Oracle Day4
P34 序列
序列主要用作为表做自增。
创建一个序列,查询该序列的下一个值:
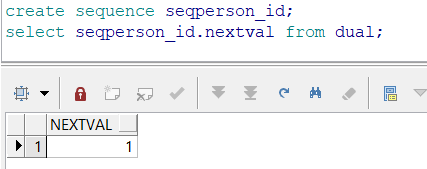
查询序列的当前值:
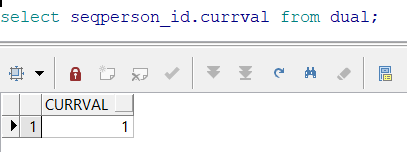
序列的使用:(常用)
在往表格中插入数据时,可以用序列的nextval填入主键,就可以利用它自增的特性了。
P35 索引
索引用于加速数据存取。
但是索引不是越多越好,因为会耗费大量的资源。
其实每张带数据的表都是自动加上索引的,可以选中表格后右击view查看:
![]()
索引分为两类,单例索引和复合索引:
1.单例索引
create index 索引名称 on 表名(列名)
当查询语句where后面用到且只用到这个列名作为查询条件时,就会自动用这个单例索引
2.复合索引
create index 索引名称 on 表名(列名1,列名2)
当查询语句where后面用到且只用到这几个列名(顺序也必须一致)作为查询条件时,就会自动用这个复合索引
P36 plsql介绍
PL/SQL指procedure language,用于sql语言的过程化扩展。包括分支,循环等。比较简洁,高效。
P37 plsql变量
基本语法:declare 声明阶段 begin 语句序列 exception 异常处理 end;
下面看一个简单的定义变量,赋值,输出的语句
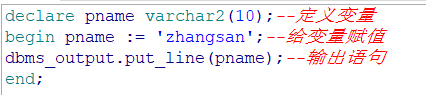
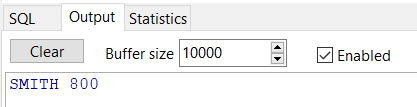
可以在output里看到输出的结果:
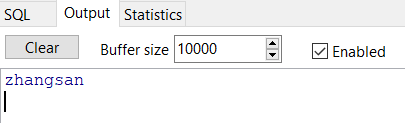
定义常量的写法:
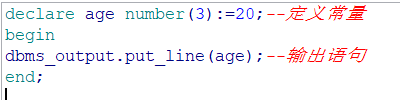
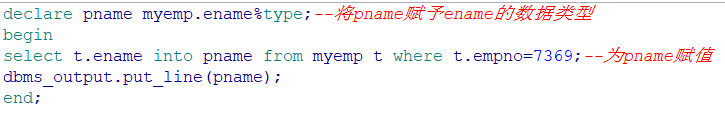
引用数据类型变量的写法(直接引用某表某列的数据类型):(重要!)
select into语句很重要,需要掌握
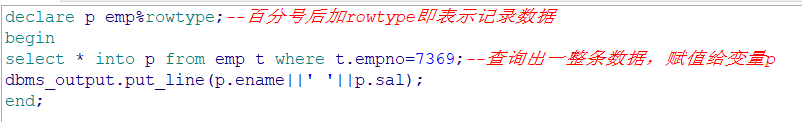
记录型变量:
||表示字符串连接
P38 if分支
写if语句一共有三种写法,下面一一介绍:
写法1:
declare pno number(4):=# begin if pno<5 then dbms_output.put_line('编号小于5'); end if; end;
这里只有一条分支语句。
写法2:
declare pno number(4):=# begin if pno=1 then dbms_output.put_line('我是1'); else dbms_output.put_line('我不是1'); end if; end;
这里有两条分支语句
写法3:
declare pno number(4):=# begin if pno=1 then dbms_output.put_line('我是1'); elsif pno=2 then dbms_output.put_line('我是2'); else dbms_output.put_line('其他'); end if; end;
注意中间的elsif,不是elseif,也不是else if!
P39 loop循环
循环也有三种方法,其中第二种最常用
写法1:
declare total number(4):=0; begin while total<10 loop total:=total+1; dbms_output.put_line(total); end loop; end;
输出结果:

写法2:(最常见,重要)
declare total number(4):=0; begin loop exit when total = 10; total := total+1; dbms_output.put_line(total); end loop; end;
写法3:适合连续数值的遍历
declare total number(4):=0; begin for total in 1..10 loop dbms_output.put_line(total); end loop; end;
P40 游标
游标相当于java中的集合,我们直接通过三个例子来看如何使用游标:
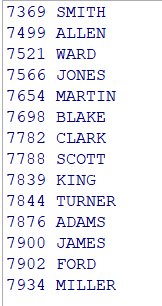
例1:使用游标方式输出emp表中的员工编号和姓名
declare cursor c1 is select * from emp;--定义游标 prec emp%rowtype;--定义prec为记录型变量 begin open c1;--打开游标 loop fetch c1 into prec;--从游标中取值,取值后游标会自动下移一步 exit when c1%notfound; dbms_output.put_line(prec.empno || ' ' || prec.ename); end loop; close c1;--关闭游标 end;
输出内容:
例2:按照员工的工种涨工资,总裁1000元,经理800元,其他人员400元
declare cursor c1 is select * from myemp; --定义游标 prec myemp%rowtype; --定义prec为记录型变量 addsal number(4); begin open c1; --打开游标 loop fetch c1 into prec; --从游标中取值,取值后游标会自动下移一步 exit when c1%notfound; if prec.job = 'PRESIDENT' then addsal := 1000; elsif prec.job = 'MANAGER' then addsal := 800; else addsal := 400; end if; update myemp t set t.sal = t.sal + addsal where t.empno = prec.empno; end loop; close c1; --关闭游标 end;
例3:为部门号为10的员工涨工资
declare cursor c1(dno myemp.deptno%type) is select * from myemp t where t.deptno = dno; --定义游标 prec myemp%rowtype; --定义prec为记录型变量 begin open c1(10); --打开游标 loop fetch c1 into prec; --从游标中取值,取值后游标会自动下移一步 exit when c1%notfound; update myemp t set t.sal = t.sal + 1000 where t.empno = prec.empno; end loop; close c1; --关闭游标 commit; end;
总结:
使用游标通常格式为:
declare 定义一个游标;定义一个记录型变量;
begin 打开游标;开始循环(游标取值,进行各种操作);结束循环;关闭游标;
end
P41 例外
例外就相当于java中的异常,在begin后,end前的exception中进行处理,具体看两个简单的例子:
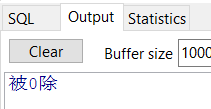
例1:
declare pnum number(4) := 5; begin pnum := pnum / 0; exception when zero_divide then dbms_output.put_line('被0除'); when value_error then dbms_output.put_line('数值转换错误'); when others then dbms_output.put_line('其他异常'); end;
输出结果:
例2:(可以自定义例外)查询部门编号是50的员工(不存在的值)
declare prec emp%rowtype; cursor c1 is select * from emp t where t.deptno = 50; no_data exception; begin open c1; loop fetch c1 into prec; if c1%notfound then raise no_data; end if; end loop; close c1; exception when no_data then dbms_output.put_line('没有员工'); when others then dbms_output.put_line('没有异常'); end;
P42 存储过程
相当于java中的方法
基本语法格式为:
create or replace procedure 存储过程名称(输入参数,输出参数)as begin 子程序体 end;
例1:
create or replace procedure hello as begin dbms_output.put_line('hello world'); end;
在文件夹中找到procedure文件夹,找到hello存储过程,右击选择test,运行测试代码
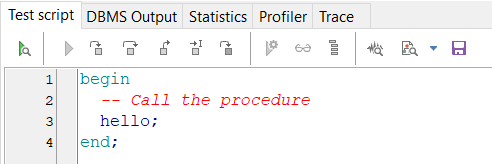
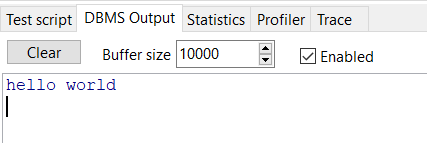
例2:有输入参数
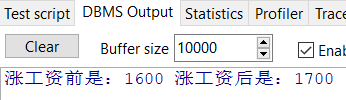
create or replace procedure addsal(pno in myemp.empno%type) as prec myemp%rowtype; begin select * into prec from myemp t where t.empno = pno; update myemp t set t.sal = t.sal + 100 where t.empno = pno; dbms_output.put_line('涨工资前是:' || prec.sal || ' 涨工资后是:' || (prec.sal + 100)); end;
测试时,pno输入7369
测试结果:
例3:有输入和输出参数
create or replace procedure countYSal(pno in emp.empno%type, ysal out number) psal emp.sal%type; pcomm emp.comm%type; begin select t.sal, t.comm into psal, pcomm from emp t where t.empno = pno; ysal := psal * 12 + nvl(pcomm, 0); end countYSal;
P43 调用存储过程
直接写存储过程名称并传入参数就表示调用了,记得先创建变量来接收返回的参数。
declare ysal number; begin countsal(7369, ysal); dbms_output.put_line(ysal); end;



