Spring事务
一、Spring事务管理
Spring 支持编程式事务管理以及声明式事务管理两种方式。
- 编程式事务管理是侵入性事务管理,编程式事务每次实现都要单独实现,但业务量大功能复杂时,使用编程式事务无疑是痛苦的,所以并不推荐使用。
- 声明式事务属于无侵入式,不会影响业务逻辑的实现,只需要在配置文件中做相关的事务规则声明或者通过注解的方式,便可以将事务规则应用到业务逻辑中。声明式事务管理建立在AOP之上,其本质是对方法前后进行拦截,然后在目标方法开始之前创建或者加入一个事务,执行完目标方法之后根据执行的情况提交或者回滚。显然声明式事务管理要优于编程式事务管理,这正是Spring倡导的非侵入式的编程方式。(必须掌握)
Spring事务的本质其实就是数据库对事务的支持,使用JDBC的事务管理机制就是利用 java.sql.Connection 对象完成对事务的提交
在企业级应用中,多用户访问数据库是常见的场景,这就是所谓的事务的并发。事务并发所可能存在的问题:
- 脏读:一个事务读到另一个事务未提交的更新数据。
- 不可重复读:一个事务两次读同一行数据,可是这两次读到的数据不一样。
- 幻读:一个事务执行两次查询,但第二次查询比第一次查询多出了一些数据行。
- 丢失更新:撤消一个事务时,把其它事务已提交的更新的数据覆盖了。
Spring诞生之后,我们再也无需去处理获得连接、关闭连接、事务提交和回滚等这些操作,使得我们把更多的精力放在处理业务上。Spring并不直接管理事务,而是提供了多种事务管理器,他们将事务管理的职责委托给Hibernate或者JTA等持久化机制所提供的相关平台框架的事务来实现。 Spring事务管理器的接口是 org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager,通过这个接口,Spring为各个平台如JDBC、Hibernate等都提供了对应的事务管理器,但是具体的实现由各个平台自己实现。
事务管理器接口 PlatformTransactionManager 通过 getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) 方法来得到事务,这个方法里面的参数是 TransactionDefinition 类,这个类就定义了一些基本的事务属性。事务属性包含了5个方面
- 是否为只读?
- 传播行为
- 隔离规则
- 回滚规则
- 事务超时
二、事务演示环境准备
1.创建一张表,用来模拟转账的案例
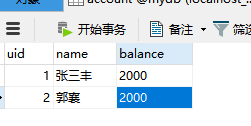
CREATE TABLE `account` ( `uid` int(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `balance` float(255,0) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`uid`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
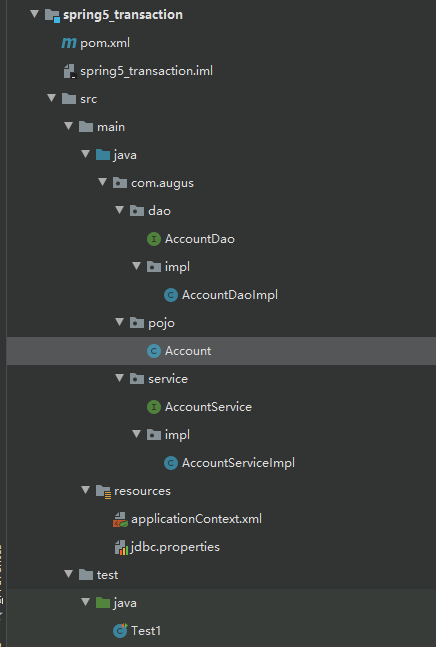
2.项目结构如下图
3.导入依赖和JdbcTemplate相同
<dependencies> <!--引入德鲁伊连接池--> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/druid --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.2.8</version> </dependency> <!--引入MySQL连接依赖--> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.28</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.3.22</version> </dependency> <!--spring切面 的包--> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-aspects --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId> <version>5.3.18</version> </dependency> <!--springJDBC包--> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-jdbc --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>5.3.18</version> </dependency> <!--spring事务控制包--> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-tx --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId> <version>5.3.18</version> </dependency> <!--spring-orm映射依赖包--> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-orm --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId> <version>5.3.18</version> </dependency> <!--织入包 spring-aspects 已经导入该包,这里可以不导入--> <!--<dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.7</version> </dependency>--> <!--aop联盟包--> <dependency> <groupId>aopalliance</groupId> <artifactId>aopalliance</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> </dependency> <!--Apache Commons日志包--> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-logging/commons-logging --> <dependency> <groupId>commons-logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> <!--导入lombok--> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.projectlombok/lombok --> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.18.22</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/junit/junit --> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13.2</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/java</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> </resource> <resource> <directory>src/main/resources</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.xml</include> <include>**/*.properties</include> </includes> </resource> </resources> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <source>6</source> <target>6</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
4.准备配置文件applicationContext.xml,内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd "> <!--开启包扫描--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.augus"></context:component-scan> <!--读取配置文件--> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder> <!--配置德鲁伊连接池--> <bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <property name="username" value="${jdbc_username}"></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc_password}"></property> <property name="url" value="${jdbc_url}"></property> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc_driver}"></property> </bean> <!--配置JDBCTemplate,并向里面注入druidDataSource--> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <!--通过set方法注入连接池--> <property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"></property> </bean> </beans>
5.准备步骤一中创建的表所对应的实体类
package com.augus.pojo; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import java.io.Serializable; @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor @Data public class Account implements Serializable { private Integer uid; private String name; private Double balance; }
6.准备dao层接口和实现类
package com.augus.dao; public interface AccountDao { //转账 int transfer(int id, Double money); }
package com.augus.dao.impl; import com.augus.dao.AccountDao; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Override public int transfer(int id, Double money) { String sql = "update account set balance = balance + ? where uid =?"; return jdbcTemplate.update(sql,money,id); } }
7.准备service层接口和实现类
package com.augus.service; public interface AccountService { //转账 int transfer(int from, int to, Double money); }
package com.augus.service.impl; import com.augus.dao.AccountDao; import com.augus.service.AccountService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired private AccountDao accountDao; @Override public int transfer(int from, int to, Double money) { //统计执行的次数 int rows = 0; //将dao层的方法调用两次,一个加一个减少 rows += accountDao.transfer(from, -money); //这里是减少的意思 rows += accountDao.transfer(to,money); return rows; } }
8.测试代码
import com.augus.service.AccountService; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Test1 { @Test public void testTransaction(){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //获取对象 AccountService accountService = context.getBean(AccountService.class); //调用方法 int rs = accountService.transfer(1, 2, 500.0); System.out.println(rs); } }
三、声明式事务管理( 基于注解方式实现 )
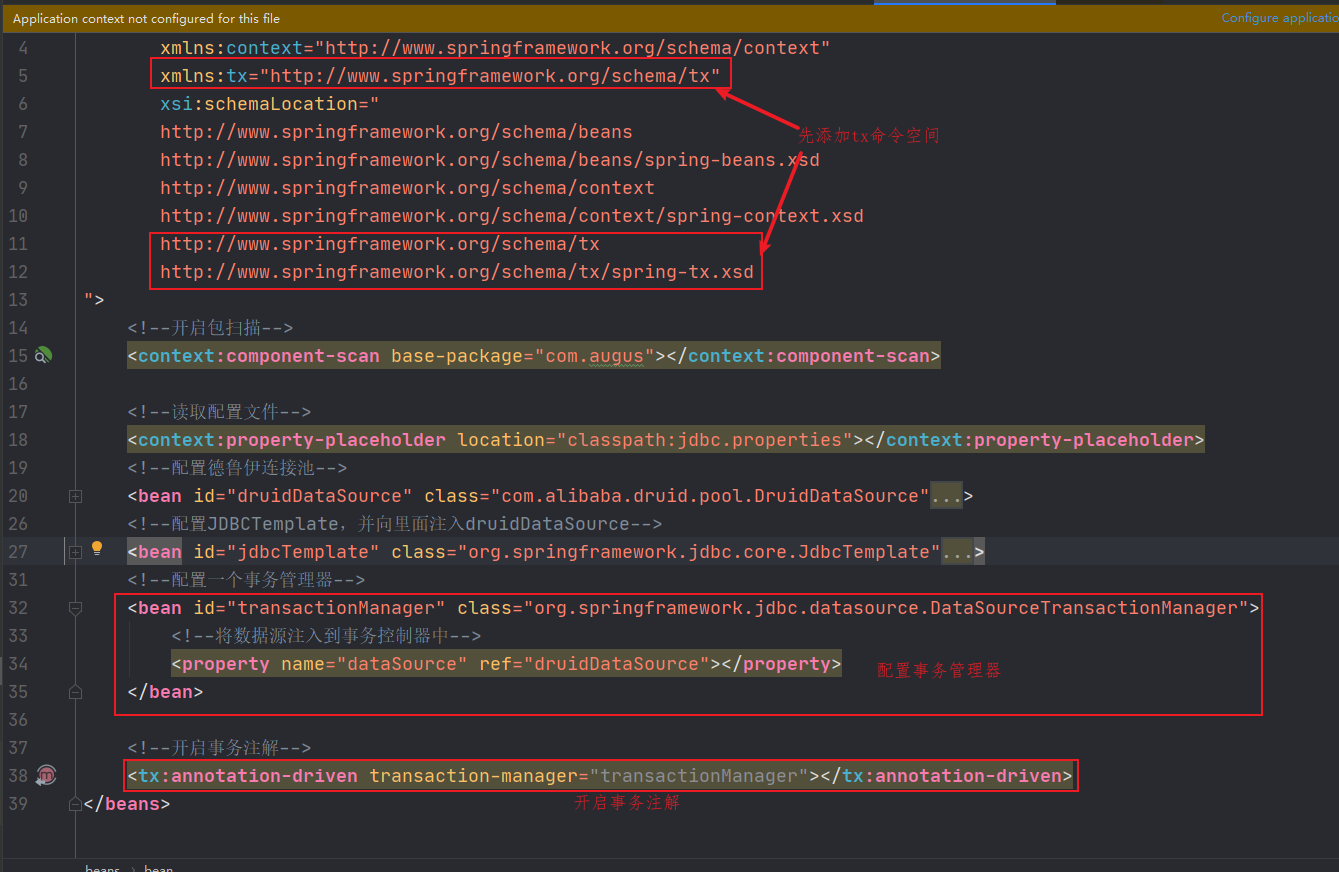
1.注解方式实现事务控制需要在applicationContext.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd "> <!--开启包扫描--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.augus"></context:component-scan> <!--读取配置文件--> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder> <!--配置德鲁伊连接池--> <bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <property name="username" value="${jdbc_username}"></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc_password}"></property> <property name="url" value="${jdbc_url}"></property> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc_driver}"></property> </bean> <!--配置JDBCTemplate,并向里面注入druidDataSource--> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <!--通过set方法注入连接池--> <property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"></property> </bean> <!--配置一个事务管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <!--将数据源注入到事务控制器中--> <property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"></property> </bean> <!--开启事务注解--> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven> </beans>
2.在Service层中添加事务的注解
package com.augus.service.impl; import com.augus.dao.AccountDao; import com.augus.service.AccountService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; @Service //@Transactional //放在类中,会对该类中的所有方法都添加事务控制 public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired private AccountDao accountDao; @Override @Transactional //放在方法上,表示仅仅对当前方法增加了事务控制 public int transfer(int from, int to, Double money) { //统计执行的次数 int rows = 0; //将dao层的方法调用两次,一个加一个减少 rows += accountDao.transfer(from, -money); //这里是减少的意思 //模拟产生异常,这里发生异常,如果没有事务就会出现一个转走了,另一个没收到钱 int i = 1/0; rows += accountDao.transfer(to,money); return rows; } }
3.测试代码
还是之前环境准备的测试代码。但是执行会发现,加上事务控制后。如果再有异常,就会回滚事务
import com.augus.service.AccountService; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Test1 { @Test public void testTransaction(){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //获取对象 AccountService accountService = context.getBean(AccountService.class); //调用方法 int rs = accountService.transfer(1, 2, 500.0); System.out.println(rs); } }
四、声明式事务管理( 基于xml方式实现 )
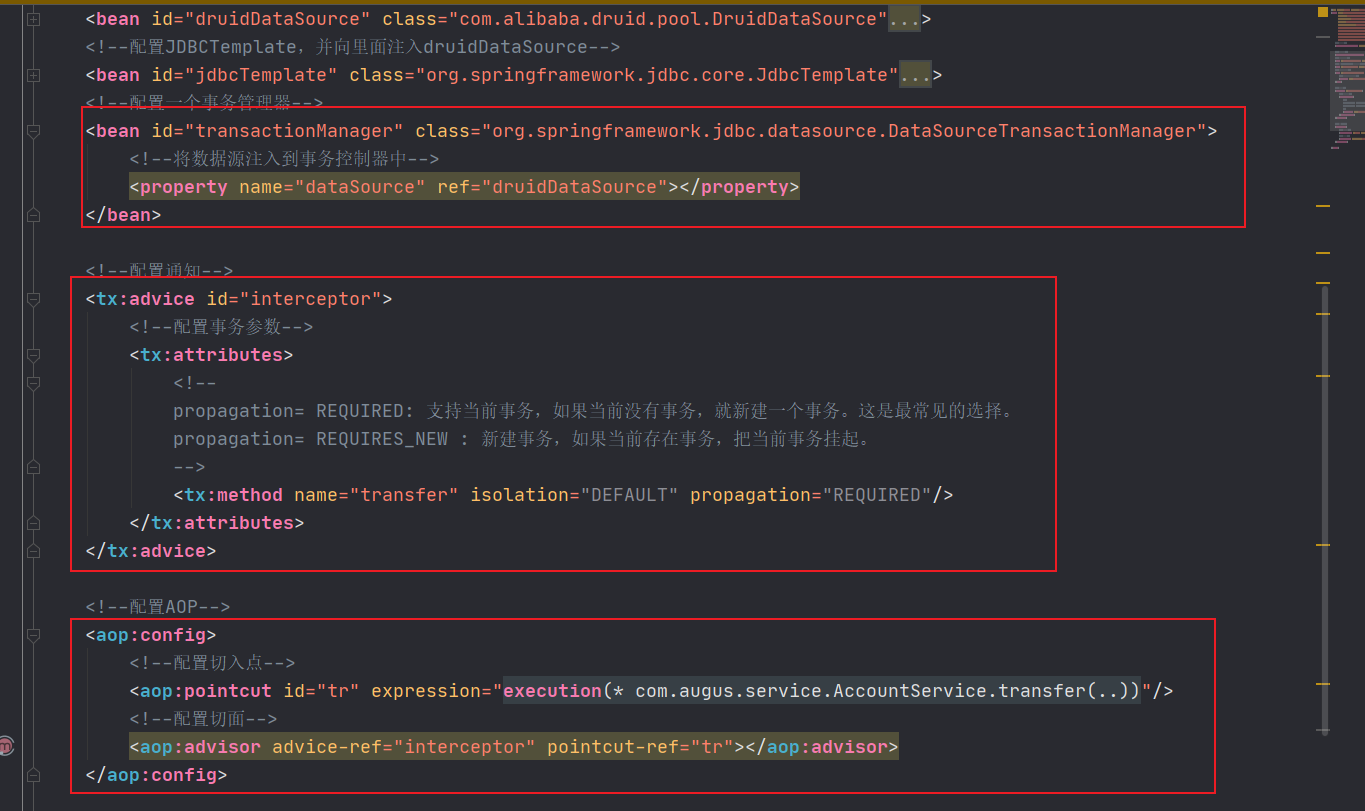
1.applicationContext中,通过AOP实现事务的控制
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!--开启包扫描--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.augus"></context:component-scan> <!--读取配置文件--> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder> <!--配置德鲁伊连接池--> <bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <property name="username" value="${jdbc_username}"></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc_password}"></property> <property name="url" value="${jdbc_url}"></property> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc_driver}"></property> </bean> <!--配置JDBCTemplate,并向里面注入druidDataSource--> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <!--通过set方法注入连接池--> <property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"></property> </bean> <!--配置一个事务管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <!--将数据源注入到事务控制器中--> <property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"></property> </bean> <!--配置通知--> <tx:advice id="interceptor"> <!--配置事务参数--> <tx:attributes> <!-- propagation= REQUIRED: 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务。这是最常见的选择。 propagation= REQUIRES_NEW : 新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。 --> <tx:method name="transfer" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!--配置AOP--> <aop:config> <!--配置切入点--> <aop:pointcut id="tr" expression="execution(* com.augus.service.AccountService.transfer(..))"/> <!--配置切面--> <aop:advisor advice-ref="interceptor" pointcut-ref="tr"></aop:advisor> </aop:config> </beans>
2.service层实现类
上面xml方式配置后,service层中实现类就不需要@Transactional注解
package com.augus.service.impl; import com.augus.dao.AccountDao; import com.augus.service.AccountService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired private AccountDao accountDao; @Override public int transfer(int from, int to, Double money) { //统计执行的次数 int rows = 0; //将dao层的方法调用两次,一个加一个减少 rows += accountDao.transfer(from, -money); //这里是减少的意思 //模拟产生异常,这里发生异常,如果没有事务就会出现一个转走了,另一个没收到钱 int i = 1/0; rows += accountDao.transfer(to,money); return rows; } }
3.测试代码
跟之间一样没有改动,只需要测试,有异常是否会回滚
import com.augus.service.AccountService; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Test1 { @Test public void testTransaction(){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //获取对象 AccountService accountService = context.getBean(AccountService.class); //调用方法 int rs = accountService.transfer(1, 2, 500.0); System.out.println(rs); } }
五、零xml实现事务控制(使用配置类实现事务控制)
1.创建配置类
package com.augus.config; import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager; import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; import javax.sql.DataSource; @Configuration //配置类标志注解 @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.augus") //开启spring包扫描 @PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties") //读取属性配置文件 @EnableTransactionManagement //开启事务注解 public class SpringConfig { //将读取回来赋值给属性 @Value("${jdbc_driver}") private String driver; @Value("${jdbc_url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc_username}") private String username; @Value("${jdbc_password}") private String password; /*创建数据库连接池*/ @Bean public DruidDataSource getDruidDataSource(){ //创建连接对象 DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource(); //设置属性 druidDataSource.setDriverClassName(driver); druidDataSource.setUrl(url); druidDataSource.setUsername(username); druidDataSource.setPassword(password); return druidDataSource; } //创建JdbcTemplate对象 @Bean public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource){ JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(); //设置数据连接池 jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource); return jdbcTemplate; } //创建事务管理器 @Bean public PlatformTransactionManager getPlatformTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource){ DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager(); //设置连接池 dataSourceTransactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource); return dataSourceTransactionManager; } }
2.service层实现类添加事务注解
package com.augus.service.impl; import com.augus.dao.AccountDao; import com.augus.service.AccountService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; @Service public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired private AccountDao accountDao; @Override @Transactional //对该方法开启事务 public int transfer(int from, int to, Double money) { //统计执行的次数 int rows = 0; //将dao层的方法调用两次,一个加一个减少 rows += accountDao.transfer(from, -money); //这里是减少的意思 //模拟产生异常,这里发生异常,如果没有事务就会出现一个转走了,另一个没收到钱 int i = 1/0; rows += accountDao.transfer(to,money); return rows; } }
3.测试代码
import com.augus.config.SpringConfig; import com.augus.service.AccountService; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class Test2 { @Test public void testTransaction(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); //获取对象 AccountService accountService = context.getBean(AccountService.class); //调用方法 int rs = accountService.transfer(1, 2, 500.0); System.out.println(rs); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号