深入学习二叉树(02)线索二叉树
1.产生背景
现在有一棵节点数目为 n 的二叉树,采用二叉链表的形式存储。对于每个节点均有指向左右孩子的两个指针域。而节点为 n 的二叉树一共有 n-1 条有效分支路径。那么二叉链表中一共
存在2n-(n-1) = n+1 个空指针域。那么这些空指针域造成了空间浪费。
如图:所示一棵二叉树一共有10个节点,空指针有 11 个
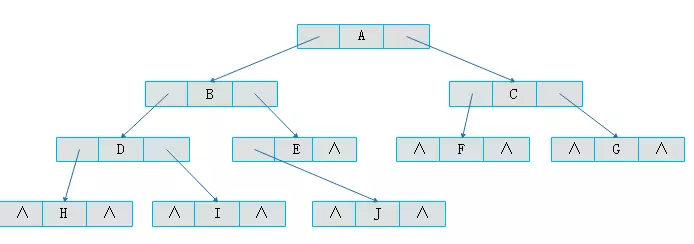
此外,当对二叉树进行中序遍历时可以得到二叉树的中序列。例如上图中二叉树中序遍历结果为 HDIBJEAFCG ,那么得知 A 的前序节点为 E ,后继节点为 F。但是这种关系的获得是建立在
完成遍历后得到的,那么是否在遍历之前就记录下前驱和后继的关系呢? 那么在寻找前驱与后继节点时,将大大的提升效率。
2.线索化
现将某节点的空指针域指向该节点的前序后继,定义规则如下
1 2 | 若结点的左子树为空,则该结点的左孩子指针指向其前驱结点。若结点的右子树为空,则该结点的右孩子指针指向其后继结点。 |
这种指向前驱和后继的指针称为线索。将一棵普通二叉树以某种次序遍历,并添加线索的过程称为线索化,按规则将上图线索化后如下图
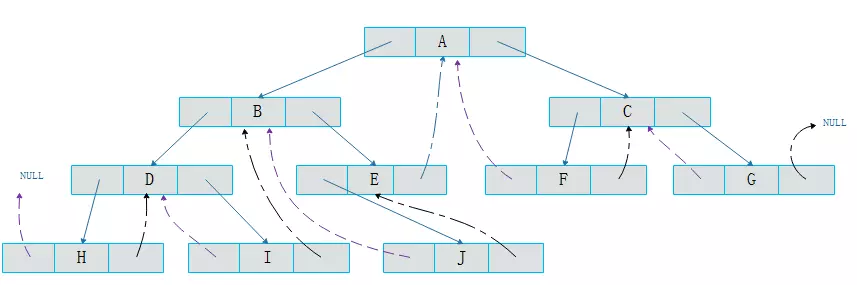
图中黑色点画线为指向后继的线索,紫色虚线为指向前驱的线索。可以看出通过线索化,即解决了空间浪费的问题,又解决了前驱后继的记录问题。
2.1 线索化带来的问题
经过上述的线索化后,可以将一棵二叉树线索化为一棵线索二叉树,那么新的问题会产生,我们如何区分一个节点的 指针域是指向孩子还是前驱后继节点呢?
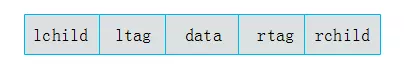
为了解决这个问题,现在需要添加标志位 ltag , rtag 并定义规则如下
1 2 | ltag为0时,指向左孩子,为1时指向前驱rtag为0时,指向右孩子,为1时指向后继 |
添加 ltag 和 rtag 属性的节点结构如下
转变为如下的二叉树

3.实现线索二叉树
3.1 中序线索二叉树
为了方便构建一棵二叉树,这里使用完全二叉树构建线索二叉树,如下图是一棵完全二叉树

构建完全二叉树参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/baizhuang/p/11612961.html
接下来需要对此二叉树进行线索化
static TreeNode *pre = NULL; void initTag(TreeNode *p){ if(p!=NULL){ initTag(p->lchild); // 递归左子树 if(p->lchild==NULL){ p->lchild=pre; p->lTag=1; } if(pre!=NULL&&pre->rchild==NULL){ pre->rchild=p; pre->rTag=1; } pre=p; initTag(p->rchild);// 递归右子树 } }
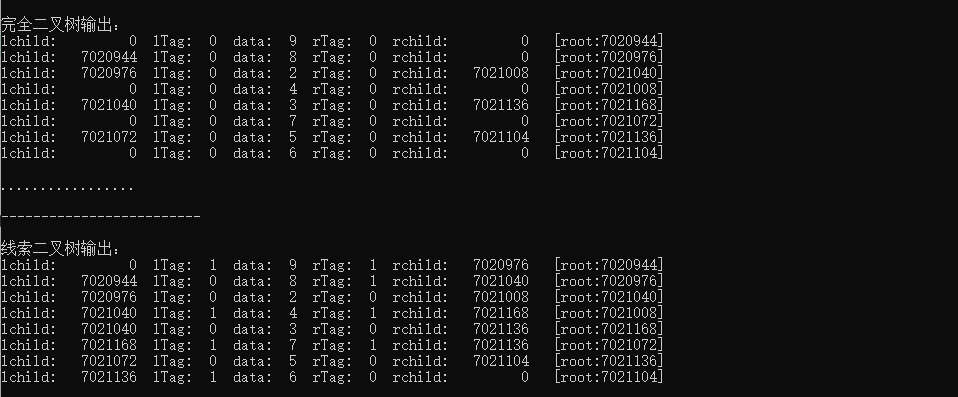
线索化后如下图

方便观察,控制台输出如下
完整代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 | #include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>typedef struct node{ int data; struct node * lchild,* rchild; int lTag,rTag;}TreeNode; static TreeNode *pre = NULL;TreeNode * createTree(int data[],int n,int index){ TreeNode *root = NULL,*lchild = NULL,*rchild = NULL; //create lchildTree if(index<=n&&index*2<=n){ lchild = createTree(data,n,index*2); } //createRigntTree if(index<=n&&index*2+1<=n){ rchild = createTree(data,n,index*2+1); } //createNode if(index<=n){ root = (TreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode)); root->data = data[index]; root->lchild = lchild; root->rchild = rchild; root->lTag = root->rTag = 0; } //return root return root;}void print(TreeNode *root){ if(root->lchild!=NULL){ print(root->lchild); } printf("lchild:%10d lTag:%3d data:%3d rTag:%3d rchild:%10d [root:%d]\n",root->lchild,root->lTag,root->data,root->rTag,root->rchild,root); if(root->rchild!=NULL){ print(root->rchild); }}void printSearchTree(TreeNode *root){ if(root!=NULL){ if(root->lTag==0){ printSearchTree(root->lchild); } printf("lchild:%10d lTag:%3d data:%3d rTag:%3d rchild:%10d [root:%d]\n",root->lchild,root->lTag,root->data,root->rTag,root->rchild,root); // printf("%d",root->lTag); if(root->rTag==0){ printSearchTree(root->rchild); } }}void initTag(TreeNode *p){ if(p!=NULL){ initTag(p->lchild); // 递归左子树 if(p->lchild==NULL){ p->lchild=pre; p->lTag=1; } if(pre!=NULL&&pre->rchild==NULL){ pre->rchild=p; pre->rTag=1; } pre=p; initTag(p->rchild);// 递归右子树 }}int main(){ int data[] ={0,3,2,5,8,4,7,6,9}; TreeNode * root = createTree(data,8,1); printf("\n完全二叉树输出:\n"); print(root); printf("\n.................\n"); initTag(root); printf("\n-------------------------\n"); printf("\n线索二叉树输出:\n"); printSearchTree(root); printf("\n-------------------------\n"); return 0;} |




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步