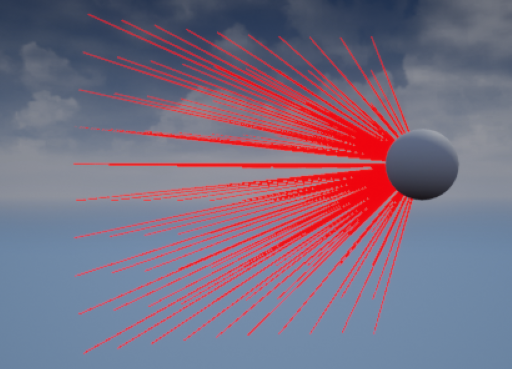
雷达效果
相位阵雷达效果

一个简单思路:
在一个扇形范围内,用多个射线检测来每tick判断
点击查看代码
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "GameFramework/Actor.h"
#include "Components/SphereComponent.h"
#include "MyActor.generated.h"
UCLASS()
class TEST_API AMyActor : public AActor
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
// Sets default values for this actor's properties
AMyActor();
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, BlueprintReadWrite, Category = "Detection Settings")
float HorizontalDetectionAngle;
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, BlueprintReadWrite, Category = "Detection Settings")
float VerticalDetectionAngle;
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, BlueprintReadWrite, Category = "Detection Settings")
float RaycastAngleIncrement;
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, BlueprintReadWrite, Category = "Detection Settings")
float RaycastLength;
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable,Category = "Detection")
TArray<AActor*> PerformRaycastDetection();
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere ,BlueprintReadWrite)
USphereComponent* DetectionSphere;
protected:
// Called when the game starts or when spawned
virtual void BeginPlay() override;
public:
// Called every frame
virtual void Tick(float DeltaTime) override;
};
// Sets default values
AMyActor::AMyActor()
{
// Set this actor to call Tick() every frame. You can turn this off to improve performance if you don't need it.
PrimaryActorTick.bCanEverTick = false;
DetectionSphere = CreateDefaultSubobject<USphereComponent>(TEXT("Detection Sphere"));
RootComponent = DetectionSphere;
HorizontalDetectionAngle = 45.0f;
VerticalDetectionAngle = 45.0f;
RaycastAngleIncrement = 5.0f;
RaycastLength = 1000.0f;
}
TArray<AActor*> AMyActor::PerformRaycastDetection()
{
TArray<AActor*> DetectedActors;
if (!DetectionSphere)
return DetectedActors;
FVector StartLocation = DetectionSphere->GetComponentLocation();
FRotator Rotation = DetectionSphere->GetComponentRotation();
float HalfHorizontalAngle = HorizontalDetectionAngle * 0.5f;
float HalfVerticalAngle = VerticalDetectionAngle * 0.5f;
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning,TEXT("HalfHorizontalAngle %f HalfVerticalAngle %f RaycastAngleIncrement %f"), HalfHorizontalAngle, HalfVerticalAngle, RaycastAngleIncrement);
for (float VerticalAngle = -HalfVerticalAngle; VerticalAngle <= HalfVerticalAngle; VerticalAngle += RaycastAngleIncrement)
{
for (float HorizontalAngle = -HalfHorizontalAngle; HorizontalAngle <= HalfHorizontalAngle; HorizontalAngle += RaycastAngleIncrement)
{
FRotator RayRotation = Rotation;
RayRotation.Pitch += VerticalAngle;
RayRotation.Yaw += HorizontalAngle;
FVector EndLocation = StartLocation + RayRotation.Vector() * RaycastLength;
DrawDebugLine(GetWorld(), StartLocation, EndLocation, FColor::Red, false, -1.0f, 0, 2.0f);
FHitResult HitResult;
if (GetWorld()->LineTraceSingleByChannel(HitResult, StartLocation, EndLocation, ECC_Visibility))
{
AActor* HitActor = HitResult.GetActor();
if (HitActor)
{
DetectedActors.AddUnique(HitActor);
}
}
}
}
return DetectedActors;
}
最后效果
吧drawdebugline换成drawdebugcone

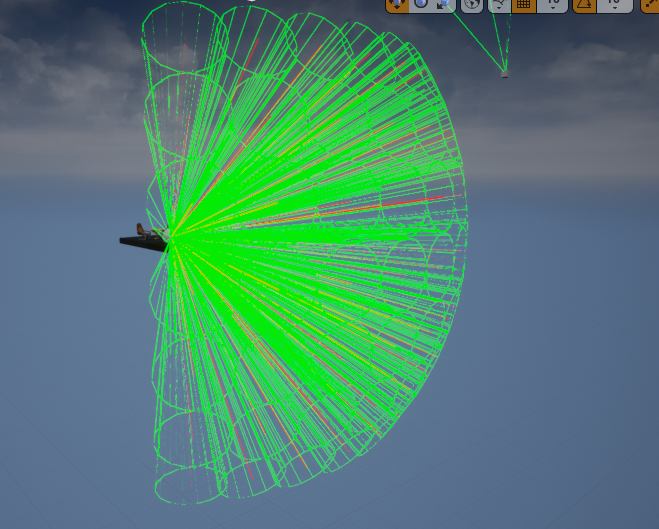
各个参数可调
无人机编队
无人机之间连线

无人机外包洛信息
三维包洛算法
如果要处理三维坐标点的凸包,那么我们需要稍微修改一下算法。基本思路是仍然使用Graham扫描算法,但需要对叉积函数和极角排序方式进行调整。
下面是修改后的C++代码:
cppCopy code#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
// 定义三维点的结构体
struct Point3D {
double x, y, z;
Point3D(double x, double y, double z) : x(x), y(y), z(z) {}
};
// 叉积计算函数
double crossProduct(const Point3D& p1, const Point3D& p2, const Point3D& p3) {
double x1 = p2.x - p1.x, y1 = p2.y - p1.y, z1 = p2.z - p1.z;
double x2 = p3.x - p1.x, y2 = p3.y - p1.y, z2 = p3.z - p1.z;
return x1 * y2 * z1 - x1 * z2 * y1 - y1 * x2 * z1 + y1 * z2 * x1 + z1 * x2 * y1 - z1 * y2 * x1;
}
// Graham扫描算法实现
vector<Point3D> grahamScan(vector<Point3D>& points) {
// 找到z坐标最小的点作为起点
auto start = min_element(points.begin(), points.end(), [](const Point3D& p1, const Point3D& p2) {
return p1.z < p2.z || (p1.z == p2.z && p1.y < p2.y) || (p1.z == p2.z && p1.y == p2.y && p1.x < p2.x);
});
// 按极角排序点
sort(points.begin(), points.end(), [&start](const Point3D& p1, const Point3D& p2) {
double cross = crossProduct(*start, p1, p2);
if (cross == 0) {
double d1 = sqrt((p1.x - start->x) * (p1.x - start->x) + (p1.y - start->y) * (p1.y - start->y) + (p1.z - start->z) * (p1.z - start->z));
double d2 = sqrt((p2.x - start->x) * (p2.x - start->x) + (p2.y - start->y) * (p2.y - start->y) + (p2.z - start->z) * (p2.z - start->z));
return d1 < d2;
}
return cross > 0;
});
// 构造凸包
vector<Point3D> hull;
for (const Point3D& p : points) {
while (hull.size() > 1 && crossProduct(hull[hull.size() - 2], hull.back(), p) <= 0) {
hull.pop_back();
}
hull.push_back(p);
}
return hull;
}
int main() {
// 假设无人机坐标存储在drones_list中
vector<vector<Point3D>> drones_list = {
{Point3D(0, 3, 1), Point3D(1, 1, 2), Point3D(2, 2, 3), Point3D(4, 4, 4), Point3D(0, 0, 0), Point3D(1, 2, 1), Point3D(3, 1, 2), Point3D(3, 3, 3)},
{Point3D(2, 3, 1), Point3D(4, 1, 2), Point3D(6, 4, 3), Point3D(5, 2, 4), Point3D(3, 0, 0), Point3D(1, 2, 1), Point3D(0, 1, 2)}
};
vector<vector<Point3D>> convex_hulls;
for (const auto& drones : drones_list) {
convex_hulls.push_back(grahamScan(drones));
}
// 输出结果
for (const auto& hull : convex_hulls) {
cout << "Convex Hull: ";
for (const Point3D& p : hull) {
cout << "(" << p.x << ", " << p.y << ", " << p.z << ") ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
但对于三维情况,就需要做一些额外的处理来确定各个面是由哪些点构成。一种常见的方法是通过计算点的顺序来确定面的方向,具体步骤如下:
对凸包点坐标序列做一个深拷贝,记为hull_copy。
按照右手法则,判断hull_copy中相邻三个点的顺序是否为逆时针(对于凸多面体,逆时针为内侧normal方向)。如果为顺时针,则将中间那个点与前一个点交换位置。
重复上一步,直到hull_copy中所有相邻三点的顺序都为逆时针。
最终hull_copy中,每相邻三点就构成了一个面。
下面是使用C++实现上述方法的代码:
cppCopy code#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Point3D {
double x, y, z;
Point3D(double x, double y, double z) : x(x), y(y), z(z) {}
};
vector<vector<Point3D>> getFaces(const vector<Point3D>& hull) {
vector<vector<Point3D>> faces;
vector<Point3D> hull_copy = hull;
// 确保点的顺序为逆时针
for (int i = 0; i < hull_copy.size(); i++) {
int j = (i + 1) % hull_copy.size();
int k = (i + 2) % hull_copy.size();
Point3D& p1 = hull_copy[i];
Point3D& p2 = hull_copy[j];
Point3D& p3 = hull_copy[k];
double x1 = p2.x - p1.x, y1 = p2.y - p1.y, z1 = p2.z - p1.z;
double x2 = p3.x - p1.x, y2 = p3.y - p1.y, z2 = p3.z - p1.z;
double cross_x = y1 * z2 - z1 * y2;
double cross_y = z1 * x2 - x1 * z2;
double cross_z = x1 * y2 - y1 * x2;
if (cross_x < 0 || (cross_x == 0 && cross_y < 0) || (cross_x == 0 && cross_y == 0 && cross_z < 0)) {
swap(hull_copy[j], hull_copy[k]);
}
}
// 构造面
for (int i = 0; i < hull_copy.size(); i++) {
int j = (i + 1) % hull_copy.size();
int k = (i + 2) % hull_copy.size();
faces.push_back({hull_copy[i], hull_copy[j], hull_copy[k]});
}
return faces;
}
int main() {
// 假设无人机坐标存储在drones_list中
vector<Point3D> drones = {
Point3D(0, 3, 1), Point3D(1, 1, 2), Point3D(2, 2, 3), Point3D(4, 4, 4),
Point3D(0, 0, 0), Point3D(1, 2, 1), Point3D(3, 1, 2), Point3D(3, 3, 3)
};
vector<Point3D> hull = grahamScan(drones); // 获取凸包点
vector<vector<Point3D>> faces = getFaces(hull); // 获取构成面的点
// 输出结果
cout << "Convex Hull Faces:" << endl;
for (const auto& face : faces) {
cout << "Face: ";
for (const Point3D& p : face) {
cout << "(" << p.x << ", " << p.y << ", " << p.z << ") ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
在上述代码中,getFaces函数实现了确定每个面的点序列的逻辑。它首先对hull做一个拷贝,然后遍历这个拷贝,对每三个相邻点,根据叉积判断它们的顺序是否为逆时针,如果不是则交换中间两点的位置。最终hull_copy中每三个相邻点就构成了一个面。
在main函数中,我们首先获取无人机坐标的凸包hull,然后调用getFaces(hull)获取每个面的点序列,最后输出结果。
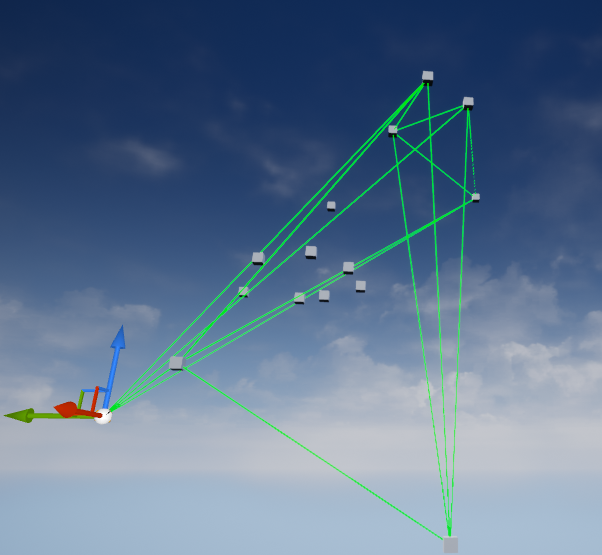
效果不好,算法有问题
接收组播消息脚本(绑定到所有接口)
python
复制代码
import socket
import struct
配置组播地址和端口
MCAST_GRP = '224.1.1.1'
MCAST_PORT = 5007
IFACE = '0.0.0.0' # 绑定到所有接口
创建 UDP 套接字
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM, socket.IPPROTO_UDP)
允许多个程序绑定到同一个地址和端口
sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
绑定到指定端口
sock.bind((IFACE, MCAST_PORT))
告诉操作系统加入组播组
mreq = struct.pack("4s4s", socket.inet_aton(MCAST_GRP), socket.inet_aton(IFACE))
sock.setsockopt(socket.IPPROTO_IP, socket.IP_ADD_MEMBERSHIP, mreq)
监听组播消息
print(f"Listening for multicast messages on {MCAST_GRP}:{MCAST_PORT}")
while True:
data, addr = sock.recvfrom(1024)
print(f"Received message from {addr}: {data.decode('utf-8')}")
发送组播消息脚本
python
复制代码
import socket
import struct
import time
配置发送端的IP和端口
SRC_IP = '192.168.1.100' # 发送端的IP地址
SRC_PORT = 5008 # 发送端的端口
配置组播地址和端口
MCAST_GRP = '224.1.1.1'
MCAST_PORT = 5007
MESSAGE = "Hello, Multicast!"
创建 UDP 套接字
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM, socket.IPPROTO_UDP)
绑定到发送端的IP和端口
sock.bind((SRC_IP, SRC_PORT))
设置组播 TTL(生存时间)
ttl = struct.pack('b', 1)
sock.setsockopt(socket.IPPROTO_IP, socket.IP_MULTICAST_TTL, ttl)
发送组播消息
while True:
sock.sendto(MESSAGE.encode('utf-8'), (MCAST_GRP, MCAST_PORT))
print(f"Sent message: {MESSAGE}")
time.sleep(1)
运行方法


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号