为 14 的船舶并将包装分成 (2, 3, 4, 5), (1, 6, 7), (8), (9), (10) 是不允许的。
class Solution { public int shipWithinDays(int[] weights, int days) { int left = 0; int right = 0; for (int i : weights) { left = Math.max(left, i); right += i; } while (left < right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2; if (match(weights, days, mid)) { right = mid; } else { left = mid + 1; } } return left; } private boolean match(int[] weights, int days, int mid) { int tmp = 0; int cnt = 1; for (int i = 0; i < weights.length; i++) { tmp += weights[i]; if (tmp > mid) { tmp = weights[i]; cnt++; if (cnt > days) { return false; } } } return true; } }
2.3 搜索二维矩阵(No.74)
给你一个满足下述两条属性的 m x n 整数矩阵:
- 每行中的整数从左到右按非严格递增顺序排列。
- 每行的第一个整数大于前一行的最后一个整数。
给你一个整数 target ,如果 target 在矩阵中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:

输入:matrix = [[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 3 输出:true
class Solution { public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) { // 先二分检索第一列找到pos, 再二分检索行[pos][n] int left = 0; int right = matrix.length - 1; int pos = 0; while (left <= right) { int mid = (left + right) >> 1; if (matrix[mid][0] == target) { return true; } else if (matrix[mid][0] < target) { left = mid + 1; pos = mid; } else if (matrix[mid][0] > target) { right = mid - 1; pos = mid == 0 ? 0 : mid - 1; } } left = 0; right = matrix[0].length - 1; while (left <= right) { int mid = (left + right) >> 1; if (matrix[pos][mid] == target) { return true; } else if (matrix[pos][mid] < target) { left = mid + 1; } else { right = mid - 1; } } return false; } }
2.4 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置(No.34)
给你一个按照非递减顺序排列的整数数组 nums,和一个目标值 target。请你找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置。
如果数组中不存在目标值 target,返回 [-1, -1]。 你必须设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8
输出:[3,4]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 6
输出:[-1,-1]
class Solution { public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) { int left = 0; int right = nums.length - 1; int first = -1; int last = -1; while (left <= right) { // 第一个等于target的位置 int middle = (left + right) >> 1; if (nums[middle] == target) { first = middle; right = middle - 1; //重点 } else if (nums[middle] > target) { right = middle - 1; } else { left = middle + 1; } } left = 0; right = nums.length - 1; while (left <= right) { // 最后一个等于target的位置 int middle = (left + right) / 2; if (nums[middle] == target) { last = middle; left = middle + 1; //重点 } else if (nums[middle] > target) { right = middle - 1; } else { left = middle + 1; } } return new int[]{first, last}; } }
2.5 搜索旋转排序树组(No.33)
整数数组 nums 按升序排列,数组中的值 互不相同 。
在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标 k(0 <= k < nums.length)上进行了 旋转,使数组变为 [nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]](下标 从 0 开始 计数)。例如, [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 在下标 3 处经旋转后可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] 。
给你 旋转后 的数组 nums 和一个整数 target ,如果 nums 中存在这个目标值 target ,则返回它的下标,否则返回 -1 。
你必须设计一个时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
输出:4
示例 2:
输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3
输出:-1
非最优解,时间打败7%,思想上没问题~
class Solution { public int search(int[] nums, int target) { int maxIndex = findMaxIndex(nums, 0 ,nums.length - 1); if (maxIndex == -1) { return binarySearch(nums, 0, nums.length - 1, target); } if (target >= nums[0]) { return binarySearch(nums, 0, maxIndex, target); } else { return binarySearch(nums, maxIndex + 1, nums.length - 1, target); } } private int binarySearch(int[] nums, int left, int right, int target) { while (left <= right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2; if (nums[mid] == target) { return mid; } else if (nums[mid] > target) { right = mid - 1; } else if (nums[mid] < target) { left = mid + 1; } } return -1; } private int findMaxIndex(int[] nums, int left, int right) { if (right - left == 0) { return -1; } if (right - left == 1) { return nums[left] < nums[right] ? -1 : left; } while (left <= right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2; if (mid == 0 || mid == nums.length - 1) { return mid; } if (nums[mid] >= nums[mid - 1] && nums[mid] <= nums[mid + 1]) { //没找到 int leftIndex = findMaxIndex(nums, left, mid); if (leftIndex != -1) { return leftIndex; } else { return findMaxIndex(nums, mid, right); } } else if (nums[mid] < nums[mid - 1]) { return mid - 1; } else if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1]) { return mid; } } return -1; } }
三 滑动窗口
3.1 无重复字符的最长子串(No.3)
给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的最长子串的长度。
示例 1:
输入: s = "abcabcbb"
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",所以其长度为 3。
这种是map一直不删除,但左指针是一直递进推移的
class Solution { public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) { if (s == null || s.length() == 0) { return 0; } char chs[] = s.toCharArray(); HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap(); int maxLen = 0; int left = 0; for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) { if (map.containsKey(chs[i])) { // 注意下由于map没有remove操作, 所以重复可能出现在left前也可能在后 left = Math.max(left, map.get(chs[i]) + 1); } map.put(chs[i], i); maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, i - left + 1); } return maxLen; } }
这种比上一种好理解一点,就是一旦重复了就执行删除操作,保证map里面的都是无重复的
class Solution { public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) { char[] chs = s.toCharArray(); if (chs == null || chs.length == 0) { return 0; } HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap(); int maxLen = 1; int left = 0; for (int right = 0; right < chs.length; right++) { if (!map.containsKey(chs[right])) { map.put(chs[right], right); maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, right - left + 1); } else { int index = map.get(chs[right]); for (int i = left; i <= index; i++) { map.remove(chs[i]); } left = index + 1; map.put(chs[right], right); } } return maxLen; } }
3.2 找到字符串中所有字母异位和(No.438)
给定两个字符串 s 和 p,找到 s 中所有 p 的 异位词 的子串,返回这些子串的起始索引。不考虑答案输出的顺序。
异位词 指由相同字母重排列形成的字符串(包括相同的字符串)。
示例 1:
输入: s = "cbaebabacd", p = "abc" 输出: [0,6] 解释: 起始索引等于 0 的子串是 "cba", 它是 "abc" 的异位词。 起始索引等于 6 的子串是 "bac", 它是 "abc" 的异位词。
class Solution { public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) { List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList(); char[] chs = p.toCharArray(); HashMap<Character, Integer> ansMap = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) { ansMap.put(chs[i], ansMap.getOrDefault(chs[i], 0) + 1); } char[] origin = s.toCharArray(); int left = 0; HashMap<Character, Integer> originMap = new HashMap<>(); for (int right = 0; right < origin.length; right++) { if (!ansMap.containsKey(origin[right])) { originMap = new HashMap<>(); left = right + 1; continue; } if (right - left + 1 <= chs.length) { originMap.put(origin[right], originMap.getOrDefault(origin[right], 0) + 1); if (right - left + 1 == chs.length) { if (compare(originMap, ansMap)) { resultList.add(left); } int minusCount = originMap.get(origin[left]); if (minusCount == 1) { originMap.remove(origin[left]); } else { originMap.put(origin[left], minusCount - 1); } left++; } } } return resultList; } private boolean compare(HashMap<Character, Integer> originMap, HashMap<Character, Integer> ansMap) { for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> entry : ansMap.entrySet()) { Character key = entry.getKey(); Integer value = entry.getValue(); Integer exceptedValue = originMap.get(key); if (exceptedValue == null || (int) exceptedValue != value) { return false; } } return true; } }
3.3 最小覆盖子串(No.76) - hard题
给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 "" 。
注意:对于 t 中重复字符,我们寻找的子字符串中该字符数量必须不少于 t 中该字符数量; 如果 s 中存在这样的子串,我们保证它是唯一的答案。
示例 1:
输入:s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC" 输出:"BANC" 解释:最小覆盖子串 "BANC" 包含来自字符串 t 的 'A'、'B' 和 'C'。
class Solution {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
Map<Character, Integer> need = new HashMap<>();
Map<Character, Integer> window = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {
need.put(t.charAt(i), need.getOrDefault(t.charAt(i), 0) + 1);
}
int right = 0, left = 0;
int valid = 0;
int start = 0, minLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while (right < s.length()) {
char cur = s.charAt(right);
right++;
// 进行窗口数据一系列更新
if (need.containsKey(cur)) {
Integer total = window.getOrDefault(cur, 0);
window.put(cur, total + 1);
if (window.get(cur).equals(need.get(cur))) {
valid++;
}
}
while (need.size() == valid) {
if (right - left < minLen) {
start = left;
minLen = right - left;
}
// d 是将移除窗口的字符串
char d = s.charAt(left);
// 左边移动窗口
left++;
// 进行窗口内数据当一系列更新
if (window.containsKey(d)) {
if (window.get(d).equals(need.get(d))) {
valid--;
}
window.put(d, window.get(d) - 1);
}
}
}
return minLen == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(start, start + minLen);
}
}
3.4 滑动窗口最大值(No.239) - hard题
给你一个整数数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。返回 滑动窗口中的最大值 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3 输出:[3,3,5,5,6,7] 解释: 滑动窗口的位置 最大值 --------------- ----- [1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3 1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3 1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5 1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5 1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6 1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
class Solution { public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) { int n = nums.length; PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<int[]>(new Comparator<int[]>() { public int compare(int[] pair1, int[] pair2) { return pair1[0] != pair2[0] ? pair2[0] - pair1[0] : pair2[1] - pair1[1]; } }); for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) { pq.offer(new int[]{nums[i], i}); } int[] ans = new int[n - k + 1]; ans[0] = pq.peek()[0]; for (int i = k; i < n; ++i) { pq.offer(new int[]{nums[i], i}); while (pq.peek()[1] <= i - k) { pq.poll(); } ans[i - k + 1] = pq.peek()[0]; } return ans; } }
四 链表
4.1 两个有序单链表合并成一个有序链表(No.21)
Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new list. The new list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Example:
Input: 1->2->4, 1->3->4 Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4
按位置比较插入新链表
public class Test1218 { public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode head = new ListNode(-1); ListNode cur = head; while (l1 != null & l2 != null) { if (l1.val < l2.val) { cur.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; } else { cur.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1; return head.next; } }
4.2 两两交换链表中的节点(No.24)
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]
class Solution { public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0); dummyHead.next = head; ListNode temp = dummyHead; while (temp.next != null && temp.next.next != null) { ListNode node1 = temp.next; ListNode node2 = temp.next.next; temp.next = node2; node1.next = node2.next; node2.next = node1; temp = node1; } return dummyHead.next; } }
非递归的迭代写法
class Solution { public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0); dummyHead.next = head; ListNode temp = dummyHead; while (temp.next != null && temp.next.next != null) { ListNode node1 = temp.next; ListNode node2 = temp.next.next; temp.next = node2; node1.next = node2.next; node2.next = node1; temp = node1; } return dummyHead.next; } }
4.3 链表成环及交点中的节点(No.142)
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
示例 1:

输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) { return null; } ListNode slow = head, fast = head; boolean hasCircle = false; while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (slow == fast) { hasCircle = true; break; } } if (!hasCircle) { return null; } ListNode cur = head; while (cur != slow) { cur = cur.next; slow = slow.next; } return slow; } }
4.4 排序链表(No.148)
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
示例 1:
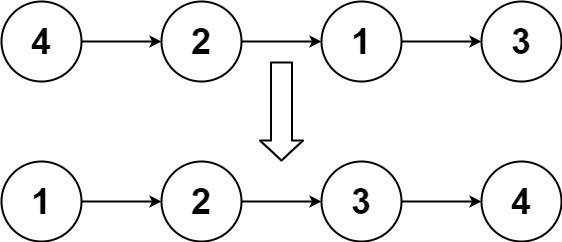
输入:head = [4,2,1,3] 输出:[1,2,3,4]
class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { return sortList(head, null); } public ListNode sortList(ListNode head, ListNode tail) { if (head == null) { return head; } if (head.next == tail) { head.next = null; return head; } ListNode slow = head, fast = head; while (fast != tail) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; if (fast != tail) { fast = fast.next; } } ListNode mid = slow; ListNode list1 = sortList(head, mid); ListNode list2 = sortList(mid, tail); ListNode sorted = merge(list1, list2); return sorted; } public ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0); ListNode temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2; while (temp1 != null && temp2 != null) { if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) { temp.next = temp1; temp1 = temp1.next; } else { temp.next = temp2; temp2 = temp2.next; } temp = temp.next; } if (temp1 != null) { temp.next = temp1; } else if (temp2 != null) { temp.next = temp2; } return dummyHead.next; } }
4.5 删除链表的倒数第N个节点(No.19)
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:
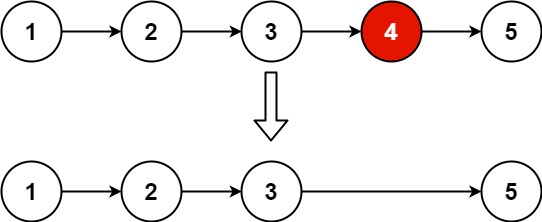
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5]
class Solution { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) { ListNode cur = head; ListNode tmp = head; int len = 0; while (head != null) { // 遍历获得链表的size head = head.next; len++; } // 如果删除的是第一个节点 if (n == len) { tmp = tmp.next; return tmp; } int cnt = 0; while (cnt + n < len - 1) { // 找到倒数第n个节点 len = 5 n = 2 cnt==2时候跳出 tmp = tmp.next; cnt++; } tmp.next = tmp.next.next; return cur; } }
4.6 K个一组翻转链表(No.25)
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:
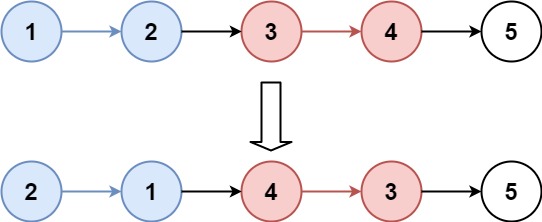
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
class Solution { /** 题解 https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/solutions/10416/tu-jie-kge-yi-zu-fan-zhuan-lian-biao-by-user7208t/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked */ public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy.next = head; ListNode pre = dummy; ListNode end = dummy; while (end.next != null) { for (int i = 0; i < k && end != null; i++) end = end.next; if (end == null) break; ListNode start = pre.next; ListNode next = end.next; end.next = null; pre.next = reverse(start); start.next = next; pre = start; end = pre; } return dummy.next; } private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null; ListNode curr = head; while (curr != null) { ListNode next = curr.next; curr.next = pre; pre = curr; curr = next; } return pre; } }
4.7 回文链表(No.234)
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为
示例 1:
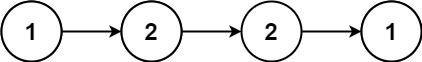
输入:head = [1,2,2,1] 输出:true
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
//通过快慢指针找到中点
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//如果fast不为空,说明链表的长度是奇数个
if (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
}
//反转后半部分链表
slow = reverse(slow);
fast = head;
while (slow != null) {
//然后比较,判断节点值是否相等
if (fast.val != slow.val)
return false;
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = pre.next;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode nex = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nex;
}
head.next = null;
return pre;
}
}
4.8 合并K个升序链表(No.234)
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6] 解释:链表数组如下: [ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6 ] 将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]] 输出:[]
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
return merge(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode[] lists, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {
return lists[l];
}
if (l > r) {
return null;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
return mergeTwoLists(merge(lists, l, mid), merge(lists, mid + 1, r));
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode a, ListNode b) {
if (a == null || b == null) {
return a != null ? a : b;
}
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode tail = head, aPtr = a, bPtr = b;
while (aPtr != null && bPtr != null) {
if (aPtr.val < bPtr.val) {
tail.next = aPtr;
aPtr = aPtr.next;
} else {
tail.next = bPtr;
bPtr = bPtr.next;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = (aPtr != null ? aPtr : bPtr);
return head.next;
}
}
4.9 LRU缓存(No.146)
LRUCache 类:LRUCache(int capacity)以 正整数 作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字key已经存在,则变更其数据值value;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组key-value。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过capacity,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例:
输入 ["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"] [[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]] 输出 [null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
public class LRUCache { class DLinkedNode { int key; int value; DLinkedNode prev; DLinkedNode next; public DLinkedNode() {} public DLinkedNode(int _key, int _value) {key = _key; value = _value;} } private Map<Integer, DLinkedNode> cache = new HashMap<Integer, DLinkedNode>(); private int size; private int capacity; private DLinkedNode head, tail; public LRUCache(int capacity) { this.size = 0; this.capacity = capacity; // 使用伪头部和伪尾部节点 head = new DLinkedNode(); tail = new DLinkedNode(); head.next = tail; tail.prev = head; } public int get(int key) { DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key); if (node == null) { return -1; } // 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再移到头部 moveToHead(node); return node.value; } public void put(int key, int value) { DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key); if (node == null) { // 如果 key 不存在,创建一个新的节点 DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode(key, value); // 添加进哈希表 cache.put(key, newNode); // 添加至双向链表的头部 addToHead(newNode); ++size; if (size > capacity) { // 如果超出容量,删除双向链表的尾部节点 DLinkedNode tail = removeTail(); // 删除哈希表中对应的项 cache.remove(tail.key); --size; } } else { // 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再修改 value,并移到头部 node.value = value; moveToHead(node); } } private void addToHead(DLinkedNode node) { node.prev = head; node.next = head.next; head.next.prev = node; head.next = node; } private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node) { node.prev.next = node.next; node.next.prev = node.prev; } private void moveToHead(DLinkedNode node) { removeNode(node); addToHead(node); } private DLinkedNode removeTail() { DLinkedNode res = tail.prev; removeNode(res); return res; } }
五 二叉树
5.1 二叉树左右对称(No.101)
返回是否一个二叉树为左右对称结构, 非递归实现如下
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) { Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>(); q.add(root); q.add(root); while (!q.isEmpty()) { TreeNode t1 = q.poll(); TreeNode t2 = q.poll(); if (t1 == null && t2 == null) continue; if (t1 == null || t2 == null) return false; if (t1.val != t2.val) return false; q.add(t1.left); q.add(t2.right); q.add(t1.right); q.add(t2.left); } return true; }
5.2 二叉树转化为链表(No.114)
给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你将它展开为一个单链表:
- 展开后的单链表应该同样使用
TreeNode,其中right子指针指向链表中下一个结点,而左子指针始终为null。 - 展开后的单链表应该与二叉树 先序遍历 顺序相同。
示例 1:
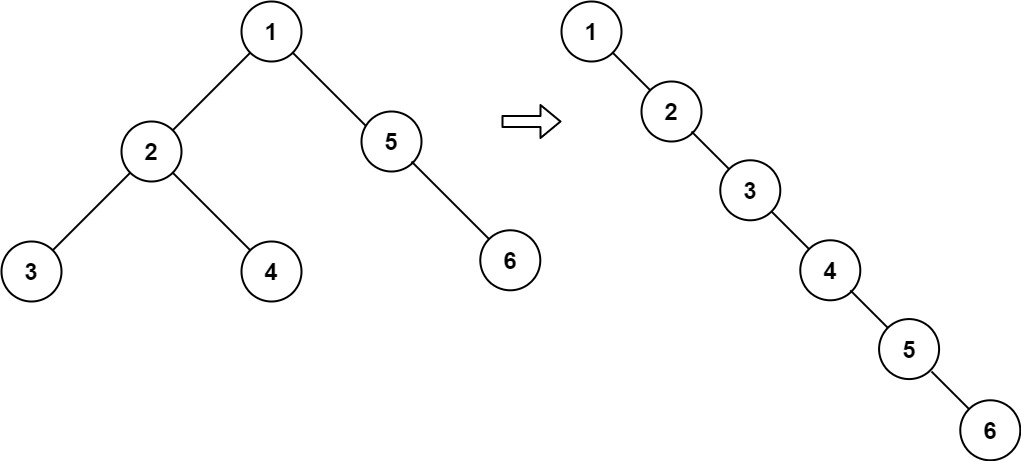
输入:root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] 输出:[1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
TreeNode node = root;
List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(node);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
if (top == null) {
continue;
}
list.add(top);
stack.push(top.right);
stack.push(top.left);
}
int index = 0;
TreeNode pre = null;
while (index < list.size()) {
TreeNode curNode = list.get(index);
if (index > 0) {
pre.right = curNode;
pre.left = null;
}
index++;
pre = curNode;
}
}
}
5.3 二叉树的直径(No.543)
给你一棵二叉树的根节点,返回该树的 直径 。
二叉树的 直径 是指树中任意两个节点之间最长路径的 长度 。这条路径可能经过也可能不经过根节点 root 。
两节点之间路径的 长度 由它们之间边数表示。
示例 1:

输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:3 解释:3 ,取路径 [4,2,1,3] 或 [5,2,1,3] 的长度。
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2] 输出:1
class Solution {
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftValue = Math.max(0, diameterOfBinaryTree(root.left));
int rightValue = Math.max(0, diameterOfBinaryTree(root.right));
int result = Math.max(leftValue, rightValue);
return Math.max(result, contribute(root.left) + contribute(root.right));
}
private int contribute(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
return 1 + Math.max(contribute(node.left), contribute(node.right));
}
}
5.4 将有序数组转化为二叉搜索树(No.108)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中元素已经按 升序 排列,请你将其转换为一棵 平衡二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
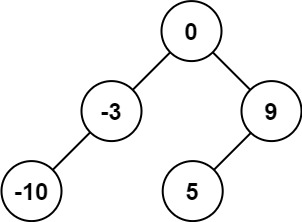
输入:nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9] 输出:[0,-3,9,-10,null,5] 解释:[0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] 也将被视为正确答案:

class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return null;
}
return construct(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode construct(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if (left == right) {
return new TreeNode(nums[left], null, null);
} else if (left > right) {
return null;
}
int len = left + right + 1;
int middle = len / 2;
TreeNode leftNode = construct(nums, left, middle - 1);
TreeNode rightNode = construct(nums, middle + 1, right);
return new TreeNode(nums[middle], leftNode, rightNode);
}
}
5.5 二叉树的最近公共祖先(No.236)
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 输出:3 解释:节点5和节点1的最近公共祖先是节点3 。
class Solution { private TreeNode ans; private boolean dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root == null) return false; boolean lson = dfs(root.left, p, q); boolean rson = dfs(root.right, p, q); if ((lson && rson) || ((root.val == p.val || root.val == q.val) && (lson || rson))) { ans = root; } return lson || rson || (root.val == p.val || root.val == q.val); } public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { this.dfs(root, p, q); return this.ans; } }
六 动态规划
6.1 字符串中的最大回文串(No.5)
给你一个字符串s,找到s中最长的回文子串
示例 1:
输入:s = "babad" 输出:"bab" 解释:"aba" 同样是符合题意的答案。
示例 2:
输入:s = "cbbd" 输出:"bb"
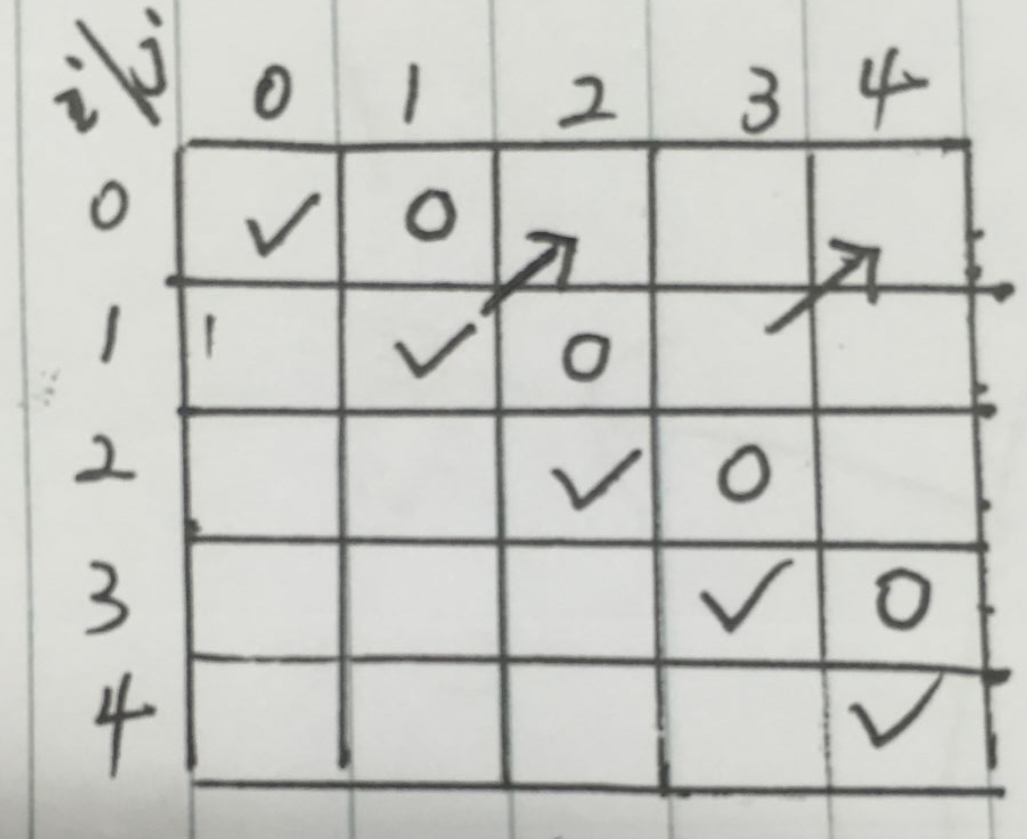
思路: 设 p[i][j] 代表下标从i至j的子字符串是否是回文串,取值为boolean
转移方程 p[i][j] = p[i+1][j-1] && chars[i] == chars[j]
初始化的状态为 p[i][i] = true p[i][i+1] = chars[i] == chars[i+1]
看下面手绘图理解一下,打勾的对角线p[i][i] 恒为true, 只有这一列是不够状态转移的,因为按照转移方程,必须要图示的↗️方向递推,那么要需要有圆圈的一列初始化,这列对应的是p[i][i+1]。 剩下的递推即可,比如图中的箭头栗子🌰,p[0][2]要根据p[1][1]加上元素值推演过来,而p[0][4]需要p[1][3]的值推演过来。所以更新下表的顺序是打勾列向↗️更新
public class Solution { public String longestPalindrome(String s) { int len = s.length(); if (len < 2) { return s; } int maxLen = 1; int begin = 0; boolean[][] dp = new boolean[len][len]; // dp[i][j] 表示 s[i..j] 是否是回文串 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { // 初始化:所有长度为 1 的子串都是回文串 dp[i][i] = true; } char[] charArray = s.toCharArray(); for (int j = 1; j < len; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) { if (charArray[i] != charArray[j]) { dp[i][j] = false; } else { if (j - i < 3) { dp[i][j] = true; } else { dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1]; } } if (dp[i][j] && j - i + 1 > maxLen) { maxLen = j - i + 1; begin = i; } } } return s.substring(begin, begin + maxLen); } }
6.2 销售利润最大化(No.2830)
给你一个整数 n 表示数轴上的房屋数量,编号从 0 到 n - 1 。
另给你一个二维整数数组 offers ,其中 offers[i] = [starti, endi, goldi] 表示第 i 个买家想要以 goldi 枚金币的价格购买从 starti 到 endi 的所有房屋。
作为一名销售,你需要有策略地选择并销售房屋使自己的收入最大化。
返回你可以赚取的金币的最大数目。
注意 同一所房屋不能卖给不同的买家,并且允许保留一些房屋不进行出售。
示例 1:
输入:n = 5, offers = [[0,0,1],[0,2,2],[1,3,2]] 输出:3 解释: 有 5 所房屋,编号从 0 到 4 ,共有 3 个购买要约。 将位于 [0,0] 范围内的房屋以 1 金币的价格出售给第 1 位买家,并将位于 [1,3] 范围内的房屋以 2 金币的价格出售给第 3 位买家。 可以证明我们最多只能获得 3 枚金币。
class Solution { public int maximizeTheProfit(int n, List<List<Integer>> offers) { Map<Integer, List<List<Integer>>> map = new HashMap<>(); for (List<Integer> list : offers) { List<List<Integer>> each = map.getOrDefault(list.get(1), new ArrayList()); each.add(Arrays.asList(list.get(0), list.get(2))); map.put(list.get(1), each); } int dp[] = new int[n + 1]; for (int end = 0; end < n; end++) { List<List<Integer>> each = map.getOrDefault(end, new ArrayList()); dp[end + 1] = dp[end]; for (List<Integer> list : each) { dp[end + 1] = Math.max(dp[end + 1], dp[list.get(0)] + list.get(1)); } } return dp[n]; } }
6.3 乘积最大子数组和(No.152)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你找出数组中乘积最大的非空连续子数组(该子数组中至少包含一个数字),并返回该子数组所对应的乘积。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [2,3,-2,4]
输出:
6
解释: 子数组 [2,3] 有最大乘积 6。
示例 2:
输入: nums = [-2,0,-1]
输出: 0
解释: 结果不能为 2, 因为 [-2,-1] 不是子数组。
class Solution {
public int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
int maxF = nums[0], minF = nums[0], ans = nums[0];
int length = nums.length;
for (int i = 1; i < length; ++i) {
int mx = maxF, mn = minF;
maxF = Math.max(mx * nums[i], Math.max(nums[i], mn * nums[i]));
minF = Math.min(mn * nums[i], Math.min(nums[i], mx * nums[i]));
ans = Math.max(maxF, ans);
}
return ans;
}
}
6.4 最长递增子序列(No.300)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,找到其中最长严格递增子序列的长度。
子序列 是由数组派生而来的序列,删除(或不删除)数组中的元素而不改变其余元素的顺序。例如,[3,6,2,7] 是数组 [0,3,1,6,2,2,7] 的子序列
示例 1:
输入:nums = [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18] 输出:4 解释:最长递增子序列是 [2,3,7,101],因此长度为 4 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1,0,3,2,3] 输出:4
class Solution { public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) { int dp[] = new int[nums.length]; dp[0] = 1; int max = 1; for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) { dp[i] = 1; for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { if (nums[i] > nums[j]) { dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1); } } max = Math.max(max, dp[i]); } return max; } }
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
int len = 1, n = nums.length;
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] d = new int[n + 1];
d[len] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
if (nums[i] > d[len]) {
d[++len] = nums[i];
} else {
int l = 1, r = len, pos = 0; // 如果找不到说明所有的数都比 nums[i] 大,此时要更新 d[1],所以这里将 pos 设为 0
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (d[mid] < nums[i]) {
pos = mid;
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
d[pos + 1] = nums[i];
// d[l] = nums[i];
}
}
return len;
}
}
6.5 零钱兑换(No.322)
给你一个整数数组coins, 表示不同面额的硬币; 以及一个整数amount, 表示总金额。
计算并返回可以凑成总金额所需的 最少的硬币个数 。如果没有任何一种硬币组合能组成总金额,返回 -1 。
你可以认为每种硬币的数量是无限的。
示例 1:
输入:coins = [1, 2, 5], amount = 11
输出:3
解释:11 = 5 + 5 + 1
示例 2:
输入:coins = [2], amount = 3
输出:-1
示例 3:
输入:coins = [1], amount = 0
输出:0
class Solution { public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) { if (amount == 0) { return 0; } int dp[] = new int[amount + 1]; Arrays.fill(dp, amount + 1); dp[0] = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) { for (int j = coins.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) { if (coins[j] <= i) { dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coins[j]] + 1); } } } return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount]; } }
七 数组
7.1 合并区间(No.56) - 模拟
以数组 intervals 表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回 一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间 。
示例 1:
输入:intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]] 输出:[[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]] 解释:区间 [1,3] 和 [2,6] 重叠, 将它们合并为 [1,6].
示例 2:
输入:intervals = [[1,4],[4,5]] 输出:[[1,5]] 解释:区间 [1,4] 和 [4,5] 可被视为重叠区间。
class Solution { public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) { if (intervals.length == 1) { return intervals; } Arrays.sort(intervals, new Comparator<>() { public int compare(int[] interval1, int[] interval2) { return interval1[0] - interval2[0]; } }); int[][] ans = new int[intervals.length][2]; int ansCnt = 0; int[] pre = intervals[0]; for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) { int [] cur = intervals[i]; int left = pre[1]; int right = cur[0]; if (left < right) { ans[ansCnt] = pre; pre = cur; ansCnt++; } else if (left >= right) { // 上一个结果值要更新下, pre也要更新下 pre = new int[]{pre[0], Math.max(pre[1], cur[1])}; } if (i == intervals.length - 1) { //最后一个值直接加上 ans[ansCnt] = pre; } } int[][] finalAns = new int[ansCnt + 1][2]; System.arraycopy(ans, 0, finalAns, 0, ansCnt + 1); return finalAns; } }
7.2 轮转数组(No.189) - 数组模拟(带gcd)
给定一个整数数组 nums,将数组中的元素向右轮转 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k = 3
输出: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
解释:
向右轮转 1 步: [7,1,2,3,4,5,6]
向右轮转 2 步: [6,7,1,2,3,4,5]
向右轮转 3 步: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
class Solution { public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) { if (k == 0 || (k == 1 && nums.length == 1)) { return; } k = k % nums.length; for (int i = 0; i < gcd(k, nums.length); i++) { func(nums, i, k); } } private void func(int[] nums, int index, int k) { int pre = nums[index]; int newIndex = -1; int oldIndex = index; int next = nums[index]; while (newIndex != index) { pre = next; // pre=4 newIndex = (oldIndex + k) % nums.length; next = nums[newIndex]; // next=4; next=nums[6]=7; nums[newIndex] = pre; // nums[3]=1 nums[7]=4 oldIndex = newIndex; // oldIndex=3 oldIndex=6 } } private int gcd(int x, int y) { return y > 0 ? gcd(y, x % y) : x; } }
7.3 除自身以外数组的乘积(No.238) - 数组模拟
给你一个整数数组 nums,返回 数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 等于 nums 中除 nums[i] 之外其余各元素的乘积 。
题目数据 保证 数组 nums之中任意元素的全部前缀元素和后缀的乘积都在 32 位 整数范围内。
请不要使用除法,且在 O(n) 时间复杂度内完成此题。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,4]
输出: [24,12,8,6]
class Solution { public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) { int length = nums.length; // L 和 R 分别表示左右两侧的乘积列表 int[] L = new int[length]; int[] R = new int[length]; int[] answer = new int[length]; // L[i] 为索引 i 左侧所有元素的乘积 // 对于索引为 '0' 的元素,因为左侧没有元素,所以 L[0] = 1 L[0] = 1; for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) { L[i] = nums[i - 1] * L[i - 1]; } // R[i] 为索引 i 右侧所有元素的乘积 // 对于索引为 'length-1' 的元素,因为右侧没有元素,所以 R[length-1] = 1 R[length - 1] = 1; for (int i = length - 2; i >= 0; i--) { R[i] = nums[i + 1] * R[i + 1]; } // 对于索引 i,除 nums[i] 之外其余各元素的乘积就是左侧所有元素的乘积乘以右侧所有元素的乘积 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { answer[i] = L[i] * R[i]; } return answer; } }
八 回溯
8.1 分割回文串(NO.131)
给你一个字符串 s,请你将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是回文串 。返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
示例 1:
输入:s = "aab" 输出:[["a","a","b"],["aa","b"]]
示例 2:
输入:s = "a" 输出:[["a"]]
class Solution { List<List<String>> ansList = new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<String>> partition(String s) { dfs(0, s, new ArrayList()); return ansList; } private void dfs(int index, String s, List<String> curList) { if (index == s.length()) { ansList.add(new ArrayList(curList)); return; } for (int i = index; i < s.length(); i++) { String sub = s.substring(index, i + 1); if (judge(sub)) { curList.add(sub); dfs(i + 1, s, curList); curList.remove(curList.size() - 1); } } } private boolean judge(String s) { char chs[] = s.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0; i < chs.length/ 2; i++) { if (chs[i] != chs[chs.length - i - 1]) { return false; } } return true; } }
8.2 子集(No.78)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中的元素 互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。你可以按 任意顺序 返回解集。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0] 输出:[[],[0]]
class Solution { private List<List<Integer>> ansList = new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { dfs(0, nums, new ArrayList<>()); return ansList; } private void dfs(int i, int[] nums, List<Integer> tmpList) { tmpList = new ArrayList(tmpList); if (i == nums.length) { ansList.add(tmpList); return; } // 没选i dfs(i + 1, nums, tmpList); // 选i tmpList.add(nums[i]); dfs(i + 1, nums, tmpList); } }
8.3 全排列(No.46)
给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> ansList = new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { dfs(0, nums, new ArrayList()); return ansList; } private void dfs(int index, int[] nums, List<Integer> list) { if (index == nums.length) { ansList.add(list); return; } for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { List<Integer> copyList = new ArrayList(list); if (!list.contains(nums[i])) { copyList.add(nums[i]); dfs(index + 1, nums, copyList); } } } }
九 矩阵
9.1 旋转图像(No.48)
给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵 matrix 表示一个图像。请你将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。
你必须在 原地 旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。请不要 使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像。
示例 1:
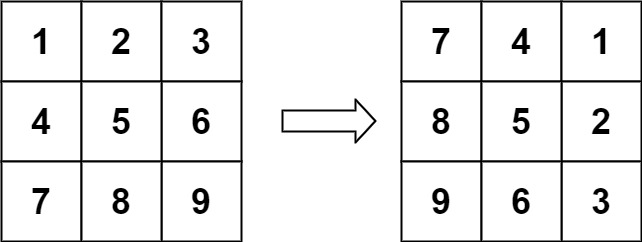
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] 输出:[[7,4,1],[8,5,2],[9,6,3]]
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
int n = matrix.length;
// 水平翻转
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[n - i - 1][j];
matrix[n - i - 1][j] = temp;
}
}
// 主对角线翻转
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
int temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i];
matrix[j][i] = temp;
}
}
}
}
9.2 搜索二维矩阵2 (No.240)
编写一个高效的算法来搜索 m x n 矩阵 matrix 中的一个目标值 target 。该矩阵具有以下特性:
- 每行的元素从左到右升序排列。
- 每列的元素从上到下升序排列。
示例 1:
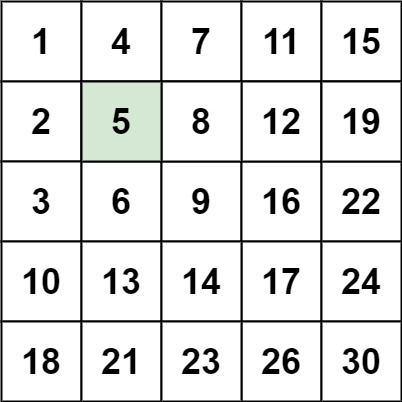
输入:matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 5 输出:true
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int x = 0, y = n - 1;
while (x < m && y >= 0) {
if (matrix[x][y] == target) {
return true;
}
if (matrix[x][y] > target) {
--y;
} else {
++x;
}
}
return false;
}
}
9.3 螺旋矩阵 (No.54)
给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
示例 1:
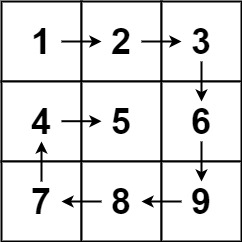
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] 输出:[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
class Solution { int [][] visit = new int[12][12]; public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList(); int curM = 0; int curN = 0; visit[curM][curN] = 1; result.add(matrix[curM][curN]); while (true) { boolean allVisit = true; if (canVisit(matrix, curM, curN + 1)) { // 如果可以向右 allVisit = false; while (canVisit(matrix, curM, curN + 1)) { curN = curN + 1; visit[curM][curN] = 1; result.add(matrix[curM][curN]); } } if (canVisit(matrix, curM + 1, curN)) { // 如果可以向下 allVisit = false; while (canVisit(matrix, curM + 1, curN)) { curM = curM + 1; visit[curM][curN] = 1; result.add(matrix[curM][curN]); } } if (canVisit(matrix, curM, curN - 1)) { // 如果可以向左 allVisit = false; while (canVisit(matrix, curM, curN - 1)) { curN = curN - 1; visit[curM][curN] = 1; result.add(matrix[curM][curN]); } } if (canVisit(matrix, curM - 1, curN)) { // 如果可以向上 allVisit = false; while (canVisit(matrix, curM - 1, curN)) { curM = curM - 1; visit[curM][curN] = 1; result.add(matrix[curM][curN]); } } if (allVisit) { break; } } return result; } private boolean canVisit(int [][]matrix, int m, int n) { if (m < 0 || m > matrix.length - 1 || n < 0 || n > matrix[0].length - 1) { return false; } if (visit[m][n] == 1) { return false; } return true; } }
十 其他
10.1 判断是否为回文的整数(NO.9) - 智力题
Determine whether an integer is a palindrome. Do this without extra space.
换成char[], 遍历一半(空间复杂度非最优)
class Solution {public static boolean isPalindrome(int x) { if (x < 0) { x = -x; } char[] charArray = String.valueOf(x).toCharArray(); int length = charArray.length; for (int i = 0; i < length >> 1; i++) { if (charArray[i] == charArray[length - 1 - i]) { return true; } } return false; } }
按位除法&取余处理,构造出逆序的字串进行比较
class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome(int x) { // 特殊情况: // 如上所述,当 x < 0 时,x 不是回文数。 // 同样地,如果数字的最后一位是 0,为了使该数字为回文, // 则其第一位数字也应该是 0 // 只有 0 满足这一属性 if (x < 0 || (x % 10 == 0 && x != 0)) { return false; } int revertedNumber = 0; while (x > revertedNumber) { revertedNumber = revertedNumber * 10 + x % 10; x /= 10; } // 当数字长度为奇数时,我们可以通过 revertedNumber/10 去除处于中位的数字。 // 例如,当输入为 12321 时,在 while 循环的末尾我们可以得到 x = 12,revertedNumber = 123, // 由于处于中位的数字不影响回文(它总是与自己相等),所以我们可以简单地将其去除。 return x == revertedNumber || x == revertedNumber / 10; } }
10.2 top K问题(No.347) 优先队列/桶排序
给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 输出: [1,2]
1. 桶排序解法,比如a出现3次, b出现6次,c出现3次,那么构造出bucket[3] = Arrays.asList(a, c), bucket[6] = Arrays.asList(b)
public class TTest { public static List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { Map<Integer, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); List<Integer>[] bucket = new List[nums.length]; List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); for (int num : nums) { map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1); } for (int key : map.keySet()) { int frequency = map.get(key); if (bucket[frequency] == null) { bucket[frequency] = new ArrayList<>(); } bucket[frequency].add(key); } for (int pos = bucket.length - 1; pos >= 0; pos--) { if (bucket[pos] != null) { for (int i = 0; i < bucket[pos].size() && res.size() < k; i++) res.add(bucket[pos].get(i)); } } return res; } }
堆排序解法,用集合中的PriorityQueue
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { Map<Integer, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); for (int n : nums) { map.put(n, map.getOrDefault(n, 0) + 1); } PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((l, r) -> r.getValue() - l.getValue()); heap.addAll(map.entrySet()); List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); int[] ret = new int[k]; int cnt = 0; while (cnt < k) { ret[cnt++] = heap.poll().getKey(); } return ret; }
另一种优先队列的写法
class Solution { public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { Map<Integer, Integer> occurrences = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); for (int num : nums) { occurrences.put(num, occurrences.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1); } // int[] 的第一个元素代表数组的值,第二个元素代表了该值出现的次数 PriorityQueue<int[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<int[]>(new Comparator<int[]>() { public int compare(int[] m, int[] n) { return m[1] - n[1]; } }); for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : occurrences.entrySet()) { int num = entry.getKey(), count = entry.getValue(); if (queue.size() == k) { if (queue.peek()[1] < count) { queue.poll(); queue.offer(new int[]{num, count}); } } else { queue.offer(new int[]{num, count}); } } int[] ret = new int[k]; for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) { ret[i] = queue.poll()[0]; } return ret; } }
10.3 最长连续序列(No.128) hash
给定一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,找出数字连续的最长序列(不要求序列元素在原数组中连续)的长度。
请你设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2]
输出:4
解释:最长数字连续序列是 [1, 2, 3, 4]。它的长度为 4。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,3,7,2,5,8,4,6,0,1] 输出:9
不排序的hash解法
class Solution { public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) { HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>(); for (int num : nums) { set.add(num); } int max = 0; for (int num : set) { if (set.contains(num - 1)) { continue; } int tmpNum = num; int curMax = 1; while (set.contains(tmpNum + 1)) { curMax++; tmpNum++; } max = Math.max(max, curMax); } return max; } }
10.4 和为K的子数组(No.560) - 前缀和
给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你统计并返回 该数组中和为 k 的子数组的个数 。
子数组是数组中元素的连续非空序列。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,1], k = 2 输出:2
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1,2,3], k = 3 输出:2
class Solution { public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); int result = 0; int dp[] = new int[nums.length]; map.put(0, 1); for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { dp[i] = i == 0 ? nums[i] : dp[i - 1] + nums[i]; if (map.containsKey(dp[i] - k)) { result += map.get(dp[i] - k); } map.put(dp[i], map.getOrDefault(dp[i], 0) + 1); } return result; } }
10.5 下一个排列(No.31) - track
整数数组的一个 排列 就是将其所有成员以序列或线性顺序排列。
- 例如,
arr = [1,2,3],以下这些都可以视作arr的排列:[1,2,3]、[1,3,2]、[3,1,2]、[2,3,1]。
整数数组的 下一个排列 是指其整数的下一个字典序更大的排列。更正式地,如果数组的所有排列根据其字典顺序从小到大排列在一个容器中,那么数组的 下一个排列 就是在这个有序容器中排在它后面的那个排列。如果不存在下一个更大的排列,那么这个数组必须重排为字典序最小的排列(即,其元素按升序排列)。
- 例如,
arr = [1,2,3]的下一个排列是[1,3,2]。 - 类似地,
arr = [2,3,1]的下一个排列是[3,1,2]。 - 而
arr = [3,2,1]的下一个排列是[1,2,3],因为[3,2,1]不存在一个字典序更大的排列。
给你一个整数数组 nums ,找出 nums 的下一个排列。
必须 原地 修改,只允许使用额外常数空间。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[1,3,2]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,1] 输出:[1,2,3]
class Solution { public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) { if (nums.length <= 1) { return; } //12354 下个排列是 12435 // 第一步:从尾部到前部,找到第一个升序的俩个值,i-1和i,那i-1就是我们要置换的位置,在12354里我们找到3这个值 // 跟谁换?跟右边倒数第一个大于它的值换(第二步) int pos = -1; for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 1; i--) { if (nums[i - 1] < nums[i]) { pos = i - 1; break; } } //没有更大的排列了,题目要求返回最小排列,就直接整体排序 if (pos == -1) { reverse(nums, 0); return; } //第二步:找到第一个大于nums[pos]的值 交换,12354里交换3和4变成 12453 for (int i = nums.length - 1; i > pos; i--) { if (nums[pos] < nums[i]) { swap(nums, pos, i); break; } } //第三步:给 [pos+1,length) 倒转一下,12453变成12435 reverse(nums, pos + 1); } private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; } private void reverse(int[] nums, int start) { int left = start, right = nums.length - 1; while (left < right) { swap(nums, left, right); left++; right--; } } }
10.6 寻找重复数(No.287) - track
给定一个包含 n + 1 个整数的数组 nums ,其数字都在 [1, n] 范围内(包括 1 和 n),可知至少存在一个重复的整数。
假设 nums 只有 一个重复的整数 ,返回 这个重复的数 。
你设计的解决方案必须 不修改 数组 nums 且只用常量级 O(1) 的额外空间。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,3,4,2,2] 输出:2
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,1,3,4,2] 输出:3
class Solution { public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) { int len = nums.length; // n+1=len n=len-1 int l = 0, r = len - 1, ans = -1; // 1~4选择 while (l <= r) { int mid = (l + r) >> 1; // mid = 2 int cnt = 0; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { if (nums[i] <= mid) { cnt++; } } if (cnt <= mid) { // 搜索区间[mid + 1, right] l = mid + 1; } else { // 搜索区间[left, mid - 1] r = mid - 1; ans = mid; } } return ans; // 或者不赋值ans. 直接返回left } }
快慢指针
class Solution { public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) { int slow = 0, fast = 0; while (true) { slow = nums[slow]; fast = nums[nums[fast]]; if (slow == fast) { break; } } slow = 0; while (slow != fast) { slow = nums[slow]; fast = nums[fast]; } return slow; } }
10.7 最小栈(No.155) - 栈
设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
实现 MinStack 类:
MinStack()初始化堆栈对象。void push(int val)将元素val推入堆栈。void pop()删除堆栈顶部的元素。int top()获取堆栈顶部的元素。int getMin()获取堆栈中的最小元素。
示例 1:
输入: ["MinStack","push","push","push","getMin","pop","top","getMin"] [[],[-2],[0],[-3],[],[],[],[]] 输出: [null,null,null,null,-3,null,0,-2] 解释: MinStack minStack = new MinStack(); minStack.push(-2); minStack.push(0); minStack.push(-3); minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -3. minStack.pop(); minStack.top(); --> 返回 0. minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -2.
class MinStack {
Deque<Integer> xStack;
Deque<Integer> minStack;
public MinStack() {
xStack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
minStack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
minStack.push(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public void push(int x) {
xStack.push(x);
minStack.push(Math.min(minStack.peek(), x));
}
public void pop() {
xStack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return xStack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
10.8 课程表 (No.207) - dfs图论
你这个学期必须选修 numCourses 门课程,记为 0 到 numCourses - 1 。
在选修某些课程之前需要一些先修课程。 先修课程按数组 prerequisites 给出,其中 prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] ,表示如果要学习课程 ai 则 必须 先学习课程 bi 。
- 例如,先修课程对
[0, 1]表示:想要学习课程0,你需要先完成课程1。
请你判断是否可能完成所有课程的学习?如果可以,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0]] 输出:true 解释:总共有 2 门课程。学习课程 1 之前,你需要完成课程 0 。这是可能的。
示例 2:
输入:numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0],[0,1]] 输出:false 解释:总共有 2 门课程。学习课程 1 之前,你需要先完成课程 0 ;并且学习课程 0 之前,你还应先完成课程 1 。这是不可能的。
class Solution {
int visit[];
HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>>();
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
for (int i = 0; i < prerequisites.length; i++) { // 初始化有向图
int left = prerequisites[i][0];
int right = prerequisites[i][1];
if (map.containsKey(left)) {
List<Integer> list = map.get(left);
list.add(right);
} else {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(right);
map.put(left, list);
}
}
visit = new int[2002];
for (Map.Entry<Integer, List<Integer>> entry : map.entrySet()) {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
List<Integer> valueList = entry.getValue();
if (visit[key] != 0) {
continue;
}
boolean ret = dfs(key, valueList);
if (!ret) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean dfs(int left, List<Integer> valueList) {
if (visit[left] == 1) { // 访问过成环了
return false;
}
visit[left] = 1; // 标记为访问过
for (Integer value : valueList) { // dfs扩散
List<Integer> list = map.get(value);
if (list == null) {
continue;
}
if (visit[value] == 2) {
continue;
}
boolean ret = dfs(value, list);
if (!ret) {
return false;
}
}
visit[left] = 2; // 标记为访问完
return true;
}
}
10.9 跳跃游戏 (No.55) - 贪心
给你一个非负整数数组 nums ,你最初位于数组的 第一个下标 。数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
判断你是否能够到达最后一个下标,如果可以,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,3,1,1,4] 输出:true 解释:可以先跳 1 步,从下标 0 到达下标 1, 然后再从下标 1 跳 3 步到达最后一个下标。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,1,0,4] 输出:false 解释:无论怎样,总会到达下标为 3 的位置。但该下标的最大跳跃长度是 0 , 所以永远不可能到达最后一个下标。
public class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int rightmost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (i <= rightmost) {
rightmost = Math.max(rightmost, i + nums[i]);
if (rightmost >= n - 1) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
10.10 前/中/后序遍历二叉树 - 树
class Node { private Node left; private Node right; private char c; public Node getLeft() { return left; } public void setLeft(Node left) { this.left = left; } public Node getRight() { return right; } public void setRight(Node right) { this.right = right; } public char getC() { return c; } public void setC(char c) { this.c = c; } } public class Test1121 { private static String str = "abd##eg##h##c#f##"; private static int count = str.length(); public static void main(String[] args) { Node node = initTree(); System.out.print("先序遍历结果:"); preOrder(node); System.out.println(); System.out.print("中序遍历结果:"); inOrder(node); System.out.println(); System.out.print("后序遍历结果:"); postOrder(node); System.out.println(); System.out.print("层次遍历结果:"); levelOrder(node); System.out.println(); System.out.print("二叉树的深度是:"); System.out.println(getDepth(node)); System.out.println(getDepth2(node)); } /** * 递归初始化树 */ private static Node initTree() { char c = str.charAt(str.length() - count--); if (c == '#') { return null; } Node node = new Node(); node.setC(c); node.setLeft(initTree()); node.setRight(initTree()); return node; } /** * 非递归先序遍历树 */ private static void preOrder(Node node) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(node); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { Node top = stack.pop(); if (top == null) { continue; } System.out.print(top.getC()); stack.push(top.getRight()); stack.push(top.getLeft()); } } /** * 非递归中序遍历树 */ private static void inOrder(Node node) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { if (node != null) { stack.push(node); node = node.getLeft(); } else { node = stack.pop(); System.out.print(node.getC()); node = node.getRight(); } } } /** * 非递归后序遍历树 */ private static void postOrder(Node node) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); Node flag = new Node(); while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { while (node != null) { stack.push(node); node = node.getLeft(); } node = stack.peek(); if (node.getRight() == null || node.getRight() == flag) { System.out.print(node.getC()); flag = node; stack.pop(); if (stack.isEmpty()) { return; } node = null; } else { node = node.getRight(); } } } /** * 层次遍历遍历树 */ private static void levelOrder(Node node) { Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(); queue.add(node); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node first = queue.remove(); System.out.print(first.getC()); if (first.getLeft() != null) { queue.add(first.getLeft()); } if (first.getRight() != null) { queue.add(first.getRight()); } } } /** * 递归求树深度 */ private static int getDepth(Node node) { if (node == null) { return 0; } int left = getDepth(node.getLeft()); int right = getDepth(node.getRight()); return left > right ? left + 1 : right + 1; } /** * 非递归求树深度 */ private static int getDepth2(Node node) { Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(); queue.add(node); int cur; int last; int level = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { cur = 0; last = queue.size(); while (cur < last) { Node first = queue.remove(); cur++; if (first.getLeft() != null) { queue.add(first.getLeft()); } if (first.getLeft() != null) { queue.add(first.getRight()); } } level++; } return level; } }
10.11 堆排序 - 树
/** * 堆排序演示 * * @author Lvan */ public class HeapSort { public static void main(String[] args) { // int[] arr = {5, 1, 7, 3, 1, 6, 9, 4}; int[] arr = {16, 7, 3, 20, 17, 8}; heapSort(arr); for (int i : arr) { System.out.print(i + " "); } } /** * 创建堆, * @param arr 待排序列 */ private static void heapSort(int[] arr) { //创建堆 for (int i = (arr.length - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) { //从第一个非叶子结点从下至上,从右至左调整结构 adjustHeap(arr, i, arr.length); } //调整堆结构+交换堆顶元素与末尾元素 for (int i = arr.length - 1; i > 0; i--) { //将堆顶元素与末尾元素进行交换 int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[0]; arr[0] = temp; //重新对堆进行调整 adjustHeap(arr, 0, i); } } /** * 调整堆 * @param arr 待排序列 * @param parent 父节点 * @param length 待排序列尾元素索引 */ private static void adjustHeap(int[] arr, int parent, int length) { //将temp作为父节点 int temp = arr[parent]; //左孩子 int lChild = 2 * parent + 1; while (lChild < length) { //右孩子 int rChild = lChild + 1; // 如果有右孩子结点,并且右孩子结点的值大于左孩子结点,则选取右孩子结点 if (rChild < length && arr[lChild] < arr[rChild]) { lChild++; } // 如果父结点的值已经大于孩子结点的值,则直接结束 if (temp >= arr[lChild]) { break; } // 把孩子结点的值赋给父结点 arr[parent] = arr[lChild]; //选取孩子结点的左孩子结点,继续向下筛选 parent = lChild; lChild = 2 * lChild + 1; } arr[parent] = temp; } }
10.12 限流 - 滑动窗口/令牌桶
滑动窗口
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; public class SlidingTimeRateLimiter implements RateLimiter { // 滑动窗口总分块个数 private int initialCapacity = 60; private int[] slidingWindow; // 存储当前窗口请求量游标 private int currentCur = 0; // 滑动窗口分块边界 private long left = 0, right = 0; // 滑动窗口分块大小 private int minWindowSize = 10; // 当前累计请求量 private int requestCount = 0; // 窗口请求量限制 private int maxCount = 10; public SlidingTimeRateLimiter(int initialCapacity, int minWindowSize, int maxCount) { this.initialCapacity = initialCapacity; this.slidingWindow = new int[initialCapacity]; this.minWindowSize = minWindowSize; this.maxCount = maxCount; } private void refreshWindow(long now) { if (right == 0) { right = now; } else { do { currentCur = (currentCur + 1) % initialCapacity; requestCount -= slidingWindow[currentCur]; slidingWindow[currentCur] = 0; right += minWindowSize; System.out.println("time window reload timestamp:" + now + " left:" + left + " right:" + right); } while (now > right); } left = right - minWindowSize; } /* now ∈ (left, right] 判断请求量是否达到上限,否则该窗口请求加一 now > right 移动到后面的窗口,并清空最初窗口的累计值 */ @Override public synchronized boolean tryAcquire() { long now = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (now > right) { refreshWindow(now); } if (requestCount < maxCount) { slidingWindow[currentCur]++; requestCount++; System.out.println("try acquire success! current requestCount:" + requestCount + " current:" + now + " left:" + left + " right:" + right); return true; } else { System.out.println("try acquire fail. current:" + now + " left:" + left + " right:" + right); return false; } } }
令牌桶限流
public class MayiktRateLimiter { private LinkedBlockingDeque<String> tokenBlockingDeque; public MayiktRateLimiter(int permitsPerSecond) { // 创建令牌桶 设定固定的容量 tokenBlockingDeque = new LinkedBlockingDeque<String>(permitsPerSecond); // 初始化 init(permitsPerSecond); start(); } public static MayiktRateLimiter create(int permitsPerSecond) { return new MayiktRateLimiter(permitsPerSecond); } public void init(int permitsPerSecond) { for (int i = 0; i < permitsPerSecond; i++) { tokenBlockingDeque.offer("#"); } } /** * 从队列中获取token * * @return */ public boolean tryAcquire() { return tokenBlockingDeque.poll() == null ? false : true; } /** * 单独开启一个向令牌桶投递 token */ private void start() { /** * 每隔1s时间 向队列中投递固定容量大小的token */ Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1).scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { addToken(); } }, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } public void addToken() { /** * 向队列投递token */ tokenBlockingDeque.offer("#"); } public static void main(String[] args) { MayiktRateLimiter mayiktRateLimiter = MayiktRateLimiter.create(1); MayiktRateLimiter mayiktRateLimiter2 = MayiktRateLimiter.create(2); System.out.println(mayiktRateLimiter2.tryAcquire()); System.out.println(mayiktRateLimiter2.tryAcquire()); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (Exception e) { } System.out.println(mayiktRateLimiter2.tryAcquire()); } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号