IPC之实例复习
一.IPC概念
1.//AIDL中支持以下的数据类型
//1. 基本数据类型
//2. String 和CharSequence
//3. List 和 Map ,List和Map 对象的元素必须是AIDL支持的数据类型;
//4. AIDL自动生成的接口(需要导入-import)
//5. 实现android.os.Parcelable 接口的类(需要导入-import)
2.aidl通信的步骤:
服务器端和客户端(最简单的为例):两个进程角色的具体使用步骤:
服务器端(Service)
步骤1:新建定义AIDL文件,并声明该服务需要向客户端提供的接口
步骤2:在Service子类中实现AIDL中定义的接口方法,并定义生命周期的方法(onCreat、onBind())
步骤3:在AndroidMainfest.xml中注册服务 & 声明为远程服务
客户端(Client)
步骤1:拷贝服务端的AIDL文件到目录下
步骤2:使用Stub.asInterface接口获取服务器的IBinder,将IBinder对象传换成了ICalculate接口对象。根据需要调用服务提供的接口方法
步骤3:通过Intent指定服务端的服务名称和所在包,绑定远程Service
二. AIDL用法:
1. 生成AIDL文件
首先创建一个AIDL文件,在AndroidStudio中当创建一个AIDL文件时会自动为创件一个AILD文件夹,用于存放AIDL文件。创建完之后重新rebuild会自动生成aidl实现类。
在下面例子中,将Service单独作为一个应用在系统中运行,在另一个用于访问Service的client也单独作为一个应用运行在系统中。
这样保证两个程序分别运行在两个进程中。

AIDL简单用法:
在Service中我们对客户端传来的两个整数做了一次加法运算并返回到客户端中。
按钮: Bind Service
按钮: UnBind Service
按钮: 2+4
AIDL代码
// ICalculate.aidl
package com.ljd.aidl;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface ICalculate {
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
int add(int first, int second);
}
服务端代码:
package com.ljd.aidl.service;
import android.app.Service;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import com.ljd.aidl.ICalculate;
public class CalculateService extends Service {
public CalculateService() {}
private Binder mBinder = new ICalculate.Stub(){
@Override
public int add(int first, int second) {
return first + second;
}
};
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}
}
客户端代码
package com.ljd.aidl.activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import com.ljd.aidl.ICalculate;
import com.ljd.aidl.client.R;
public class Demo1Activity extends AppCompatActivity {
private final String TAG = "DEMO1";
private boolean mIsBindService;
private ICalculate mCalculate;
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
Log.d(TAG,"bind service success");
mCalculate = ICalculate.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
//重新绑定Service防止系统将服务进程杀死而产生的调用错误。
bindService();
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
setContentView(R.layout.activity_demo1);
mIsBindService = false;
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
unbindService();
ButterKnife.unbind(this);
super.onDestroy();
}
public void onClickButton(View v) {
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.bind_demo1_btn:
bindService();
break;
case R.id.unbind_demo1_btn:
unbindService();
break;
case R.id.calculate_btn:
if (mIsBindService && mCalculate != null ){
int result = mCalculate.add(2,4);
Log.d(TAG,String.valueOf(result));
} else {
Toast.makeText("not bind service").show();
}
break;
}
}
private void bindService(){
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction("com.ljd.aidl.action.CALCULATE_SERVICE");
bindService(intent,mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
mIsBindService = true;
}
private void unbindService(){
if(mIsBindService){
mIsBindService = false;
unbindService(mConnection);
}
}
}
2. AIDL高级用法(自定义Bean类):
演示:
在计算机商店中需要采购笔记本进行销售,在服务端中我们添加两台笔记本,在客户端中我们为商店加购一台dell笔记本。
Button: Bind Service
Button: Unbind Service
Button: Test
Button: Clear
1. 实体类代码 首先构建一个计算机实体类,并且实现Parcelable接口,在AndroidStudio中会为我们自动构造代码。 package com.ljd.aidl.entity; import android.os.Parcel; import android.os.Parcelable; public class ComputerEntity implements Parcelable{ public int computerId; //id public String brand; //品牌 public String model; //型号 public ComputerEntity(int computerId, String brand, String model) { this.brand = brand; this.computerId = computerId; this.model = model; } protected ComputerEntity(Parcel in) { computerId = in.readInt(); brand = in.readString(); model = in.readString(); } public static final Creator<ComputerEntity> CREATOR = new Creator<ComputerEntity>() { @Override public ComputerEntity createFromParcel(Parcel in) { return new ComputerEntity(in); } @Override public ComputerEntity[] newArray(int size) { return new ComputerEntity[size]; } }; @Override public int describeContents() { return 0; } @Override public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) { dest.writeInt(computerId); dest.writeString(brand); dest.writeString(model); } } 2.AIDL代码: 1)在AIDL中对实体类进行声明,包名和文件名必须与实体类一致。在AndroidStudio中新建一个与实体类同名的AIDL文件会报错,需要先用一个其它名字,然后修改与实体类名一致即可。 package com.ljd.aidl.entity; //包名必须和对用实体类的包名一致 //Declare any non-default types here with import statements parcelable ComputerEntity; 2) 添加两个接口,分别为添加一台笔记本和获取全部笔记本,在该文件中使用到了ComputerEntity类,显示的import进来。 package com.ljd.aidl; import com.ljd.aidl.entity.ComputerEntity; // Declare any non-default types here with import statements interface IComputerManager { // Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters and return values in AIDL. void addComputer(ComputerEntity computer); List<ComputerEntity> getComputerList(); } 3.服务端代码 package com.ljd.aidl.service; import android.app.Service; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.IBinder; import android.os.RemoteException; import com.ljd.aidl.IComputerManager; import com.ljd.aidl.entity.ComputerEntity;import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList; public class ComputerService extends Service { private CopyOnWriteArrayList<ComputerEntity> mComputerList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); public ComputerService() { } private final IComputerManager.Stub mBinder = new IComputerManager.Stub() { @Override public void addComputer(ComputerEntity computer){ mComputerList.add(computer); } @Override public List<ComputerEntity> getComputerList(){ return mComputerList; } }; @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); mComputerList.add(new ComputerEntity(0,"apple","macbookpro")); mComputerList.add(new ComputerEntity(1,"microsoft","surfacebook")); mComputerList.add(new ComputerEntity(2,"dell","XPS13")); } @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return mBinder; } } 注意:在该类中使用了CopyOnWriteArrayList,CopyOnWriteArrayList能够自动进行线程同步。可是在AIDL中接收和返回的只能是ArrayList,其实AIDL支持的是抽象的List, 在Binder中会按照List访问数据并最终形成一个ArrayList,所以在AIDL中返回的还是一个ArrayList。 由于Binder是有可能会意外死亡的,也就是Service所在进程被系统杀死,这时候我们调用Service的方法就会失败。 1)在第一例子中通过onServiceDisconnected方法中重新绑定服务。 2)在此例采用另外一种方法即死亡代理方式: 由于在Binder中提供两个配对方法linkToDeath()和unlinkToDeath(),通过linkToDeath可以给Binder设置一个死亡代理,Binder死亡时回调binderDied(), 在binderDied方法中我们重新绑定服务即可。 4.客户端代码 package com.ljd.aidl.activity; import android.content.ServiceConnection; import android.os.IBinder; import android.os.RemoteException;
import com.ljd.aidl.IComputerManager; import com.ljd.aidl.client.R; import com.ljd.aidl.entity.ComputerEntity; public class Demo2Activity extends AppCompatActivity{ LinearLayout mShowLinear; private boolean mIsBindService; private IComputerManager mRemoteComputerManager; private IBinder.DeathRecipient mDeathRecipient = new IBinder.DeathRecipient() { @Override public void binderDied() { if(mRemoteComputerManager != null){ mRemoteComputerManager.asBinder().unlinkToDeath(mDeathRecipient,0); mRemoteComputerManager = null; bindService();//重新绑定service } } }; private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { mIsBindService = true; Toast.makeText(this,"bind service success").show(); mRemoteComputerManager = IComputerManager.Stub.asInterface(service); mRemoteComputerManager.asBinder().linkToDeath(mDeathRecipient,0); } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { mRemoteComputerManager = null; } }; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_demo2); mIsBindService = false; } @Override protected void onDestroy() { unbindService(); ButterKnife.unbind(this); super.onDestroy(); } public void onClickButton(View v) { switch (v.getId()){ case R.id.bind_demo2_btn: bindService(); break; case R.id.unbind_demo2_btn: unbindService(); break; case R.id.test_demo2_btn: if (!mIsBindService || mRemoteComputerManager == null){ Toast.makeText("not bind service").show(); return; } List<ComputerEntity> computerList = mRemoteComputerManager.getComputerList(); for (int i =0;i<computerList.size();i++){ String str = "computerId:" + String.valueOf(computerList.get(i).computerId) + " brand:" + computerList.get(i).brand + " model:" + computerList.get(i).model ; TextView textView = new TextView(this); textView.setText(str); mShowLinear.addView(textView); } break; case R.id.clear_demo2_btn: mShowLinear.removeAllViews(); break; } } private void bindService(){ Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("com.ljd.aidl.action.COMPUTER_SERVICE"); mIsBindService = bindService(intent,mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } private void unbindService(){ if(!mIsBindService){ return; } mIsBindService = false; unbindService(mConnection); } }
3. AIDL用法拓展:
当我们需要一种笔记本的时候,由于商店缺货,这时候我们会给卖家说一声,我所需要的这款笔记本到货后通知我。也就成了所谓的观察者模式。
在Android系统中为我们提供了一个RemoteCallbackList,RemoteCallbackList是系统专门用来删除跨进程的listener接口,并且在RemoteCallbackList中自动实现了线程同步功能。
演示:
客户端注册服务以后,服务端每隔三秒会添加一台笔记本,并通知给客户端显示。
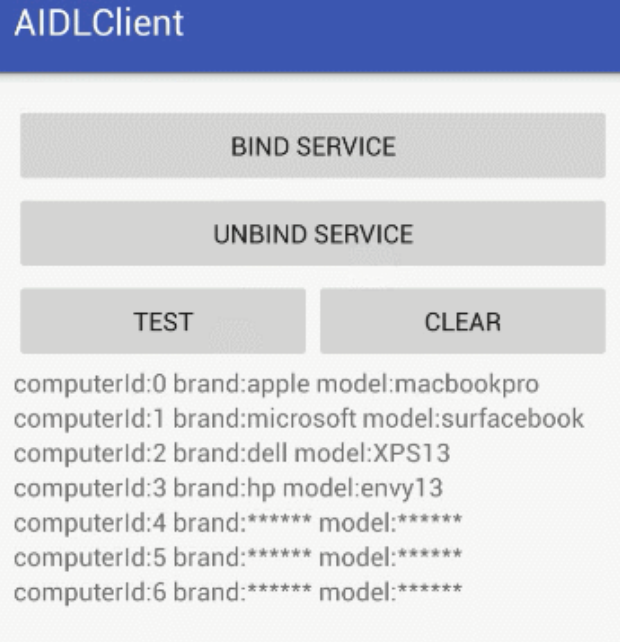
AIDL代码 到货后的AIDL监听接口 package com.ljd.aidl; import com.ljd.aidl.entity.ComputerEntity; // Declare any non-default types here with import statements interface IOnComputerArrivedListener { /** * Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters * and return values in AIDL. */ void onComputerArrived(in ComputerEntity computer); } 在IComputerManager接口中添加两个方法。显示importIOnComputerArrivedListener ,即使在同一个包下面。 // IComputerManagerObserver.aidl package com.ljd.aidl; import com.ljd.aidl.entity.ComputerEntity; import com.ljd.aidl.IOnComputerArrivedListener; // Declare any non-default types here with import statements interface IComputerManagerObserver { /** * Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters * and return values in AIDL. */ void addComputer(in ComputerEntity computer); List<ComputerEntity> getComputerList(); void registerUser(IOnComputerArrivedListener listener); void unRegisterUser(IOnComputerArrivedListener listener); } 服务端代码 import android.app.Service; import android.os.Binder; import android.os.IBinder; import android.os.RemoteCallbackList; import android.os.RemoteException; import com.ljd.aidl.IComputerManagerObserver; import com.ljd.aidl.IOnComputerArrivedListener; import com.ljd.aidl.entity.ComputerEntity; import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean; public class ComputerObserverService extends Service{ public ComputerObserverService() { } private CopyOnWriteArrayList<ComputerEntity> mComputerList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); private RemoteCallbackList<IOnComputerArrivedListener> mComputerArrivedListenerList = new RemoteCallbackList<>(); private AtomicBoolean mIsServiceDestroy = new AtomicBoolean(false); private Binder mBinder = new IComputerManagerObserver.Stub(){ @Override public void addComputer(ComputerEntity computer) { mComputerList.add(computer); } @Override public List<ComputerEntity> getComputerList(){ return mComputerList; } @Override public void registerUser(IOnComputerArrivedListener listener){ mComputerArrivedListenerList.register(listener); } @Override public void unRegisterUser(IOnComputerArrivedListener listener){ mComputerArrivedListenerList.unregister(listener); } }; @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); mComputerList.add(new ComputerEntity(0,"apple","macbookpro")); mComputerList.add(new ComputerEntity(1,"microsoft","surfacebook")); mComputerList.add(new ComputerEntity(2,"dell","XPS13")); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (!mIsServiceDestroy.get()){ try { Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000); ComputerEntity computer = new ComputerEntity(mComputerList.size(),"******","******"); mComputerList.add(computer); final int COUNT = mComputerArrivedListenerList.beginBroadcast(); //通知所有注册过的用户 for (int i=0;i<COUNT;i++){ IOnComputerArrivedListener listener = mComputerArrivedListenerList.getBroadcastItem(i); if (listener != null){ listener.onComputerArrived(computer); } } mComputerArrivedListenerList.finishBroadcast(); } } } }).start(); } @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return mBinder; } @Override public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); mIsServiceDestroy.set(true); } } 注意:RemoteCallbackList并不是一个List,所以我们不能像操作List一样操作RemoteCallbackList。 并且遍历RemoteCallbackList时,beginBroadcast和finishBroadcast是配对使用的。 客户端代码 import android.content.ComponentName;import android.content.ServiceConnection; import android.os.Handler; import android.os.IBinder; import android.os.Message; import com.ljd.aidl.IComputerManagerObserver; import com.ljd.aidl.IOnComputerArrivedListener; import com.ljd.aidl.client.R; import com.ljd.aidl.entity.ComputerEntity; public class Demo3Activity extends AppCompatActivity { LinearLayout mShowLinear; private boolean mIsBindService; private static final int MESSAGE_COMPUTER_ARRIVED = 1; private IComputerManagerObserver mRemoteComputerManager; private Handler mHandler = new Handler() { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { switch (msg.what){ case MESSAGE_COMPUTER_ARRIVED: ComputerEntity computer = (ComputerEntity)msg.obj; String str = "computerId:" + String.valueOf(computer.computerId) + " brand:" + computer.brand + " model:" + computer.model ; TextView textView = new TextView(Demo3Activity.this); textView.setText(str); mShowLinear.addView(textView); break; } } }; private IBinder.DeathRecipient mDeathRecipient = new IBinder.DeathRecipient() { @Override public void binderDied() { if(mRemoteComputerManager != null){ mRemoteComputerManager.asBinder().unlinkToDeath(mDeathRecipient,0); mRemoteComputerManager = null; bindService(); } } }; private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { mIsBindService = true; Toast.makeText("bind service success").show(); mRemoteComputerManager = IComputerManagerObserver.Stub.asInterface(service); mRemoteComputerManager.asBinder().linkToDeath(mDeathRecipient,0); } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { mRemoteComputerManager = null; } }; private IOnComputerArrivedListener mOnComputerArrivedListener = new IOnComputerArrivedListener.Stub(){ @Override public void onComputerArrived(ComputerEntity computer) throws RemoteException { mHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_COMPUTER_ARRIVED,computer).sendToTarget(); } }; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); mIsBindService = false; } @Override protected void onDestroy() { unbindService(); super.onDestroy(); } public void onClickButton(View v){ switch (v.getId()){ case R.id.bind_demo3_btn: bindService(); break; case R.id.unbind_demo3_btn: Toast.makeText("unbind service success"); unbindService(); break; case R.id.test_demo3_btn: if (!mIsBindService || mRemoteComputerManager == null){ Toast.makeText(this,"not bind service"); return; } try { ComputerEntity computer = new ComputerEntity(3,"hp","envy13"); mRemoteComputerManager.addComputer(computer); List<ComputerEntity> computerList = mRemoteComputerManager.getComputerList(); for (int i =0;i<computerList.size();i++){ String str = "computerId:" + String.valueOf(computerList.get(i).computerId) + " brand:" + computerList.get(i).brand + " model:" + computerList.get(i).model ; TextView textView = new TextView(this); textView.setText(str); mShowLinear.addView(textView); } mRemoteComputerManager.registerUser(mOnComputerArrivedListener); } break; case R.id.clear_demo3_btn: mShowLinear.removeAllViews(); break; } } private void bindService(){ Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("com.ljd.aidl.action.COMPUTER_OBSERVER_SERVICE"); mIsBindService = bindService(intent,mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } private void unbindService(){ if(!mIsBindService){ return; } if (mRemoteComputerManager != null && mRemoteComputerManager.asBinder().isBinderAlive()){ try { mRemoteComputerManager.unRegisterUser(mOnComputerArrivedListener); } } unbindService(mConnection); mIsBindService = false; } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号