something basic about the table
This article has a detailed introduction to basic concepts of a table, which is very helpful for me to learn Django.
Overview
A table is a database object that you use to store data about a particular subject, such as employees or products. A table consists of records and fields.
Each record contains data about one instance of the table subject, such as a particular employee. A record is also commonly called a row or an instance.
Each field contains data about one aspect of the table subject, such as first name or e-mail address. A field is also commonly called a column or an attribute.
A record consists of field values, such as Contoso, Ltd. or someone@example.com. A field value is also commonly called a fact.
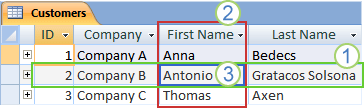
1. A record
2. A field
3. A field value
A database can contain many tables, each storing information about a different subject. Each table can contain many fields of different types of data, such as text, numbers, dates, and hyperlinks.
Table relationships
Although each table stores data about a different subject, tables in a database usually store data about subjects that are related to each other. For example, a database might contain:
-
A customers table that lists your company’s customers and their addresses.
-
A products table that lists the products that you sell, including prices and pictures for each item.
-
An orders table that tracks customer orders.
Because you store data about different subjects in separate tables, you need some way to tie the data together so that you can easily combine related data from those separate tables. To connect the data stored in different tables, you create relationships. A relationship is a logical connection between two tables that specifies fields that the tables have in common.
Keys
Fields that are part of a table relationship are called keys. A key usually consists of one field, but may consist of more than one field. There are two kinds of keys:
-
Primary key A table can have only one primary key. A primary key consists of one or more fields that uniquely identify each record that you store in the table. Often, there is a unique identification number, such as an ID number, a serial number, or a code, that serves as a primary key. For example, you might have a Customers table where each customer has a unique customer ID number. The customer ID field is the primary key of the Customers table. When a primary key contains more than one field, it is usually composed of pre-existing fields that, taken together, provide unique values. For example, you might use a combination of last name, first name, and birth date as the primary key for a table about people.
-
Foreign key A table can also have one or more foreign keys. A foreign key contains values that correspond to values in the primary key of another table. For example, you might have an Orders table in which each order has a customer ID number that corresponds to a record in a Customers table. The customer ID field is a foreign key of the Orders table.
The correspondence of values between key fields forms the basis of a table relationship. You use a table relationship to combine data from related tables. For example, suppose that you have a Customers table and an Orders table. In your Customers table, each record is identified by the primary key field, ID.
To associate each order with a customer, you add a foreign key field to the Orders table that corresponds to the ID field of the Customers table, and then create a relationship between the two keys. When you add a record to the Orders table, you use a value for customer ID that comes from the Customers table. Whenever you want to view any information about an order's customer, you use the relationship to identify which data from the Customers table corresponds to which records in the Orders table.
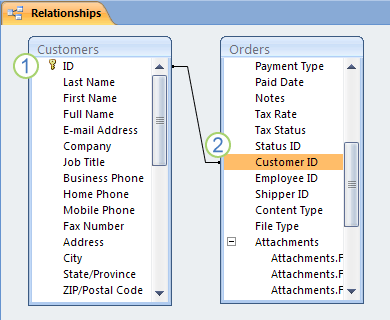
1. A primary key, identified by the key icon next to the field name.
2. A foreign key — note the absence of the key icon.
Benefits of using relationships
Keeping data separated in related tables produces the following benefits:
-
Consistency Because each item of data is recorded only once, in one table, there is less opportunity for ambiguity or inconsistency. For example, you store a customer's name only once, in a table about customers, rather than storing it repeatedly (and potentially inconsistently) in a table that contains order data.
-
Efficiency Recording data in only one place means you use less disk space. Moreover, smaller tables tend to provide data more quickly than larger tables. Finally, if you don't use separate tables for separate subjects, you will introduce null values (the absence of data) and redundancy into your tables, both of which can waste space and impede performance.
-
Comprehensibility The design of a database is easier to understand if the subjects are properly separated into tables.
Copy Link:
https://support.office.com/en-US/article/Introduction-to-tables-03F58E81-86CD-46AD-8199-4122152C7EFF


