Java GUI编程
AWT
- AWT(Abstract Window Toolkit)包括了很多类的接口,用于Java Application的GUI(Graphics User Interface图形用户界面)编程。
- GUI的各种元素(如:窗口,按钮,文本框)由Java类实现。
- 使用AWT所涉及的类一般在 java.awt 包及其子包中。
- Container 和 Component 是AWT中的两个和心态。
Component & Container
- Java的图形用户界面的最基本组成部分是Component, Component类及其子类的对象用来描述以图形化的方式显示在屏幕上并能与用户进行交互的GUI元素,例如一个按钮,一个标签等。
- 一般的Component对象不能独立地显示出来,必须将“放在”某一的Container对象中才可以显示出来。
- Container是Component子类,Container子类对象可以“容纳”别的Component对象。
- Container对象可以使用方法 add(...) 向其中添加其他Component对象。
- Container是Component的子类,因此Container对象也可以被当作Component对象添加到其他Container对象中。
两种常用的Container:
- Window:其对象表示自由停泊的顶级窗口。
- Panel:其对象可作为容纳其他Component对象,但不能独立存在,必须添加到其他Container中(如Window 或 Applet)。
Frame
- Frame是Window的子类,由Frame或其子类创建的对象为一个窗体。
- Frame的常用构造方法:
Frame() Frame(String s) //创建标题栏为字符串s的窗口

示例1:
import java.awt.*; public class test{ public static void main( String args[]) { Frame f = new Frame("My First Test"); f.setLocation(300, 300); f.setSize( 170,100); f.setBackground( Color.blue); f.setResizable(false); f.setVisible( true); } }
示例2:
import java.awt.*; public class test { public static void main(String args[]) { MyFrame f1 = new MyFrame(100,100,200,200,Color.BLUE); MyFrame f2 = new MyFrame(300,100,200,200,Color.YELLOW); MyFrame f3 = new MyFrame(100,300,200,200,Color.GREEN); MyFrame f4 = new MyFrame(300,300,200,200,Color.MAGENTA); } } class MyFrame extends Frame{ static int id = 0; MyFrame(int x,int y,int w,int h,Color color){ super("MyFrame " + (++id)); setBackground(color); setLayout(null); setBounds(x,y,w,h); setVisible(true); } }
Panel
- Panel对象可以看成可以容纳Component的空间。
- Panel对象可以拥有自己的布局管理器。
- Panel类拥有从父类继承来的


示例1:
import java.awt.*; public class TestPanel { public static void main(String args[]) { Frame f = new Frame("Java Frame with Panel"); Panel p = new Panel(null); f.setLayout(null); f.setBounds(300,300,500,500); f.setBackground(new Color(0,0,102)); p.setBounds(50,50,400,400); p.setBackground(new Color(204,204,255)); f.add(p); f.setVisible(true); } }
示例2:
import java.awt.*; public class test{ public static void main( String args[]) { new MyFrame2("MyFrameWithPanel",300,300,400,300); } } class MyFrame2 extends Frame{ private Panel p1,p2,p3,p4; MyFrame2(String s,int x,int y,int w,int h){ super(s); setLayout(null); p1 = new Panel(null); p2 = new Panel(null); p3 = new Panel(null); p4 = new Panel(null); p1.setBounds(0,0,w/2,h/2); p2.setBounds(0,h/2,w/2,h/2); p3.setBounds(w/2,0,w/2,h/2); p4.setBounds(w/2,h/2,w/2,h/2); p1.setBackground(Color.BLUE); p2.setBackground(Color.GREEN); p3.setBackground(Color.YELLOW); p4.setBackground(Color.MAGENTA); add(p1);add(p2);add(p3);add(p4); setBounds(x,y,w,h); setVisible(true); } }
事件监听
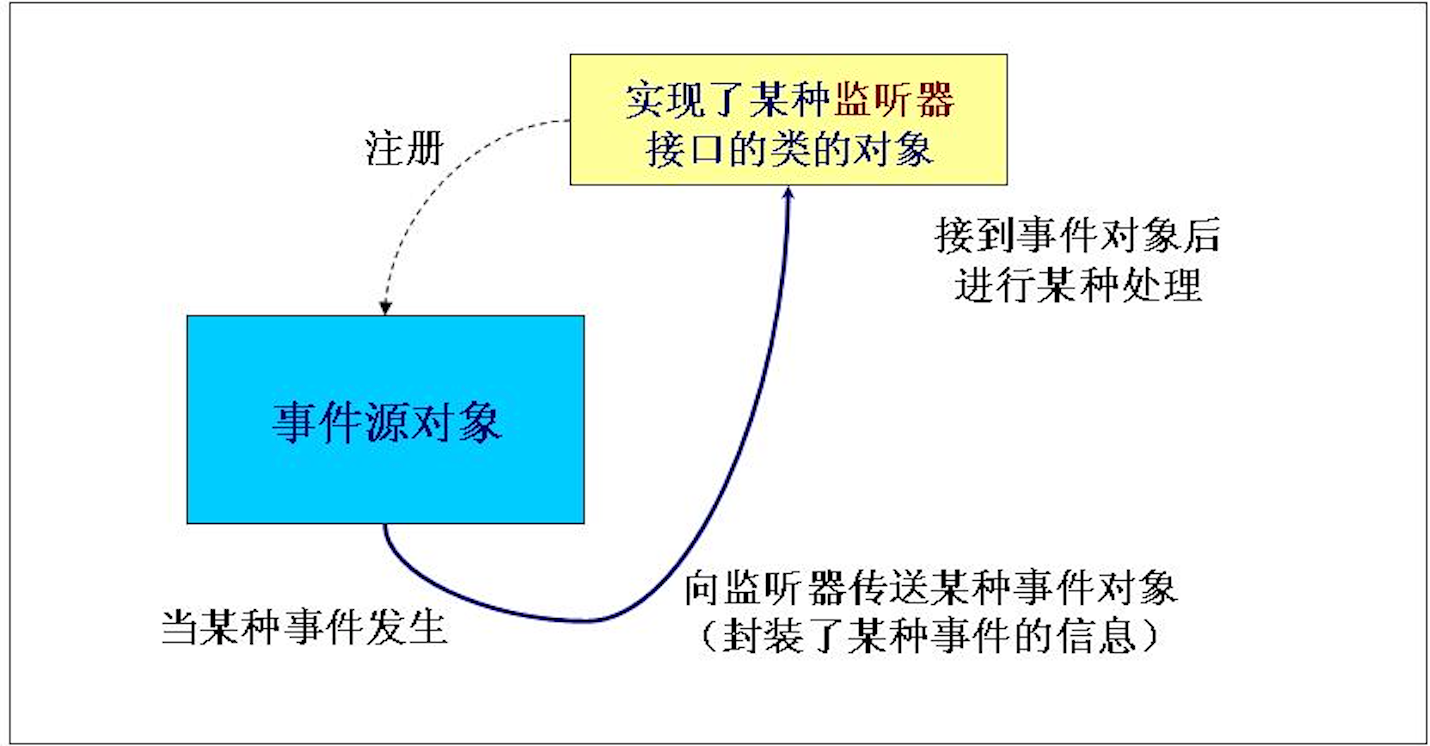
Button事件监听
示例:
import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; public class test { public static void main(String args[]) { Frame f = new Frame("Test"); Button b = new Button("Press Me!"); Monitor bh = new Monitor(); b.addActionListener(bh); f.add(b,BorderLayout.CENTER); f.pack(); //调整此窗口大小,以适应其组件的首先大小和布局 f.setVisible(true); } } class Monitor implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { System.out.println("a button has been pressed"); } }
TextField类
- java.awt.TextFieldl类用来创建文本框对象。
- TextField有如下常用方法:

TextField事件监听
- TextField对象可能发生Action(光标在文本框内敲回车)事件。与该事件对应的事件类是 java.awt.event.ActionListener接口的类的对象。ActionListener接口定义有方法: public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
- 实现该接口的类主要在该方法中添加处理事件(Action)的语句。
- 使用 addActionListener(ActionListener I) 方法为 TextField 对象注册一个 ActionListener 对象,当 TextField 对象发生 Action 时,会生成一个 ActionEvent 对象,该对象作为参数传递给 ActionListener 对象的 actionPerformer 方法在方法中可以获取该对象的信息,并做相应的处理。
import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; public class TFPassword { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub new TFFrame2(); } } class TFFrame2 extends Frame { TFFrame2() { TextField tf = new TextField(); add(tf); tf.addActionListener(new TFActionListener2()); tf.setEchoChar('*'); pack(); setVisible(true); } } class TFActionListener2 implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { TextField tf = (TextField)e.getSource(); System.out.println(tf.getText()); tf.setText(""); } }
内部类
好处:
- 可以方便的访问包装类的成员。
- 可以更清楚的组织逻辑,防止不应该被其他类访问的类进行访问。
何时使用:
- 该类不允许或不需要其他类访问时。
Graphics类 Paint方法
- 每个 Component 都有一个 paint(Graphics g)用于实现绘图目的,每次重画该 Component 时都自动调用 paint 方法。
- Graphics 类中提供了许多绘图方法,具体查询API。
示例:
import java.awt.*; public class TestPaint { public static void main(String[] args) { new PaintFrame().launchFrame(); } } class PaintFrame extends Frame { public void launchFrame() { setBounds(200,200,640,480); setVisible(true); } public void paint(Graphics g) { Color c = g.getColor(); g.setColor(Color.red); g.fillOval(50, 50, 30, 30); g.setColor(Color.green); g.fillRect(80,80,40,40); g.setColor(c); } }
鼠标事件适配器
- 抽象类 java.awt.event.MouseAdapter 实现了 MouseListener 接口,可以使用其子类作为 MouseEvent接口,可以使用其子类作为 MouseEvent 的监听器,只要重写其相应的方法即可。
- 对于其他的监听器,也有对应的适配器。
- 使用适配器可以避免监听器类定义没有必要的空方法。
- GUI/MyMouseAdapter.java 鼠标适配器
- repaint-update()-paint();
Window事件
- Window事件所对应的事件类为WindowEvent,所对应的事件监听接口为WindowListener。
- WindowListener定义的方法有:

- 与WindowListener对应的适配器为 WindowAdapter。





