远程处理Remoting
日程
•应用程序域
•Remoting和原理
•编程式和管理式配置实例
用应用程序域
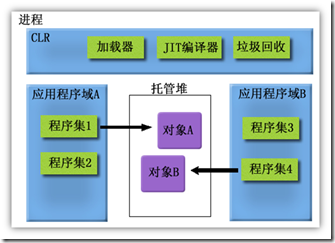
操作系统和运行库环境通常会在应用程序间提供某种形式的隔离。例如,Microsoft Windows 使用进程来隔离应用程序。为确保在一个应用程序中运行的代码不会对其他不相关的应用程序产生不良影响,这种隔离是必需的。
用应用程序域优点
1.在一个应用程序中出现的错误不会影响其他应用程序。因为类型安全的代码不会导致内存错误,所以使用应用程序域可以确保在一个域中运行的代码不会影响进程中的其他应用程序。
2.能够在不停止整个进程的情况下停止单个应用程序。使用应用程序域使您可以卸载在单个应用程序中运行的代码。
3.在一个应用程序中运行的代码不能直接访问其他应用程序中的代码或资源。为了强制实施此隔离,公共语言运行库禁止在不同应用程序域中的对象之间进行直接调用。要在各域之间传递对象,可以复制这些对象,或通过代理访问这些对象。如果复制对象,那么对该对象的调用为本地调用。也就是说,调用方和被引用的对象位于同一应用程序域中。如果通过代理访问对象,那么对该对象的调用为远程调用。在此情况下,调用方和被引用的对象位于不同的应用程序域中。域间调用所采用的远程调用基础结构与两个进程间的调用或两台计算机间的调用的基础结构相同。因此,被引用的对象的元数据必须对于两个应用程序域均可用,以便用 JIT 正确编译该方法调用。如果调用域对被调用对象的元数据没有访问权,则编译可能失败,并引发类型为 System.IO.FileNotFound 的异常。
4.代码行为的作用范围由它运行所在的应用程序决定。换言之,应用程序域将提供应用程序版本策略等配置设置、它所访问的任意远程程序集的位置,以及加载到该域中的程序集的位置信息。
5.向代码授予的权限可以由代码运行所在的应用程序域来控制。
CLR与应用程序域中
.net CLR本身是一套采用非托管C++实现的Windows动态链接库。这些动态链接库提供了托管理堆、垃圾回收器、即时编译器、程序集解析器和加载器及其托管代码需要的其他元给。应用程序域的作用就是使它加载的程序集能够访问这些服务,事实上,这就是应用程序域连接托管世界的秘诀。然而有一点很重要:同一进程的所有应用程序域共享同一托管堆。
应用程序域类
AppDomain表示应用程序域,它是一个应用程序在其中执行的独立环境。
Console.WriteLine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.FriendlyName);
Console.Read();
当需要应用程序域时,公共语言运行库宿主会自动创建它们。不过,您可以创建自己的应用程序域并将它们加载到需要亲自管理的程序集中。您也可以创建从中执行代码的应用程序域。
创建应用程序域中
AppDomain domain = AppDomain.CreateDomain(“mydomain"); Console.WriteLine("Host domain: " + AppDomain.CurrentDomain.FriendlyName); Console.WriteLine("child domain: " + domain.FriendlyName);
卸载应用程序域
AppDomain.Unload(domain)
Remoting
利用 .NET 远程处理,可以方便地生成广泛分布的应用程序,而不论应用程序组件是全部集中在一台计算机上,还是分布在世界各地。生成的客户端应用程序可以使用同一台计算机(或可通过其网络连接到的任何其他计算机)上其他进程中的对象。您还可以在同一进程中使用 .NET 远程处理与其他应用程序域进行通信。
.NET 远程处理为进程间通信提供了一种抽象方法,它能够将可远程处理的对象从特定的客户端或服务器应用程序域以及特定的通信机制中分离出来。因此,它可以灵活、轻松地进行自定义。您可以用一种通信协议来替换另一种通信协议,或用一种序列化格式来替换另一种序列化格式,而不用重新编译客户端或服务器。此外,远程处理系统假定没有特殊的应用程序模型。您可以从 Web 应用程序、控制台应用程序、Windows 服务等您要使用的几乎任何应用程序进行通信。远程处理服务器还可以是任意类型的应用程序域。任何应用程序都可以承载远程处理对象,进而为其计算机或网络上的任何客户端提供服务。
若要使用 .NET 远程处理生成一个应用程序,并让其中两个组件直接跨应用程序域边界进行通信,只需要生成以下内容:
1.一个可远程处理的对象。
2.一个服务端应用程序域用(也叫宿主应用程序域中),于侦听针对该对象的请求。
3.一个客户端应用程序域,用于发出针对该对象的请求。
由于客户端和服务端不一定在一个程序域或不一定在同一台机器上,所以客户端调用远程对象就成为问题。客户端在不同应用程序域调用对象时使用代理连接到远程对象。代理是一个提供了和真实对象完全一样的接口、公共方法、属性等成员的对象。在运行过程中,.NET Remoting基于对象元数据生成代理。代理只提供接口,不提供对象的状态,因为对象的真正状态在宿主应用程序域中存储。代理在这里只转发调用。转发调用到一个对象叫封送处理。封送处理的目标是让客户端调用服务端时感觉不到是在与远端对象交流,而是与本地对象在交流。
如果通过代理来访问对象,该对象必需是从 MarshalByRefObject抽象类派生。
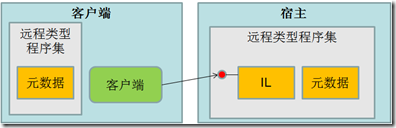
宿主应用程序域中
.net将包含服务器对象的应用程序域称为宿主应用程序域。要成为一个宿主,应用程序域必须在.net中注册自己,让.net知道宿主可以接受那些对象的远程调用,以怎样的方式调用。宿主必须在客户端调用前运行。
客户端在编译时,需要远程对象,因为只需要对象内类型成员列表的元数据,不需要IL代码,用远程对象成员来完成远程对象的调用。宿主是需要远程对象的全部数据的,因为不但要调用还要维护对象内部数据的状态。
远程对象类型
.net对于跨域边界访问提供了两种选择:
1.按值封送
2.按引用封送
按值封送
就是把一个对象序死到一个流,然后在远程应用程序域反序列化成对象。
按引用封送
采用引用封送时,客户羰通过一个代理来访问远程对象,代理会转发所有的调用给实际对象。为了指明一个对象是引用封送,类必须派生自MarshalByRefObject,这个类派生的对象始终和创建它的应用程序域绑定,永不脱离该域。
引用封送
客户端激活
服务器端激活
Single-Call
Singleton
激活方式
客户端激活:为每个客户端在宿主上创建一个新对象,并且这个对象会一直在宿主上存在,不被垃圾回收器回收。
Single-Call激活:当客户端使用一个服务器激活Single-Call对象时,.net为每个方法调用创建一个新地象,让其为调用服务,然后销毁。
Single-Call工作步骤:
1.对象代表远程客户端执行一个方法调用
2.当方法调用返回时,如果对象实现了IDisposable接口,.net调用对象的IDisposable.Dispose()。.net释放所有对该对象的引用,让其准备被垃圾回收。其间,客户端继续持有指向代理的一个引用,但是它不知道真的对象其实已经被销毁了。
3.客户端在代理上进行另一个调用。
4.代理转发调用到远程服务器。
5..net创建一个对象并且调用其方法。
●
Singleton激活:为所有客户端提供了一个单一的,共知的对象。当第一个客户端试图访问时,Singleton被创建。后续客户端创建的新对象的调用和后结的访问都跑旱船引导到同一个Singleton对象。
Remoting架构
编程式信道注册-客户端激活
远程对象
public class MyClass:MarshalByRefObject
{
public MyClass()
{
string con = "时间:" + DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss") + "远程对象构造函数被调用。";
File.AppendAllText(@"F:/a.txt", con + "\r\n");
}
public void WriteFile(string content)
{
string con = "时间:" + DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss") + " 内容:" + content;
File.AppendAllText(@"F:/a.txt", con+"\r\n");
}
}
宿主
using RemoteServer;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Tcp;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Http;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Ipc;
using System.Runtime.Remoting;
private void ServerHostDialog_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
IChannel tcpChannel = new TcpChannel(12345);
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(tcpChannel,false);
IChannel httpChannel = new HttpChannel(45678);
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(httpChannel,false );
IChannel ipcChannel = new IpcChannel("MyIPC");
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(ipcChannel,true );
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Type serverType = typeof(MyClass);
RemotingConfiguration.RegisterActivatedServiceType(serverType);
}
客户端
using RemoteServer;
using System.Runtime.Remoting;
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MyClass obj= new MyClass();
obj.WriteFile("名柄为"+this.Handle .ToString ());
}
Type serverType = typeof(MyClass);
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
RemotingConfiguration.RegisterActivatedClientType(serverType, “tcp://localhost:12345”);//第二个参数可换成: http://localhost:45678或ipc://MyIPC
}
编程式信道注册-Single Call激活
远程对象不变
宿主
using RemoteServer;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Tcp;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Http;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Ipc;
using System.Runtime.Remoting;
private void ServerHostDialog_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
IChannel tcpChannel = new TcpChannel(12345);
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(tcpChannel,false);
IChannel httpChannel = new HttpChannel(45678);
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(httpChannel,false );
IChannel ipcChannel = new IpcChannel("MyIPC");
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(ipcChannel,true );
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Type serverType = typeof(MyClass); RemotingConfiguration.RegisterWellKnownServiceType(serverType,“RemoteServer”, WellKnownObjectMode.SingleCall);//RemoteServer为远程对象的名称空间
}
客户端
using RemoteServer;
using System.Runtime.Remoting;
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MyClass obj= new MyClass();
obj.WriteFile("名柄为"+this.Handle .ToString ());
}
Type serverType = typeof(MyClass);
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
RemotingConfiguration.RegisterWellKnownClientType(serverType, "tcp://localhost:12345/RemoteServer");
//第二个参数可换成: http://localhost:45678/RemoteServer或ipc://MyIPC/RemoteServer
}
编程式信道注册-Singleton激活
远程对象不变
宿主
using RemoteServer;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Tcp;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Http;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Ipc;
using System.Runtime.Remoting;
private void ServerHostDialog_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
IChannel tcpChannel = new TcpChannel(12345);
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(tcpChannel,false);
IChannel httpChannel = new HttpChannel(45678);
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(httpChannel,false );
IChannel ipcChannel = new IpcChannel("MyIPC");
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(ipcChannel,true );
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Type serverType = typeof(MyClass); RemotingConfiguration.RegisterWellKnownServiceType(serverType,“RemoteServer”, WellKnownObjectMode. Singleton);//RemoteServer为远程对象的名称空间
}
客户端
using RemoteServer;
using System.Runtime.Remoting;
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MyClass obj= new MyClass();
obj.WriteFile("名柄为"+this.Handle .ToString ());
}
Type serverType = typeof(MyClass);
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
RemotingConfiguration.RegisterWellKnownClientType(serverType, "tcp://localhost:12345/RemoteServer");
//第二个参数可换成: http://localhost:45678/RemoteServer或ipc://MyIPC/RemoteServer
}
管理式配置
依照上面的例子,远程对象不变,只用在宿主端和客户端的项目中添加“应用程序配置文件”(App.config)文件。
配置文件保存后的名称为:应用程序名.exe.config
比如宿主的配置文件名为RemoteServerHost.exe.config
客户商配置文件名为Client.exe.config
在宿主中和客户端,读取配置文件
在Main函数中
using System.Runtime.Remoting;
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
RemotingConfiguration.Configure(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.FriendlyName + ".config",false);
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
远程对象依然不变
宿主端配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<system.runtime.remoting >
<application>
<service>
<!--<activated type="RemoteServer.MyClass,RemoteServer"></activated>-->
<!--<wellknown type="RemoteServer.MyClass,RemoteServer" mode="Singleton" objectUri="RemoteServer"></wellknown>-->
<wellknown type="RemoteServer.MyClass,RemoteServer" mode="SingleCall" objectUri="RemoteServer"></wellknown>
</service>
<channels>
<channel ref="tcp" port="8005"></channel>
<channel ref="http" port="8006"></channel>
<channel ref="ipc" portName="MyIPC"></channel>
</channels>
</application>
</system.runtime.remoting>
</configuration>
客户端配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<system.runtime.remoting >
<application>
<!--<client url="tcp://localhost:8005">-->
<!--<activated type="RemoteSrerver.MyClass,ServerAssembly"></activated>-->
<!--</client>-->
<client>
<wellknown type="RemoteServer.MyClass,RemoteServer" url="tcp://localhost:8005/RemoteServer"></wellknown>
</client>
</application>
</system.runtime.remoting>
</configuration>
一句话总结:Remoting就是把对象分开到不同的应用程序域中执行的技术。
《asp.net core精要讲解》 https://ke.qq.com/course/265696
《asp.net core 3.0》 https://ke.qq.com/course/437517
《asp.net core项目实战》 https://ke.qq.com/course/291868
《基于.net core微服务》 https://ke.qq.com/course/299524



(8WX2T%7DP84XDV_thumb.jpg)