SpringMVC入手项目注解版
SpringMVC入手项目注解版
1.创建Maven项目在pom.xml文件引入相关的依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId> <artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId> <version>2.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
由于Maven可能存在资源过滤的问题,我们将配置完善
<build> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/java</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>false</filtering> </resource> <resource> <directory>src/main/resources</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>false</filtering> </resource> </resources> </build>
2.配置web.xml
<!--1.注册servlet--> <servlet> <servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <!--通过初始化参数指定SpringMVC配置文件的位置,进行关联--> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:springmvc-servlet.xml</param-value> </init-param> <!-- 启动顺序,数字越小,启动越早 --> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <!--所有请求都会被springmvc拦截 --> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
/ 和 /* 的区别:< url-pattern > / </ url-pattern > 不会匹配到.jsp, 只针对我们编写的请求;即:.jsp 不会进入spring的 DispatcherServlet类 。< url-pattern > /* </ url-pattern > 会匹配 *.jsp,会出现返回 jsp视图 时再次进入spring的DispatcherServlet 类,导致找不到对应的controller所以报404错。
- 注意web.xml版本问题,要最新版!
- 注册DispatcherServlet
- 关联SpringMVC的配置文件
- 启动级别为1
- 映射路径为 / 【不要用/*,会404】
3、添加Spring MVC配置文件
在resource目录下添加springmvc-servlet.xml配置文件,配置的形式与Spring容器配置基本类似,为了支持基于注解的IOC,设置了自动扫描包的功能,具体配置信息如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"> <!-- 自动扫描包,让指定包下的注解生效,由IOC容器统一管理 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.bai.controller"/> <!-- 让Spring MVC不处理静态资源: .html .css .js --> <mvc:default-servlet-handler /> <!-- 支持mvc注解驱动 在spring中一般采用@RequestMapping注解来完成映射关系 要想使@RequestMapping注解生效 必须向上下文中注册DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping 和一个AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter实例 这两个实例分别在类级别和方法级别处理。 而annotation-driven配置帮助我们自动完成上述两个实例的注入。 --> <mvc:annotation-driven /> <!-- 视图解析器 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" id="internalResourceViewResolver"> <!-- 前缀 --> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/" /> <!-- 后缀 --> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /> </bean> </beans>
在视图解析器中我们把所有的视图都存放在/WEB-INF/目录下,这样可以保证视图安全,因为这个目录下的文件,客户端不能直接访问。
- 让IOC的注解生效
- 静态资源过滤 :HTML . JS . CSS . 图片 , 视频 .....
- MVC的注解驱动
- 配置视图解析器
4、创建Controller
package com.bai.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller @RequestMapping("/HelloController") public class HelloController { //真实访问地址 : 项目名/HelloController/hello @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(Model model) { // 封装数据 //向模型中添加属性msg与值,可以在JSP页面中取出并渲染 model.addAttribute("msg", "Hello SpringMVC-Annotaion!"); return "hello";//会被视图解析器处理 //web-inf/jsp/hello.jsp } @RequestMapping("/hello1") //建议直接将路径写死,不需要外面一层 public String hello1(Model model) { // 封装数据 //向模型中添加属性msg与值,可以在JSP页面中取出并渲染 model.addAttribute("msg", "Hello SpringMVC-Annotaion!"); return "hello1";//会被视图解析器处理 //web-inf/jsp/hello1.jsp } }
- @Controller是为了让Spring IOC容器初始化时自动扫描到;
- @RequestMapping是为了映射请求路径
- 方法中声明Model类型的参数是为了把Action中的数据带到视图中;
- 方法返回的结果是视图的名称hello,加上配置文件中的前后缀变成WEB- INF/jsp/hello.jsp。
5、创建视图层
在WEB-INF/ jsp目录中创建hello.jsp , 视图可以直接取出并展示从Controller带回的信息;
可以通过EL表示取出Model中存放的值,或者对象;
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>SpringMVC</title> </head> <body> ${msg} </body> </html>
6、配置Tomcat运行
配置Tomcat , 开启服务器 , 访问 对应的请求路径!
可能遇到的问题:访问出现404,排查步骤:
- 查看路径是否写错
- 查看控制台输出,看一下是不是缺少了什么jar包。
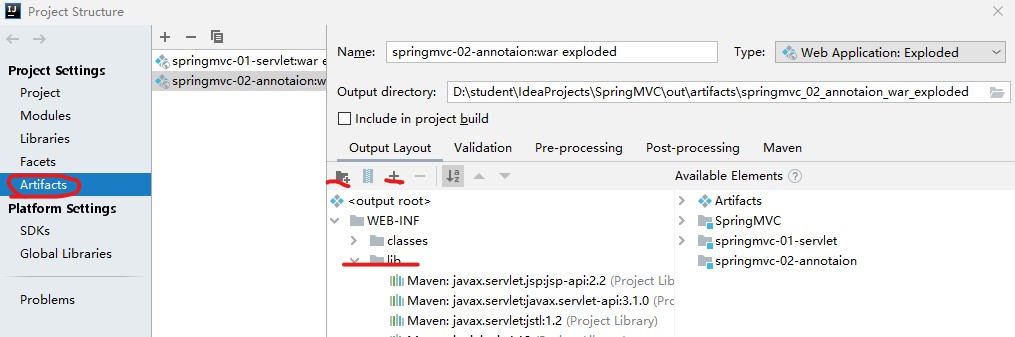
- 如果jar包存在,显示无法输出,就在IDEA的项目发布中,添加lib依赖!
- 重启Tomcat 即可解决!

小结
实现步骤其实非常的简单:
-
新建一个web项目
-
导入相关jar包
-
编写web.xml , 注册DispatcherServlet
-
编写springmvc配置文件
-
接下来就是去创建对应的控制类 , controller
-
最后完善前端视图和controller之间的对应
-
测试运行调试.
使用springMVC必须配置的三大件:
处理器映射器、处理器适配器、视图解析器
通常,我们只需要手动配置视图解析器,而处理器映射器和处理器适配器只需要开启注解驱动即可,而省去了大段的xml配置
使用注解@Controller
- @Controller注解类型用于声明Spring类的实例是一个控制器(在讲IOC时还提到了另外3个注解);
- Spring可以使用扫描机制来找到应用程序中所有基于注解的控制器类,为了保证Spring能找到你的控制器,需要在配置文件中声明组件扫描。
<!-- 自动扫描指定的包,下面所有注解类交给IOC容器管理 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.kuang.controller"/>
增加一个ControllerTest2类,使用注解实现;
//@Controller注解的类会自动添加到Spring上下文中 @Controller public class ControllerTest2{ //映射访问路径 @RequestMapping("/t2") public String index(Model model){ //Spring MVC会自动实例化一个Model对象用于向视图中传值 model.addAttribute("msg", "ControllerTest2"); //返回视图位置 return "test"; } }
注解方式是平时使用的最多的方式!
@RequestMapping
@RequestMapping注解用于映射url到控制器类或一个特定的处理程序方法。可用于类或方法上。用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径。
方法级别的注解变体有如下几个:组合注解
@GetMapping @PostMapping @PutMapping @DeleteMapping @PatchMapping
@GetMapping 是一个组合注解,平时使用的会比较多!
它所扮演的是 @RequestMapping(method =RequestMethod.GET) 的一个快捷方式。





· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术