01_spring源码分析-XmlBeanFactory
Spring源码分析之BeanFactory
献自己:
枯燥无味的学习之路有时真的是无法静下心来苦心钻研;没有掌声,没有鲜花,只有自己内心浮躁不安。
谨记:戒骄戒躁,潜心求知。
一、工程代码如下:
//实体类
public class Person { private String name; public String getName() { return "Axuduo"; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
//测试类
public class TestBean { @Test public void getPerson(){ BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("spring-bean.xml")); Person person = (Person) beanFactory.getBean("person"); Assert.assertEquals("Axuduo",person.getName()); } }
//配置文件:spring-bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="person" class="com.oops.pojo.Person"/> </beans>
二、基础容器XmlBeanFactory
首先将分析实例化XmlBeanFactory开始;对应代码:
BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("spring-bean.xml"));
1、封装配置文件
时序图如下:
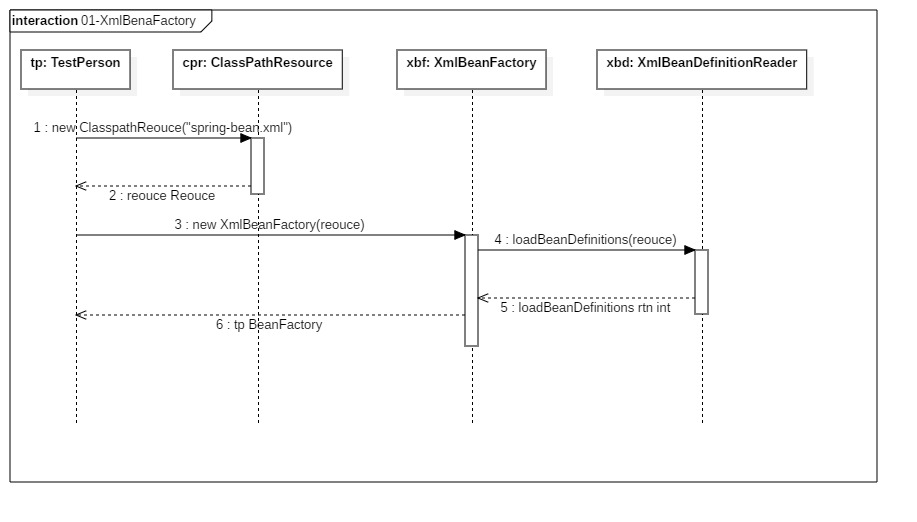
归纳:测试类首先调用ClassPathResouce的构造函数,构造Resource资源文件的实例对象;将Resource对象传递给XMLBeanFactory进行实例化该对象初始化。
那么,ClassPathResouce都做了哪些操作呢?
其实Spring对其内部使用到的资源实现了自己的抽象结构,Resource接口封装底层资源。其中InputStreamSource接口封装任何可能返回InputStream的类,它只定义了一个方法getInputStream方法,该方法返回一个InputStream对象。
在得到InputStream后就可以利用Resource及其子类为我们提供的特性进行后续开发了。有了Resource接口便可以对所有资源文件统一处理了。具体Resource接口如下:
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource { /** * 是否存在*/ boolean exists(); /** * 可读性*/ default boolean isReadable() { return exists(); } /** * 是否打开状态*/ default boolean isOpen() { return false; } /** * 是否是一个文件*/ default boolean isFile() { return false; } /** * 获取URL资源*/ URL getURL() throws IOException; /** * 获取URI资源*/ URI getURI() throws IOException; /** * 获取文件资源*/ File getFile() throws IOException; /** * 取消读取*/ default ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException { return Channels.newChannel(getInputStream()); } /** * 内容长度*/ long contentLength() throws IOException; /** * 最后修改时间*/ long lastModified() throws IOException; /** * 创建一个相对资源*/ Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException; /** * 获取文件名*/ @Nullable String getFilename(); /** * 获取文件描述*/ String getDescription(); }
当通过Resource相关类完成了对配置文件进行封装后;配置文件的读取工作就全部交给XmlBeanFactory来处理了。
2、XmlBeanFactory
XmlBeanFactory通过封装后的Resource进行实例化对象。代码如下:
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory { private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this); /** * 构造函数需要:Resource 对象*/ public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException { this(resource, null); } /** * 待自身构造调用;委派至XMLBeanDeinitionReader*/ public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException { super(parentBeanFactory); // 注意父类中执行了两个或多个类的自动装配功能 this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); } }
3、加载Bean
首先看一下时序图
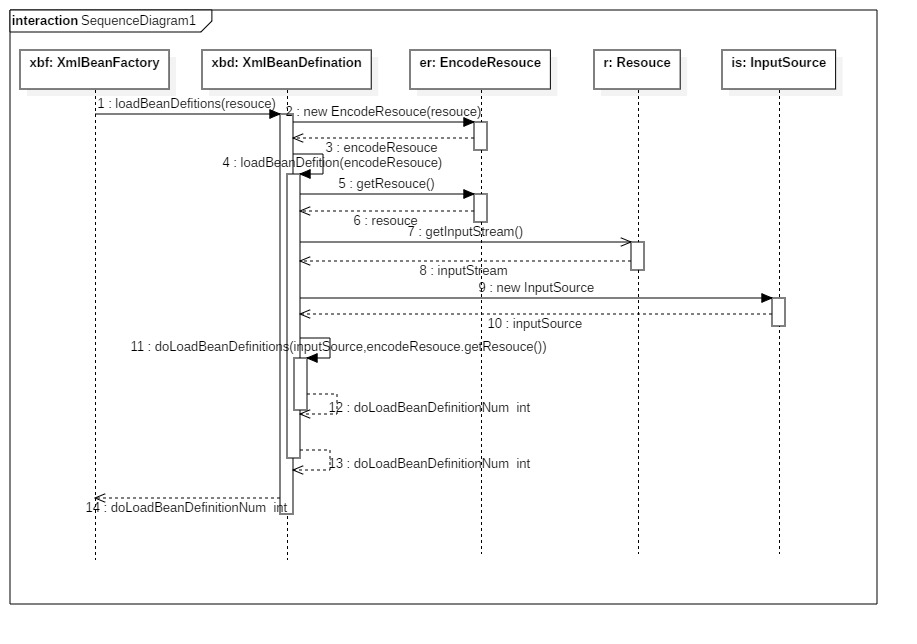
流程梳理:
1、封装资源文件。当进入XMlBeanDefiinitionReader后首先对参数Resource使用EncodedResource类进行封装。
2、获取输入流。从Resouce中获取对应的InputStream 并构造InputSource.
3、通过构造的InputSource实例和Resouce实例继续调用函数doLoadBeanDefinitions.
EncodeResource主要是对资源文件进行编码处理;如果有指定编码则使用指定编码;没有则采用默认。方法如下
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource)); }
通过上面的对资源文件的处理后将进入最核心的部位了:doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource,Resouce resource)
//代码经过去除catch部位
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { try { Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); // 将资源文件传缓存 document int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); // 执行注册 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource); } return count; } }
至此可以清晰的看见只有两部操作:1、转换Document;2、执行注册;
到此完成注册流程。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号