HW 7
俗话说的好:自闭从不单行,永远双至。果然这一场又自闭了。C语言没学好。。。。
Problem A: 字符串类(I)
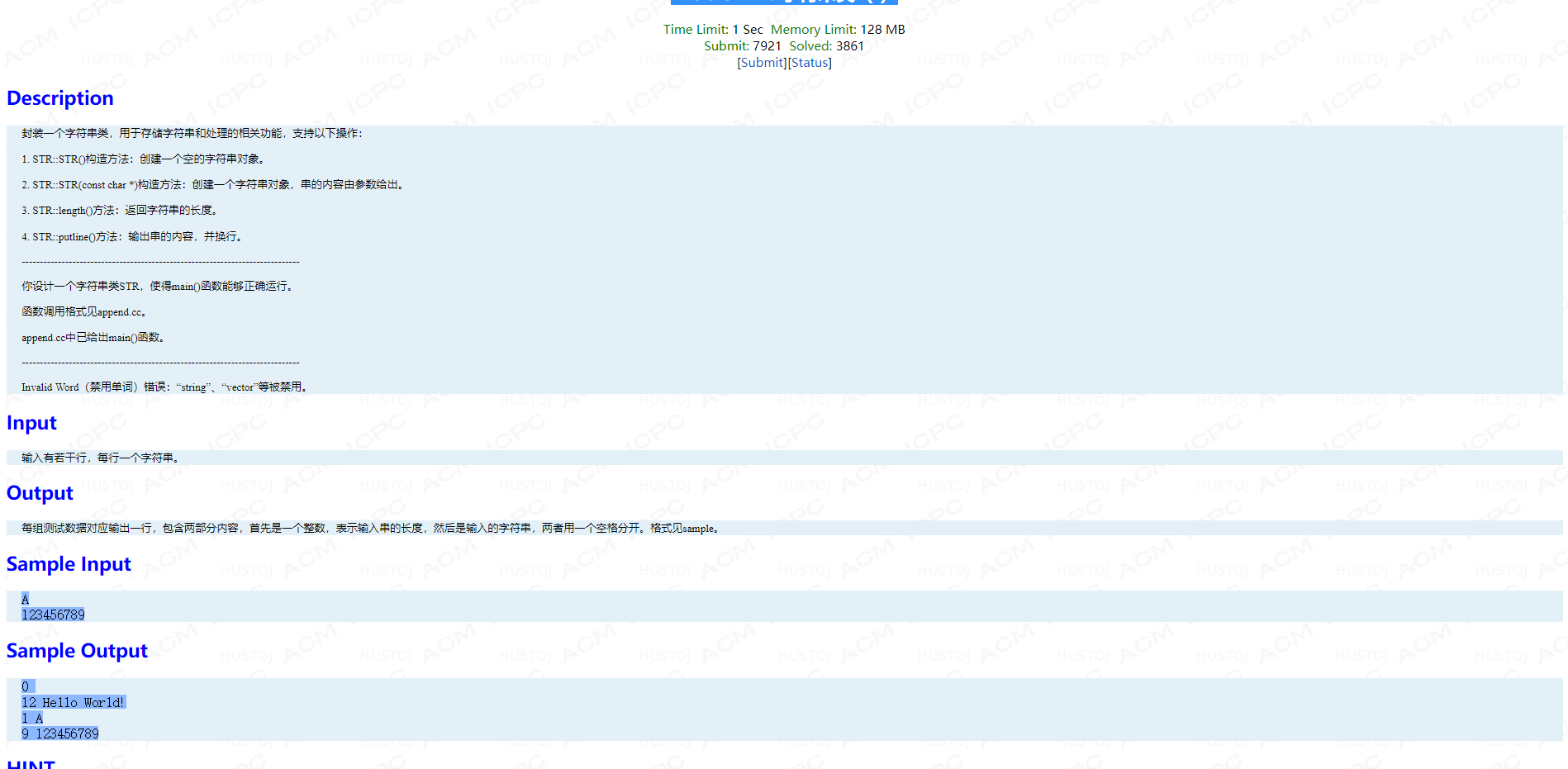
main 函数:
int main() { STR e; STR h("Hello World!"); char s[100001]; cout << e.length() << " "; e.putline(); cout << h.length() << " "; h.putline(); while(gets(s) != NULL) { STR str(s); cout << str.length() << " "; str.putline(); } }
怎么说那,本来以为RE到绝望了。。。。。,没想到还有B题。
总体来说还是水题,怎么说的怎么写吧。
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class STR { char *p; int len; public: STR():p(NULL),len(0){}; STR(const char *s){len = strlen(s);p = new char[len+1];strcpy(p,s);}; int length() { return len; } void putline() { if(p==NULL) cout << endl; else cout << p << endl; } ~STR() { len = 0; if(p!=NULL) delete []p; } }; int main() { STR e; STR h("Hello World!"); char s[100001]; cout << e.length() << " "; e.putline(); cout << h.length() << " "; h.putline(); while(gets(s) != NULL) { STR str(s); cout << str.length() << " "; str.putline(); } }
Problem B: 字符串类(II)

main 函数:
int main() { STR e; STR h("Hello World!"); STR he = e + h; cout << he.length() << " "; he.putline(); cout << e.length() << " "; e.putline(); cout << h.length() << " "; h.putline(); e += h; cout << e.length() << " "; e.putline(); cout << h.length() << " "; h.putline(); char s1[100001], s2[100001]; while(gets(s1) != NULL && gets(s2) != NULL) { STR str1(s1), str2(s2); STR str = str1 + str2; cout << str.length() << " "; str.putline(); cout << str1.length() << " "; str1.putline(); cout << str2.length() << " "; str2.putline(); str2 += str1; cout << str2.length() << " "; str2.putline(); cout << str1.length() << " "; str1.putline(); } }
这个题RE到自闭,分析原因应该是忘记老师之前讲过的指针悬空问题,对于+=函数没有返回引用,也没有写拷贝构造函数,导致指针悬空,在析构的时候发生了错误。
附博客(讲返回对象与引用区别的):
https://www.cnblogs.com/JMLiu/p/7928425.html
AC代码1(不返回引用):
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class STR { char *p; int len; //static int num; public: STR():p(NULL),len(0){}; STR(const char *s){len = strlen(s);p = new char[len+1];strcpy(p,s); p[len] = '\0';}; STR(const STR &b){len = strlen(b.p);p = new char[len+1];strcpy(p,b.p); p[len] = '\0';}; int length() { return len; } void putline() { if(p==NULL) cout << endl; else cout << p << endl; } STR operator + (const STR&b) { char *s ; s = new char[len+b.len+1]; strcpy(s,p); strcat(s,b.p); return STR(s); } STR operator+=(const STR &b) { STR c = *this+b; p = new char[c.len+1]; len = c.len; strcpy(p,c.p); return *this; } ~STR() { cout << "s = " << p << endl; if(len!=0) delete []p; len = 0; } };
AC2(返回引用):
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class STR { char *p; int len; public: STR():p(NULL),len(0){}; STR(const char *s){len = strlen(s);p = new char[len+1];strcpy(p,s); p[len] = '\0';}; int length() { return len; } void putline() { if(p==NULL) cout << endl; else cout << p << endl; } STR operator + (const STR&b) { char *s ; s = new char[len+b.len+1]; int i = 0; for(i = 0;i<len;i++) s[i] = p[i]; for(int j = 0 ;j<b.len;i++,j++) s[i] = b.p[j]; s[i] = '\0'; //cout << s << endl; return STR(s); } STR& operator+=(const STR &b) { STR c = *this+b; //cout << c.p << endl; p = new char [c.len+1]; strcpy(p,c.p); //cout << p << endl; len = c.len; return *this; } ~STR() { if(len!=0) delete []p; len = 0; } };
Problem C: 学生干部虚基类:
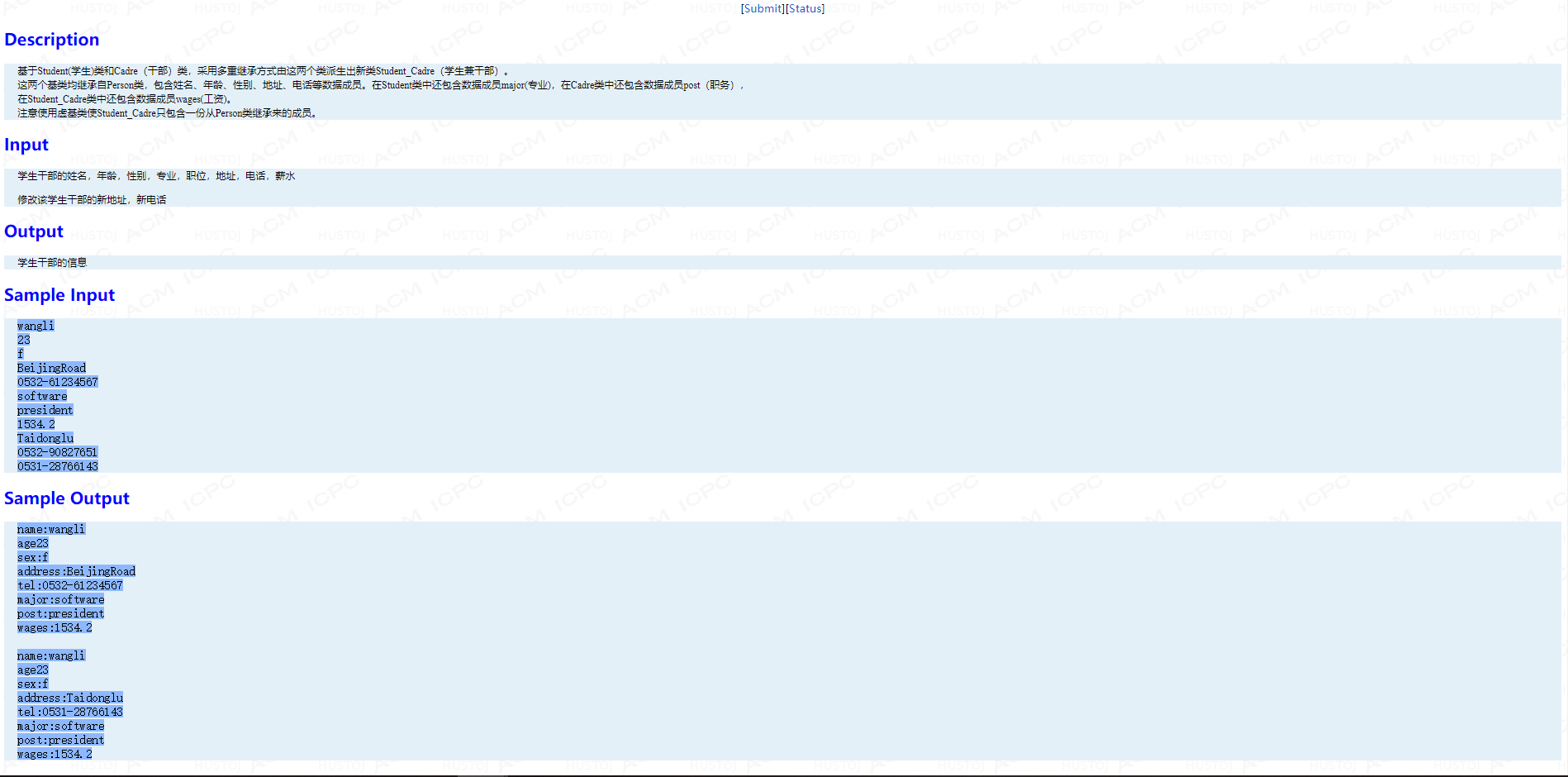
main 函数:
int main( ) { string name, major, post, addr, tel; int age; char sex; float wage; cin>>name>>age>>sex>>addr>>tel>>major>>post>>wage; Student_Cadre st_ca(name, age, sex, addr, tel, major, post,wage); st_ca.display( ); cout<<endl; string newAddr, newTel1, newTel2; cin>>newAddr>>newTel1>>newTel2; st_ca.setAddr(newAddr); st_ca.Student::setTel(newTel1); st_ca.Cadre::setTel(newTel2); st_ca.display( ); return 0; }
类的虚继承,打比方来说,类D继承于类B和类C,而类C和类B有相同的基类A,因此在类D中事实上存在两个类A的对象和方法,在类D中调用类A的对象或方法时,就会产生二义性,但如果采用虚拟继承,在这个继承的过程中,就只会产生一个类A的对象及方法,就不会产生二义性。
最后CE了两发,没想到竟然是万能头害的,major居然是个关键字,自闭。。。。
AC代码:
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; class Person { string name,addr,tel; int age; char sex; friend class Student_Cadre; friend class Student; friend class Cadre; public: //Person(){}; Person(string _name,int _age,char _sex,string _addr,string _tel):name(_name),sex(_sex),tel(_tel),addr(_addr),age(_age){}; void setAddr(string _add){addr = _add;} void setTel(string _tel){tel = _tel;} }; class Student:virtual public Person { string major; friend class Student_Cadre; public: //Student(){}; Student(string _name,int _age,char _sex,string _addr,string _tel,string _major):Person(_name,_age,_sex,_addr,_tel),major(_major){}; }; class Cadre:virtual public Person { string post; friend class Student_Cadre; public: // Cadre(){}; Cadre(string _name,int _age,char _sex,string _addr,string _tel,string _post):Person(_name,_age,_sex,_addr,_tel),post(_post){}; }; class Student_Cadre:public Student,public Cadre { float wages; public: Student_Cadre(string _name,int _age,char _sex,string _addr,string _tel,string _major,string _post,float _wages):Person(_name,_age,_sex,_addr,_tel),Student(_name,_age,_sex,_addr,_tel,_major),Cadre(_name,_age,_sex,_addr,_tel,_post),wages(_wages){}; void display() { cout << "name:" << this->name << endl; cout << "age" << age << endl; cout << "sex:" << sex << endl; cout << "address:" << addr << endl; cout << "tel:" << tel << endl; cout << "major:" << major << endl; cout << "post:" << post << endl; cout << "wages:" << wages << endl; } };
Problem D: 选举班干部了!

main 函数:
int main() { int num; string name, position; bool sex; int grade; Student *header, *student, *curStudent; cin>>name>>sex>>grade>>position; header = new StudentCadre(name, sex, grade,position); curStudent = header; cin>>num; for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { cin>>name>>sex>>grade; student = new Student(name, sex, grade); curStudent -> setNext(student); curStudent = curStudent -> getNext(); } ((StudentCadre*)header) -> showInfo(); cout<<endl; curStudent = header; while (curStudent -> getNext() != NULL) { curStudent = curStudent -> getNext(); curStudent->showInfo(); cout<<endl; } curStudent = header; while (curStudent != NULL) { student = curStudent; curStudent = curStudent -> getNext(); delete student; } return 0; }
继承水题:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Student { string name; bool sex; int grade; Student *next; friend class StudentCadre; public: Student(){}; Student(string _name,bool _sex,int _grade):name(_name),sex(_sex),grade(_grade),next(NULL){cout << "A student named by " << name << " is created!" << endl;} Student(Student&b){name = b.name,sex = b.sex,grade = b.grade; *next = *(b.next);} void showInfo() { cout << "name = " << name <<", sex = " << sex << ", grade = "<< grade << ";" ; } Student* getNext() { return next; } void setNext(Student *s) { next = s; } ~Student() { //delete next; cout << "A student named by " << name << " is erased." << endl; } }; class StudentCadre:public Student { string postion; public: //StudentCadre(){cout << 2 << endl;} StudentCadre(string _name, bool _sex, int _grade, string pos):Student(_name,_sex,_grade),postion(pos){cout << "A student cadre with position " << postion << " is created." << endl;}; StudentCadre(StudentCadre &b) { name = b.name,sex = b.sex,grade = b.grade; postion = b.postion; *next = *(b.next); } void showInfo() { cout << "name = " << name <<", sex = " << sex << ", grade = "<< grade << "; " << "position = " << postion << "." ; } };
Problem E: 立体空间中的点(I)
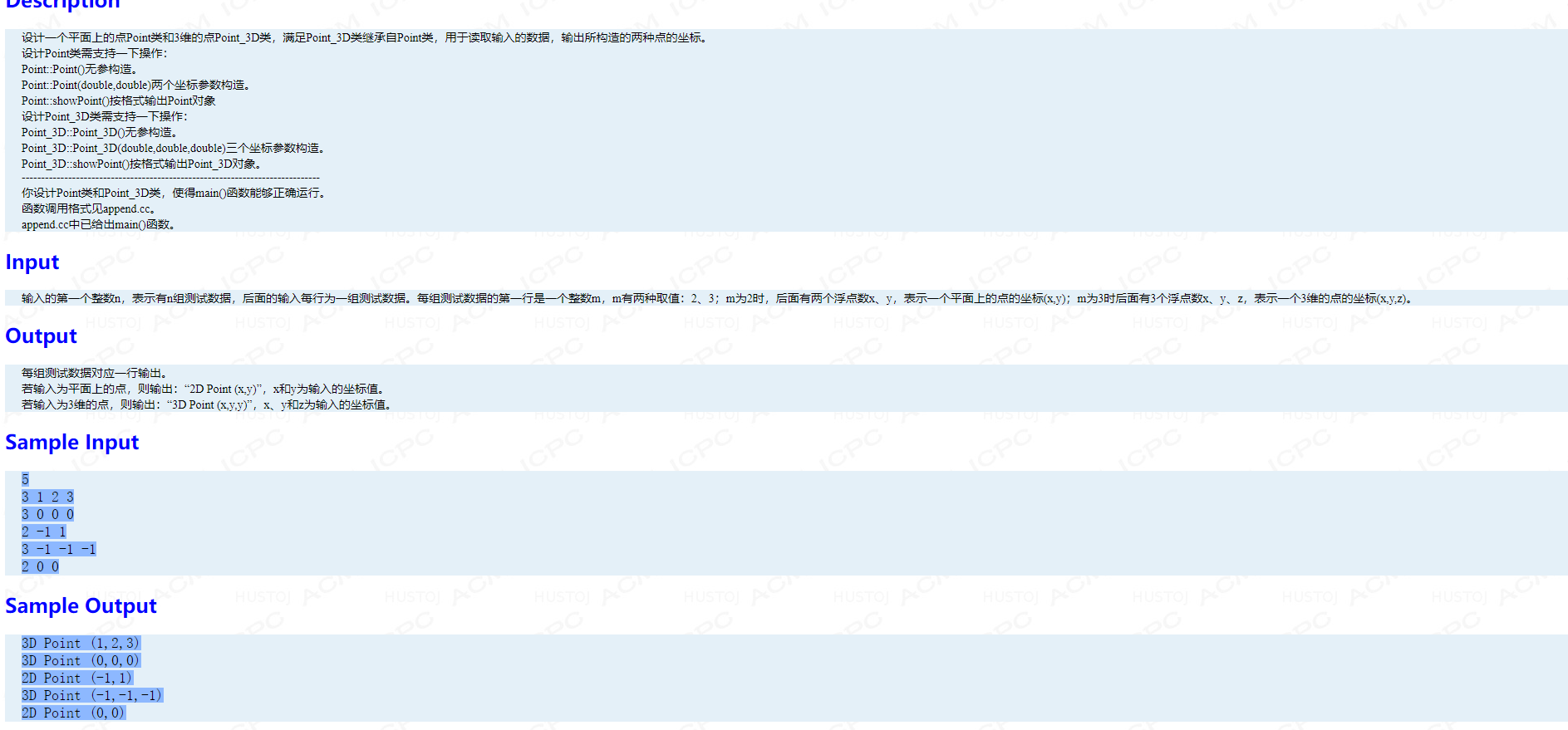
main 函数:
int main() { int cases; cin>>cases; for(int i = 1; i <= cases; i++) { double x, y, z; int point_type; cin>>point_type; if(point_type == 2) { cin>>x>>y; Point p(x, y); p.showPoint(); } if(point_type == 3) { cin>>x>>y>>z; Point_3D p(x, y, z); p.showPoint(); } } }
继承水,但不用继承写也能过,事实上也没有多大差别,但还是放继承的代码吧:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Point { double x,y; friend class Point_3D; public: Point(){}; Point(double _x,double _y):x(_x),y(_y){}; void showPoint() { cout << "2D Point (" << x << "," << y << ")" << endl; } }; class Point_3D:public Point { double z; public: Point_3D(){}; Point_3D(double _x,double _y,double _z):Point(_x,_y),z(_z){}; void showPoint() { cout << "3D Point (" << x << "," << y << "," << z << ")" << endl; } };
Problem F: 立体空间中的点(II)
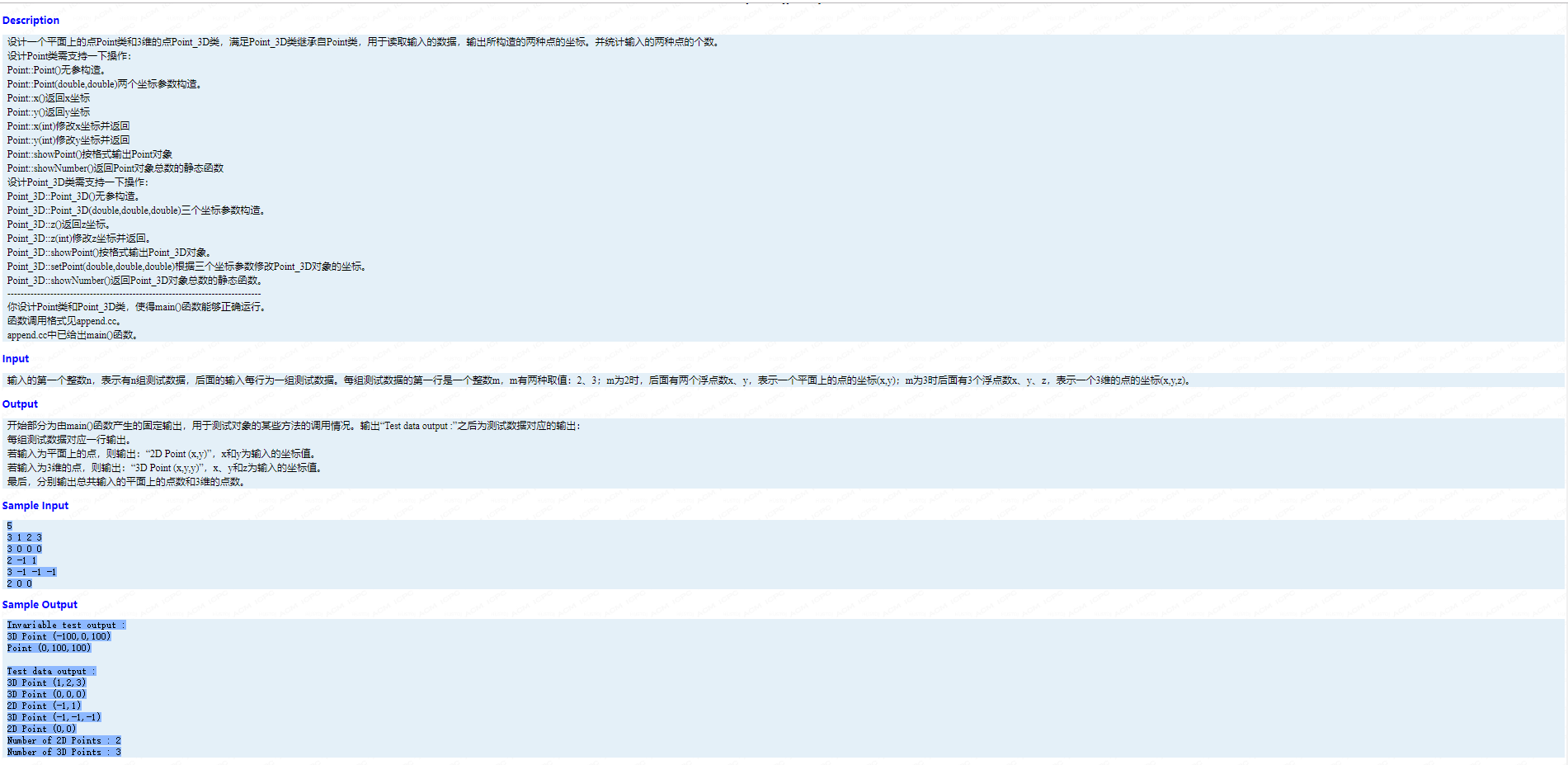
mian 函数:
int main() { cout<<"Invariable test output :"<<endl; Point_3D p3d; p3d.setPoint(-100, 0, 100); p3d.showPoint(); p3d.x(0); p3d.y(100); cout<<"Point ("<<p3d.x()<<","<<p3d.y()<<","<<p3d.z()<<")"<<endl; cout<<"\nTest data output :"<<endl; int cases; cin>>cases; for(int i = 1; i <= cases; i++) { double x, y, z; int point_type; cin>>point_type; if(point_type == 2) { cin>>x>>y; Point p(x, y); p.showPoint(); } if(point_type == 3) { cin>>x>>y>>z; Point_3D p(x, y, z); p.showPoint(); } } cout<<"Number of 2D Points : "<<Point::showNumber() - Point_3D::showNumber()<<endl; cout<<"Number of 3D Points : "<<Point_3D::showNumber() - 1<<endl; }
继承水:
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Point { double x1,y1; static int N_P; friend class Point_3D; public: Point(){N_P++;}; Point(double _x,double _y):x1(_x),y1(_y){N_P++;}; void showPoint() { cout << "2D Point (" << x1 << "," << y1 << ")" << endl; } void x(double _x){x1 =_x;} void y(double _y){y1 = _y;} double x() { return x1; } double y() { return y1; } static int showNumber(){return N_P;} }; class Point_3D:public Point { double z1; static int N_P3; public: Point_3D(){N_P3++;}; Point_3D(double _x,double _y,double _z):Point(_x,_y),z1(_z){N_P3++;}; double z() { return z1; } void z(double _z) { z1 = _z; } void setPoint(double _x,double _y,double _z) { x1 =_x; y1 = _y; z1 = _z; } static int showNumber() { return N_P3; } void showPoint() { cout << "3D Point (" << x1 << "," << y1 << "," << z1 << ")" << endl; } }; int Point::N_P = 0; int Point_3D::N_P3 = 0;
过往不恋 未来不迎 当下不负


