二叉树 遍历 先序 中序 后序 深度 广度
目录
二叉树遍历
测试案例
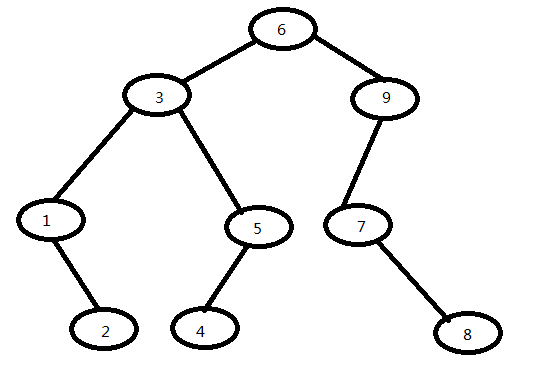
遍历结果:
先序遍历:631254978
中序遍历:123456789
后序遍历:214538796
广度优先:639157248
构造二叉树
public static Node init() {
//注意必须逆序建立,先建立子节点,再逆序往上建立,因为非叶子结点会使用到下面的节点
Node J = new Node(8, null, null);
Node H = new Node(4, null, null);
Node G = new Node(2, null, null);
Node F = new Node(7, null, J);
Node E = new Node(5, H, null);
Node D = new Node(1, null, G);
Node C = new Node(9, F, null);
Node B = new Node(3, D, E);
Node A = new Node(6, B, C);
return A; //返回根节点
}
结点定义
class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int value, Node left, Node right) {
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
深度优先 Depth First Search
使用递归遍历
其过程简要来说是对每一个可能的分支路径深入到不能再深入为止,而且每个节点只能访问一次。
public static void preOrderTraversal(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.value); //先(根)序遍历
preOrderTraversal(root.left); //递归遍历左孩子
preOrderTraversal(root.right); //递归遍历右孩子
}
}
public static void inOrderTraversal(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
inOrderTraversal(root.left);
System.out.print(root.value); //中(根)序遍历
inOrderTraversal(root.right);
}
}
public static void postOrderTraversal(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
postOrderTraversal(root.left);
postOrderTraversal(root.right);
System.out.print(root.value); //后(根)序遍历
}
}
使用栈遍历
public static void preOrderTraversalStack(Node root) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.value); //压栈之前先访问,先序遍历
stack.push(root); //压栈
root = root.left; //访问左叶子节点
} else { //没有左(右)叶子节点
root = stack.pop(); //返回最近压入栈的结点【核心】
root = root.right; //访问右叶子节点
}
}
}
public static void preOrderTraversalStack2(Node root) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.value); //先序遍历
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
}
public static void inOrderTraversalStack(Node root) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Node node = root;
while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
} else {
node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.value); //中序遍历
node = node.right;
}
}
}
public static void postOrderTraversalStack(Node root) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Node> output = new Stack<>();//构造一个中间栈来存储逆后序遍历的结果
Node node = root;
while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (node != null) {
output.push(node);
stack.push(node);
node = node.right;
} else {
node = stack.pop();
node = node.left;
}
}
while (!output.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(output.pop().value); //后序遍历
}
}
广度优先(队列) Breadth First Search
又叫宽度优先搜索,或横向优先搜索。
对每一层节点依次访问,访问完一层进入下一层,而且每个节点只能访问一次
public static void levelTraversal(Node root) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>(); //LinkedList是Java中最普通的一个队列
queue.offer(root); //add、addLast
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.poll();//removeFirst
if (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.value);
queue.offer(node.left);
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
2018-12-8
本文来自博客园,作者:白乾涛,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/baiqiantao/p/10087670.html
分类:
01 新版 MarkDown
标签:
2018



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现