升级:In-Place Upgrade升级MySQL5.6.26
升级需谨慎,事前先备份
MySQL升级的实质是对数据字典的升级,数据字典有:sys、mysql、information_schema、performance_schema 。
MySQL升级的两种方式:
1、in-place upgrade(适合小版本的升级)
关闭当前的MySQL,替换原来的安装目录和my.cnf配置文件,mysql_upgrade脚本升级数据字典,在现有的数据目录上重启MySQL,
特点:不改变数据文件,升级速度快;这种方式先停掉数据库,在进行升级操作,所以停机时间长;但,不可以跨操作系统,不可以跨大版本(5.5—>5.7).
2、logical upgrade(适合不同操作系统的MySQL升级,大版本之间的升级)
使用mysqldump 或 mydumper 导入导出数据,实现版本的升级。可以利用gtid或者主从增量恢复数据。
特点:可以跨操作系统,跨大版本,整理表碎片;但,数据量大的情况下升级速度慢,容易出现乱码等问题。升级时间长,但是切换时间短
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1.升级方法介绍
单台服务器在mysql5.7上启动mysql5.6的配置文件
ip:192.168.163.21
mysql:5.6.26->5.7.29
2.升级步骤
2.1操作之前,查看版本
[root@rhel7 /]# /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql --version

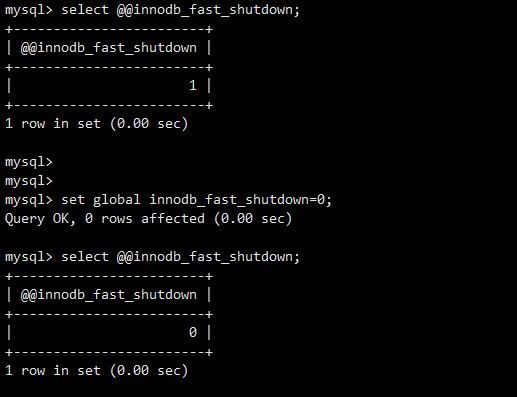
2.2设置参数innodb_fast_shutdown为0
需要将innodb_fast_shutdown参数设置为0
set global innodb_fast_shutdown=0;
注:innodb_fast_shutdown有0、1、2三个值。
参数值为0代表MySQL关闭,InnoDB需要完成所有的full purge和merge Insert buffer操作,这个过程需要一定的时间,有时可能会花上几个小时。
参数值为1是该参数的默认值,表示关闭MySQL时不完成full purge和Merge insert buffe操作,但是缓冲池中的脏页还是会写到磁盘中。
参数值为2时,表示既不完成full purge和Merge insert buffer操作,也不将缓冲池中的脏页刷新到磁盘,而是将日志写入日志文件中。
mysql> set global innodb_fast_shutdown=0;
mysql> select @@innodb_fast_shutdown;
2.3关闭MySQL服务
命令如下:
[root@rhel7 local]# /etc/init.d/mysql stop
2.4替换MySQL软件
需要执行unlink mysql命令,取消链接到MySQL 5.6.47版本的链接文件。
解压新版本的MySQL软件包,然后重新做链接并赋予MySQL权限。命令如下:
cd /usr/local
unlink mysql
tar -zxvf mysql-5.7.20-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
ln -s mysql-5.7.20-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 mysql
chown -R mysql:mysql mysql
[root@rhel7 /]# cp -rp /data /data56
[root@rhel7 /]# cp /etc/init.d/mysql mysql56
[root@rhel7 /]# cp -rp /usr/local/mysql /usr/local/mysql56
[root@rhel7 local]# tar -zxvf mysql-5.7.32-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
[root@rhel7 local]# mv mysql /tmp
[root@rhel7 local]# mv mysql-5.7.32-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 mysql
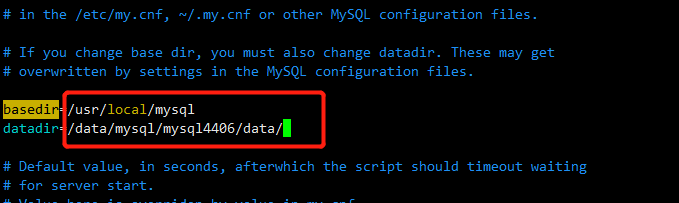
2.5替换参数文件
把MySQL5.6的配置文件替换成5.7版本的my.cnf。
[root@rhel7 /]# cp /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysql
2.6启动MySQL实例
注:在启动过程中,需要添加–skip-grant-tables和–skip-networking参数,来保证没有 任何的应用连接,让升级过程更加安全。
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking &
或者采用服务模式
[root@rhel7 /]# /etc/init.d/mysql restart

2.7升级系统表数据字典信息
[root@rhel7 local]# /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql_upgrade -uroot -p
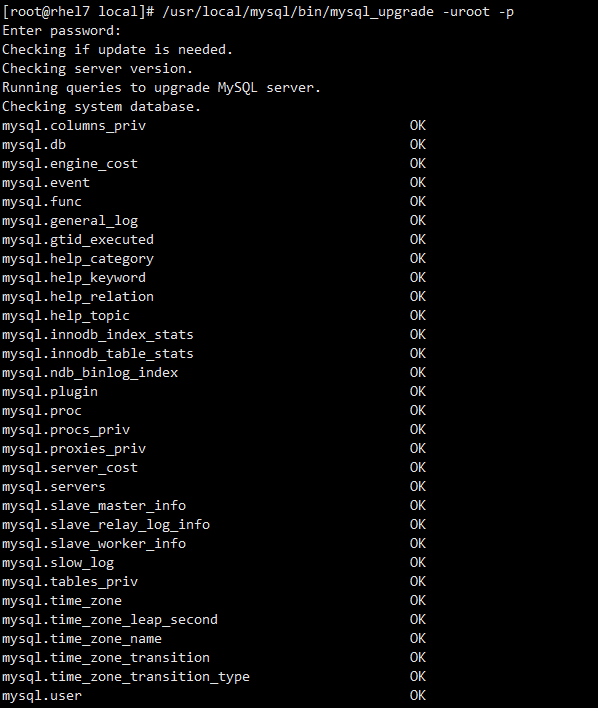
没有报错,表示系统表数据字典信息升级成功。
2.8重启MySQL服务
首先停掉MySQL服务,命令如下:
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqladmin -uroot -poracle123 shutdown
然后正常启动MySQL服务,命令如下:
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf &
说明:正常启动MySQL数据库,不要使用–skip-grant-tables和-skip-networking参数。
[root@rhel7 /]# /etc/init.d/mysql restart
2.9验证MySQL版本
目前己经是MySQL5.7版本,证明升级成功:
[root@rhel7 local]# /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql -V
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql Ver 14.14 Distrib 5.7.20, for linux-glibc2.12 (x86_64) using EditLine wrapper



.jpg)

【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· DeepSeek在M芯片Mac上本地化部署