Java进阶学习
一、IO框架学习
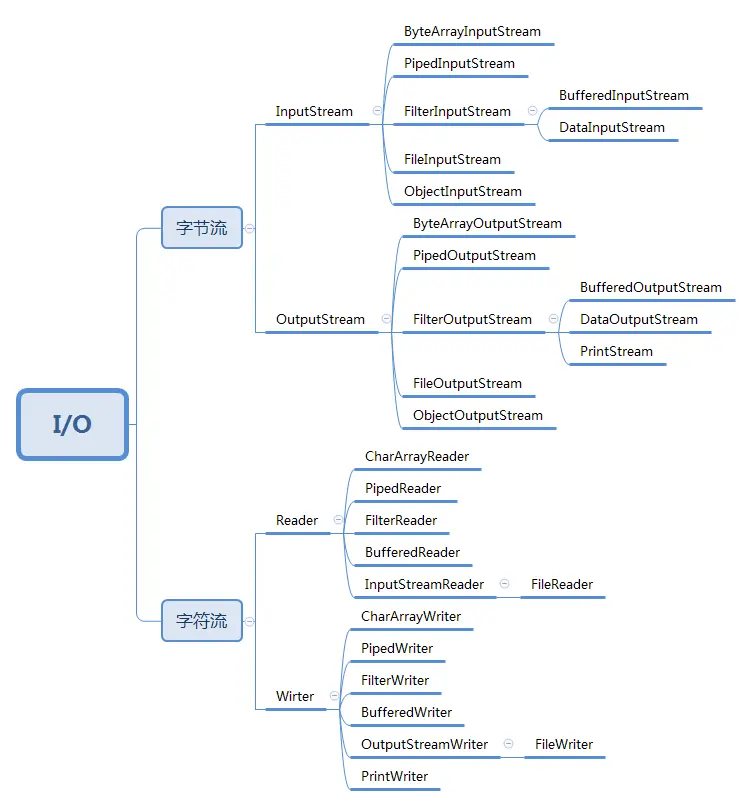
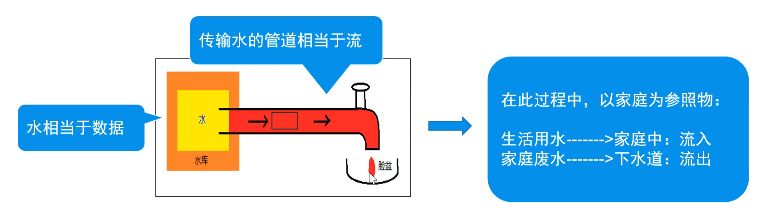
1.流的概念
内存与存储设备之间传输数据的通道
2.流的分类
按方向【重点】
- 输入流:将<存储设备>中的内容读到<内存>中
- 输出流:将<内存>中的内容写到<存储设备>中
按单位
- 字节流:以字节为单位,可以读写所有数据
- 字符流:以字符为单位,只能读写文本数据
按功能
- 节点流:具有实际传输数据的读写功能
- 过滤流:在节点流的基础之上增强功能
3.字节流
字节流的父类(抽象类)
// InputStream 字节输入流
public int read(){}
public int read(byte[] b){}
public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len){}
// OutputStream 字节输出流
public void write(int n){}
public void write(byte[] b){}
public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len){}
文件字节流
文件输入流

package IO.byteStream;
import com.sun.org.apache.bcel.internal.generic.NEW;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
//字节输入流
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建FileInputStream 并指定文件路径
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("e://a.txt");
//2.读取文件 返回-1证明读取完毕
//int a=fileInputStream.read();
//System.out.println(a);
//3.循环读取 单字节读取!
//int data=0;
//while ((data=fileInputStream.read())!=-1){
// System.out.println((char) data);
//}
//4.多字节读取
//每次读取3个字节
/*
byte[] str=new byte[3];
int read = fileInputStream.read(str);
System.out.println("实际读取的个数:"+read);
System.out.println(new String(str));
int read02 = fileInputStream.read(str);
System.out.println("实际读取的个数:"+read02);
System.out.println(new String(str));
*/
int count=0;
byte[] buff = new byte[4];
while ((count=fileInputStream.read(buff))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(buff,0,count));
}
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
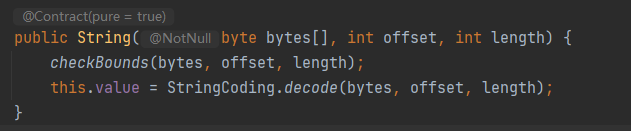
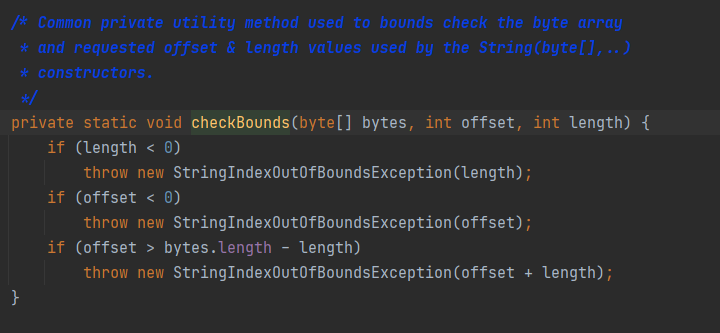
拓展:new String()
new String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length)
文件输出流
package IO.byteStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建文件字节输出流
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("e://b.txt",true); // true表示不覆盖 接着写 默认为 false
// 2 写入文件
fileOutputStream.write(97);
fileOutputStream.write('c');
fileOutputStream.write('c');
fileOutputStream.write('\n');
// 3 写入字符串
String str = new String("helloworld");
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
fileOutputStream.close();
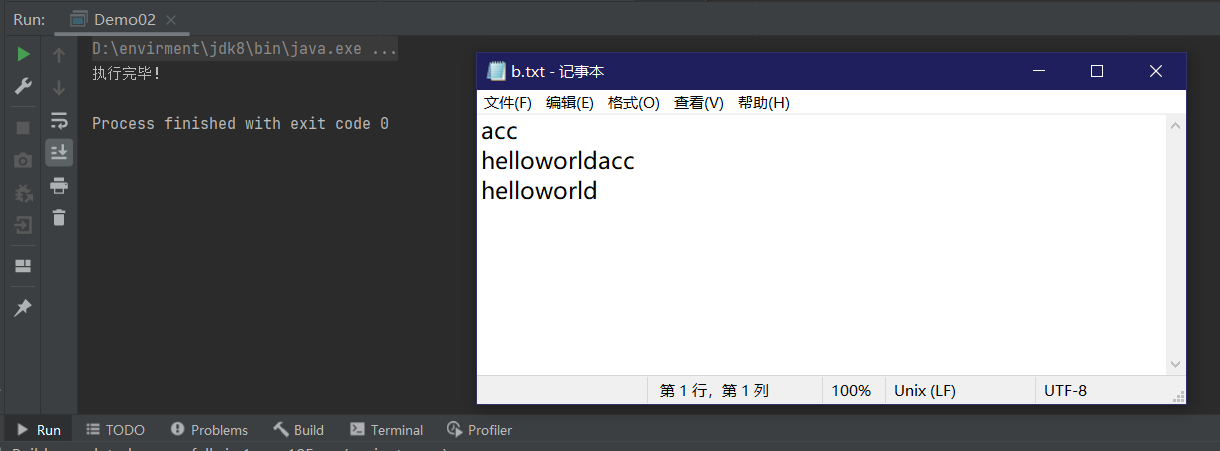
System.out.println("执行完毕!");
}
}
图片复制案例
package IO.byteStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建流
// 1.1 文件字节输入流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("e://a.jpg");
// 1.2 文件字节输出流
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("e://b.jpg");
// 2 边读边写
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int count=0;
while ((count=fileInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,0,count);
}
// 3 关闭
fileOutputStream.close();
fileInputStream.close();
System.out.println("执行完毕!");
}
}
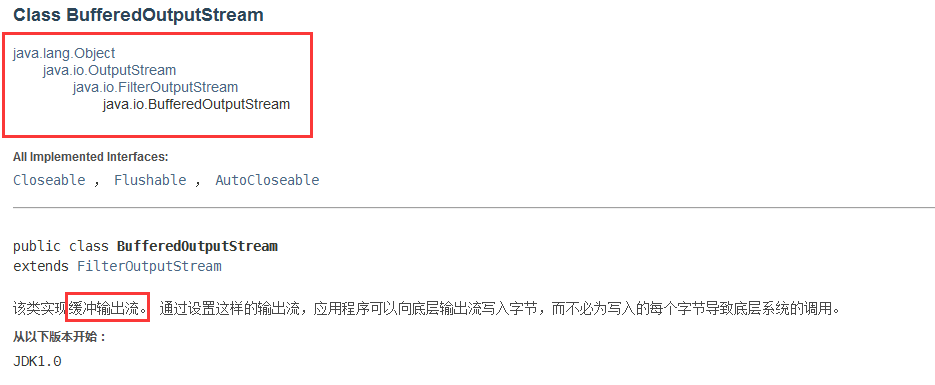
字节缓冲流
缓冲流:BufferedInputStream/ BufferedOutputStream
- 提高IO效率,减少访问磁盘次数
- 数据存储在缓冲区中,flush是将缓冲区的内容写入文件中,也可以直接close

package IO.BufferedStream;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo01 {
// 使用字节缓冲流 读取 文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建BufferedInputStream
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("e://a.txt");
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream);
// 2 使用字节缓冲流读取
/*
int data= 0;
while ((data=bufferedInputStream.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char) data);
}
System.out.println();
*/
// 3 自己写一个缓冲区
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int count = 0;
while ((count=fileInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,count));
}
// 4 只需要关闭缓冲流即可!
bufferedInputStream.close();
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
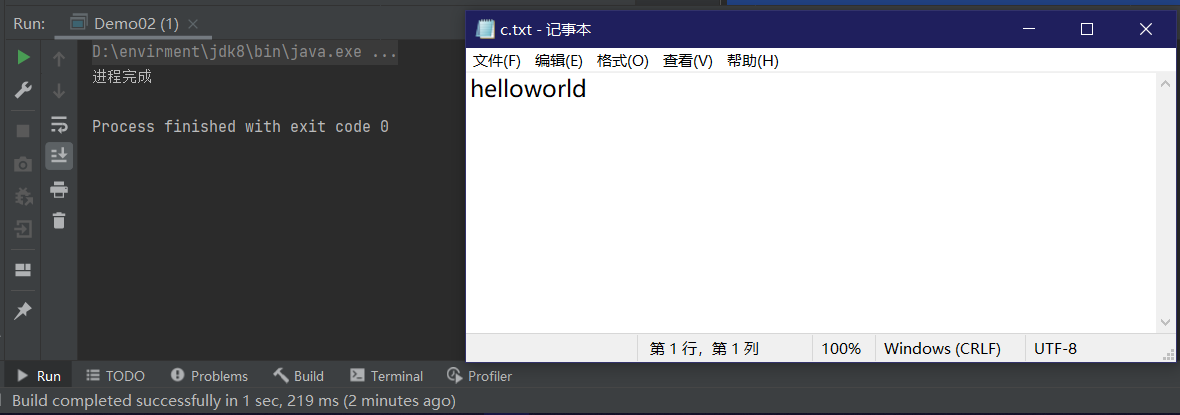
package IO.BufferedStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class Demo02 {
// 使用字节缓冲流 写入 文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("e://c.txt",false);
// 1 创建BufferedInputStream
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
String str = new String("helloworld");
// 2 写入文件
bufferedOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));// 写入8k缓冲区
bufferedOutputStream.flush();//刷新到硬盘
// 3 关闭缓冲流
bufferedOutputStream.close();
System.out.println("进程完成");
}
}
4.对象流
ObjectOutputStream / ObjectInputStream
- 增强了缓冲区功能
- 增强了读写8种基本数据类型和字符串的功能
- 增强了读写对象的功能
readObject()从流中读取一个对象writeObject(Object obj)向流中写入一个对象
使用流传输对象的过程称为序列化、反序列化
ObjectOutputStream
ObjectOutputStream将Java对象的原始数据类型和图形写入OutputStream。可以使用ObjectInputStream读取(重构)对象。可以通过使用流的文件来实现对象的持久存储。如果流是网络套接字流,则可以在另一个主机上或另一个进程中重构对象。
只有支持java.io.Serializable接口的对象才能写入流中。 每个可序列化对象的类被编码,包括类的类名和签名,对象的字段和数组的值以及从初始对象引用的任何其他对象的关闭。
方法writeObject用于将一个对象写入流中。 任何对象,包括字符串和数组,都是用writeObject编写的。 多个对象或原语可以写入流。 必须从对应的ObjectInputstream读取对象,其类型和写入次序相同。
序列化
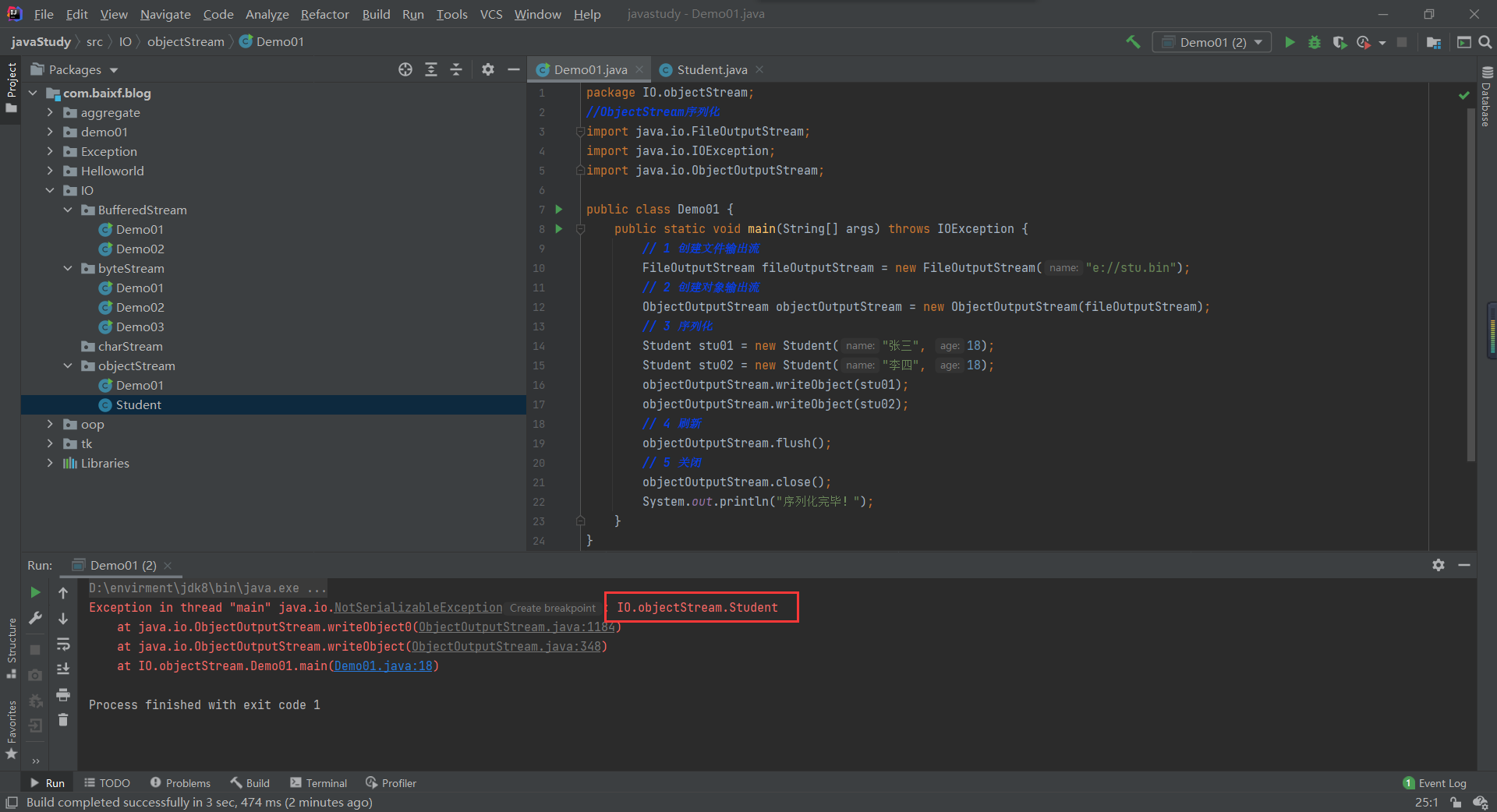
package IO.objectStream;
//ObjectStream序列化
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建文件输出流
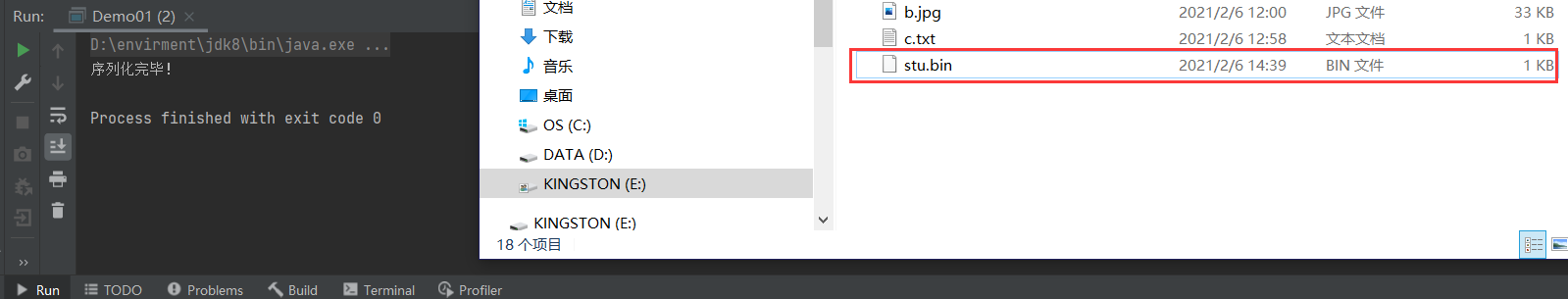
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("e://stu.bin");
// 2 创建对象输出流
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
// 3 序列化
Student stu01 = new Student("张三", 18);
Student stu02 = new Student("李四", 18);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(stu01);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(stu02);
// 4 刷新
objectOutputStream.flush();
// 5 关闭
objectOutputStream.close();
System.out.println("序列化完毕!");
}
}
//Student类需要实现 Serializable 接口 这个接口仅仅标识这个类可以实现序列化
public interface Serializable {
}
//Student类
package IO.objectStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
ObjectInputStream
ObjectInputStream反序列化先前使用ObjectOutputStream编写的原始数据和对象。
ObjectOutputStream和ObjectInputStream可以分别为与FileOutputStream和FileInputStream一起使用的对象图提供持久性存储的应用程序。 ObjectInputStream用于恢复先前序列化的对象。 其他用途包括使用套接字流在主机之间传递对象,或者在远程通信系统中进行封送和解组参数和参数。
ObjectInputStream确保从流中创建的图中的所有对象的类型与Java虚拟机中存在的类匹配。 根据需要使用标准机制加载类。
只能从流中读取支持java.io.Serializable或java.io.Externalizable接口的对象。
反序列化
package IO.objectStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class Demo02 {
// 使用ObjectInputSteam实现反序列化(读取重构对象)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 1 创建文件输入流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("e://stu.bin");
// 2 创建对象流
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
// 3 读取文件(反序列化)
Student student01 = (Student) objectInputStream.readObject();
Student student02 = (Student) objectInputStream.readObject();
// 4 关闭
objectInputStream.close();
System.out.println("执行完毕!");
// 5 输出
System.out.println(student01.toString());
System.out.println(student02.toString());
}
}
Serializable 接口
类的序列化由实现
java.io.Serializable接口的类启用。 不实现此接口的类将不会使任何状态序列化或反序列化。 可序列化类的所有子类型都是可序列化的。 序列化接口没有方法或字段,仅用于标识可串行化的语义。
注意事项
- 某个类要想序列化必须实现
Serializable接口 - 序列化类中对象属性要求实现
Serializable接口 - 序列化版本号ID,保证序列化的类和反序列化的类是同一个类
- 使用transient修饰属性,这个属性就不能序列化
- 静态属性不能序列化
- 序列化多个对象,可以借助集合来实现
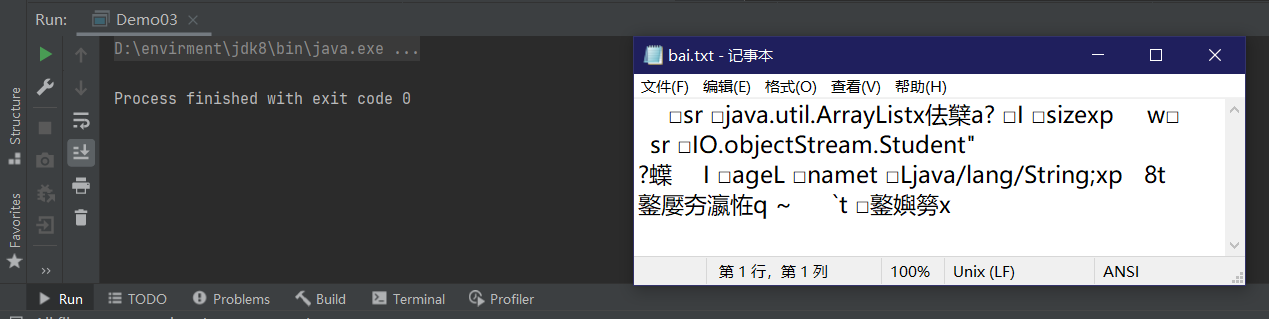
package IO.objectStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("e://bai.txt");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
Student student = new Student("王麻子", 56);
Student student1 = new Student("王二", 96);
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(student);
students.add(student1);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(students);
objectOutputStream.close();
}
}
package IO.objectStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("e://bai.txt");
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
ArrayList arrayList = (ArrayList) objectInputStream.readObject();
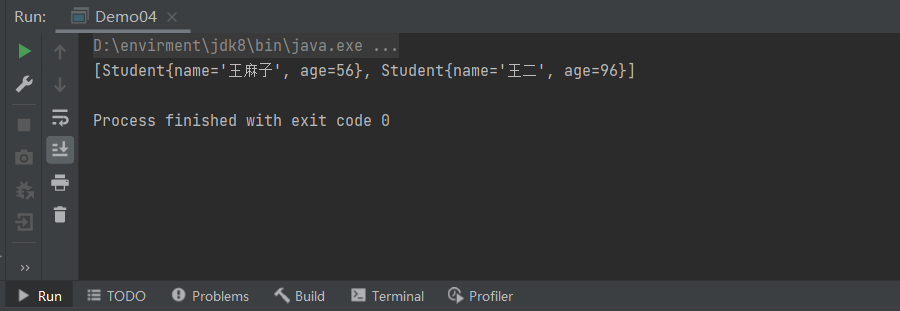
System.out.println(arrayList);
objectInputStream.close();
}
}
5.编码方式
常见编码
-
ASCII 码
- 学过计算机的人都知道 ASCII 码,总共有 128 个,用一个字节的低 7 位表示,0~31 是控制字符如换行回车删除等;32~126 是打印字符,可以通过键盘输入并且能够显示出来。
-
GBK(扩展GB2312)
- 全称叫《汉字内码扩展规范》,是国家技术监督局为 windows95 所制定的新的汉字内码规范,它的出现是为了扩展 GB2312,加入更多的汉字,它的编码范围是 8140~FEFE(去掉 XX7F)总共有 23940 个码位,它能表示 21003 个汉字,它的编码是和 GB2312 兼容的,也就是说用 GB2312 编码的汉字可以用 GBK 来解码,并且不会有乱码。
-
GB18030(兼容GB2312)
- 全称是《信息交换用汉字编码字符集》,是我国的强制标准,它可能是单字节、双字节或者四字节编码,它的编码与 GB2312 编码兼容,这个虽然是国家标准,但是实际应用系统中使用的并不广泛。
-
Unicode编码集
- UTF-8
- UTF-16 统一采用两个字节表示一个字符,虽然在表示上非常简单方便,但是也有其缺点,有很大一部分字符用一个字节就可以表示的现在要两个字节表示,存储空间放大了一倍,在现在的网络带宽还非常有限的今天,这样会增大网络传输的流量,而且也没必要。而 UTF-8 采用了一种变长技术,每个编码区域有不同的字码长度。不同类型的字符可以是由 1~6 个字节组成。
- UTF-8 有以下编码规则:
- 如果一个字节,最高位(第 8 位)为 0,表示这是一个 ASCII 字符(00 - 7F)。可见,所有 ASCII 编码已经是 UTF-8 了。
- 如果一个字节,以 11 开头,连续的 1 的个数暗示这个字符的字节数,例如:110xxxxx 代表它是双字节 UTF-8 字符的首字节。
- 如果一个字节,以 10 开始,表示它不是首字节,需要向前查找才能得到当前字符的首字节
- UTF-8
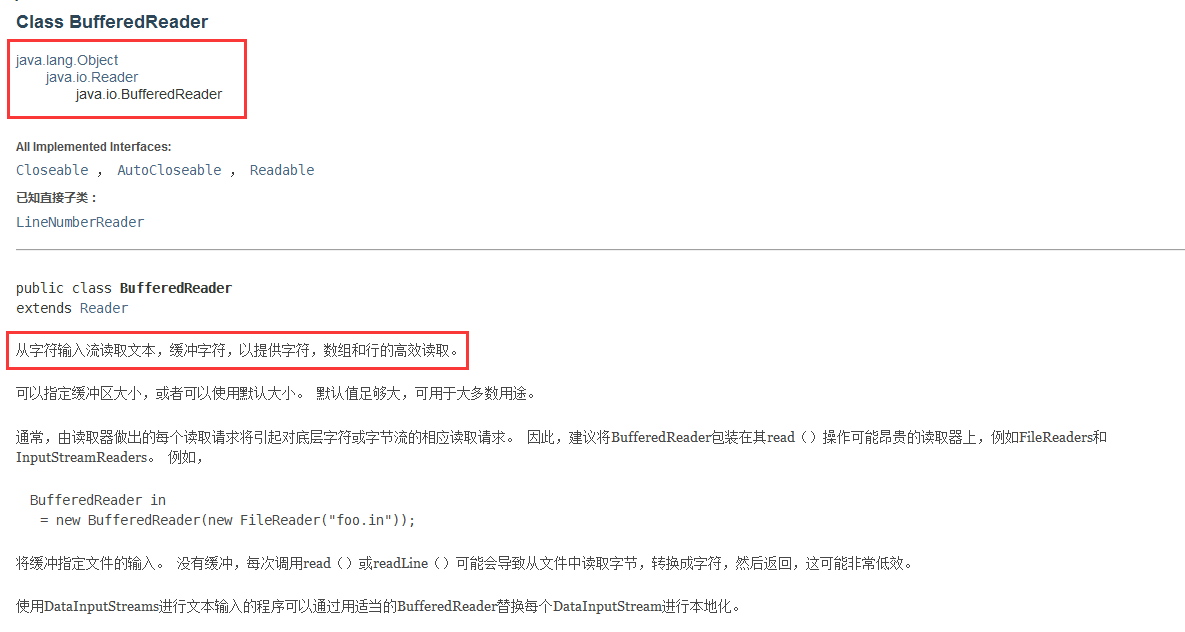
Reader类
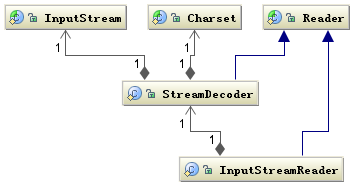
Reader 类是 Java 的 I/O 中读字符的父类,而 InputStream 类是读字节的父类,InputStreamReader 类就是关联字节到字符的桥梁,它负责在 I/O 过程中处理读取字节到字符的转换,而具体字节到字符的解码实现它由 StreamDecoder 去实现,在 StreamDecoder 解码过程中必须由用户指定 Charset 编码格式。值得注意的是如果你没有指定 Charset,将使用本地环境中的默认字符集,例如在中文环境中将使用 GBK 编码。
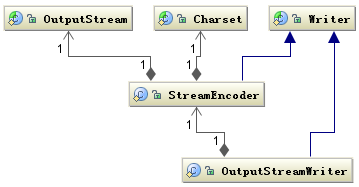
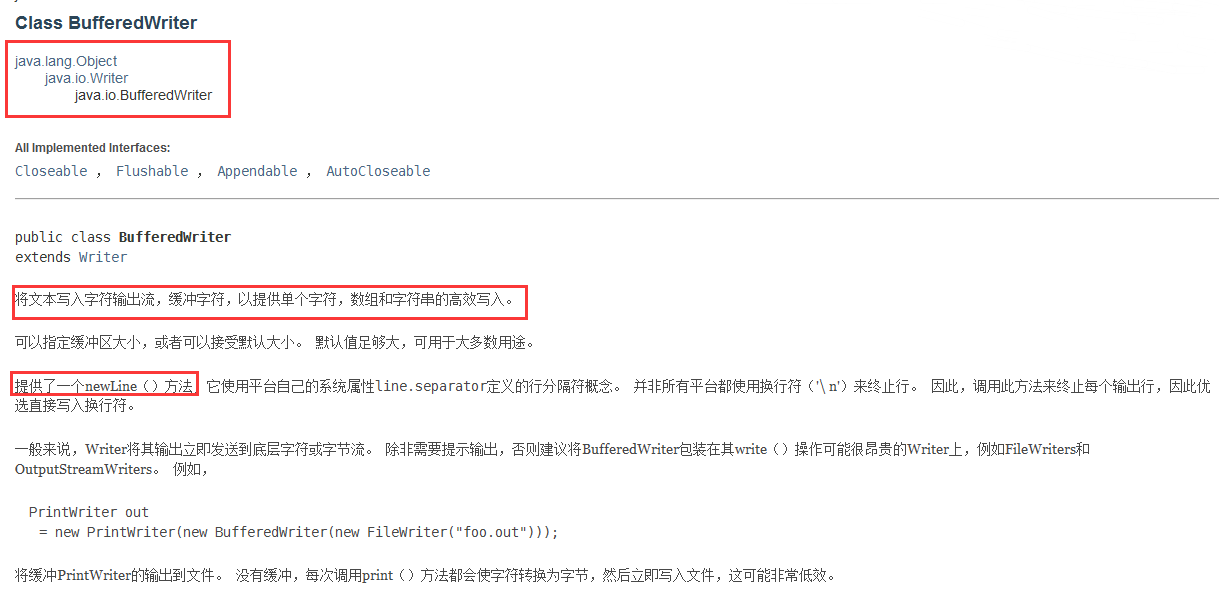
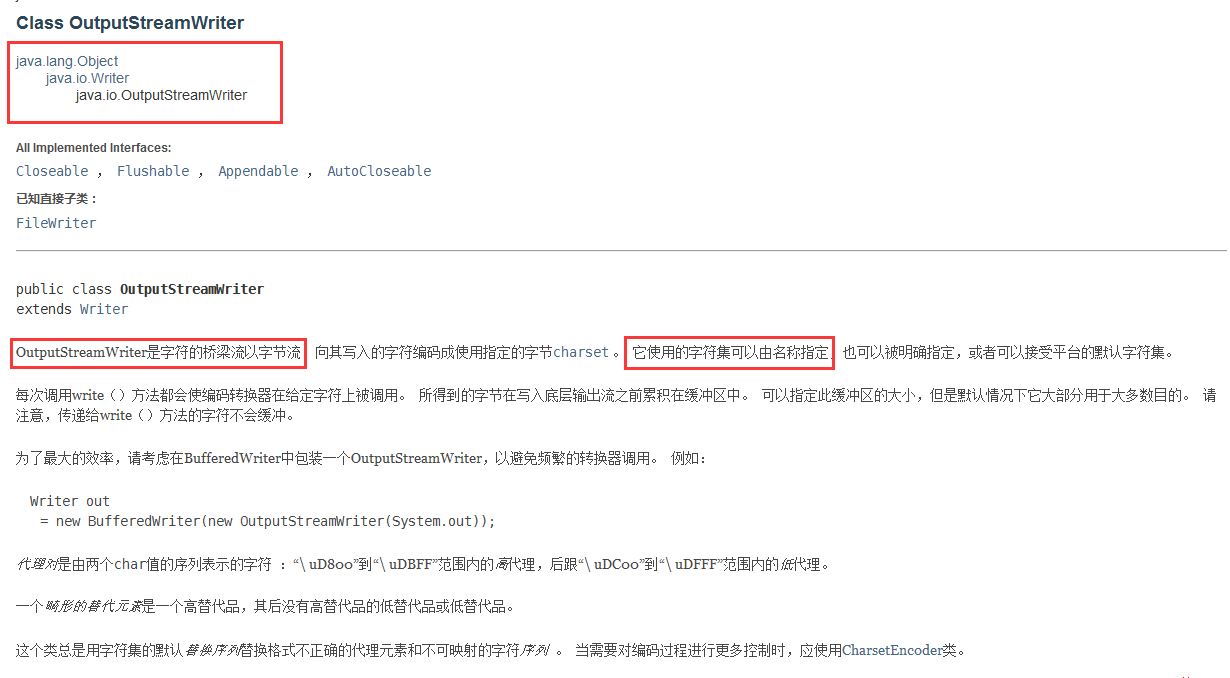
Writer类
字符的父类是 Writer,字节的父类是 OutputStream,通过 OutputStreamWriter 转换字符到字节。如下图所示:
6.字符流
问题引入
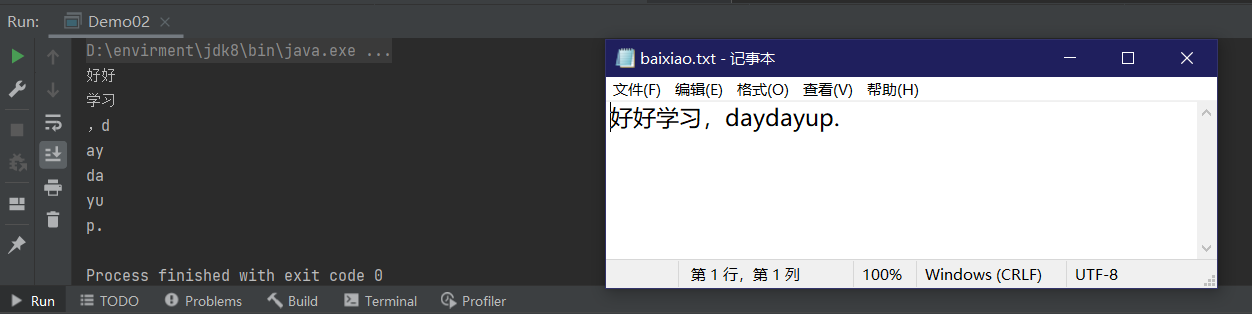
package IO.charStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
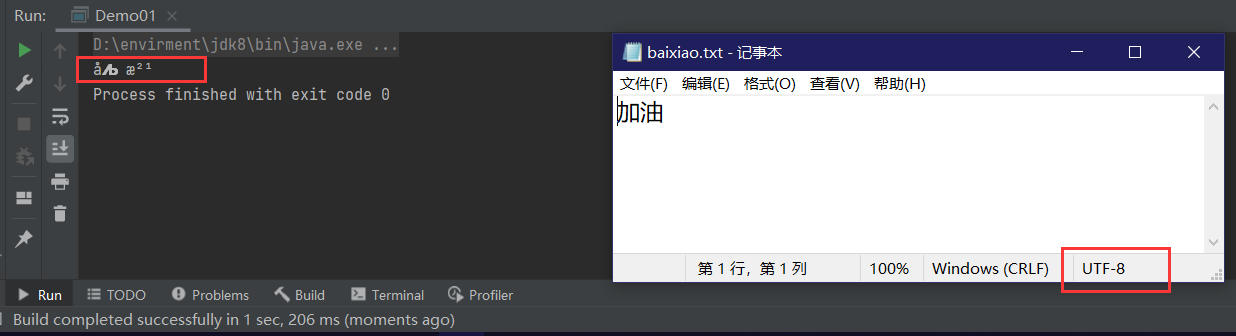
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("e://baixiao.txt");
int data=0;
while ((data=fileInputStream.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)data); //2个字 6个字节
}
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
字符流的父类(抽象类)
reader 字符输入流
public int read(){}public int read(char[] c){}public int read(char[] b, int off, int len){}
Writer 字符输出流
public void write(int n){}public void write(String str){}public void write(char[] c){}
FileReader
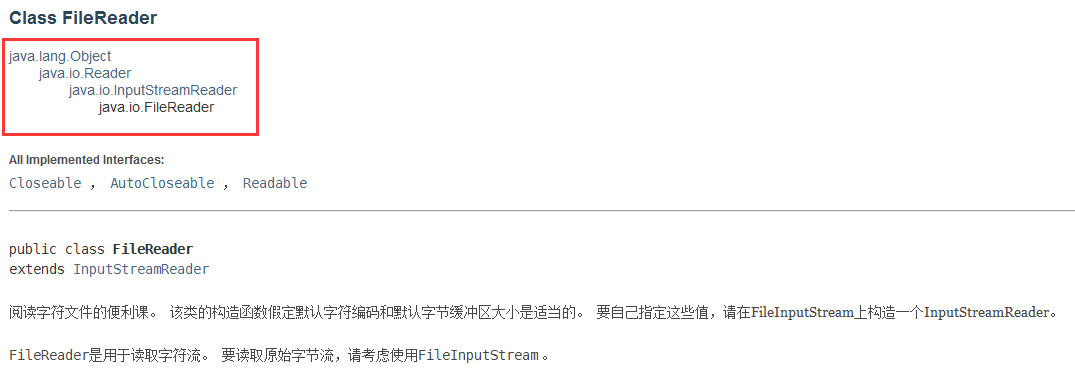
package IO.charStream;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建FileReader 文件字符输入流
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("e://baixiao.txt");
// 2 单个字符读取
/*
int data=0;
while ((data=fileReader.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char) data);// 读取一个字符
System.out.println(data);
}
*/
// 3 创建字符缓冲区读取
char[] chars = new char[2];
int data=0;
while ((data=fileReader.read(chars))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(chars, 0, data));
}
// 4 关闭
fileReader.close();
}
}
FileWriter
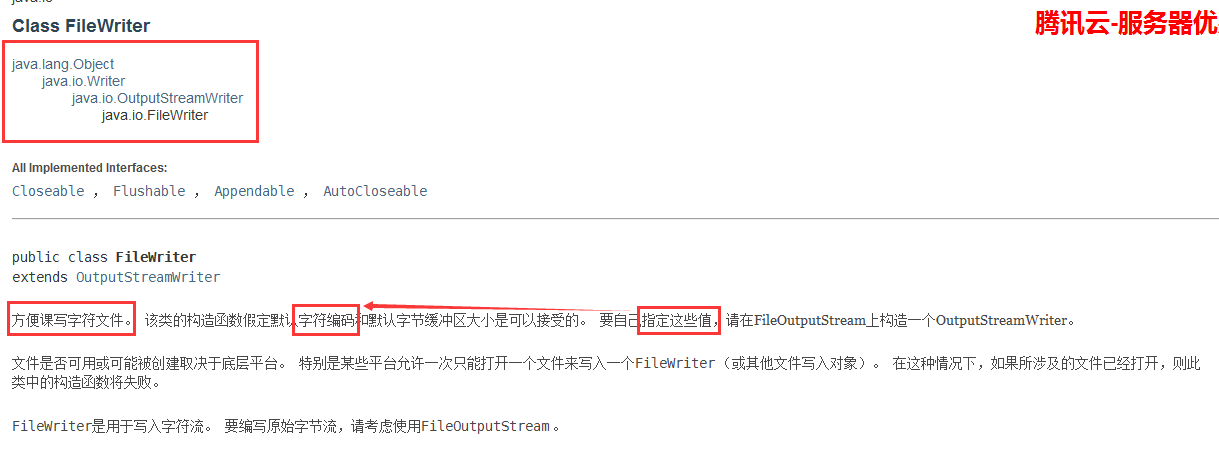
package IO.charStream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("e://hahah.txt");
String str="Java是世界上最好的语言!";
for (int i=0;i<5;i++) {
fileWriter.write(str);
}
fileWriter.close();
System.out.println("执行完毕!");
}
}
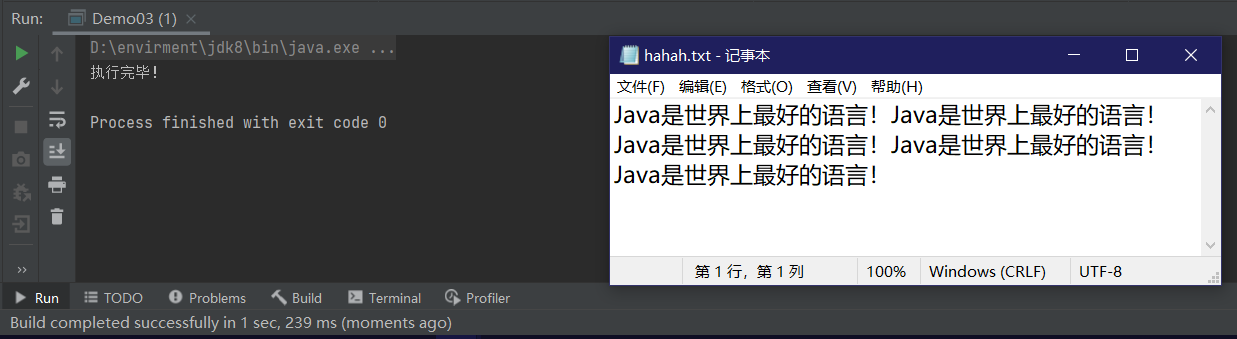
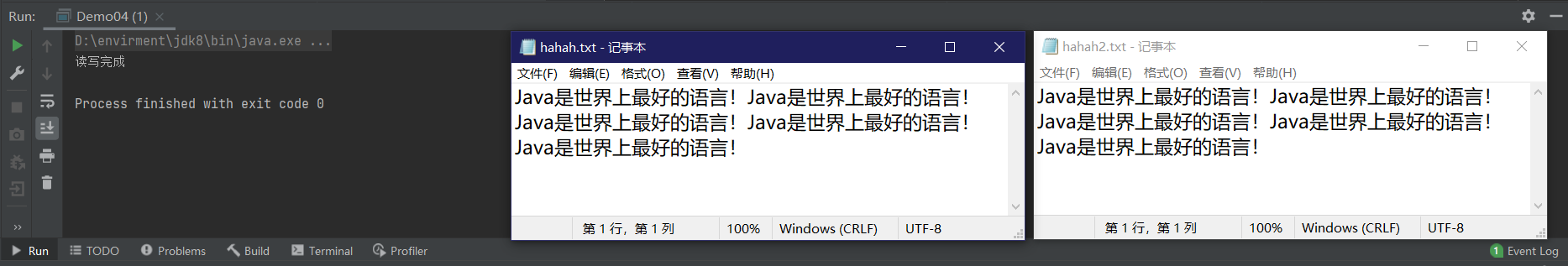
进行文本文件复制
不能复制图片或二进制文件(声音图片),但是使用字节流可以复制任意文件
package IO.charStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("e://hahah.txt");
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("e://hahah2.txt");
// 2 读写
int data=0;
while ((data=fileReader.read())!=-1){
fileWriter.write(data);
fileWriter.flush();
}
// 3 关闭
fileReader.close();
fileWriter.close();
System.out.println("读写完成");
}
}
字符流不能读取图片原因分析:
二进制文件没有字符编码,不能读取,读取到的都是乱码,更别提写入了!
字符缓冲流
BufferedReader / BufferedWriter
高效读写、支持输入换行符、可一次写一行读一行
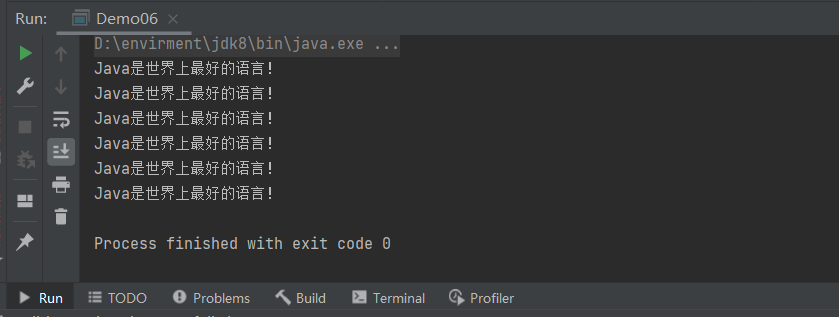
package IO.fileStream;
import java.io.*;
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建缓冲流
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("e://writer.txt");
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
// 2 读取
/*
int data=0;
while ((data=bufferedReader.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char) data);
}
*/
// 3 readline()
String line=null;
while ((line=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
// 4 关闭
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
package IO.charStream;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Writer;
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 创建BufferedWriter对象
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("e://writer.txt");
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(fileWriter);
// 2. 写入
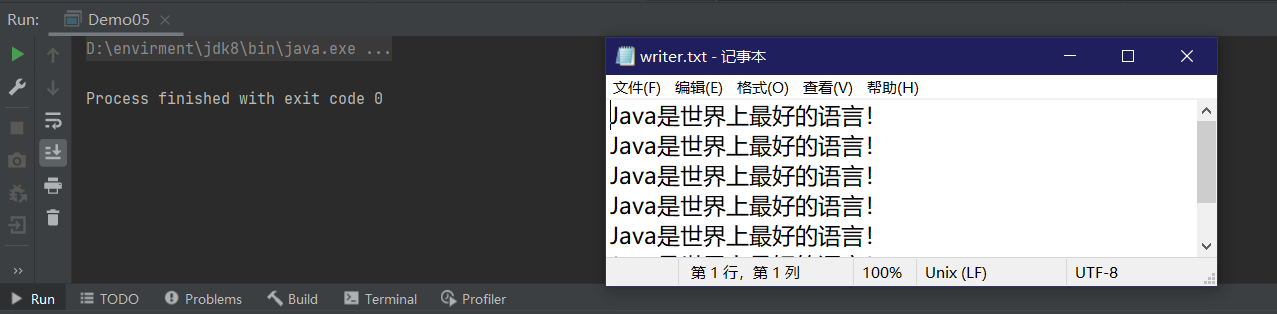
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
bufferedWriter.write("Java是世界上最好的语言!");
bufferedWriter.write("\n");// 写入一个换行符
bufferedWriter.flush();
}
// 3. 关闭
bufferedWriter.close();
}
}
打印流(PrintWriter)
封装了print() / println() 方法 支持写入后换行
支持数据原样打印
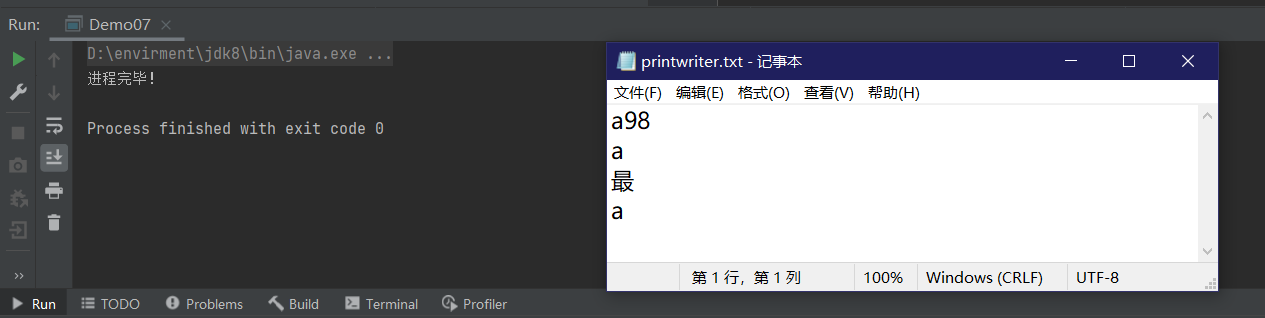
package IO.fileStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
// 1 创建打印流
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter("e://printwriter.txt");
// 2 打印
printWriter.write(97);
printWriter.println(98);
printWriter.println('a');
printWriter.println('最');
printWriter.append((char) 97);
// 3 关闭
printWriter.close();
System.out.println("进程完毕!");
}
}
转换流
桥转换流 InputStreamReader / OutputStreamWriter
可将字节流转换为字符流
可设置字符的编码方式
package IO.fileStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建InputStreamReader对象
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("e://a.jpg");
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream,"utf-8");
// 2 读取文件
int data=0;
while ((data=inputStreamReader.read())!=-1){
System.out.println(data);
}
// 3 关闭
inputStreamReader.close();
}
}
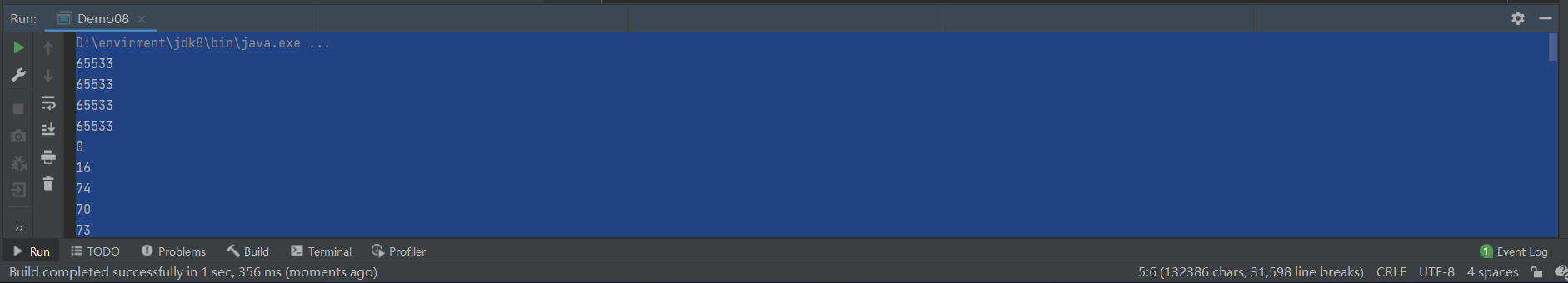
package IO.fileStream;
import java.io.*;
public class demo09 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建InputStreamReader对象
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("e://a.jpg");
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream,"utf-8");
// 2 OutputStreamWriter对象
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("e://c.jpg");
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream,"GBK");
// 3 读取文件
int data=0;
while ((data=inputStreamReader.read())!=-1){
// 4 写入文件
System.out.println(data);
outputStreamWriter.write(data);
outputStreamWriter.flush();
}
inputStreamReader.close();
outputStreamWriter.close();
System.out.println("储存完毕");
}
}
7.File类
概念:代表物理盘符中的一个文件或者文件夹

文件操作
package IO.File;
import javax.xml.crypto.Data;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Date;
//File类的使用
//1. 分隔符
//2. 文件操作
//3. 文件夹操作
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
separator();
touchFile("e://a.txt");
//removeFile("e://a.txt");
//jvmRemove("e://a.txt");
catFileInfo("e://a.txt");
judgeFile("e://a.txt");
}
// 1 分隔符
public static void separator(){
System.out.println("路径分隔符:" + File.pathSeparator);
System.out.println("名称分隔符:" + File.separator);
}
// 2 文件操作
// 2.1 创建文件
public static void touchFile(String url) throws Exception {
File file = new File(url);
if (!file.exists()) {
System.out.println("创建结果:" + file.createNewFile());
} else {
System.out.println("文件已存在!");
}
}
// 2.2 删除文件
public static void removeFile(String url)throws Exception{
File file = new File(url);
if (file.exists()){
System.out.println("删除结果:"+file.delete());
}else{
System.out.println("文件不存在呀,主人!");
}
}
// 2.3 使用JVM退出时删除文件
public static void jvmRemove(String url) throws InterruptedException {
File file = new File(url);
if (file.exists()){
file.deleteOnExit();
Thread.sleep(5000);
}else{
System.out.println("文件不存在呀,主人!");
}
}
// 3 获取文件信息
public static void catFileInfo(String url){
File file = new File(url);
if (file.exists()){
System.out.println("文件的绝对路径:"+file.getAbsoluteFile());
System.out.println("文件的路径:"+file.getPath());
System.out.println("文件名称:"+file.getName());
System.out.println("文件的父目录:"+file.getParent());
System.out.println("文件的长度:"+file.length());
System.out.println("文件的修改时间:"+(new Date(file.lastModified()).toLocaleString()));
}else{
System.out.println("文件不存在呀,主人!");
}
}
// 4 判断
public static void judgeFile(String url) throws InterruptedException {
File file = new File(url);
if (file.exists()){
System.out.println("文件可读:"+file.canRead());
System.out.println("文件可写:"+file.canWrite());
System.out.println("文件可执行:"+file.canExecute());
System.out.println("是否是文件"+file.isFile());
System.out.println("文件是否隐藏了:"+file.isHidden());
}else{
System.out.println("文件不存在呀,主人!");
}
}
}
文件夹操作
package IO.File;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Date;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//touchDir("e://aaa");
//removeDir("e://aaa");
//jvmRemove("e://aaa");
catDirInfo("e://aaa");
}
// 1 分隔符
public static void separator(){
System.out.println("路径分隔符:" + File.pathSeparator);
System.out.println("名称分隔符:" + File.separator);
}
// 2 文件操作
// 2.1 创建文件
public static void touchDir(String url) throws Exception {
File dir = new File(url);
if (!dir.exists()) {
System.out.println("创建结果:" + dir.mkdir());
} else {
System.out.println("文件已存在!");
}
}
// 2.2 删除文件夹(只能删除空目录)
public static void removeDir(String url)throws Exception{
File dir = new File(url);
if (dir.exists()){
System.out.println("删除结果:"+dir.delete());
}else{
System.out.println("文件不存在呀,主人!");
}
}
// 2.3 使用JVM退出时删除文件
public static void jvmRemove(String url) throws InterruptedException {
File dir = new File(url);
if (dir.exists()){
dir.deleteOnExit();
Thread.sleep(5000);
}else{
System.out.println("文件不存在呀,主人!");
}
}
// 3 获取文件信息
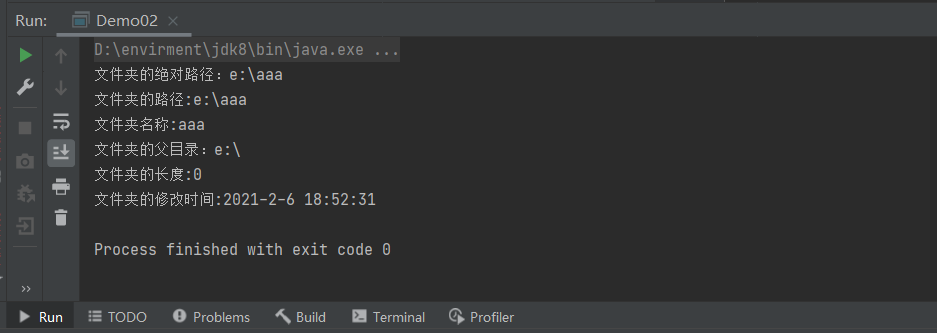
public static void catDirInfo(String url){
File dir = new File(url);
if (dir.exists()){
System.out.println("文件夹的绝对路径:"+dir.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("文件夹的路径:"+dir.getPath());
System.out.println("文件夹名称:"+dir.getName());
System.out.println("文件夹的父目录:"+dir.getParent());
System.out.println("文件夹的修改时间:"+(new Date(dir.lastModified()).toLocaleString()));
}else{
System.out.println("文件不存在呀,主人!");
}
}
// 4 判断
public static void judgeDir(String url) throws InterruptedException {
File dir = new File(url);
if (dir.exists()){
System.out.println("文件可读:"+dir.canRead());
System.out.println("文件可写:"+dir.canWrite());
System.out.println("文件可执行:"+dir.canExecute());
System.out.println("是否是文件夹"+dir.isDirectory());
System.out.println("文件是否隐藏了:"+dir.isHidden());
}else{
System.out.println("文件不存在呀,主人!");
}
}
}
递归遍历文件夹
package IO.File;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Date;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
listDir("e://");
}
// 5 遍历文件夹
public static void listDir(String url){
File dir = new File(url);
String[] list = dir.list();
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
递归删除文件夹
package IO.File;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Date;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
deleteDir("e://aaa");
// 递归删除文件夹
public static void deleteDir(String url){
File dir = new File(url);
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
int count=files.length;
if(files != null && files.length > 0){
for(File file : files){
System.out.println(file+"删除结果:"+file.delete());
count--;
}
}
if(count==0) {
dir.delete();
System.out.println("删除完成!");
}
}
}
FileFilter接口
这是一个功能界面,因此可以用作lambda表达式或方法引用的赋值对象。
//FileFilter接口的使用
package IO.File;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File dir = new File("C:\\Users\\Bai\\Pictures");
File[] files = dir.listFiles(new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
if (pathname.getName().endsWith("jpg")){
return true; //符合条件返回true
}else{
return false;
}
}
});
for (File file : files) {
System.out.println(file.getName());
}
}
}
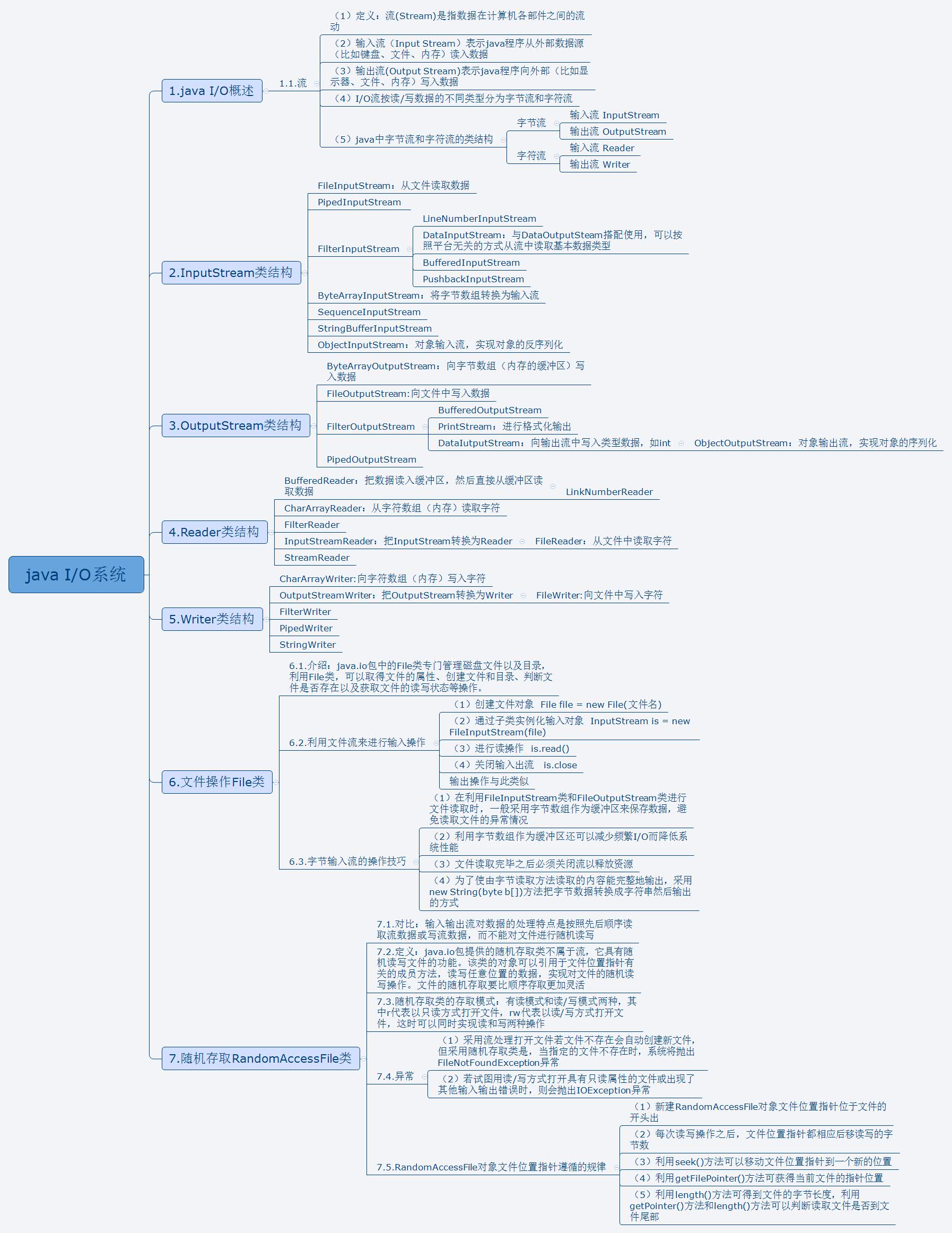
8.小结
二、Java集合框架
1.集合的概念
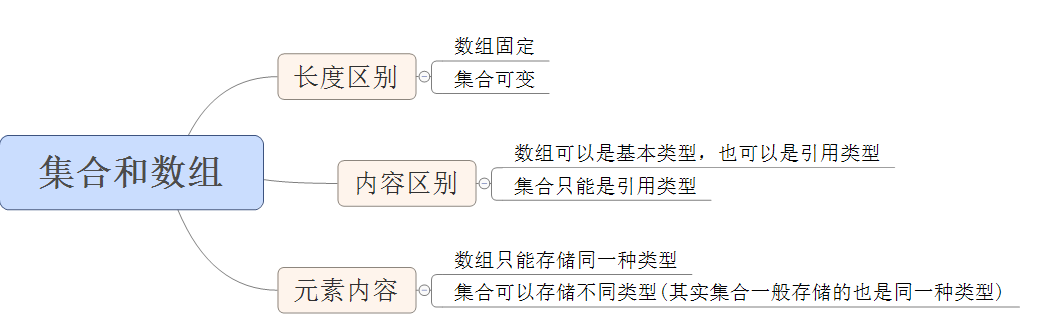
- 概念:对象的容器,定义了对多个对象进行操作的常用方法。可实现数组的功能。
和数组区别
-
数组长度固定,集合长度不固定
-
数组可以存储基本类型和引用类型,集合只能存储引用类型
- 位置: java.util.*;

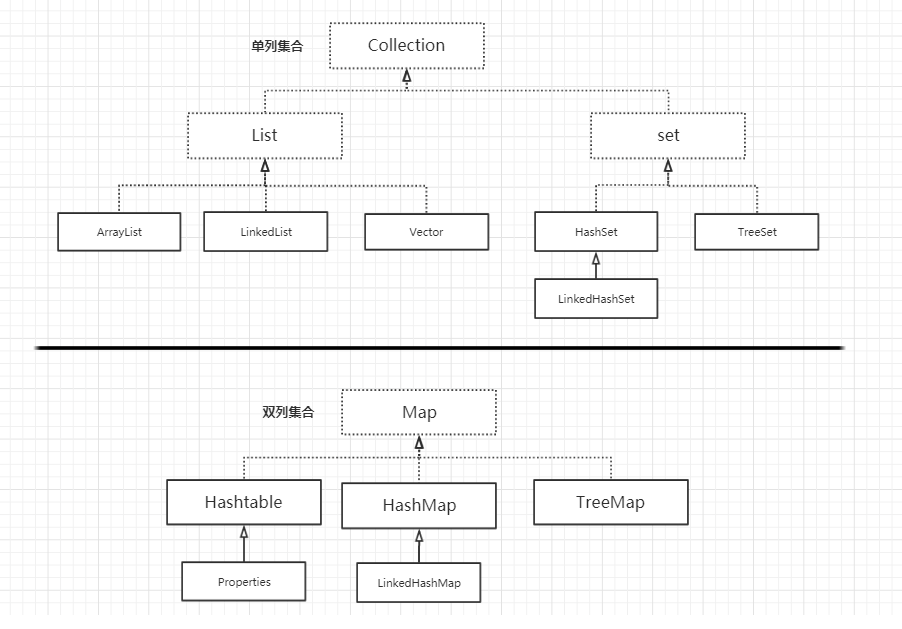
常见集合分类
Collection 接口的接口 对象的集合(单列集合)
├——-List 接口:元素按进入先后有序保存,可重复
│—————-├ LinkedList 接口实现类, 链表, 插入删除, 没有同步, 线程不安全
│—————-├ ArrayList 接口实现类, 数组, 随机访问, 没有同步, 线程不安全
│—————-└ Vector 接口实现类 数组, 同步, 线程安全
│ ———————-└ Stack 是Vector类的实现类
└——-Set 接口: 仅接收一次,不可重复,并做内部排序
├—————-└HashSet 使用hash表(数组)存储元素
│————————└ LinkedHashSet 链表维护元素的插入次序
└ —————-TreeSet 底层实现为二叉树,元素排好序
Map 接口 键值对的集合 (双列集合)
├———Hashtable 接口实现类, 同步, 线程安全
├———HashMap 接口实现类 ,没有同步, 线程不安全-
│—————–├ LinkedHashMap 双向链表和哈希表实现
│—————–└ WeakHashMap
├ ——–TreeMap 红黑树对所有的key进行排序
└———IdentifyHashMap
2.Collection接口
Collection体系集合
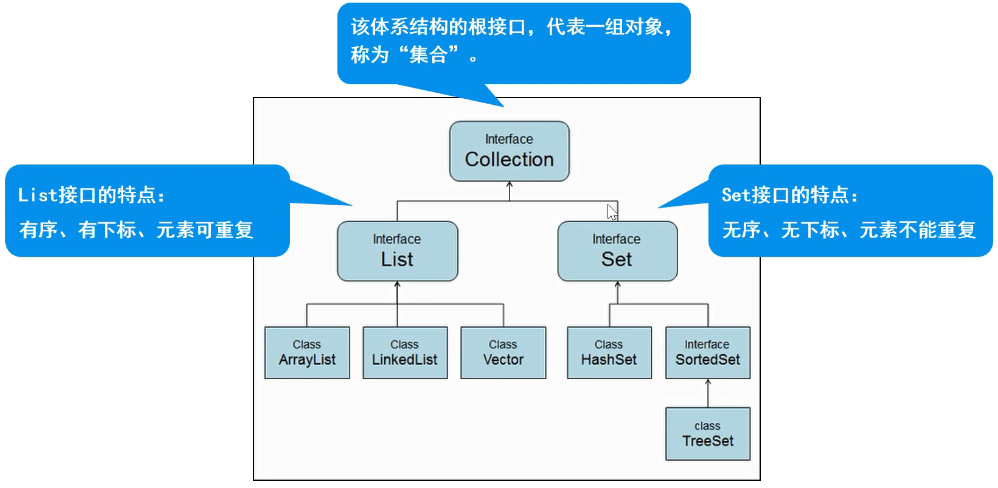
Collection父接口
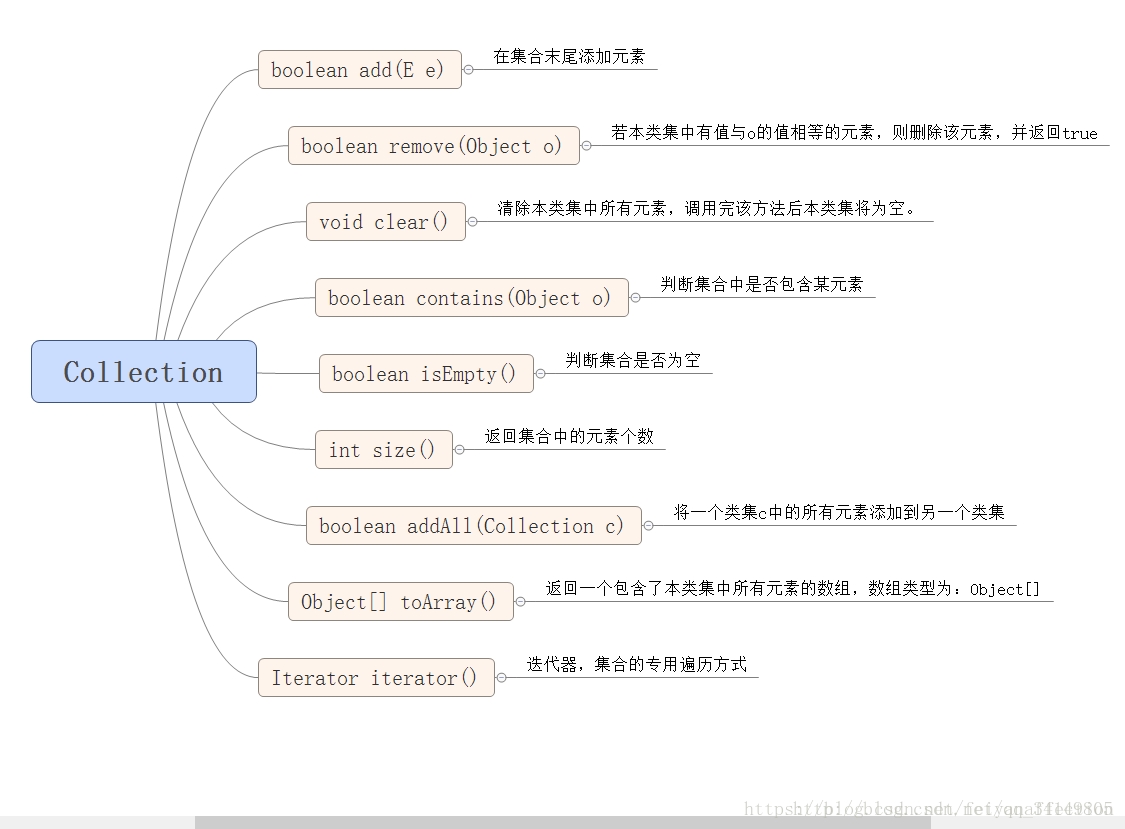
Collection的简单使用
package aggregate.Collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Demo01 {
//Collection接口的使用
//添加元素--删除元素--遍历元素--判断元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
ArrayList<Object> collection = new ArrayList<>();
//添加元素
collection.add("冰冰");
collection.add("Lisa");
collection.add("IU");
collection.add("书欣");
collection.add("白小飞");
//打印元素个数
System.out.println(collection.size());
//打印collection
System.out.println(collection);
//删除元素
collection.remove("白小飞");
//打印元素个数
System.out.println("老婆的个数:"+collection.size());
//打印collection
System.out.println(collection);
//遍历集合
//增强for循环,不能使用普通for,因为没有下标
/*
for (int i = 0; i < collection.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(collection[i]);
}
*/
System.out.println("===增强for循环遍历====");
for (Object o : collection) {
System.out.println(o);
}
System.out.println("===Iterator遍历====");
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String string = (String) iterator.next();
System.out.println(string);
// 在迭代过程中不允许使用collection.remove()方法
//collection.remove(string); ConcurrentModificationException:collection
iterator.remove();
}
System.out.println("======判断======");
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());
System.out.println(collection.contains("白小飞"));
System.out.println("====删除集合全部元素=====");
//删除集合全部
collection.clear();
//判断集合是否为空
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());
//打印collection
System.out.println(collection);
}
}
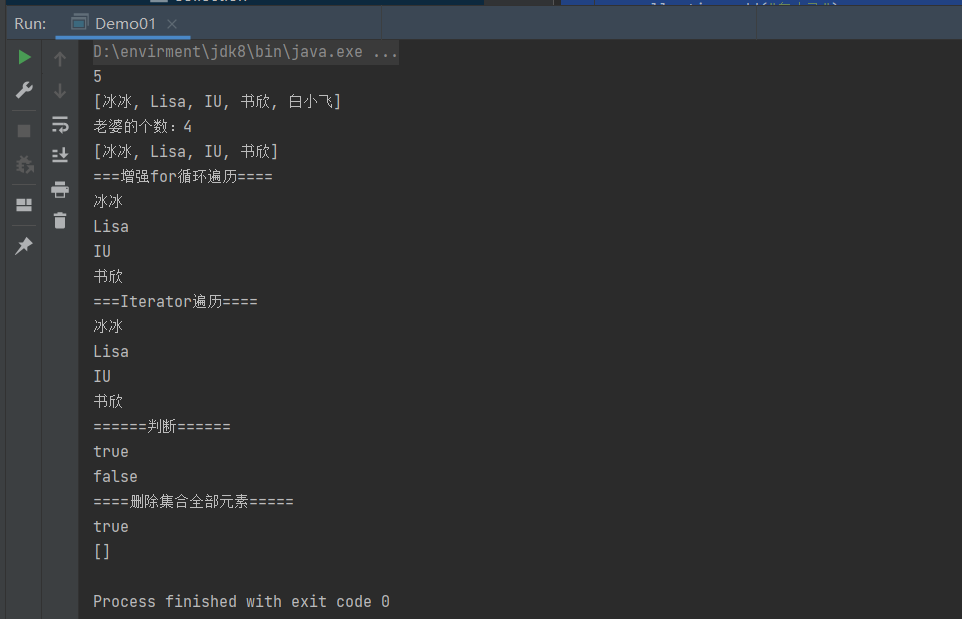
内存分析
3.List集合
List子接口
特点:有序、有下标、元素可以重复。
package aggregate.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.ListIterator;
//List接口的使用
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先创建集合
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
//添加元素
arrayList.add("小米");
arrayList.add("小米");
arrayList.add("苹果");
arrayList.add("华为");
System.out.println("========按照索引进行添加============");
arrayList.add(0,"荣耀");
//打印个数
System.out.println(arrayList.size());
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
//删除
arrayList.remove("小米");
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
System.out.println("===========按照下标索引进行删除==========");
arrayList.remove(1);
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
//遍历
System.out.println("========普通for循环遍历==========");
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(arrayList.get(i));
}
System.out.println("======增强for循环遍历========");
for (Object o : arrayList) {
System.out.println(o);
}
System.out.println("=======迭代器======");
Iterator iterator = arrayList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println("=========列表迭代器从前往后=========");
ListIterator listIterator = arrayList.listIterator();
while (listIterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(listIterator.nextIndex()+":"+listIterator.next());
}
System.out.println("=========列表迭代器从后往前=========");
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(listIterator.previousIndex()+":"+listIterator.previous());
}
System.out.println("==========判断=========");
System.out.println(arrayList.contains("小米"));
System.out.println(arrayList.contains("荣耀"));
System.out.println("=========获取元素位置==========");
System.out.println(arrayList.indexOf("华为"));
}
}
package aggregate.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List arrayList = new ArrayList();
//添加数字(自动集箱)
arrayList.add(10);
arrayList.add(30);
arrayList.add(10);
arrayList.add(50);
arrayList.remove(0);
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
System.out.println("========通过数值进行删除的方法=======");
arrayList.remove((Object) 10);
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
arrayList.remove(new Integer(50));
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
//添加数据
arrayList.add(10);
arrayList.add(30);
arrayList.add(10);
arrayList.add(50);
System.out.println("添加数据后:"+arrayList);
System.out.println("=======返回子集合=====");
List list = arrayList.subList(2,3);
//List list02 = arrayList.subList(2,6); 越界
System.out.println(list);
}
}
List的实现类
ArrayList(重点)
- 数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢;
- JDK1.2版本,运行效率快、线程不安全。
package aggregate.List.ArrayList;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.ListIterator;
//ArrayList的使用
//存储结构:数组 ,查找 遍历速度快,增删慢
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
//添加元素
Student g1 = new Student("冰冰", 18);
Student g2 = new Student("虞书欣", 18);
Student g3 = new Student("李知恩", 18);
Student g4 = new Student("白小飞", 18);
arrayList.add(g1);
arrayList.add(g2);
arrayList.add(g3);
arrayList.add(0,g4);
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
arrayList.remove(2);
System.out.println("=====迭代器======");
Iterator iterator = arrayList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next().toString());
}
System.out.println("=====列表迭代器======");
ListIterator listIterator = arrayList.listIterator();
while (listIterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(listIterator.next().toString());
}
System.out.println("反向List迭代器");
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(listIterator.previous().toString());
}
System.out.println("=======判断=======");
System.out.println(arrayList.contains("白小飞"));
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
System.out.println("========找位置=======");
System.out.println(arrayList.indexOf("白小飞"));
}
}
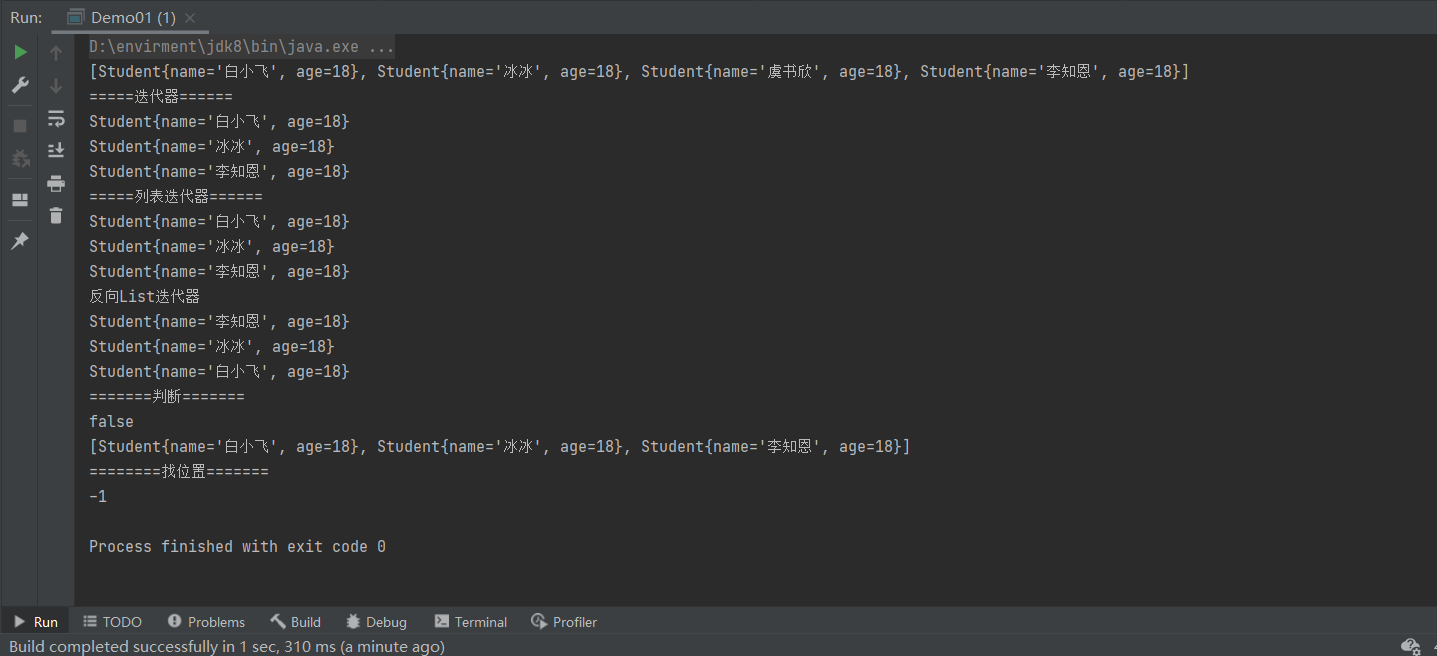
删除元素 arrayList.remove(new Student("name", 10));
这里重写了 equals(this == obj) 方法
public boolean equals(Object obj){
//1 判断是不是同一个对象
if(this == obj){
return true;
}
//2 判断是否为空
if(obj == null){
return false;
}
//3 判断是否是Student类型
if(obj instanceof Student){
Student == (Student)obj;
//4 比较属性
if(this.name.equals(s.getName()) && this.age == s.getAge()){
return true;
}
}
//5 不满足条件返回false
return false;
}
原码分析
DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; //默认容量
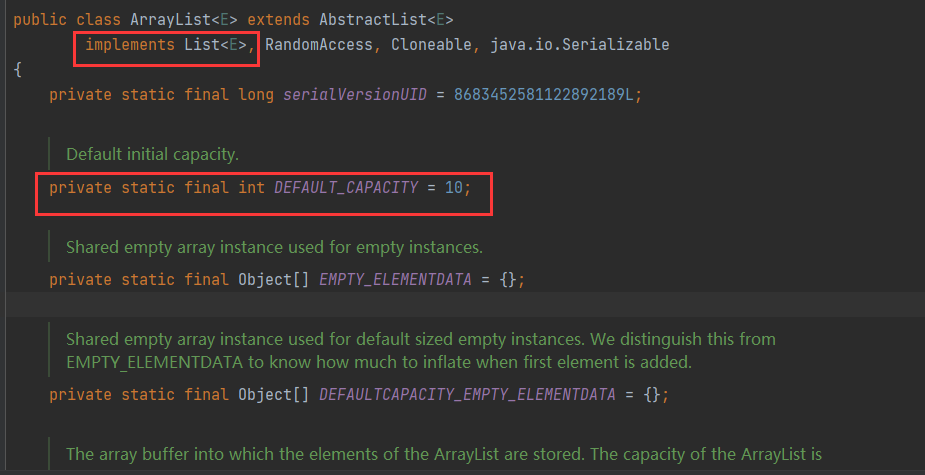
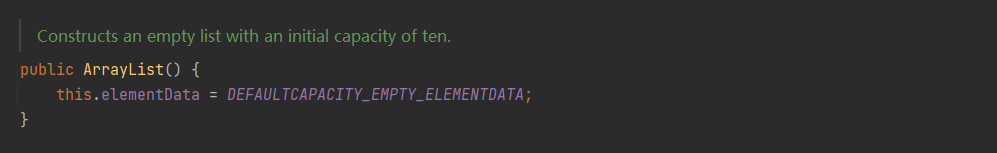
注意:如果没有向集合中添加任何元素时,容量0;添加一个后,容量为10;每次扩容是原来的1.5倍
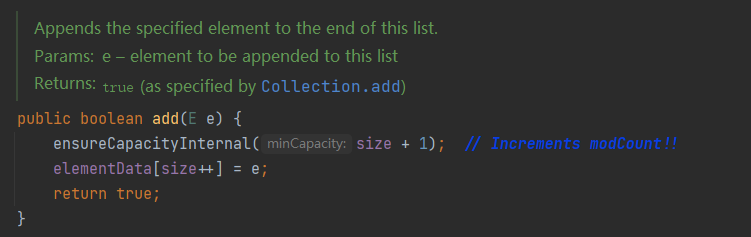
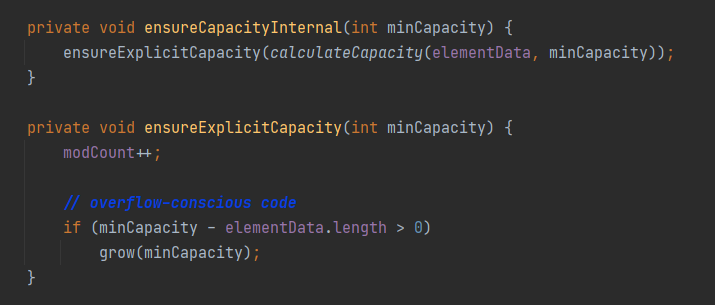
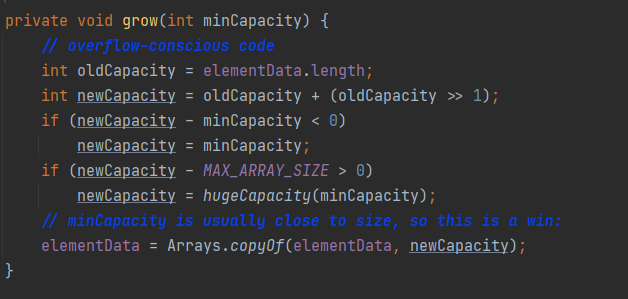
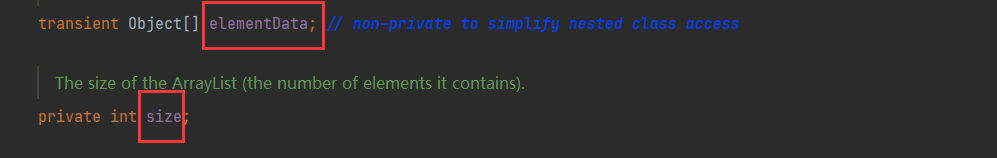
elementData存放元素的数组
size 实际元素个数
Vector(向量)
- 数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢;。
- JDK1.0版本,运行效率慢、线程安全。
package aggregate.List.Vector;
import java.util.*;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("====创建===");
Vector vector = new Vector<>();
System.out.println("====添加元素===");
vector.add("王冰冰");
vector.add("Lisa");
vector.add("白小飞");
vector.add("王冰冰");
vector.add("IU");
System.out.println("===删除元素===");
vector.remove("白小飞");
vector.remove(0);
System.out.println("===打印集合===");
System.out.println(vector.toString());
System.out.println("===普通for遍历===");
for (int i = 0; i < vector.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(vector.get(i));
}
System.out.println("===增强for遍历===");
for (Object o : vector) {
String str = (String)o;
System.out.println(str);
}
System.out.println("===普通迭代器===");
Iterator iterator = vector.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println("===List迭代器遍历===");
ListIterator listIterator = vector.listIterator();
while (listIterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(listIterator.next().toString());
}
System.out.println("===List反向迭代器遍历===");
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(listIterator.previousIndex()+":"+listIterator.previous());
}
System.out.println("===特有枚举器===");
Enumeration elements = vector.elements();
while (elements.hasMoreElements()){
System.out.println((String)elements.nextElement());
}
System.out.println("===判断冰冰是否存在===");
System.out.println(vector.contains("王冰冰"));
System.out.println("===判断是否为空===");
System.out.println(vector.isEmpty());
System.out.println("===获取第一个元素===");
System.out.println(vector.firstElement());
System.out.println("===获取最后一个元素===");
System.out.println(vector.lastElement());
System.out.println("===获取下标为2的元素===");
System.out.println(vector.elementAt(2));
}
}
LinkedList
- 链表结构实现,增删快,查询慢。
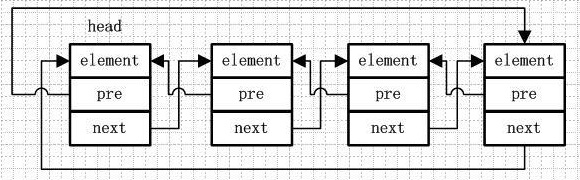
package aggregate.List.LinkedList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.ListIterator;
//LinkedList
//存储结构:双向链表
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("===创建集合===");
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
System.out.println("===添加元素===");
Student stu1 = new Student("白小飞", 10);
Student stu2 = new Student("杨洪利", 10);
Student stu3 = new Student("哈哈哈", 10);
linkedList.add(stu1);
linkedList.add(stu2);
linkedList.add(stu3);
System.out.println("===输出长度及数据===");
System.out.println(linkedList.size());
System.out.println(linkedList.toString());
System.out.println("====删除数据===");
linkedList.remove(2);
System.out.println(linkedList.toString());
System.out.println("===for遍历===");
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(linkedList.get(i));
}
System.out.println("===增强for遍历===");
for (Object o : linkedList) {
Student o1 = (Student) o;
System.out.println(o1);
}
System.out.println("===普通迭代器===");
Iterator iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next().toString());
}
System.out.println("===listIterator迭代器===");
ListIterator listIterator = linkedList.listIterator();
while (listIterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(listIterator.next());
}
System.out.println("===listIterator反向迭代器===");
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(listIterator.previous().toString());
}
System.out.println("===判断并获取===");
System.out.println(linkedList.contains("白小飞"));
System.out.println(linkedList.indexOf(stu1));
}
}
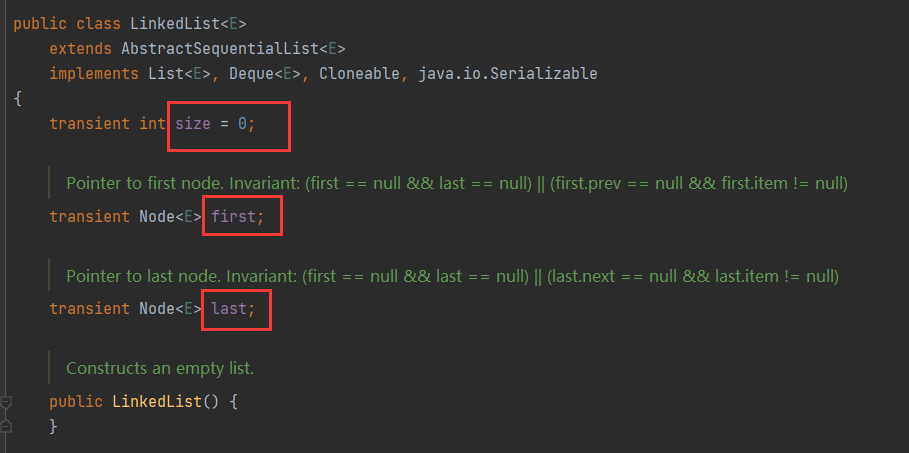
源码分析
int size():集合的大小
Node first:链表的头节点!
Node last:链表的尾节点

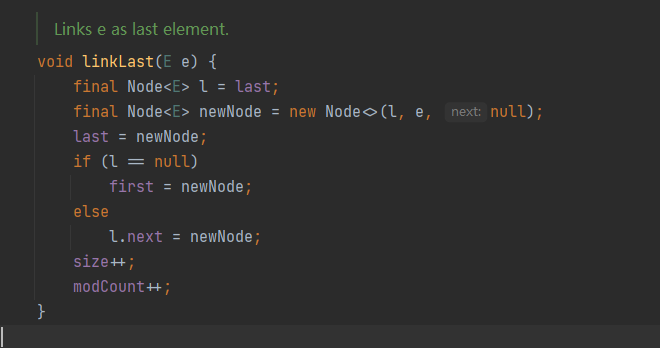
remove速度快:只是改变节点关系,数据不需要移动
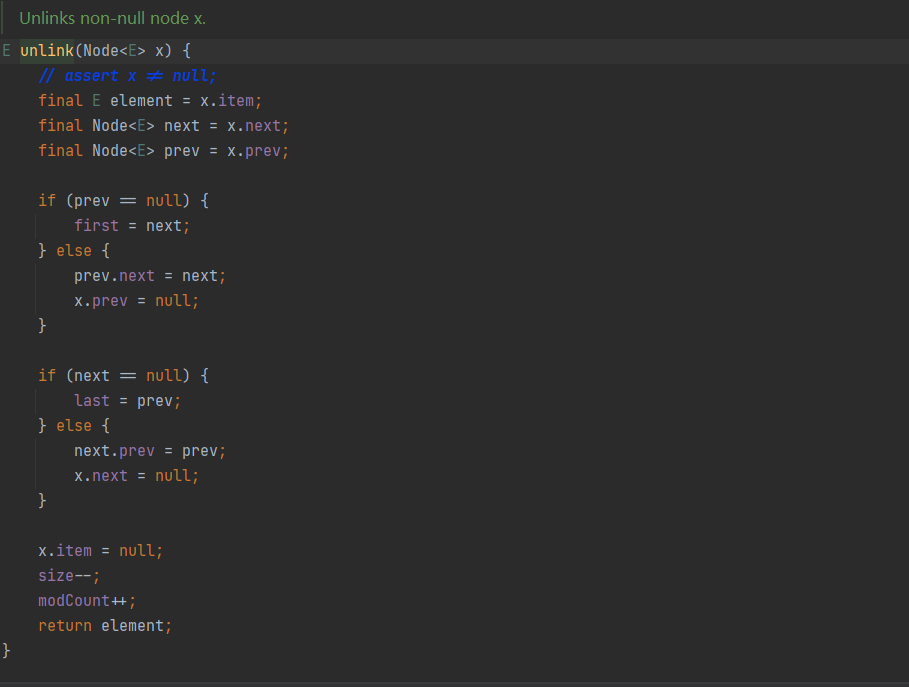

不同结构实现方式
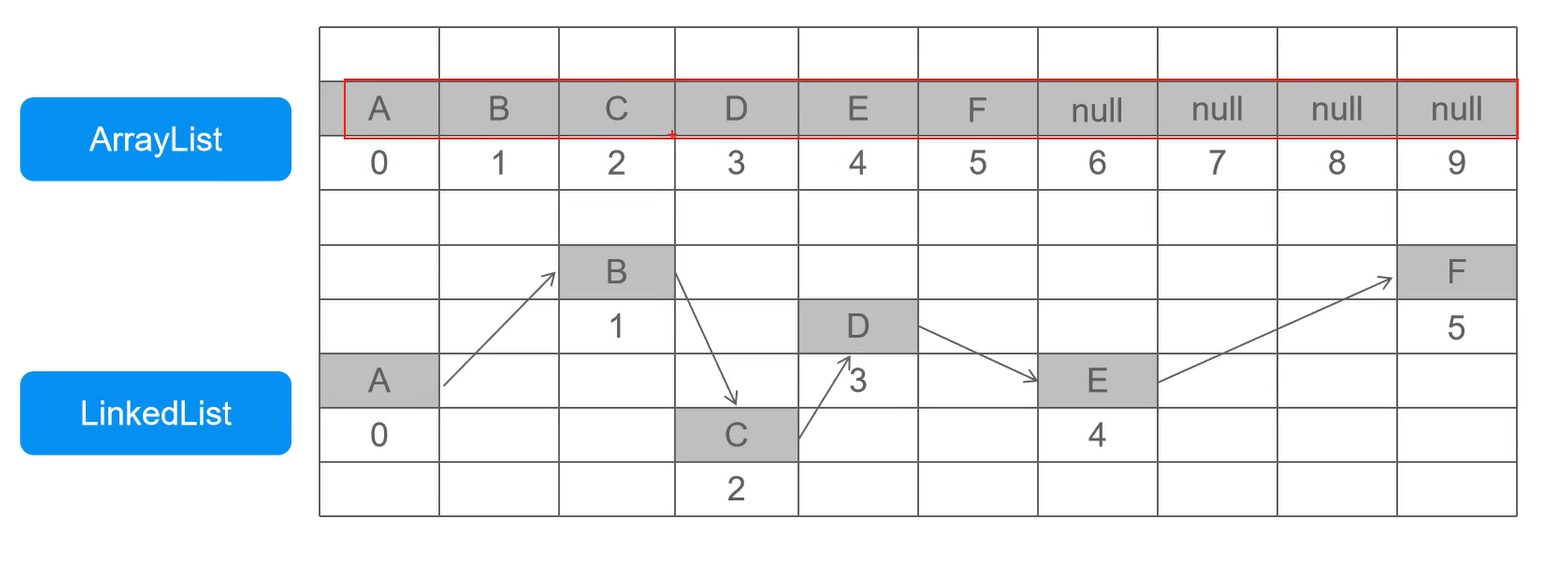
-
ArrayList:必须开辟连续空间,查询快,增删慢。
-
LinkedList:无需开辟连续空间,查询慢,增删快。
List与数组转化
//list.toArrary()
package aggregate.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
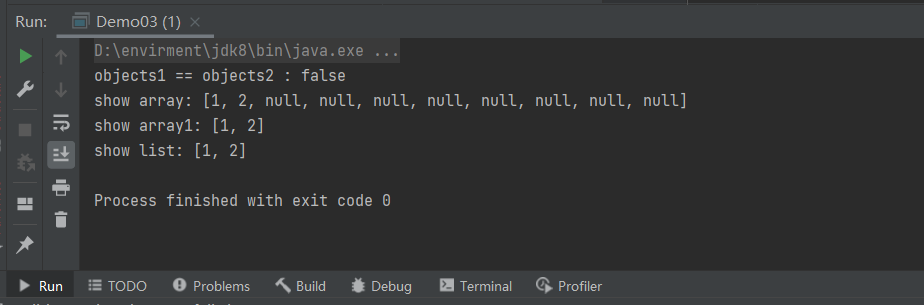
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
Integer[] array = list.toArray(new Integer[10]);
Integer[] array1 = list.toArray(new Integer[2]);
System.out.println("objects1 == objects2 : "+(array == array1));
System.out.println("show array: "+ Arrays.toString(array));
System.out.println("show array1: "+ Arrays.toString(array1));
System.out.println("show list: "+list);
}
}
package aggregate.List;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
//数组转集合
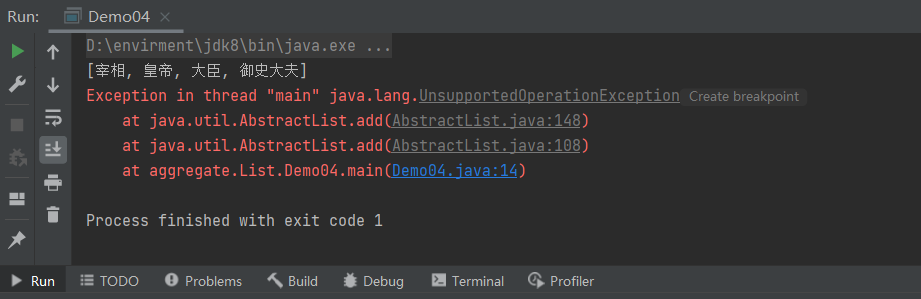
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] students = {"宰相","皇帝","大臣","御史大夫"};
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList(students);
//这个集合是受限集合,不支持增加删除
//System.out.println(strings);
//strings.add("秦王");
//strings.remove("宰相");
System.out.println(strings);
}
}
这个集合是受限集合,不支持增加删除操作!
//把基本类型数组转成集合时,需要修改为包装类型
Integer[] nums01={1,2,3,5,6};
List<Integer> integers = Arrays.asList(nums01);
//List<int[]> integers02 = Arrays.asList(nums01);
System.out.println(integers);
拓展
Java中int和Integer关系是比较微妙的。关系如下:
- int是基本的数据类型,Integer是int的封装类(复杂数据类型);
- int和Integer都可以表示某一个数值;
- int和Integer不能够互用,因为他们两种不同的数据类型;
- 在类进行初始化时int类的变量初始为0.而Integer的变量则初始化为null
小结:只是用来进行一些加减乘除的运算or作为参数进行传递,那么就可以直接声明为int基本数据类型,但如果要像对象一样来进行处理,那么就要用Integer来声明一个对象,因为java是面向对象的语言,因此当声明为对象时能够提供很多对象间转换的方式。
4.泛型
泛型
本质是参数化类型,把类型作为参数传递
语法: <T,.....>成为类型占位符,表示一种引用类型,可以写多个逗号隔开
- 泛型类
package aggregate.SegmentFault;
//泛型类
//语法:类名<T>
//T表示类型占位符,可以有多个
public class Demo01<T> {
//泛型可以用于创建变量,但是不能实例化对象 new
//使用泛型创建变量
T t;
//作为方法的参数
public void print(T t){
System.out.println(t);
}
//泛型作为方法的返回值
public T getT(){
return t;
}
}
package aggregate.SegmentFault;
//泛型类的创建
public class TestDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo01<String> demo01 = new Demo01<>();
demo01.t="hello";
demo01.print("大家好");
System.out.println(demo01.getT());
Demo01<Integer> integerDemo01 = new Demo01<>();
integerDemo01.t=12;
integerDemo01.print(15);
System.out.println(integerDemo01.getT());
}
}
注意:1.泛型只能使用引用类型;2.不同泛型类型对象不能相互赋值
- 泛型接口
//Demo02
package aggregate.SegmentFault;
//泛型接口
//注意:不能创建泛型静态常量
public interface Demo02<K> {
String name="白小飞";
K server(K k);
}
//方法一
package aggregate.SegmentFault;
//继承string类型的范型类接口
public class Demo02Impl01 implements Demo02<String>{
@Override
public String server(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
return s;
}
}
//方法二
package aggregate.SegmentFault;
//实现泛型类接口的类也是泛型类
public class Demo02Impl02<T> implements Demo02<T>{
@Override
public T server(T t) {
System.out.println(t);
return t;
}
}
//main()
package aggregate.SegmentFault;
public class TestDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo02Impl01 demo02 = new Demo02Impl01();
demo02.server("白小飞");
Demo02Impl02<String> demo02Impl02 = new Demo02Impl02<>();
demo02Impl02.server("hello");
}
}
- 泛型方法
package aggregate.SegmentFault;
//泛型方法
public class Demo03 {
public <t> void say(){
System.out.println("say!");
}
public <T> T haha(T t){
System.out.println(t);
return t;
}
}
package aggregate.SegmentFault;
//调用泛型方法
//类型不需要定义,它会根据传入的值确定类型
public class TestDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo03 demo03 = new Demo03();
demo03.say();
demo03.haha("中国加油!");
demo03.haha(111);
}
}
好处
- 提高代码重用性 ,类似于重载,一个方法可以传递各种参数!
- 防止类型转换异常,提高代码安全性
泛型集合
package aggregate.SegmentFault;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("原迭代器遍历");
LinkedList<Object> objects = new LinkedList<>();
objects.add("划水");
objects.add("摸鱼");
objects.add("吃饭");
objects.add(555);
objects.add(666);
Iterator<Object> iterator = objects.iterator();
//while (iterator.hasNext()){
//System.out.println(iterator.toString());
//String str = (String) iterator.next();
//System.out.println(str);
//}
LinkedList<Integer> integers = new LinkedList<>();
integers.add(1);
integers.add(4);
integers.add(3);
integers.add(2);
Iterator<Integer> iterator1 = integers.iterator();
while (iterator1.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator1.next());
}
Student stu1 = new Student("白小飞", 12);
Student stu2 = new Student("冰冰", 12);
Student stu3 = new Student("虞书欣", 12);
Student stu4 = new Student("IU", 12);
LinkedList<Student> students = new LinkedList<>();
students.add(stu1);
students.add(stu2);
students.add(stu3);
students.add(stu4);
Iterator<Student> iterator2 = students.iterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator2.next());
}
}
}
5.Set集合
Set接口
package aggregate.Set.HashSet;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class Demo01 {
//测试 Set 接口的使用
//特点:无序 、没有下标 、 不能重复
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
Set<String> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
//添加数据
//不能重复!重复的将不会存储!
hashSet.add("白小飞");
hashSet.add("白小飞");
hashSet.add("王冰冰");
hashSet.add("吃花椒");
hashSet.add("喵酱");
System.out.println(hashSet.size());
System.out.println(hashSet.toString());
//删除操作
//hashSet.remove("白小飞");
//遍历
System.out.println("===使用增强for===");
for (String s : hashSet) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("===使用迭代器===");
Iterator<String> iterator = hashSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println("===判断===");
System.out.println(hashSet.contains("王冰冰"));
}
}
Set实现类
- HashSet
package aggregate.Set.HashSet;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
//HashSet
//存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树)
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//新建集合
HashSet<String> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
//添加元素
hashSet.add("王冰冰");
hashSet.add("蔡徐坤");
hashSet.add("双厨");
hashSet.add("央视");
System.out.println(hashSet.size());
System.out.println(hashSet);
//删除元素
hashSet.remove("央视");
hashSet.add("央视");
System.out.println(hashSet);
System.out.println("===增强for迭代===");
for (String s : hashSet) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("===迭代器===");
Iterator<String> iterator = hashSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println("===判断===");
System.out.println(hashSet.contains("蔡徐坤"));
}
}
package aggregate.Set.HashSet;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
HashSet<Person> people = new HashSet<Person>();
Person p1 = new Person("白小飞", 11);
Person p2 = new Person("qdwq", 11);
Person p3 = new Person("qdqw", 11);
Person p4 = new Person("caixe", 11);
//添加元素
people.add(p1);
people.add(p2);
people.add(p3);
people.add(p4);
people.add(new Person("lisa",18));
//下面new又存储了一个相同的元素!!
//存了两个白小飞!!
people.add(new Person("白小飞", 11));
//输出元素
System.out.println(people.toString());
System.out.println("===增强for循环===");
for (Person person : people) {
System.out.println(person.toString());
}
System.out.println("===迭代器循环===");
Iterator<Person> iterator = people.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
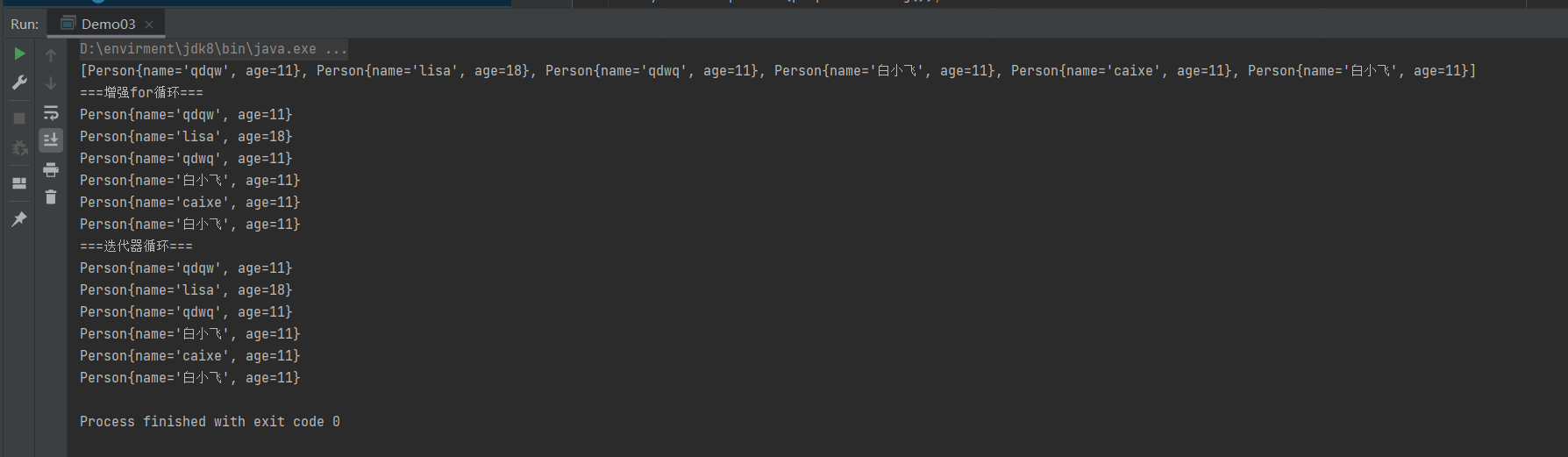
存储过程(重复依据)
- 根据hashCode计算保存的位置,如果位置为空,直接保存,若不为空,进行第二步
- 再执行equals方法,如果equals为true,则认为是重复,否则形成链表
//方法重写 可以通过new进行remove删除以及不能通过new重复存储了
//alt+insert 重写 hasCode 和 equal方法
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
return age == person.age && Objects.equals(name, person.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
在hashCode方法中存在了一个31,它的作用:
1.31是一个质数,尽量减少散列冲突
2.31提高执行效率 31*i=i<<5-i (将乘法换成移位操作,底层计算,效率快)

TreeSet
- 基于排列顺序实现元素不重复
- 实现了SortedSet接口,对集合元素自动排序
- 元素对象的类型必须实现Comparable接口,指定排序规则
- 通过CompareTo方法确定是否为重复元素
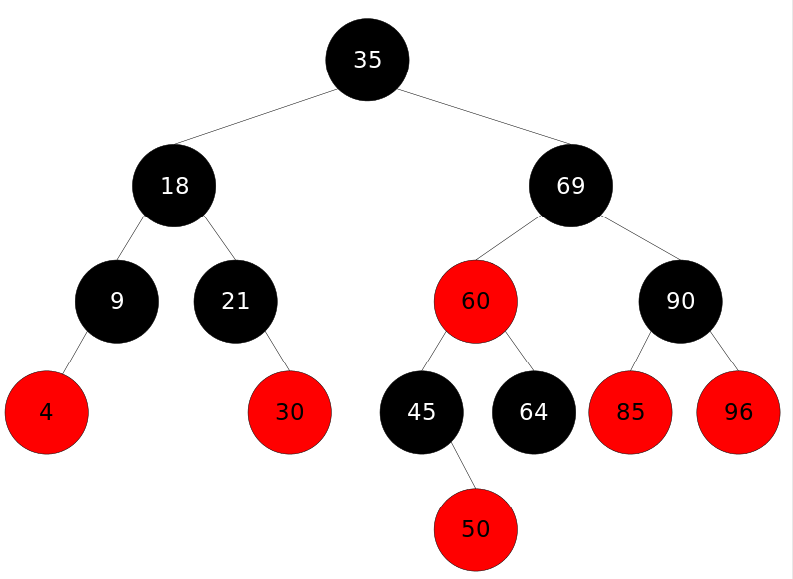
普通数据默认比较
package aggregate.TreeSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
//使用TreeSet保存数据
//存储结构:红黑树
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<String>();
treeSet.add("asda");
treeSet.add("xya");
treeSet.add("ii");
treeSet.add("a");
System.out.println("个数:"+treeSet.size());
System.out.println(treeSet.toString());
System.out.println("===增强for===");
for (String s : treeSet) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("===迭代器===");
Iterator<String> iterator = treeSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
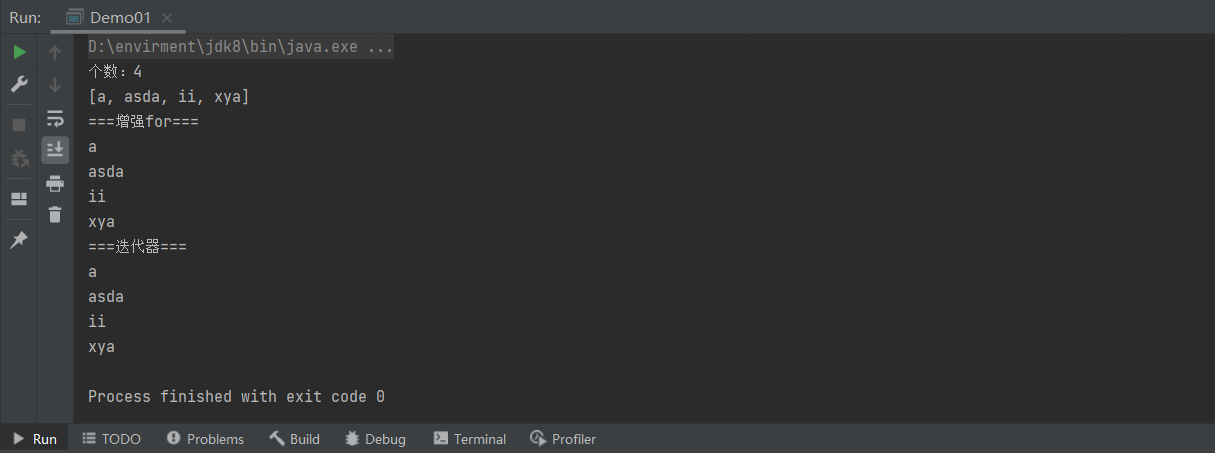
实现 Comparable接口
//Person
package aggregate.TreeSet;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
//比较规则:先按姓名比,再按年龄比
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
int name=this.name.compareTo(o.name);
int age=this.age-o.age;
return name==0?age:name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
return age == person.age && Objects.equals(name, person.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}
package aggregate.TreeSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
//使用TreeSet保存数据
//存储结构:红黑树
//要求:元素必须要实现 Comparable接口,CompareTo() 返回值为0,认为是重复元素
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Person> people = new TreeSet<>();
Person p1 = new Person("xyz", 11);
Person p2 = new Person("lisa",11);
Person p3 = new Person("bai",11);
Person p4 = new Person("iu",11);
people.add(p1);
people.add(p2);
people.add(p3);
people.add(p4);
System.out.println(people.size());
System.out.println(people.toString());
Person p5 = new Person("iu",18);
Person p6 = new Person("iu",18);
people.add(p5);
people.add(p6);
System.out.println(people.toString());
for (Person person : people) {
System.out.println(person.toString());
}
Iterator<Person> iterator = people.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
//重写hashSet方法后,将不会储存重复的new 对象
//重写hashSet方法后,可以通过new 对象删除具有相同属性的元素
System.out.println(people.toString());
people.add(new Person("iu",11));
System.out.println(people.toString());
people.remove(new Person("iu",18));
System.out.println(people.toString());
}
}
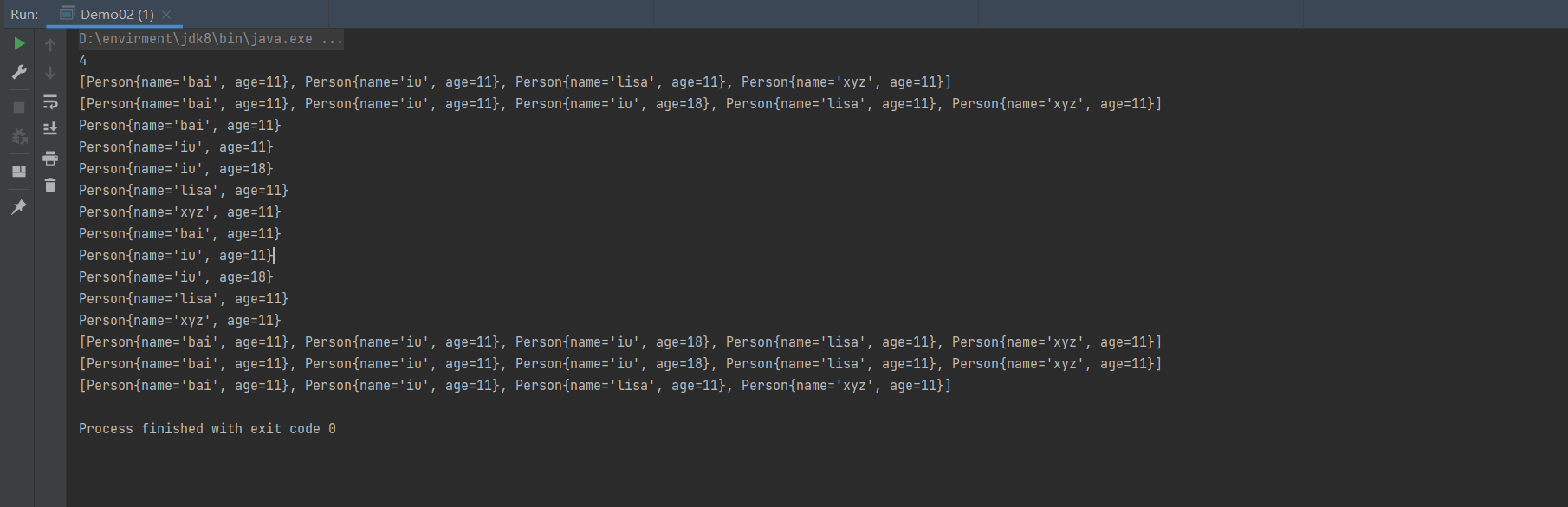
Comparator 实现定制比较(定制器)
package aggregate.TreeSet;
//Comparator 定制比较
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合并定制比较规则
TreeSet<Person> people = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
int n1 = o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());
int n2 = o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();
return n1==0?n2:n1;
}
});
Person p1 = new Person("xyz", 11);
Person p2 = new Person("lisa",11);
Person p3 = new Person("bai",11);
Person p4 = new Person("iu",11);
people.add(p1);
people.add(p2);
people.add(p3);
people.add(p4);
System.out.println(people);
}
}
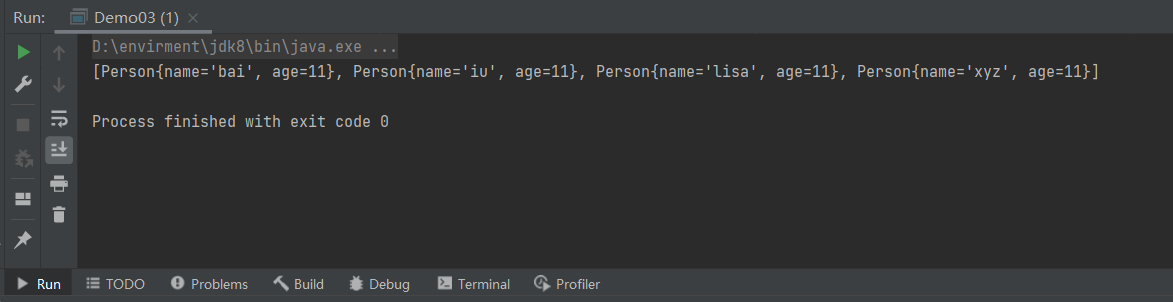
example
要求:使用TreeSet集合实现字符串长度排序
compare :
1:前面的数>后面的数,是降序(从大到小)排列,如果想要改为升序排列,就需要返回1
-1:前面的数<后面的数,是升序(从小到大)排列,不改变位置就返回-1;
0:二者相等,不进行交换,也就不排序。
package aggregate.TreeSet;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<String> strings = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
int n1=o1.length()-o2.length();
//n1 == 0 说明 长度相等
//compare :
//1:前面的数>后面的数,是降序(从大到小)排列,如果想要改为升序排列,就需要返回1
//-1:前面的数<后面的数,是升序(从小到大)排列,不改变位置就返回-1;
//0:二者相等,不进行交换,也就不排序。
int n2=o1.compareTo(o2);
//按照默认首字母比较
return n1==0?n2:n1;
}
});
strings.add("aaaa");
strings.add("zasas");
strings.add("asasd");
strings.add("ada");
strings.add("wd");
System.out.println(strings);
}
}

6.Map集合
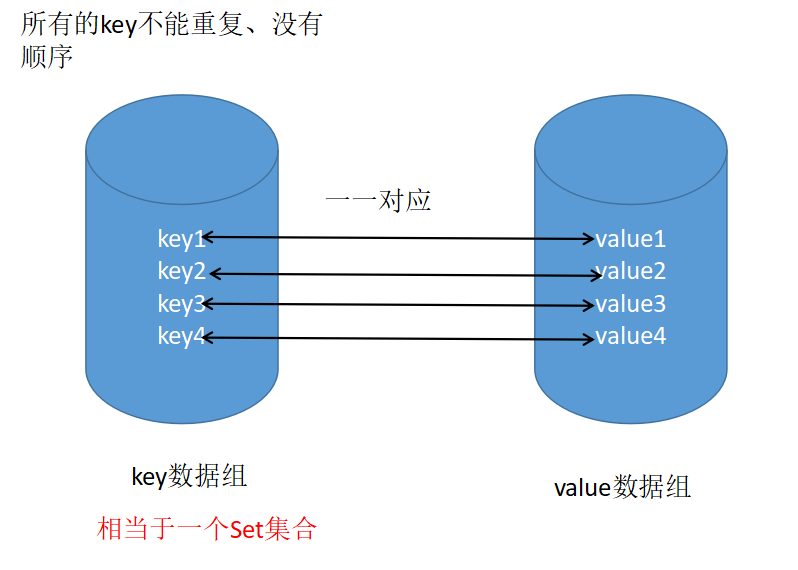
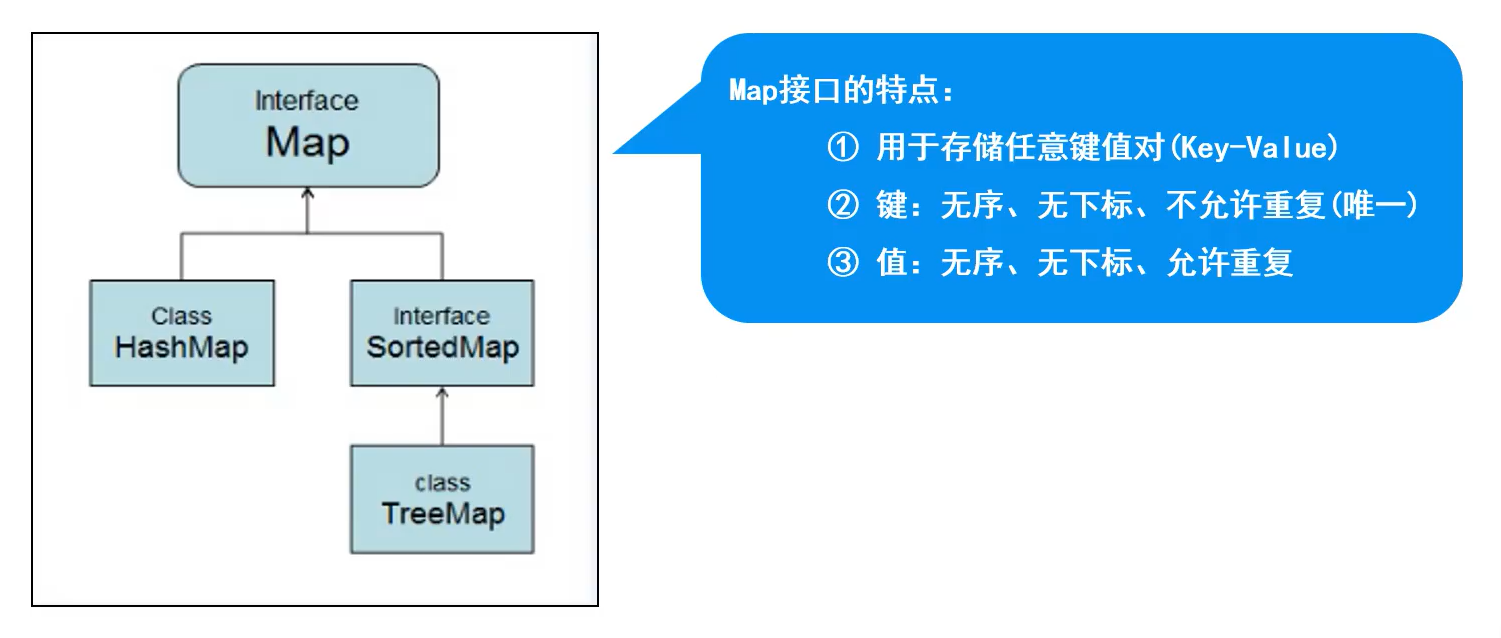
Map父接口
Map接口的特点
- 用于存储任意键值对(key - value)
- 键:无序、无下标、不允许重复(唯一)
- 值:无序、无下标、允许重复
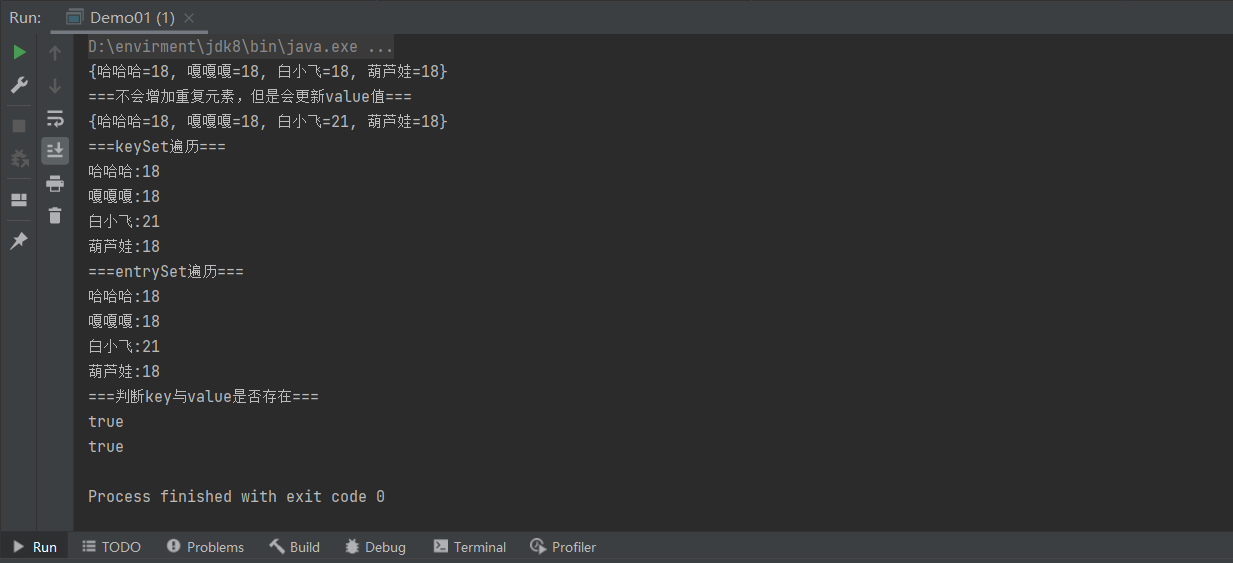
package aggregate.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
//Map接口的使用
//特点:(1)存储键值对;(2)键不能重复,值可以重复;(3)无序
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> stringIntegerHashMap = new HashMap<>();
stringIntegerHashMap.put("白小飞",18);
stringIntegerHashMap.put("葫芦娃",18);
stringIntegerHashMap.put("哈哈哈",18);
stringIntegerHashMap.put("嘎嘎嘎",18);
System.out.println(stringIntegerHashMap.toString());
System.out.println("===不会增加重复元素,但是会更新value值===");
stringIntegerHashMap.put("白小飞",21);
System.out.println(stringIntegerHashMap.toString());
System.out.println("===keySet遍历===");
Set<String> strings = stringIntegerHashMap.keySet();
for (String string : strings) {
System.out.println(string+":"+stringIntegerHashMap.get(string));
}
System.out.println("===entrySet遍历===");
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = stringIntegerHashMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entries) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+":"+entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("===判断key与value是否存在===");
System.out.println(stringIntegerHashMap.containsKey("白小飞"));
System.out.println(stringIntegerHashMap.containsValue(18));
}
}
KeySet与EntrySet
entrySet效率较高,可一次性查出key与value。
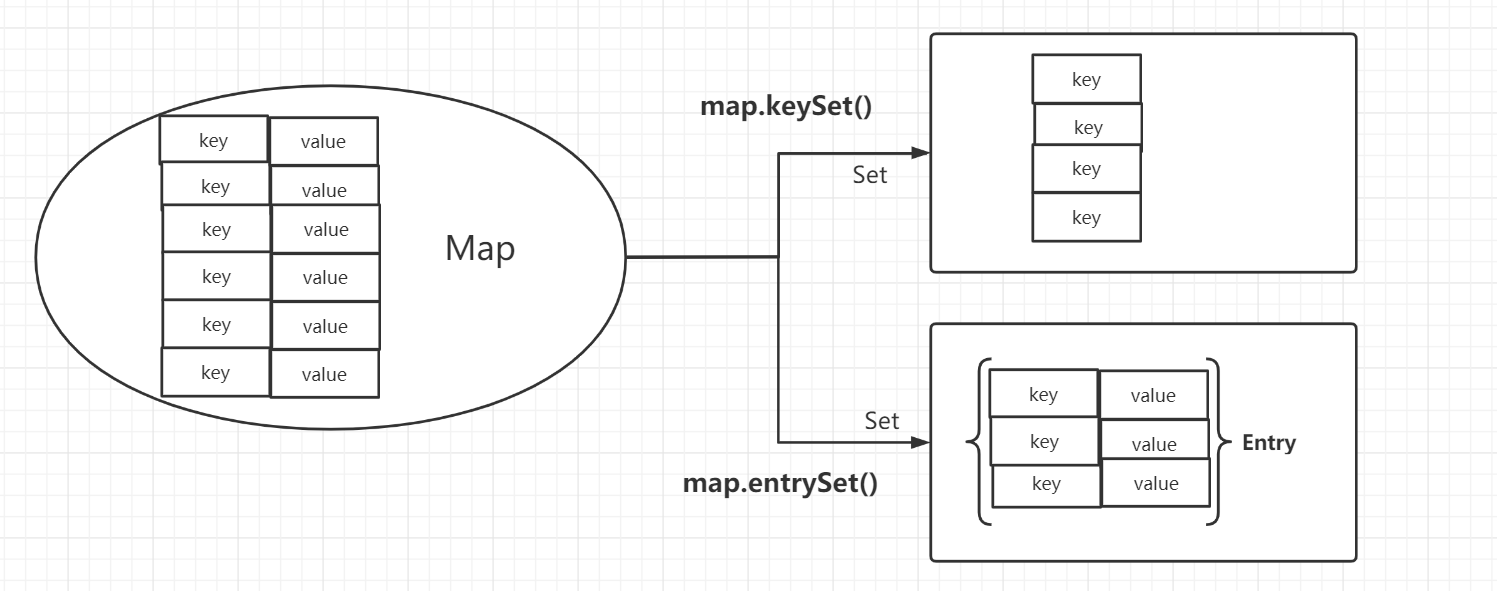
Map集合的实现类
HashMap(重点)
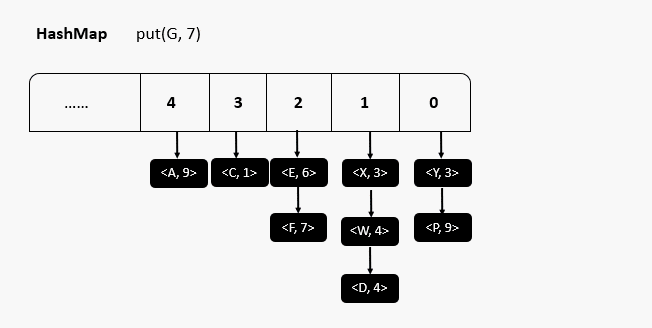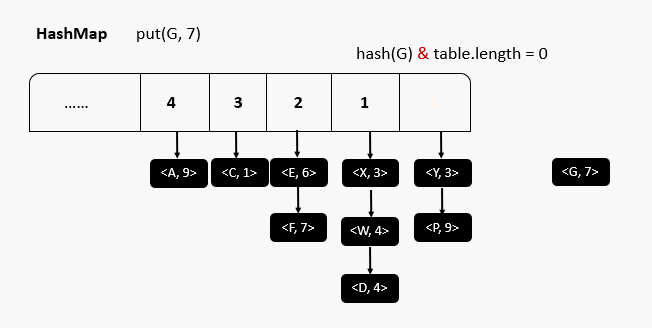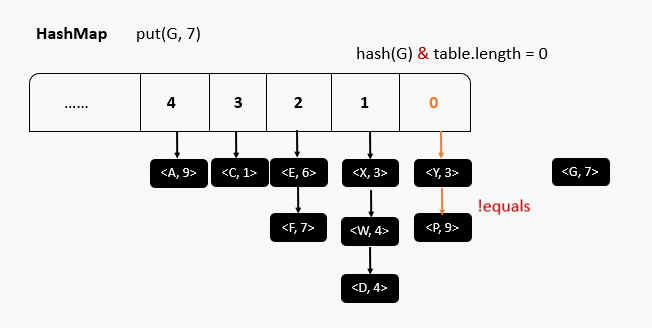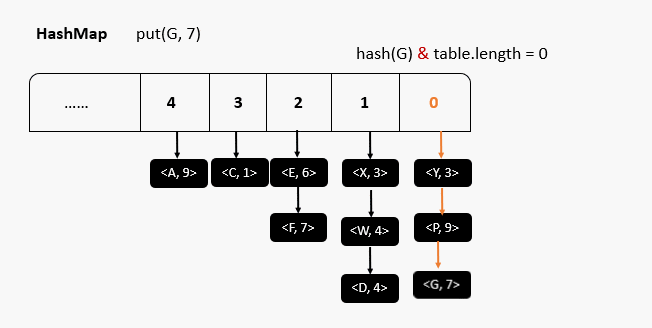
- 存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树)
- 使用key可使hashcode和equals作为重复
- 增、删、遍历、判断与上述一致
//Student
package aggregate.Map.HashMap;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int stuNo;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int stuNo) {
this.name = name;
this.stuNo = stuNo;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getStuNo() {
return stuNo;
}
public void setStuNo(int stuNo) {
this.stuNo = stuNo;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", stuNo=" + stuNo +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return stuNo == student.stuNo && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, stuNo);
}
}
//Application
package aggregate.Map.HashMap;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
//HashMap集合
//存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树)
//使用hashCode 和 equals 方法
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Student, String> studentStringHashMap = new HashMap<>();
//key值不可以重复,但是value值可以!value值也会覆写!!
Student stu01 = new Student("孙悟空", 100);
Student stu02 = new Student("猪八戒", 102);
Student stu03 = new Student("唐三藏", 103);
studentStringHashMap.put(stu01,"上海");
studentStringHashMap.put(stu02,"杭州");
studentStringHashMap.put(stu03,"北京");
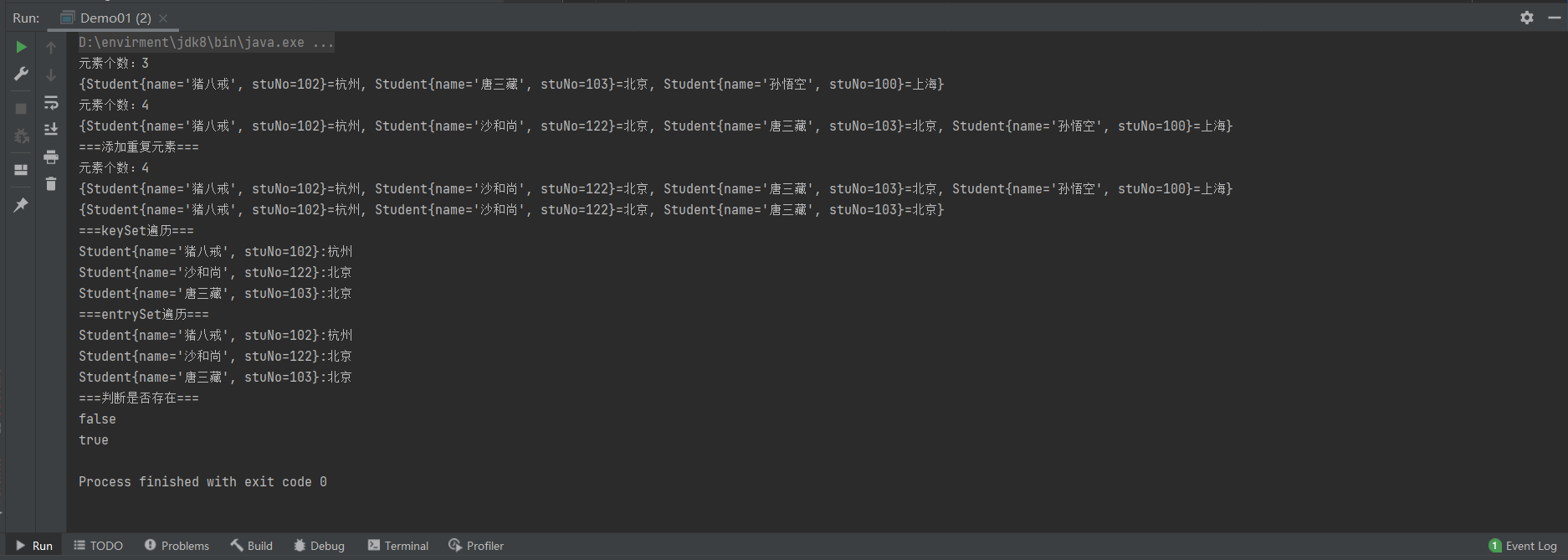
System.out.println("元素个数:"+studentStringHashMap.size());
System.out.println(studentStringHashMap.toString());
studentStringHashMap.put(new Student("沙和尚",122),"北京");
System.out.println("元素个数:"+studentStringHashMap.size());
System.out.println(studentStringHashMap.toString());
System.out.println("===添加重复元素==="); //重写hashCode 和 equals 方法实现不允许存储重复数据
studentStringHashMap.put(new Student("唐三藏", 103),"北京");
System.out.println("元素个数:"+studentStringHashMap.size());
System.out.println(studentStringHashMap.toString());
studentStringHashMap.remove(stu01);
System.out.println(studentStringHashMap);
//studentStringHashMap.clear();
System.out.println("===keySet遍历===");
Set<Student> students = studentStringHashMap.keySet();
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student+":"+studentStringHashMap.get(student));
}
System.out.println("===entrySet遍历===");
Set<Map.Entry<Student, String>> entries = studentStringHashMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Student, String> entry : entries) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+":"+entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("===判断是否存在===");
System.out.println(studentStringHashMap.containsValue("泰安"));
//由于重写了equals 和 hashSet 方法, 所以可以通过 new 一个具有相同属性的对象 删除原有元素
System.out.println(studentStringHashMap.containsKey(new Student("唐三藏", 103)));
}
}
原码分析
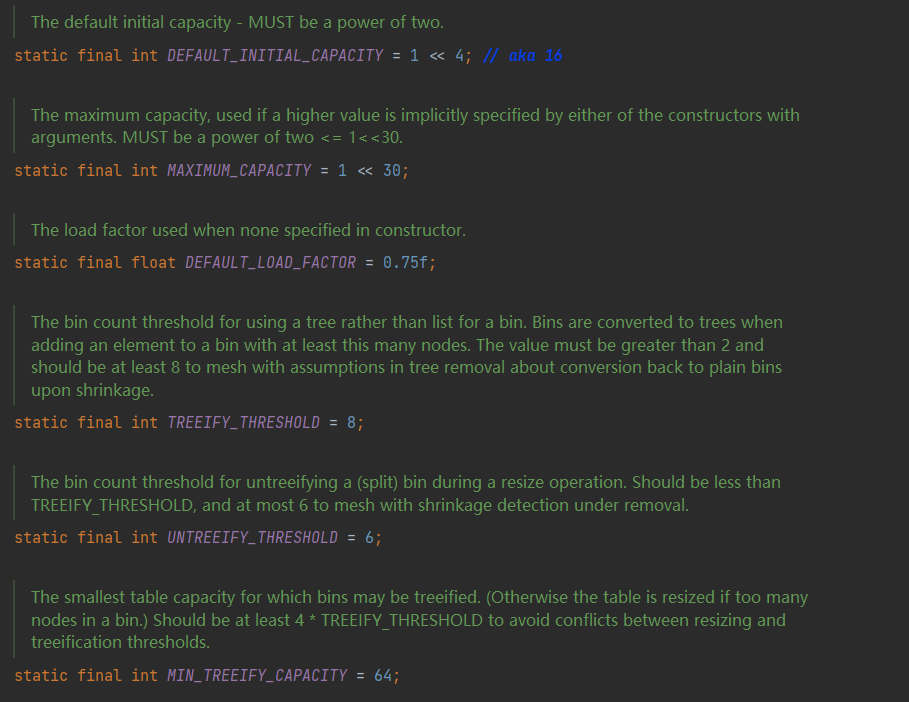
//默认的初始化容量为16
static final int DEFAULT_INITAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
//最大的容量,容量的值必须是2的幂并且小于最大容量,最大值为2的30此房
static final int MAXMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
//加载因子默认值为0.75
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
//计数阀值,超过这个值将会使用树形结构替代链表结构
static final int TREEIFYTHRESHOLD = 8;
//由树形结构转换成链表结构的阀值
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
//树形结构最小容量为64
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
//链表数组
transient Node<K, V>[] table;
//HashMap中value的集合
transient Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet;
//hashMap的长度
transient int size;
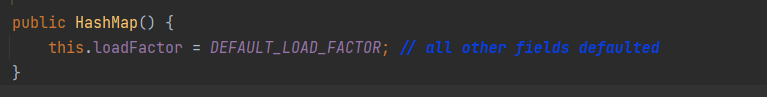
- 刚创建hashSet时table=null size=0以节省空间
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
源码分析总结
- HashMap刚创建时,table是null,节省空间,当添加第一个元素时,table容量调整为16
- 当元素个数大于阈值(16*0.75 = 12)时,会进行扩容,扩容后的大小为原来的两倍,目的是减少调整元素的个数
- jdk1.8 当每个链表长度 >8 ,并且数组元素个数 ≥64时,会调整成红黑树,目的是提高效率
- jdk1.8 当链表长度 <6 时 调整成链表
- jdk1.8 以前,链表时头插入,之后为尾插入

HashMap与HashSet
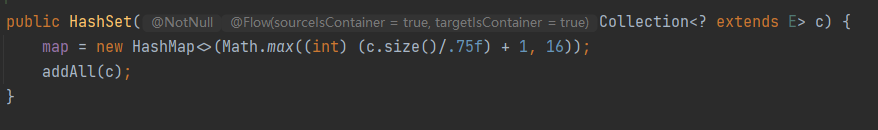
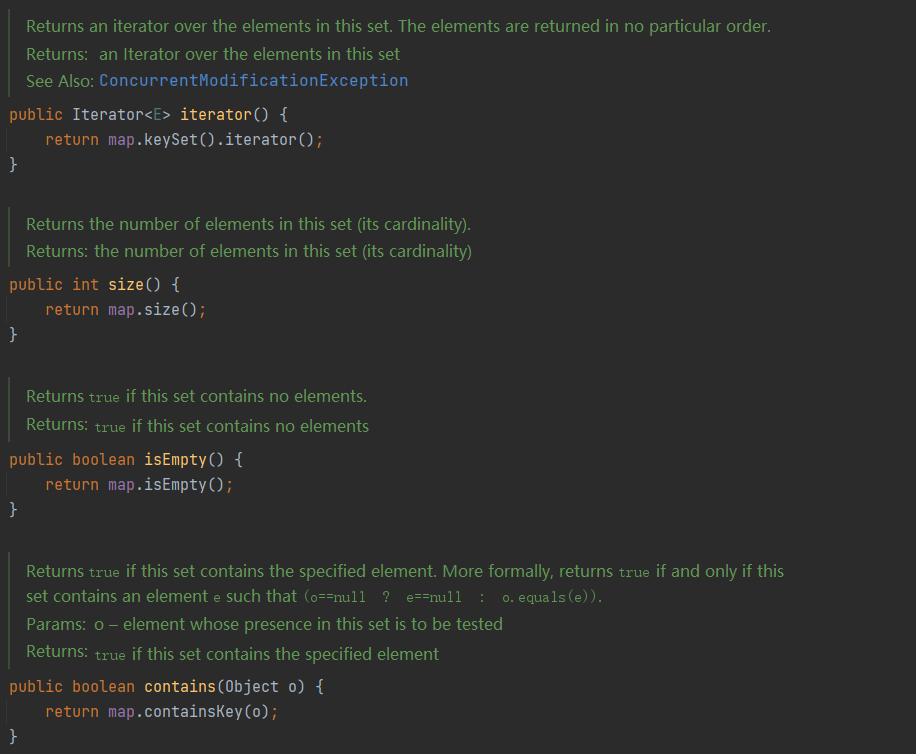
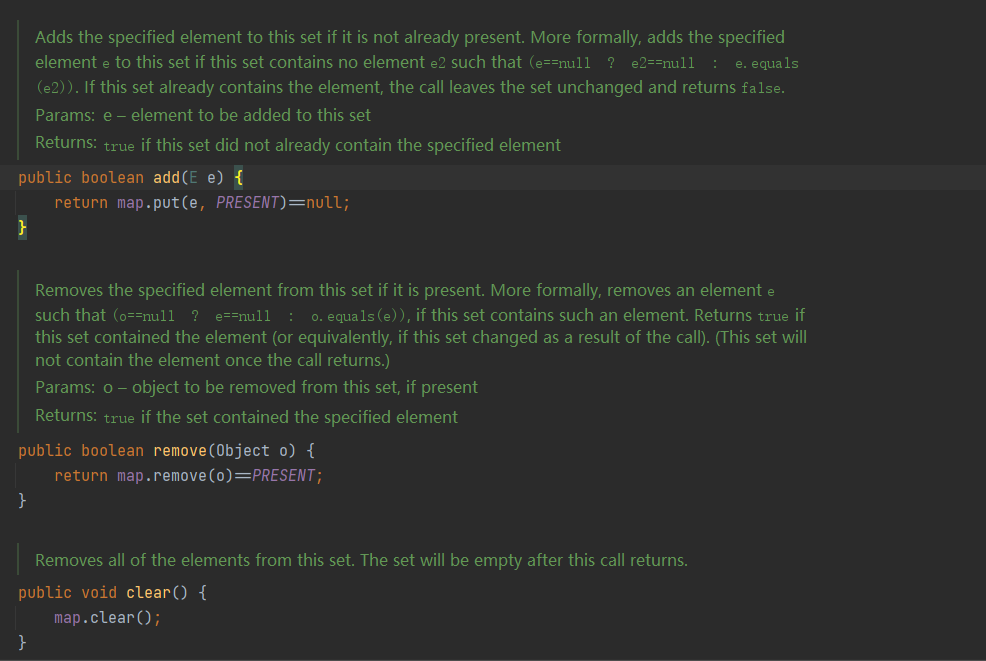
HashSet实现了 Set接口,不允许出现重复元素,但是向HashSet中存储对象必须重写对象的HashCode和equals方法。HashSet是由HashMap实现的。HashSet允许存储NULL元素,并且NULL永远存储在第一个。
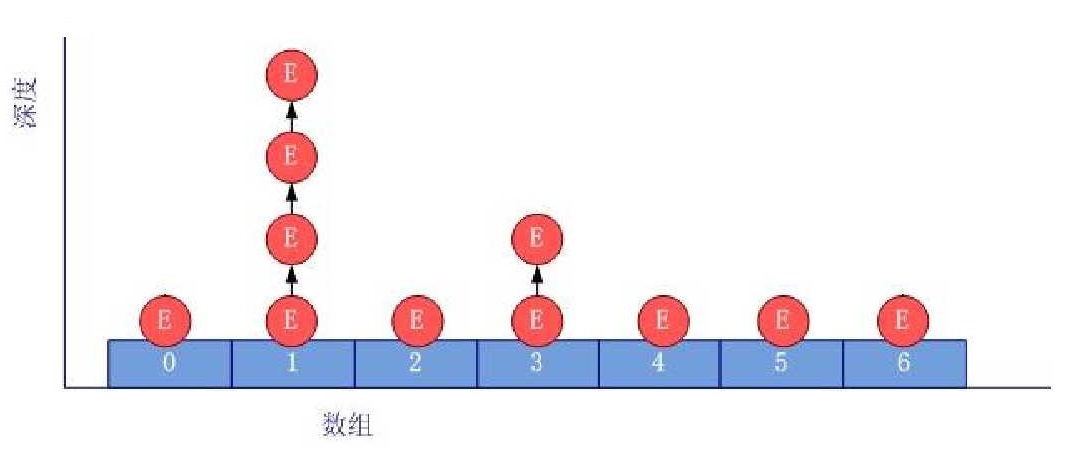
HashMap实现了Map接口,允许NULL键NULL值。使用hash寻址会发生hash冲突问题,底层使用数组加链表的结构,解决了冲突也均衡了查找和增删的效率;一般将数组中的每一个元素称作桶(segment)。
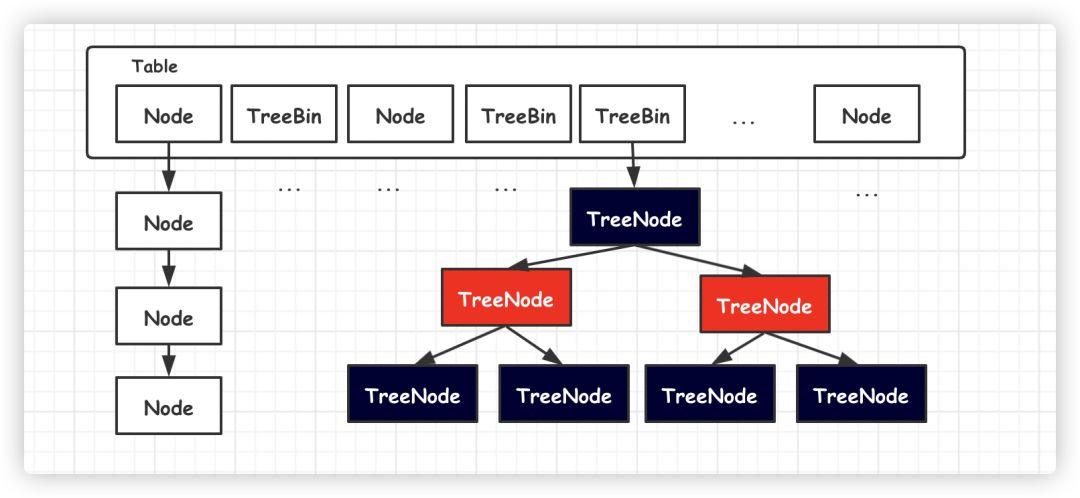
HashTable
线程安全,运行效率慢;不允许null作为key或是value
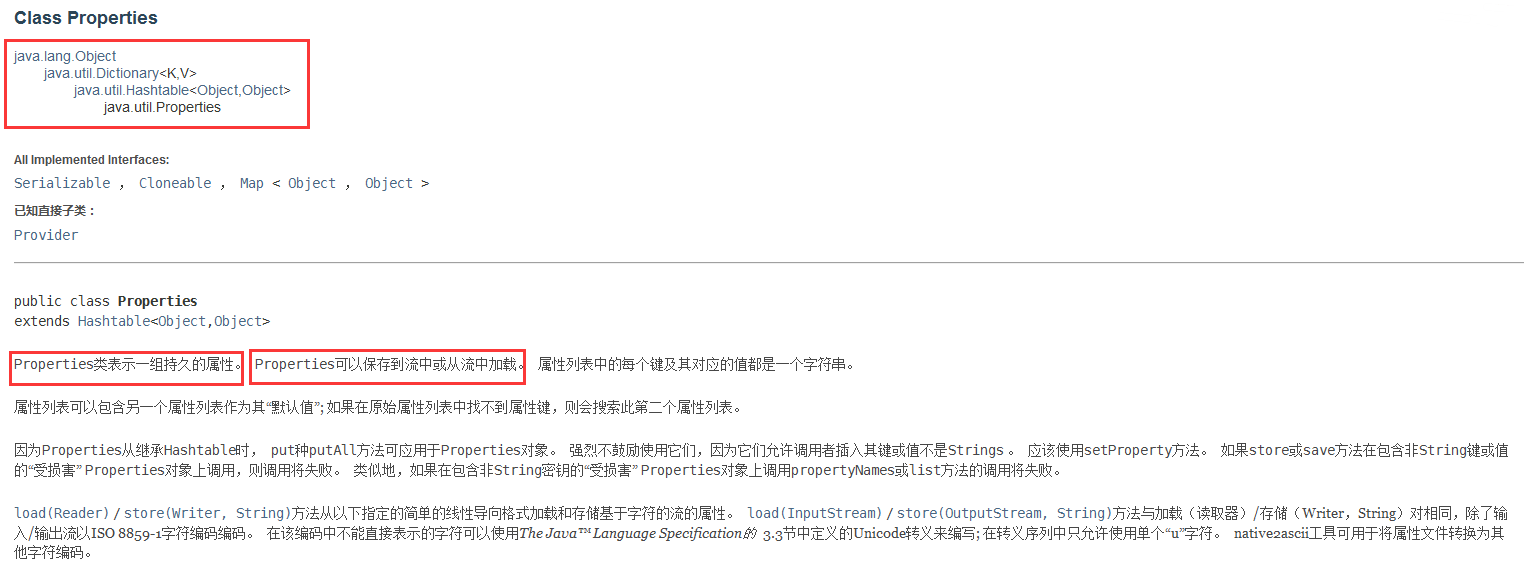
Properties(属性集合)
hashtable的子类,要求key和value都是string,通常用于配置文件的读取
特点:
- 1.存储属性名和属性值
- 2.属性名和属性值都是字符串类型
- 3.没有泛型
- 和流有关
package aggregate.Map;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class PropertiesDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建集合
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 2 添加数据
properties.setProperty("username","zhangsan");
properties.setProperty("age","18");
System.out.println(properties.toString());
// 3 遍历
// 3.1 keySet
Set<Object> objects = properties.keySet();
for (Object o : objects) {
System.out.println(o+":"+properties.getProperty((String) o));
}
// 3.2 entrySet
Set<Map.Entry<Object, Object>> entries = properties.entrySet();
System.out.println(entries.toString());
// 3.3 stringPropertyNames
Set<String> strings = properties.stringPropertyNames();
for (String string : strings) {
System.out.println(string+":"+properties.getProperty(string));
}
// 4 和流有关的方法
// 4.1 properties.list(printWriter)
//PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter("e://abc.txt");
//properties.list(printWriter);
//printWriter.close();
// 4.2 properties.store(printWriter,"注释");
//PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter("e://xyz.txt");
//properties.store(printWriter,"注释");
//printWriter.close();
System.out.println("==========");
// 4.3 properties.load(fileInputStream);
Properties properties1 = new Properties();
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("e://abc.txt");
properties1.load(fileInputStream);
fileInputStream.close();
System.out.println(properties1.toString());
}
}

TreeMap
package aggregate.Map.TreeMap;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
//TreeMap
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定制器比较
TreeMap<Student, Integer> studentIntegerTreeMap = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
int n1=o1.getStuNo()-o2.getStuNo();
return n1;
}
});
Student s1 = new Student("白小飞", 120);
Student s2 = new Student("呜呜呜", 121);
Student s3 = new Student("杨洪利", 123);
studentIntegerTreeMap.put(s1,11);
studentIntegerTreeMap.put(s2,12);
studentIntegerTreeMap.put(s3,15);
System.out.println(studentIntegerTreeMap.toString());
studentIntegerTreeMap.put(new Student("杨洪利", 123),88);
System.out.println(studentIntegerTreeMap.toString());
System.out.println("===删除===");
studentIntegerTreeMap.remove(s3);
System.out.println(studentIntegerTreeMap.toString());
System.out.println("===keyset遍历===");
Set<Student> students = studentIntegerTreeMap.keySet();
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student.toString()+":"+studentIntegerTreeMap.get(student));
}
System.out.println("===entryset遍历===");
Set<Map.Entry<Student, Integer>> entries = studentIntegerTreeMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Student, Integer> entry : entries) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+":"+entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("===判断===");
System.out.println(studentIntegerTreeMap.containsKey(new Student("白小飞", 120)));
System.out.println(studentIntegerTreeMap.containsValue(12));
}
}
7.Collections工具类
此类仅由静态方法组合或返回集合。 它包含对集合进行操作的多态算法,“包装器”,返回由指定集合支持的新集合,以及其他一些可能的和最终的。
package aggregate.Collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
//Collections工具类
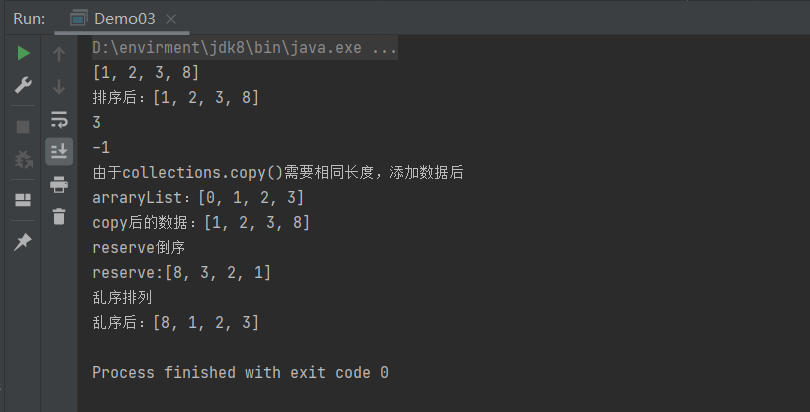
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(8);
//打印
System.out.println(list.toString());
//排序
Collections.sort(list);
//打印
System.out.println("排序后:"+list.toString());
//binarySearch
System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(list, 8));
System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(list, 0));
//copy复制
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
arrayList.add(i);
}
System.out.println("由于collections.copy()需要相同长度,添加数据后");
System.out.println("arraryList:"+arrayList.toString());
Collections.copy(arrayList,list);
System.out.println("copy后的数据:"+arrayList);
System.out.println("reserve倒序");
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println("reserve:"+list);
System.out.println("乱序排列");
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println("乱序后:"+list);
}
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix