P3008 [USACO11JAN]Roads and Planes G
题目描述
[USACO11JAN]Roads and Planes G
题面翻译
题面描述
Farmer John 正在一个新的销售区域对他的牛奶销售方案进行调查。他想把牛奶送到 \(T\) 个城镇 ( \(1 \le T \le 25,000\) ),编号为 \(1\) 到 \(T\) 。这些城镇之间通过 \(R\) 条道路 ( \(1 \le R \le 50,000\) ,编号为 \(1\) 到 \(R\) ) 和 \(P\) 条航线 ( \(1 \le P \le 50,000\) ,编号为 \(1\) 到 \(P\) ) 连接。每条道路 \(i\) 或者航线 \(i\) 连接城镇 \(A_i\) ( \(1 \le A_i \le T\) )到 \(B_i\) ( \(1 \le B_i \le T\) ),花费为 \(C_i\) 。
对于道路 \(0 \le C_i \le 10,000\) ;然而航线的花费很神奇,花费 \(C_i\) 可能是负数( \(-10,000 \le C_i \le 10,000\) )。道路是双向的,可以从 \(A_i\) 到 \(B_i\),也可以从 \(B_i\) 到 \(A_i\) ,花费都是 \(C_i\) 。然而航线与之不同,只可以从 \(A_i\) 到 \(B_i\) 。
事实上,由于最近恐怖主义太嚣张,为了社会和谐,出台 了一些政策保证:如果有一条航线可以从 \(A_i\) 到 \(B_i\),那么保证不可能通过一些道路和航线从 \(B_i\) 回到 \(A_i\) 。由于 \(FJ\) 的奶牛世界公认十分给力,他需要运送奶牛到每一个城镇。他想找到从发送中心城镇 \(S\) ( \(1 \le S \le T\)) 把奶牛送到每个城镇的最便宜的方案,或者知道这是不可能的。
输入格式
共 \(R+P+1\) 行
第 \(1\) 行:四个整数 \(T\) , \(R\) , \(P\) 和 \(S\) ,分别表示城镇的数量,道路的数量,航线的数量和中心城镇。
第 \(2\) 到 \(R+1\) 行:每行三个整数 \(A_i\) , \(B_i\) 和 \(C_i\) ,描述一条道路。
第 \(R+2\) 到 \(R+P+1\) 行:每行三个整数 \(A_i\) , \(B_i\) 和 \(C_i\) ,描述一条航线。
输出格式
共 \(T\) 行,第 \(i\) 行输出城市 \(S\) 到城市 \(i\) 的最小花费。如果不能到达,输出NO PATH
题目描述
Farmer John is conducting research for a new milk contract in a new territory. He intends to distribute milk to T (1 <= T <= 25,000) towns conveniently numbered 1..T which are connected by up to R (1 <= R <= 50,000) roads conveniently numbered 1..R and/or P (1 <= P <= 50,000) airplane flights conveniently numbered 1..P.
Either road i or plane i connects town A_i (1 <= A_i <= T) to town B_i (1 <= B_i <= T) with traversal cost C_i. For roads, 0 <= C_i <= 10,000; however, due to the strange finances of the airlines, the cost for planes can be quite negative (-10,000 <= C_i <= 10,000).
Roads are bidirectional and can be traversed from A_i to B_i or B_i to A_i for the same cost; the cost of a road must be non-negative.
Planes, however, can only be used in the direction from A_i to B_i specified in the input. In fact, if there is a plane from A_i to B_i it is guaranteed that there is no way to return from B_i to A_i with any sequence of roads and planes due to recent antiterror regulation.
Farmer John is known around the world as the source of the world's finest dairy cows. He has in fact received orders for his cows from every single town. He therefore wants to find the cheapest price for delivery to each town from his distribution center in town S (1 <= S <= T) or to know that it is not possible if this is the case.
MEMORY LIMIT: 64MB
输入格式
* Line 1: Four space separated integers: T, R, P, and S
* Lines 2..R+1: Three space separated integers describing a road: A_i, B_i and C_i
* Lines R+2..R+P+1: Three space separated integers describing a plane: A_i, B_i and C_i
输出格式
* Lines 1..T: The minimum cost to get from town S to town i, or 'NO PATH' if this is not possible
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
6 3 3 4
1 2 5
3 4 5
5 6 10
3 5 -100
4 6 -100
1 3 -10
样例输出 #1
NO PATH
NO PATH
5
0
-95
-100
提示
6 towns. There are roads between town 1 and town 2, town 3 and town 4, and town 5 and town 6 with costs 5, 5 and 10; there are planes from town 3 to town 5, from town 4 to town 6, and from town 1 to town 3 with costs -100, - 100 and -10. FJ is based in town 4.
FJ's cows begin at town 4, and can get to town 3 on the road. They can get to towns 5 and 6 using planes from towns 3 and 4. However, there is no way to get to towns 1 and 2, since they cannot go
backwards on the plane from 1 to 3.
思路
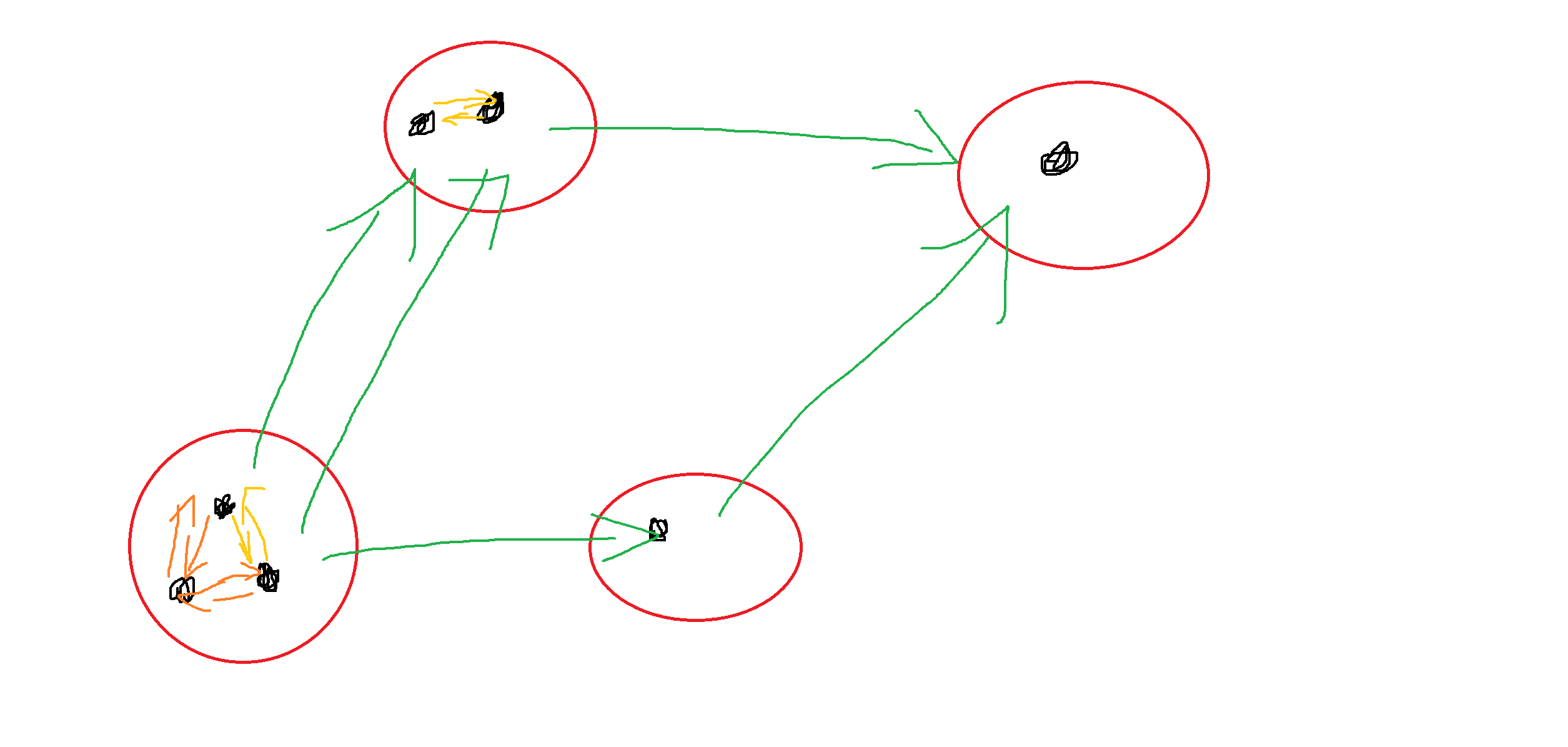
将所有点按照未加入航线时的连通性分为若干区块,同一区块内部边权全非负,可以跑dijkstra,区块之间拓扑排序后从前往后扫即可。实际过程是dijkstra处理完一个区块中找到拓扑排序的下一个区块,在dijkstra完后继续对下一个区块进行dijkstra。按照拓扑序处理最终得到最短路。
代码
// Problem: P3008 [USACO11JAN]Roads and Planes G
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3008
// Memory Limit: 125 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
// Created Time: 2022-07-11 22:16:50
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
//fw
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define zp ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
#define pii pair <int, int>
#define pll pair <ll, ll>
#define endl '\n'
#define il inline
#define pb push_back
#define fi first
#define se second
#define lc u<<1
#define rc u<<1|1
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N=3e4,M=2e5+10;
int h[N],e[M],ne[M],w[M],idx,n,mp,mr,S;
vector<int>block[N];
int id[N],bcnt;
bool st[N];
int dist[N],din[N];
queue<int>q;
void add(int a,int b,int c)
{
e[idx]=b;
w[idx]=c;
ne[idx]=h[a];
h[a]=idx++;
}
void dfs(int u,int bid)//dfs获得每个点在哪个区块
{
id[u]=bid;
block[bid].pb(u);
for(int i=h[u];~i;i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];
if(!id[j])
{
dfs(j,bid);
}
}
}
void dijkstra(int bid)
{
priority_queue<pii,vector<pii>,greater<pii>>heap;
for(auto u:block[bid])heap.push({dist[u],u});//将区块内部的所有点加入堆
while(heap.size())
{
auto t=heap.top();
heap.pop();
int dis=t.first,ver=t.second;
if(st[ver])continue;
st[ver]=true;
for(int i=h[ver];~i;i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];
if(id[j]!=id[ver]&&--din[id[j]]==0)q.push(id[j]);//如果这条边指向区块外部,并且指向区块入读为0就加入拓扑队列
if(dist[j]>dist[ver]+w[i])//更新最短路
{
dist[j]=dist[ver]+w[i];
if(id[j]==id[ver])heap.push({dist[j],j});//同一区块内部求最短路
}
}
}
}
void topsort()
{
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);//将所有距离初始化,不能放dijkstra里,不然会重复初始化,覆盖答案
dist[S]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=bcnt;i++)//将入读为0的区块入队
{
if(!din[i])
q.push(i);
}
while(q.size())
{
auto t=q.front();
q.pop();
dijkstra(t);//按拓扑序求区块内部的最短路
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>mr>>mp>>S;
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
while(mr--)//输入道路
{
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
add(a,b,c);
add(b,a,c);
}
//给每个点分出区块
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!id[i])
{
bcnt++;
dfs(i,bcnt);
}
}
while(mp--)//输入航线
{
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
add(a,b,c);
din[id[b]]++;//统计区块入度
}
//按区块拓扑排序;
topsort();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(dist[i]>INF/2)cout<<"NO PATH"<<endl;
else cout<<dist[i]<<endl;
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号