Linux内核0.11 setup文件说明
一、总体功能介绍
这是关于Linux-kernel-0.11中boot文件夹下setup.s源文件的实现功能的总结说明。
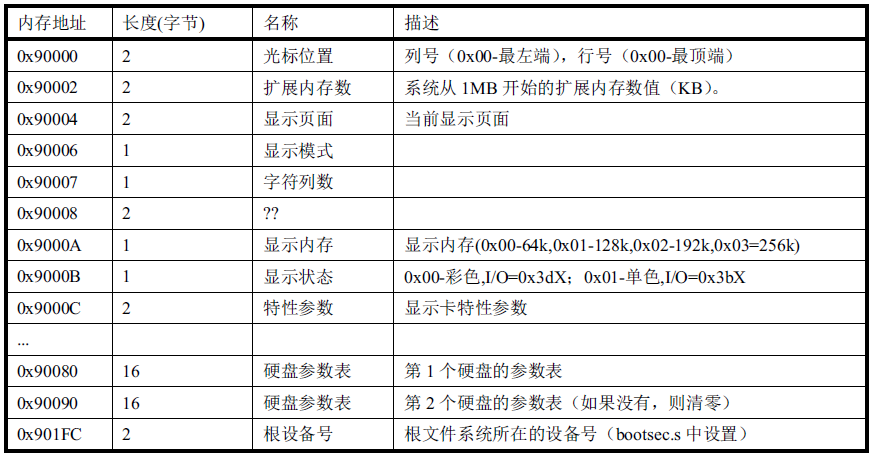
setup.s是一个操作系统加载程序,它的主要功能是利用BIOS中断读取机器系统数据,并将这些数据保存到0x90000开始的位置(覆盖了原先的bootsect.s程序),所取得的参数和保存在内存中的位置如下所示,这些参数将被内核中相关程序使用,如字符设备驱动程序集中的console.c和tty_io.c 程序等。
- setup.s程序读取并保存的参数:
然后 setup 程序将system模块从0x10000-0x8ffff处(当时认为系统内核米块system的长度不会超过512KB)整块向下移动到内存绝对地址0x00000处。 接下来加载中断描述符表寄存器(idtr)和全局描述符表(gdtr),开启A20地址线,重新设置两个中断控制器8259A,将硬件中断号重新设置为0x20-0下f。 最后设置CPU的控制寄存器CR0(也称机器状态字),从而进入32位保护模式下运行,并跳转到位于system模块最前面部分的head.s程序继续执行。
为了能让head.s在32位保护模式下运行,在本程序中临时设置了中断描述符表(IDT)和全局描述符表(GDT),并在GDT中设置了当前内核代码段的描述符和数据段的描述符,在head.s程序中会根据需要重新设置这些描述符表。
有关段描述符表的内容可以参考 操作系统分段机制。
二、代码注释
!
! setup.s (C) 1991 Linus Torvalds
!
! setup.s is responsible for getting the system data from the BIOS,
! and putting them into the appropriate places in system memory.
! both setup.s and system has been loaded by the bootblock.
!
! This code asks the bios for memory/disk/other parameters, and
! puts them in a "safe" place: 0x90000-0x901FF, ie where the
! boot-block used to be. It is then up to the protected mode
! system to read them from there before the area is overwritten
! for buffer-blocks.
!
! setup.s 负责从BIOS中获取系统数据,并将这些数据存放在内存中,此时setup.s和
! system 模块已经由bootsect引导加载到内存中。
!
! 这段代码询问BIOS有关内存/磁盘/其它参数,并将这些参数放到一个“安全”的地方:
! 0x90000-0x901FF,也就是原先bootsect代码块曾经在的地方,然后在被缓冲区覆盖之
! 由保护模式的system读取。
! NOTE! These had better be the same as in bootsect.s!
! 下面的这些参数与bootsect.s中相同
INITSEG = 0x9000 ! we move boot here - out of the way 原来bootsect所处的段
SYSSEG = 0x1000 ! system loaded at 0x10000 (65536). system在0x1000处(内存64KB处)
SETUPSEG = 0x9020 ! this is the current segment setup.s程序所在的段
.globl begtext, begdata, begbss, endtext, enddata, endbss
.text
begtext:
.data
begdata:
.bss
begbss:
.text
entry start
start:
! ok, the read went well so we get current cursor position and save it for
! posterity.
! ok, 整个读磁盘过程都很正常,现在保存光标位置以备后面使用。
! 这段代码使用BIOS中断取得当前屏幕时上光标的位置(列,行),并保存在内存0x90000处(占两个字节)。
! 控制台初始化程序会到此处读取该值。
! BIOS终端0x10 功能号 ah = 0x03,读光标位置。
! 输入: bh = 页号
! 返回: ch = 扫描开始线; cl = 扫描结束线; dh = 行号(0x00顶端); dl = 列号(0x00最左边)。
! 下面语句将ds设置为INITSEG (0x9000),这已经在bootsect程序中设置过,但是现在是setup程序,
! linus 觉得需要重新再设置一下。
mov ax,#INITSEG ! this is done in bootsect already, but...
mov ds,ax
mov ah,#0x03 ! read cursor pos 读光标位置
xor bh,bh ! 页号为0
int 0x10 ! save it in known place, con_init fetches
mov [0],dx ! it from 0x90000. 光标位置存在0x9000:0处
! Get memory size (extended mem, kB)
! 获取扩展内存的大小值(KB).
!利用BIOS中断0x15功能号 ah = 0x88 取系统所含扩展内存大小并保存在内存0x9000:2处
!返回: ax = 从0x10000(1M)处开始的扩展内存大小(KB
)。若出错则CF置位,ax = 出错码。
mov ah,#0x88
int 0x15
mov [2],ax
! Get video-card data:
! 获取显卡当前模式。
! 调用BIOS中断0x10,功能号 ah = 0x0f
! 返回: ah = 字符列数,al = 显示模式; bh = 当前显示页。
! 0x9000:4 存放当前页(1个字,两字节); 0x9000:6 存放显示模式, 0x9000:7 存放字符列数。
!
mov ah,#0x0f
int 0x10
mov [4],bx ! bh = display page
mov [6],ax ! al = video mode, ah = window width
! check for EGA/VGA and some config parameters
! 检查显示方式(EGA/VGA)并去参数。
! 调用BIOS中断0x10,附加功能选择方式信息。 功能号: ah = 0x12, bl = 0x10
! 返回: bh = 显示状态。 0x00 - 彩色模式, I/O端口 = 0x3dX; 0x01 - 单色模式,I/O端口 = 0x3bX。
! bl = 安装的显示内存。 0x00 -64K; 0x01 -128K; 0x02 -192K; 0x03 = 256K。
! cx = 显卡特性参数(见程序后面对BIOS视频中断0x10的说明)。
mov ah,#0x12
mov bl,#0x10
int 0x10
mov [8],ax
mov [10],bx
mov [12],cx
! Get hd0 data
! 取第一个硬盘的信息(复制硬盘参数表)。
!第一个硬盘参数表的首地址竟然是中断向量0x41的向量值!而第二个硬盘参数表紧接在第一个的后面,
!终端向量0x46的向量值也指向第二个硬盘的参数首地址。表的长度是16个字节(0x10)。
!下面的两段程序分别复制BIOS有关两个硬盘的参数表,0x90080处存放第一个硬盘的表,0x90090处
!存放第二个硬盘的参数表。
!lds si,[4*0x41] 从内存指定位置处读取一个长指针并放入 ds 和 si 寄存器中。ds中放段地址
! si是段内偏移地址。这里是把内存地址 4* 0x41 = 0x104 处保存的4个字节(段地址和偏移地址)读出。
mov ax,#0x0000
mov ds,ax
lds si,[4*0x41] ! 取中断向量0x41的值,也即hd0参数表的地址存入 ds:si
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov es,ax
mov di,#0x0080 !传输目的地址 0x9000:0x0080
mov cx,#0x10 !共传输16个字节。
rep
movsb
! Get hd1 data
mov ax,#0x0000
mov ds,ax
lds si,[4*0x46] ! 取中断向量0x46的值,也即hd0参数表的地址存入 ds:si
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov es,ax
mov di,#0x0090 !传输目的地址 0x9000:0x0090
mov cx,#0x10 !共传输16个字节。
rep
movsb
! Check that there IS a hd1 :-)
! 检查系统是否有第2个硬盘,如果没有则把第2个表清零。
!利用BIOS中断调用 0x13的取盘类型功能,功能号 ah = 0x15
!输入: dl = 驱动器号
!输出: ah = 类型码; 00 - 没有这个盘, 01 - 是软驱,没有change-line支持,
! 02 - 是软驱(或其他可移动设备),有changge-line支持, 03 - 是硬盘。
!
!
mov ax,#0x01500
mov dl,#0x81
int 0x13
jc no_disk1 ! 没有盘则跳转
cmp ah,#3 ! 判断是不是硬盘
je is_disk1
no_disk1: !把第2个表清零。
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov es,ax
mov di,#0x0090
mov cx,#0x10
mov ax,#0x00
rep
stosb !单字符输出指令,调用该指令后,可以将AL中的值传递到ES:DI处,并且根据DF的值来影响DI的值,如果DF为0,则调用该指令后,DI自增1
is_disk1:
! now we want to move to protected mode ... 现在,我们要进入保护模式了
cli ! no interrupts allowed ! 关中断
! first we move the system to it's rightful place
!首先,移动system模块到正确的位置(绝对地址0x00000处)
!bootsect引导程序是将system模块读到0x10000开始的位置,由于当时system模块最大长度不会超过0x80000(512KB),
!所以bootsect把自己移动到0x90000开始的地方,并把setup加载到它后面,下面的程序把整个system模块移动到0x00000位置
!即把system模块从 0x10000到0x8ffff的内存数据总共512KB整块地向内存低端移动了0x1000(64KB)的位置。
!实时模式下最大只能寻址64KB,所以512KB分成8次移动,每次移动64KB。移动64KB后,修改段地址,继续移动,循环8次。
!
mov ax,#0x0000
cld ! 'direction'=0, movs moves forward
do_move:
mov es,ax ! destination segment es:di是目的地址,初始为0x0:0x0
add ax,#0x1000
cmp ax,#0x9000 ! 已经把最后一段(从0x8000段开始的64KB)代码移动完?
jz end_move ! 移动完则跳转。
mov ds,ax ! source segment
sub di,di
sub si,si
mov cx,#0x8000 !移动0x8000个字,即64KB
rep
movsw
jmp do_move
! then we load the segment descriptors 接下来加载段描述符
end_move:
mov ax,#SETUPSEG ! right, forgot this at first. didn't work :-)
mov ds,ax
lidt idt_48 ! load idt with 0,0 加载中断描述符表
lgdt gdt_48 ! load gdt with whatever appropriate 加载GDT全局描述符表
! that was painless, now we enable A20
! 下面的代码开启A20地址线
! 为了能够访问和使用1MB以上的物理内存,我们需要首先开启A20地址线。
!
call empty_8042 !测试8042状态寄存器,等待输入缓冲器空,只有为空才能对其执行写命令。
mov al,#0xD1 ! command write 0xD1命令码,表示数据要写到8042的P2端口,P2断开的位1用于A20线的选通。
out #0x64,al !数据要写到0x64口
call empty_8042 !等待输入缓冲器空,看命令是否被接受
mov al,#0xDF ! A20 on 选通A20地址线的参数
out #0x60,al
call empty_8042 !若此时缓冲寄存器为空,则表示A20线已经选通。
! well, that went ok, I hope. Now we have to reprogram the interrupts :-(
! we put them right after the intel-reserved hardware interrupts, at
! int 0x20-0x2F. There they won't mess up anything. Sadly IBM really
! messed this up with the original PC, and they haven't been able to
! rectify it afterwards. Thus the bios puts interrupts at 0x08-0x0f,
! which is used for the internal hardware interrupts as well. We just
! have to reprogram the 8259's, and it isn't fun.
!
!8259 芯片主片端口是 0x20-0x21,从片端口是 0xA0=0xA1.输出值 0x11 表示初始化命令开始
!它是 ICW1 命令字,表示边缘触发。多片8259级联。最后要发送 ICW4 命令字。
!
mov al,#0x11 ! initialization sequence 初始化命令开始
out #0x20,al ! send it to 8259A-1 发送到8259A 主芯片
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb ! jmp $+2, jmp $+2 '$'表示当前指令的地址
out #0xA0,al ! and to 8259A-2 再次发送到8259A 从芯片
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
! linux 系统硬件中断号被设置成从 0x20开始
mov al,#0x20 ! start of hardware int's (0x20)
out #0x21,al ! 发送主芯片 ICW2 命令字,设置其实中断号,要送奇端口
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
mov al,#0x28 ! start of hardware int's 2 (0x28)
out #0xA1,al ! 发送从芯片 ICW2 命令字,设置其实中断号。
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
mov al,#0x04 ! 8259-1 is master
out #0x21,al ! 发送主芯片 ICW3 命令字,主芯片的 IR2 连接从芯片 INT
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
mov al,#0x02 ! 8259-2 is slave
out #0xA1,al ! 发送从芯片 ICW3 命令字,表示从芯片的 INT 连接到主芯片的 IR2 引脚上
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
mov al,#0x01 ! 8086 mode for both
out #0x21,al ! 发送主芯片 ICW4 命令字,8086模式; 普通 EOI、非缓冲方式
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb ! 需要发送指令来复位。初始化结束,芯片就绪。
out #0xA1,al ! 发送从芯片 ICW4 命令字,内容同上。
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
mov al,#0xFF ! mask off all interrupts for now
out #0x21,al ! 屏蔽主芯片所有中断请求
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
out #0xA1,al ! 屏蔽从芯片所有中断请求
! well, that certainly wasn't fun :-(. Hopefully it works, and we don't
! need no steenking BIOS anyway (except for the initial loading :-).
! The BIOS-routine wants lots of unnecessary data, and it's less
! "interesting" anyway. This is how REAL programmers do it.
!
! Well, now's the time to actually move into protected mode. To make
! things as simple as possible, we do no register set-up or anything,
! we let the gnu-compiled 32-bit programs do that. We just jump to
! absolute address 0x00000, in 32-bit protected mode.
mov ax,#0x0001 ! protected mode (PE) bit 保护模式比特位(PE) 置位
lmsw ax ! This is it! 就这样加载机器状态字
jmpi 0,8 ! jmp offset 0 of segment 8 (cs) 跳转到 cs 段偏移 0处
! 上面语句中偏移地址是0,而段值 8 已经是保护模式下的段选择符了。
! This routine checks that the keyboard command queue is empty
! No timeout is used - if this hangs there is something wrong with
! the machine, and we probably couldn't proceed anyway.
empty_8042:
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
in al,#0x64 ! 8042 status port
test al,#2 ! is input buffer full?
jnz empty_8042 ! yes - loop
ret
! 全局描述符表开始处
gdt:
.word 0,0,0,0 ! dummy 第一个描述符为空,不使用
! 在 GDT 表里这里的偏移量是 0x08,它是内核代码段选择符的值
.word 0x07FF ! 8Mb - limit=2047 (2048*4096=8Mb) 段限长
.word 0x0000 ! base address=0 基地址
.word 0x9A00 ! code read/exec ! 代码段为只读,可执行
.word 0x00C0 ! granularity=4096, 386 ! 颗粒度为4096,32位模式
! 在 GDT 表里这里的偏移量是 0x10,它是内核数据段选择符的值
.word 0x07FF ! 8Mb - limit=2047 (2048*4096=8Mb)
.word 0x0000 ! base address=0
.word 0x9200 ! data read/write
.word 0x00C0 ! granularity=4096, 386
! 下面是加载中断描述符表寄存器 idtr 的指令要求的 6字节操作数,前2个字节时 IDT表的限长
! 后4个字节是 idt表在线性地址空间中的 32 位基地址。cpu要求在进入保护模式前设置IDT表,因此这里先设置为空表
idt_48:
.word 0 ! idt limit=0
.word 0,0 ! idt base=0L
! 这是加载全局描述符表寄存器 gdtr 指令要求的6字节操作数,前两个字节是gdt表的限长。
! 后4字节是gdt表的线性基地址。 4字节的线性基地址为 0x0009 <<16 + 0x0200 +gdt
!即 0x90200+gdt ,gdt表的限长设置为2KB,共256个表项。
gdt_48:
.word 0x800 ! gdt limit=2048, 256 GDT entries
.word 512+gdt,0x9 ! gdt base = 0X9xxxx
.text
endtext:
.data
enddata:
.bss
endbss:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号