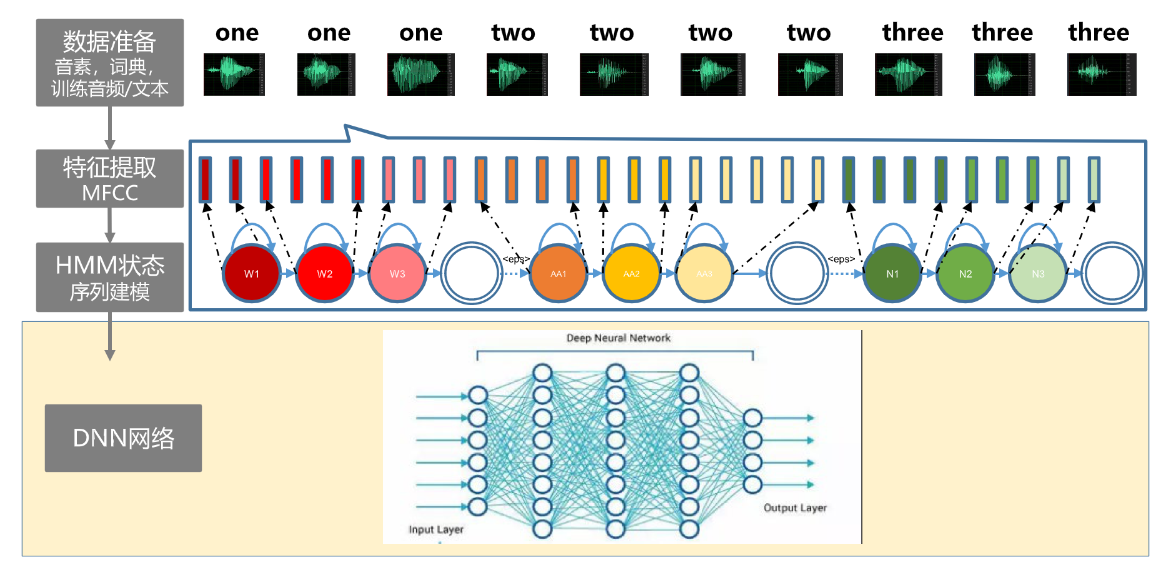
训练流程

代码
import math
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import kaldi_io
from utils import *
targets_list = ['Z', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'O']
targets_mapping = {}
for i, x in enumerate(targets_list):
targets_mapping[x] = i
def plot_loss(avg_loss, filename):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
plt.plot(avg_loss)
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.savefig(filename)
plt.show()
class Layer(object):
def forward(self, input):
''' Forward function by input
Args:
input: input, B * N matrix, B for batch size
Returns:
output when applied this layer
'''
raise 'Not implement error'
def backward(self, input, output, d_output):
''' Compute gradient of this layer's input by (input, output, d_output)
as well as compute the gradient of the parameter of this layer
Args:
input: input of this layer
output: output of this layer
d_output: accumulated gradient from final output to this
layer's output
Returns:
accumulated gradient from final output to this layer's input
'''
raise 'Not implement error'
def set_learning_rate(self, lr):
''' Set learning rate of this layer'''
self.learning_rate = lr
def update(self):
''' Update this layers parameter if it has or do nothing
'''
class ReLU(Layer):
def forward(self, input):
tem_mat = np.maximum(0, input)
assert (tem_mat.shape == input.shape)
return tem_mat.T
def backward(self, input, output, d_output):
d_mat = np.array(d_output, copy=True)
d_mat[input <= 0] = 0
assert (d_mat.shape == input.shape)
return d_mat.T
class FullyConnect(Layer):
def __init__(self, in_dim, out_dim):
self.w = np.random.randn(out_dim, in_dim) * np.sqrt(2.0 / in_dim)
self.b = np.zeros((out_dim, 1))
self.dw = np.zeros((out_dim, in_dim))
self.db = np.zeros((out_dim, 1))
def forward(self, input):
out_mat = np.dot(self.w, input.T) + self.b
assert out_mat.shape == (self.w.shape[0], input.shape[0])
return out_mat
def backward(self, input, output, d_output):
batch_size = input.shape[0]
in_diff = None
self.dw = np.dot(d_output, input) / batch_size
self.db = np.sum(d_output, axis=1, keepdims=True) / batch_size
outt_mat = np.dot(self.w.T, d_output)
assert (outt_mat.shape == input.T.shape)
assert (self.dw.shape == self.w.shape)
assert (self.db.shape == self.b.shape)
in_diff = outt_mat.T
self.dw = self.dw / batch_size
self.db = self.db / batch_size
return in_diff
def update(self):
self.w = self.w - self.learning_rate * self.dw
self.b = self.b - self.learning_rate * self.db
class Softmax(Layer):
def forward(self, input):
_input = input.T
row_max = _input.max(axis=1).reshape(_input.shape[0], 1)
x = _input - row_max
return np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=1).reshape(x.shape[0], 1)
def backward(self, input, output, d_output):
''' Directly return the d_output as we show below, the grad is to
the activation(input) of softmax
'''
return d_output
class DNN(object):
def __init__(self, in_dim, out_dim, hidden_dim, num_hidden):
self.layers = []
self.layers.append(FullyConnect(in_dim, hidden_dim))
self.layers.append(ReLU())
for i in range(num_hidden):
self.layers.append(FullyConnect(hidden_dim, hidden_dim))
self.layers.append(ReLU())
self.layers.append(FullyConnect(hidden_dim, out_dim))
self.layers.append(Softmax())
def set_learning_rate(self, lr):
for layer in self.layers:
layer.set_learning_rate(lr)
def forward(self, input):
self.forward_buf = []
out = input
self.forward_buf.append(out)
for i in range(len(self.layers)):
out = self.layers[i].forward(out)
self.forward_buf.append(out)
assert (len(self.forward_buf) == len(self.layers) + 1)
return out
def backward(self, grad):
'''
Args:
grad: the grad is to the activation before softmax
'''
self.backward_buf = [None] * len(self.layers)
self.backward_buf[len(self.layers) - 1] = grad
for i in range(len(self.layers) - 2, -1, -1):
grad = self.layers[i].backward(self.forward_buf[i],
self.forward_buf[i + 1],
self.backward_buf[i + 1].T)
self.backward_buf[i] = grad
def update(self):
for layer in self.layers:
layer.update()
def one_hot(labels, total_label):
output = np.zeros((labels.shape[0], total_label))
for i in range(labels.shape[0]):
output[i][labels[i]] = 1.0
return output
def train(dnn):
utt2feat, utt2target = read_feats_and_targets('train/feats.scp',
'train/text')
inputs, labels = build_input(targets_mapping, utt2feat, utt2target)
num_samples = inputs.shape[0]
permute = np.random.permutation(num_samples)
inputs = inputs[permute]
labels = labels[permute]
num_epochs = 200
batch_size = 100
avg_loss = np.zeros(num_epochs)
for i in range(num_epochs):
cur = 0
while cur < num_samples:
end = min(cur + batch_size, num_samples)
input = inputs[cur:end]
label = labels[cur:end]
out = dnn.forward(input)
one_hot_label = one_hot(label, out.shape[1])
loss = -np.sum(np.log(out + 1e-20) * one_hot_label) / out.shape[0]
grad = out - one_hot_label
dnn.backward(grad)
dnn.update()
print('Epoch {} num_samples {} loss {}'.format(i, cur, loss))
avg_loss[i] += loss
cur += batch_size
avg_loss[i] /= math.ceil(num_samples / batch_size)
plot_loss(avg_loss, 'loss.png')
def test(dnn):
utt2feat, utt2target = read_feats_and_targets('test/feats.scp',
'test/text')
total = len(utt2feat)
correct = 0
for utt in utt2feat:
t = utt2target[utt]
ark = utt2feat[utt]
mat = kaldi_io.read_mat(ark)
mat = splice(mat, 5, 5)
posterior = dnn.forward(mat)
posterior = np.sum(posterior, axis=0) / float(mat.shape[0])
predict = targets_list[np.argmax(posterior)]
if t == predict: correct += 1
print('label: {} predict: {}'.format(t, predict))
print('Acc: {}'.format(float(correct) / total))
def main():
np.random.seed(777)
dnn = DNN(429, 11, 128, 1)
dnn.set_learning_rate(1e-2)
train(dnn)
test(dnn)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
理论支撑
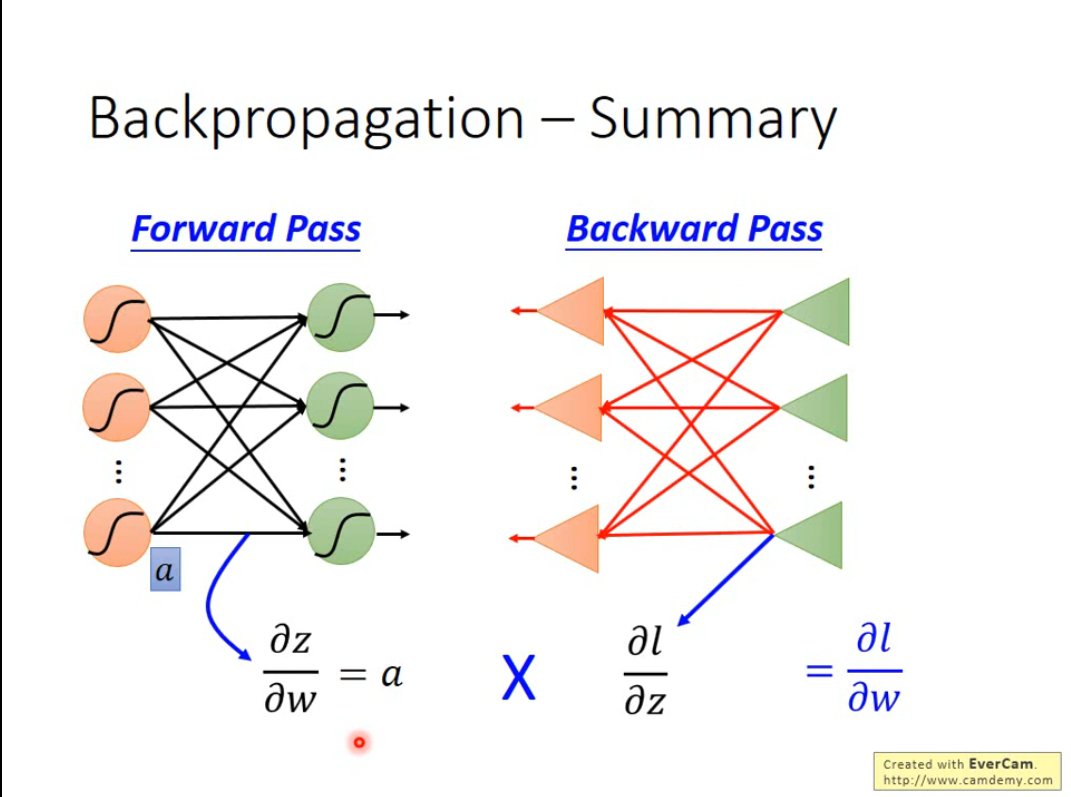
参考






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?