15.Dynamic Programming(1)
DP is a kind of tabular method, like divide-and-conquer method, applying when subproblems overlap.(sharing subsubproblems).
A DP algorithm solves each subsubproblems only once and then saves its answer in a table.
A divide-and-conquer algorithm does more work than necessary. It repeatedly solves the subsubproblems.
15.1 Rod cutting problem
| lenght i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| price pi | 1 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 17 | 17 | 20 | 24 | 30 |
For the table above, the optimal solution is:
Suppose we divide a rod into n pieces, we should have n-1 cuts at the rod. There is 2^(n-1) different cut ways of length n.
Optimal revenue values of rod n,can be caculated by
where .
We can view ,saying that the first piece has size of i = n, and the remainder has the size n-i=n-n=0 with corresponding revenue
.
As the following arithmetics,we can rewrite the formula above as
Algorithms as follows:
1.naive recursive top-down implementation
 View Code
View Code
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include <ctime> 4 //naive recursive method 5 int RotCut(int* p, int n) 6 { 7 if (n==0) 8 { 9 return 0; 10 } 11 int i; 12 int q = INT_MIN; 13 14 15 // q=max(p[i]+r[n-i]), p为数组,从0开始 16 for( i=1; i<=n; i++) 17 { 18 int k = p[i-1] + RotCut(p,n-i); 19 if (q < k) 20 { 21 q = k; 22 } 23 } 24 return q; 25 } 26 int main() 27 { 28 // p[] = {1,5,8,9,10,17,17,20,24,30} 29 int p[100] ={1,5,8,9,10,17,17,20,24}; 30 time_t tic = time(NULL); 31 int k = RotCut(p,25); 32 time_t toc = time(NULL); 33 cout<<"optimal value:"<<k<<" "<<"time: "<<(toc-tic)*1000<<"ms"<<endl; 34 return 0; 35 }
The results run by this program is listed as follows:
| n | 4 | 8 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| optimal val | 10 | 22 | 56 | 69 | 85 |
| run time | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1s | 27s |
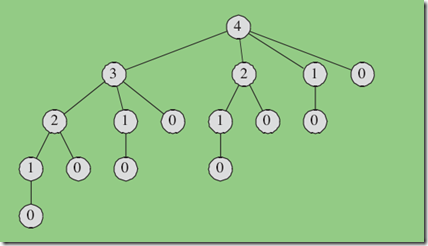
This recursive CUT_ROD is very inefficient, cause it calls itself over and over with the same parameter values, that is ,it solve the same subproblems repeatedly.For example, figure follows illustrates what happens when n is 4.The running time of CUT-ROD is exponential in n.
2.DP for optimal rod cutting
Using DP can convert CUT-ROD into an efficient algorithm, making
DP solves each subproblems only once by using additional memory to improve efficiency.There are two equivalent ways to implement DP algorithm: (1)top-down with memoization and (2)bottom-up method.
(1) Top-down with memoization
Recursively anyway, but save the result of each subproblem ( n subproblems ) in an array r[] initial with 0s or a hash table. The array is used for check wether a subproblem was solved, if the ith subproblem was solved, its value was stored in r[i] > 0.
 View Code
View Code
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include <ctime> 4 const int MAXiSIZE=2000; 5 //Top-down with memoization method 6 int MemoizedCutRodAux(int *p, int n, int *r) 7 { //using an addition array r[] to store optimal subproblems value 8 if ( r[n] >= 0) 9 return r[n]; 10 int q,i,k; 11 if ( n == 0) 12 { 13 q = 0; 14 } 15 else 16 { 17 q = INT_MIN;// iter method 18 for ( i=1; i<=n; i++) 19 { 20 k = p[i-1] + MemoizedCutRodAux(p,n-i,r); 21 if ( q<k ) 22 q =k; 23 } 24 } 25 r[n] = q; 26 return q; 27 } 28 29 int MemoizedCutRod(int *p, int n) 30 { 31 int i; 32 int r[MAXiSIZE];//auxiliary array initialized with minimum 33 for ( i=0; i<=n; i++) 34 { 35 r[i] = INT_MIN; 36 } 37 return MemoizedCutRodAux(p,n,r); 38 } 39 int main() 40 { 41 // p[] = {1,5,8,9,10,17,17,20,24,30} 42 int p[MAXISIZE] ={1,5,8,9,10,17,17,20,24}; 43 /*time_t tic = time(NULL); 44 int k = RotCut(p,25); 45 time_t toc = time(NULL); 46 cout<<"optimal value:"<<k<<" "<<"time: "<<(toc-tic)*1000<<"ms"<<endl;*/ 47 48 clock_t start = clock(); 49 int k = MemoizedCutRod(p,1000); 50 clock_t end = clock(); 51 cout<<"optimal value:"<<k<<" "<<"time: "<<double(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<"s"<<endl; 52 //int k = BottomUpCutRod(p,40); 53 //cout<<k<<endl; 54 55 //SolutionOfCutRod(p,40); 56 return 0; 57 }
| n | 4 | 20 | 30 | 1000 | 1999 |
| optimal val | 10 | 56 | 85 | 2832 | INT_MAX |
| run time | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.015s | 0.047s |
(2)bottom-up method
Not recursively, but iteratively. Solve the subproblems by size and solve them in size order, smallest first.
 View Code
View Code
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include <ctime> 4 const int MAXiSIZE=2000; 5 int BottomUpCutRod(int *p, int n) 6 { 7 int r[MAXiSIZE];//auxiliary array initialized with minimum 8 r[0] = 0; 9 10 int i,j,k; 11 for ( j=1; j<=n; j++) 12 { 13 int q = INT_MIN; 14 for ( i=1; i<=j; i++) 15 { 16 k = p[i-1] + r[j-i]; 17 if ( q < k ) 18 q = k; 19 r[j] = q; 20 } 21 } 22 return r[n]; 23 } 24 int main() 25 { 26 // p[] = {1,5,8,9,10,17,17,20,24,30} 27 int p[MAXISIZE] ={1,5,8,9,10,17,17,20,24}; 28 29 clock_t start = clock(); 30 //int k = MemoizedCutRod(p,1999); 31 int k = BottomUpCutRod(p,40); 32 clock_t end = clock(); 33 cout<<"optimal value:"<<k<<" "<<"time: "<<double(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<"s"<<endl; 34 35 return 0; 36 }
| n | 4 | 20 | 30 | 1000 | 1999 |
| optimal val | 10 | 56 | 85 | 2832 | INT_MAX |
| run time | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.016s |
3.Solution
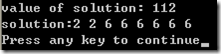
Easy part for this example, only need a list store every piece size.
 Solution
Solution
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include <ctime> 4 const int MAXiSIZE=2000; 5 int ExtendedBottomUpCutRod(int *p, int n, int* r, int *s) 6 { 7 8 int i,j,k; 9 for ( j=1; j<=n; j++) 10 { 11 int q = INT_MIN; 12 for ( i=1; i<=j; i++) 13 { 14 k = p[i-1] + r[j-i]; 15 if ( q < k ) 16 { 17 q = k; 18 s[j] = i;// here is the add item 19 } 20 r[j] = q; 21 22 } 23 } 24 return r[n]; 25 26 } 27 28 int SolutionOfCutRod(int *p, int n) 29 { 30 int s[MAXiSIZE],r[MAXiSIZE]; 31 r[0] = 0; 32 33 ExtendedBottomUpCutRod(p,n,r,s); 34 cout<<"value of solution: "<<r[n]<<endl<<"solution:"; 35 while ( n>0 ) 36 { 37 cout<<s[n]<<" "; 38 n = n - s[n]; 39 } 40 cout<<endl; 41 return r[n]; 42 43 } 44 45 int main() 46 { 47 // p[] = {1,5,8,9,10,17,17,20,24,30} 48 int p[MAXISIZE] ={1,5,8,9,10,17,17,20,24}; 49 50 SolutionOfCutRod(p,40); 51 return 0; 52 }