vue客户端项目的基本搭建以及ElementUI
1. 客户端项目搭建
1.1 创建项目目录(安装时路由选n先,下面装)
cd E:\vue_project\renran
vue init webpack renran_pc
之后用pycharm打开项目
1.2 初始化项目
清除默认的HelloWorld.vue组件和APP.vue中的默认模板代码和默认css样式,以及index.js中默认导入的HelloWorld
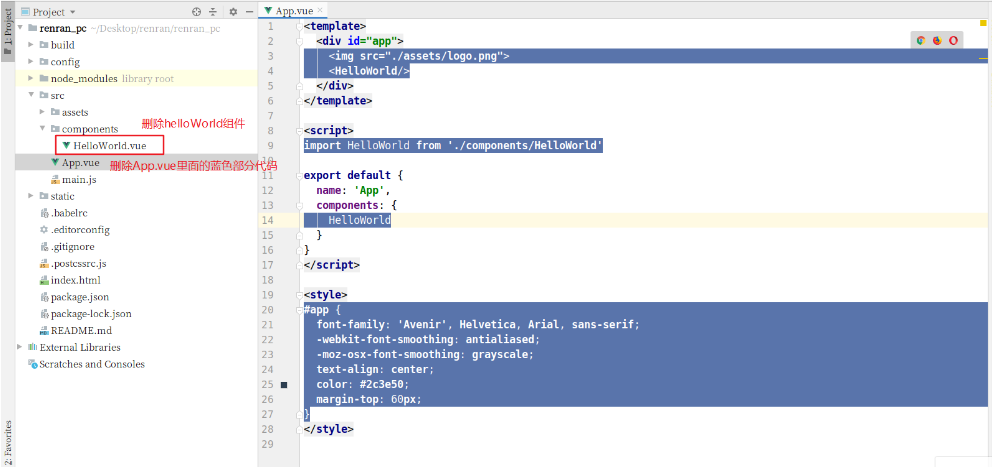
App.vue
<template> <div id="app"> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', components: { } } </script> <style> </style>
浏览器访问:就是空白
1.3 安装路由vue-router
官方文档:https://router.vuejs.org/zh/
npm i vue-router -S # npm install vue-router --save # 安装指定版本 npm i vue-router@3.3.4 -S
1.3.2 配置路由
1.3.2.1 初始化路由对象
在src目录下创建router路由目录,在router目录下创建index.js路由文件
index.js路由文件中,编写初始化路由对象的代码 .
// 1. 引入vue和vue-router组件核心对象,并在vue中通过use注册vue-router组件 import Vue from "vue"; import Router from "vue-router"; // 注册第三方组件 Vue.use(Router); // 导入组件 // 在vue中@表示src目录的路径 // import Home from "@/components/Home" // 2. 暴露vue-router对象,并在vue-router里面编写路由,提供给main.js调用 export default new Router({ // 路由显示模式,默认为hash(地址栏上面默认带#,http://localhost:8080/#/login),设置路由模式为‘history’,去掉默认的# mode: "history", routes:[ // 路由列表 // { // name:"路由名称,也就是像django中别名[对应组件的name值,将来用于跳转页面]", // path: "访问url路径", // component: 组件名 // }, ] })
1.3.2.2 注册路由信息
打开main.js文件,把router路由规则对象注册到vue中,代码:
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command // (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias. import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' // 注册路由 import router from '@/router/index'; // import router from './router/index'; Vue.config.productionTip = false /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: '#app', router, // 挂载路由对象,将来所有的路由对象的属性或者方法,都可以通过vm来操作 components: { App }, template: '<App/>' });
1.3.2.3 在视图中显示路由对应的内容
在App.vue组件中,添加显示路由对应的内容。代码:
<template> <div id="app"> <!-- 调用路由组件,路由组件作用:识别访问当前站点的url地址,获取地址的路径部分,到路由列表中识别判断,标签名必须是这个rouer-view --> <router-view/>
<!--<router-view></router-view>--> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', components: { } } </script> <style> </style>
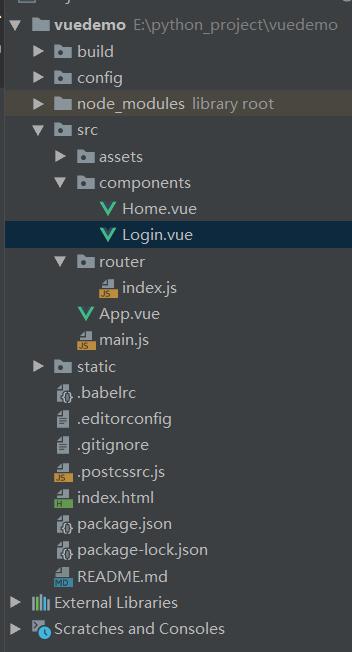
完整代码:
index.js

// 1. 引入vue和vue-router组件核心对象,并在vue中通过use注册vue-router组件 import Vue from "vue"; import Router from "vue-router"; // 注册第三方组件 Vue.use(Router); // 导入组件 // 在vue中@表示src目录的路径 import Home from "@/components/Home" import Login from "../components/Login" // 2. 暴露vue-router对象,并在vue-router里面编写路由,提供给main.js调用 export default new Router({ // 路由显示模式,默认为hash(地址栏上面默认带#,http://localhost:8080/#/login),设置路由模式为‘history’,去掉默认的# mode: "history", routes: [ // 路由列表 // { // name:"路由名称,也就是像django中别名[对应组件的name值,将来用于跳转页面]", // path: "访问url路径", // component: 组件名 // }, { path: "/home", component: Home }, { path: "/login", component: Login } ] })
main.js

// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command // (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias. import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' // 注册路由 import router from '@/router/index'; // import router from './router'; 或者用这个注册路由 Vue.config.productionTip = false; /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: '#app', router, // 挂载路由对象,将来所有的路由对象的属性或者方法,都可以通过vm来操作 components: { App }, template: '<App/>' })
App.vue

<template>
<div id="app">
<!-- 调用路由组件,路由组件作用:识别访问当前站点的url地址,获取地址的路径部分,到路由列表中识别判断,标签名必须是这个rouer-view -->
<router-view/>
<!--<router-view></router-view>-->
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
Home.vue

<template> <div> Home组件代码 </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Home" } </script> <style scoped> </style>
Login.vue

<template>
<div id="login">
Login界面
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "login"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
效果:
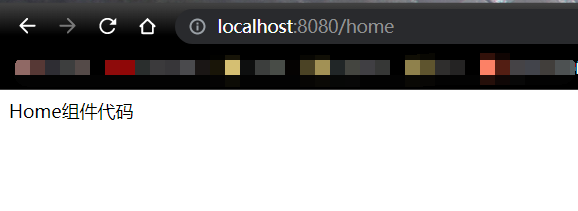
注意:如果在vue创建项目的时候,设置安装vue-router,则项目会自动帮我们生成上面的router目录和index.js里面的代码,以及自动到main.js里面注册路由对象。
1.3.3 路由对象提供的操作
在我们安装注册了vue-router组件以后,vue-router在vue项目中会帮我们在全局范围内所有组件里面创建2个对象给我们使用:
-
this.$router,可用于在js代码中进行页面跳转。 -
this.$route,可用于获取地址栏上面的url参数。
1.3.3.1 页面跳转
在vue-router提供的操作中, 进行页面跳转有2种方式:
-
使用
<router-link to="url地址">来跳转 -
在
<script>中使用this.$router.push(url地址)来跳转在
<script>中还可以使用this.$router.go(整数),表示跳转返回上一页或者上几页,下一个或者下几页
1.3.3.1.1 router-link标签
例如,我们就可以在Home.vue组件中,使用router-link跳转到User.vue组件中。
routes/index.js,代码:
// 1. 引入vue和vue-router组件核心对象,并在vue中通过use注册vue-router组件 import Vue from "vue"; import Router from "vue-router"; Vue.use(Router); // Router是类 // 2. 暴露vue-router对象,并在vue-router里面编写路由,提供给main.js调用 // 导入组件 // import 组件名 from "../components/组件名" import Home from "../components/Home"; import User from "../components/User"; export default new Router({ mode:"history", // 路由地址的显示模式: 默认hash,表示地址栏上面出现# routes:[ // { // name:"路由名称[对应组件的name值,将来用于跳转页面]", // path: "访问url路径", // component: 组件名 // }, { name:"Home", path: "/", component: Home },{ name:"User", path: "/user", component: User }, ], }); // vue-router除了可以进行组件和url地址的绑定以外,还可以 // 进行不同组件的页面跳转,
Home.vue代码:
<template> <div> 首页页面组件 <a href="/user">个人中心</a> <!-- router-link标签,本质上就是a标签,只是由vue-router进行加工处理 可以显示局部页面刷新,不会重新加载内容,进行ajax跳转 --> <router-link to="/user">个人中心</router-link> <router-link :to="url">个人中心</router-link> <router-link :to="{name:'User'}">个人中心</router-link> // 反向解析,这里的name就是index.js中路由列表的/user路由的name别名 </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Home", data(){ return { url: "/user", } }, methods:{ } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
<template> <div> 首页页面组件 <a href="/user">个人中心</a> <!-- router-link标签,本质上就是a标签,只是由vue-router进行加工处理 可以显示局部页面刷新,不会重新加载内容,进行ajax跳转 --> <router-link to="/user">个人中心</router-link> <router-link :to="url">个人中心</router-link> <router-link :to="{name:'User'}">个人中心</router-link> <button @click="jump">个人中心</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Home", data(){ return { url: "/user", } }, methods:{ jump(){ // 开发中可以先进行权限,登录之类的判断,然后再进行跳转 // this.$router.back(); // 返回上一页,本质上就是 location.back() // this.$router.go(-1); // 返回上一页,本质上就是 location.go(n),n<0,则返回上n页,n>0,则前进n页 // this.$router.forward(); // 跳转到下一页,本质上就是 location.forward() this.$router.push("/user"); // 跳转到站内的制定地址页面中,本质上就是 location.href // 注意,this.$router.push() 不能跳转到其他网站。如果真的要跳转外站,则使用location.href="站外地址,记得加上http://协议" } } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
1.3.3.2 参数传递
vue-router提供了this.$route,可以让我们接收来自其他页面的附带参数。参数有2种:
-
查询字符串(
query string),就是地址栏上面?号后面的参数,例如:
http://localhost:8008/user?name=xiaoming&pwd=123,这里name=xiaoming&pwd=123就是查询字符串参数。 -
路由参数(
router params),就是地址栏上面路由路径的一部分,例如:
http://localhost:8080/user/300/xiaoming,此时,300属于路由路径的一部分,这个300就是路由参数.,当然,xiaoming,或者user也可以理解是路由参数,就是看我们的页面中是否需要接收而已。
1.3.3.2.1 获取查询字符串
1.必须先有一个页面跳转发送参数。例如,在Home组件中跳转到User组件中,需要传递name和pwd查询字符串。
Home.vue代码:
<template>
<div>
首页页面组件
<!--<a href="/user">个人中心</a>
<!– router-link标签,本质上就是a标签,只是由vue-router进行加工处理
可以显示局部页面刷新,不会重新加载内容,进行ajax跳转
–>
<router-link to="/user">个人中心</router-link>
<router-link :to="url">个人中心</router-link>
<router-link :to="{name:'User'}">个人中心</router-link>
<button @click="jump">个人中心</button>-->
<!--参数传递方式-->
<router-link :to="`/user?name=${name}&pwd=${pwd}`">查询字符串参数</router-link>
<br>
<router-link :to="/user?name='+name+'&pwd='+pwd">查询字符串参数</router-link>
<br>
<router-link :to="{path:'/login',query:{'name':'xiaoming','pwd':'123'}}">传递查询字符串参数</router-link>
<br>
<router-link :to="{name:'Login',query:{'name':'xiaoming','pwd':'123'}}">传递查询字符串参数</router-link>
<br>
<!--也可以在script中用this.router.push("/user?name=xiaoming&pwd=123")-->
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
data(){
return {
name: "xiaoming",
pwd: "123",
url: "/user",
}
},
methods:{
jump(){
// 开发中可以先进行权限,登录之类的判断,然后再进行跳转
// this.$router.back(); // 返回上一页,本质上就是 location.back()
// this.$router.go(-1); // 返回上一页,本质上就是 location.go()
// this.$router.forward(); // 跳转到下一页,本质上就是 location.forward()
this.$router.push("/user"); // 跳转到站内的制定地址页面中,本质上就是 location.href
// 注意,this.$router.push 不能跳转到其他网站。如果真的要跳转外站,则使用location.href="站外地址,记得加上http://协议"
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
2.可以下一个页面中,这里代表的就是User组件,接收来自Home组件的参数。
<template> <div> 用户中心页面组件 </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "User", created() { // 接收地址栏上面的参数 // this.$route是vue-router提供的一个用于接收地址参数的对象。 // 经过main.js里面注册router对象以后, // 将来在所有的子组件中,可以通过this.$route来获取参数或者通过this.$router跳转页面 // 查询字符串参数 // query是this.$route里面的一个数组,this.$route会自动收集地址栏上所有的参数保存到query里面 // let name = this.$route.query.name; // let pwd = this.$route.query.pwd; // console.log(`name=${name}&pwd=${pwd}`); // ``里面,${}圈住的内容会被js当成变量来解析 } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
页面跳转和参数传递综合案例:
index.js

import Vue from 'vue' import Router from 'vue-router' Vue.use(Router); // 导入组件 // 在vue中@表示src目录的路径 import Home from "@/components/Home" import Login from "../components/Login" import User from "../components/User" export default new Router({ mode:"history", // 路由显示模式,默认为hash(地址栏上面默认带#),设置路由模式为‘history’,去掉默认的# routes: [ { path: "/home", // 访问url地址 component: Home, // 访问url对应的组件 name: "Home" // 设置别名 }, { path: "/login", component: Login, name: "Login" }, { path: "/user/:name/:id", // 声明当前地址的2个路由参数名!!! component: User, // 自动导包 Alt+Enter name: "User", } ] })
Home.vue

<template>
<div>
Home组件代码
<h1>页面跳转</h1>
<button @click="jump">使用this.$router来跳转到登录页</button>
<br>
<router-link to="/login">使用router-link来跳转到登录页</router-link>
<br>
<router-link :to="url">使用router-link通过变量来跳转到登录页</router-link>
<br>
<router-link :to="{path:'/login'}">使用router-link通过路由列表中path来跳转到登录页</router-link>
<br>
<router-link :to="{name:'Login'}">使用router-link通过反向解析来跳转到登录页</router-link>
<br>
<a href="/login">使用a标签跳转到登录页</a>
<h1>参数传递</h1>
<button @click="func1">传递查询字符串参数</button>
<br>
<router-link to="/login?name=xiaoming&pwd=123">传递查询字符串参数</router-link>
<br>
<router-link :to="{path:'/login',query:{'name':'xiaoming','pwd':'123'}}">传递查询字符串参数</router-link>
<br>
<router-link :to="{name:'Login',query:{'name':'xiaoming','pwd':'123'}}">传递查询字符串参数</router-link>
<br>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
data(){
return {
url:"/login",
}
},
methods:{
jump(){
// 跳转页面可以使用this.$router
// 跳转页面到站内的指定路由,如果希望跳转到其他网站,
// 则需要使用原生js提供的location.href="http://www.luffycity.com"
this.$router.push("/login");
/*
this.$router.go(n); // 跳转历史记录的n页,n<0,则返回上n页,n>0,则前进n页
this.$router.go(n); // 跳转历史记录的n页,n<0,则返回上n页,n>0,则前进n页
this.$router.forward(); // 前进一页
this.$router.back(); // 返回上一页
*
*/
},
func1(){
this.$router.push("/login?name=xiaoming&pwd=123");
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
Login.vue

<template>
<div>
登录页面内容
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Login",
created() { // 需要提前接收参数或者接收服务端数据的初始化代码都写在created,此时页面还没有出来
// this.$route的其他属性
console.log(this.$route.fullPath); // /login?name=xiaoming&pwd=123 除了域名地址后面的所有内容
console.log(this.$route.path); // /login 去掉参数以后的路径
// 接收来自其他组件的查询字符串参数[query srting]
var name = this.$route.query.name;
console.log(name);
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
User.vue

<template>
<div>
<h1>用户中心的内容</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "User",
created(){
// 接收路由参数
console.log( this.$route.params ); // 获取所有的路由参数
console.log( this.$route.params.name ); // 获取name参数
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
1.3.4.2 获取路由参数
例如:我们用户的界面都是一样的,但是每一个用户来到自己的页面中,显示的内容肯定都是不一样的,此时,我们需要使用不同的路径来区分不同的用户。这时候,可以在路由路径中使用路由参数表示不同用户的id
例如:我们就需要设置一个route/index.js中路由信息里面,哪一段路由属于路由参数。
src/routes/index.js设置路由参数。
// 1. 引入vue和vue-router组件核心对象,并在vue中通过use注册vue-router组件 import Vue from "vue"; import Router from "vue-router"; Vue.use(Router); // Router是类 // 2. 暴露vue-router对象,并在vue-router里面编写路由,提供给main.js调用 // 导入组件 // import 组件名 from "../components/组件名" import Home from "../components/Home"; import User from "../components/User"; export default new Router({ mode:"history", // 路由地址的显示模式: 默认hash,表示地址栏上面出现# routes:[ // { // name:"路由名称[对应组件的name值,将来用于跳转页面]", // path: "访问url路径", // component: 组件名 // }, { name:"Home", path: "/", component: Home },{ name:"User", path: "/user/:id/img-:img_id", component: User }, ], }); // vue-router除了可以进行组件和url地址的绑定以外,还可以 // 进行不同组件的页面跳转,
然后我们就是在Home中如果需要转到User里面。
Home.vue代码:
<template> <div> 首页页面组件 <router-link to="/user/100/img-10086">路由参数</router-link> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Home", data() { return { name: "xiaoming", pwd: "123", url: "/user", } }, methods: { jump() { // 开发中可以先进行权限,登录之类的判断,然后再进行跳转 this.$router.push("/user"); // 跳转到站内的制定地址页面中,本质上就是 location.href // 注意,this.$router.push 不能跳转到其他网站。如果真的要跳转外站,则使用location.href="站外地址,记得加上http://协议" } } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
<template>
<div>
用户中心页面组件
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "User",
created() {
// 接收地址栏上面的参数
// this.$route是vue-router提供的一个用于接收地址参数的对象。
// 经过main.js里面注册router对象以后,
// 将来在所有的子组件中,可以通过this.$route来获取参数或者通过this.$router跳转页面
// 查询字符串参数
// query是this.$route里面的一个数组,this.$route会自动收集地址栏上所有的参数保存到query里面
// let name = this.$route.query.name;
// let pwd = this.$route.query.pwd;
// console.log(`name=${name}&pwd=${pwd}`); // ``里面,${}圈住的内容会被js当成变量来解析
// 路由参数
// params是this.$route里面的一个数组,this.$route会自动收集路由列表中已经标记为路由参数所有内容保存到params中
let id = this.$route.params.id;
console.log(id);
let img_id = this.$route.params.img_id;
console.log(`img_id = ${img_id}`);
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
2. ElementUI
对于前端页面布局,我们可以使用一些开源的UI框架来配合开发,常用的UI框: bootstrap,H-ui框架,lay-UI框架,Amaze UI,zui框架,ElementUI.
Vue开发前端项目中,比较常用的就是ElementUI了。
ElementUI是饿了么团队开发的一个UI组件框架,这个框架提前帮我们提供了很多已经写好的通用模块,我们可以在Vue项目中引入来使用,这个框架的使用类似于我们前面学习的bootstrap框架,也就是说,我们完全可以把官方文档中的组件代码拿来就用,有定制性的内容,可以直接通过样式进行覆盖修改就可以了。
中文官网:http://element-cn.eleme.io/#/zh-CN
文档快速入门:http://element-cn.eleme.io/#/zh-CN/component/quickstart
项目根目录执行以下命令:
npm i element-ui -S # 上面的命令等同于 `npm install element-ui --save`
2.2 配置ElementUI到项目中
在main.js中导入ElementUI,并调用。代码:
// elementUI 导入 import ElementUI from 'element-ui'; import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css'; // 调用插件 Vue.use(ElementUI);
成功引入了ElementUI以后,在组件中直接使用
<template> <div> <h1>用户中心的内容</h1> <i class="el-icon-edit"></i> </div> </template>


