多线程学习笔记
几个重要概念
程序:一个静态的概念,一般对应于操作系统中的一个可执行文件。
进程:运行中的程序。一个动态的概念。现代的操作系统都可以同时启动多个进程。
线程:一个进程可以产生多个线程。同多个进程可以共享操作系统的某些资源一样,同一进程的多个线程也可以共享此进程的某些资源(比如:代码、数据),所以线程又被称为轻量级进程。
创建线程的三种方法:
1.继承Thread类,重写run()方法(线程体),可以直接使用Thread类的start()方法。
Thread类也是Runable接口的一个实现。
简单创建一个线程:

1 public class TestThread extends Thread{ 2 public void run() { 3 for(int i=0;i<20;i++) { 4 System.out.println("一边听歌"); 5 } 6 } 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 TestThread st = new TestThread(); 9 st.start(); 10 for(int i=0;i<20;i++) { 11 System.out.println("一边敲代码"); 12 } 13 } 14 }
同时拷贝三张图片:

1 public class FigDownLoad extends Thread{ 2 private String url; 3 private String name; 4 public FigDownLoad(String url, String name) { 5 super(); 6 this.url = url; 7 this.name = name; 8 } 9 public void run() { //线程体,在开启线程后要做的事 10 Copy c = new Copy(); 11 c.download(url, name); 12 System.out.println(name); 13 } 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 FigDownLoad fdl1 = new FigDownLoad("图片地址1","图片名称1.jpg"); 16 FigDownLoad fdl2 = new FigDownLoad("图片地址2","图片名称2.jpg"); 17 FigDownLoad fdl3 = new FigDownLoad("图片地址3","图片名称3.jpg"); 18 fdl1.start(); 19 fdl2.start(); 20 fdl3.start(); 21 22 } 23 public class Copy { 24 public void download(String url,String name) { 25 try { 26 FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File(name)); 27 } catch (MalformedURLException e) { 28 System.out.println("不合法的url"); 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } catch (IOException e) { 31 System.out.println("下载失败"); 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 35 } 36 } 37 38 }
2.直接实现Runable接口,重写run()方法(线程体)。这里不能直接使用start()方法。需要先创建Thread类的对象,再调用。(推荐)
简单实现:

1 public class TestRunnable implements Runnable{ 2 private String name; 3 4 public TestRunnable(String name) { 5 super(); 6 this.name = name; 7 } 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 TestRunnable r1 = new TestRunnable("Lisa"); 10 TestRunnable r2 = new TestRunnable("Tom"); 11 Thread t1=new Thread(r1); 12 Thread t2=new Thread(r2); 13 t1.start(); 14 t2.start(); 15 } 16 public void run() { 17 for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { 18 System.out.println(name); 19 } 20 } 21 }
抢票(对同一个资源会产生并发问题):注意,run方法不能向外抛出异常,只能try catch。

1 public class Test12306 implements Runnable{ 2 private int ticketNums=20; 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Test12306 t = new Test12306(); 6 7 new Thread(t,"小明").start(); 8 new Thread(t,"小兰").start(); 9 new Thread(t,"小芳").start(); 10 } 11 12 public void run() { 13 while(true) { 14 if(ticketNums<0) { 15 break; 16 } 17 try { 18 Thread.sleep(200); 19 } 20 catch (InterruptedException e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->"+ticketNums--); 24 } 25 26 } 27 }
龟兔赛跑:

1 public class TestRace implements Runnable{ 2 private String winner; 3 4 public void run() { 5 for(int step=1;step<=100;step++) { 6 if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("兔子")&&(step==20)) {//兔子走了20步时,休息1ms再跑 7 try { 8 Thread.sleep(1); 9 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 10 e.printStackTrace(); 11 } 12 } 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+step); 14 boolean flag = gameOver(step); 15 if(flag) { 16 break; 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 21 private boolean gameOver(int step) {//判断比赛是否结束 22 if(winner!=null) { 23 return true; 24 }else { 25 if(step==100) { 26 winner=Thread.currentThread().getName();//若有人步数到100了,他就是winner 27 System.out.println("winner--->"+winner); 28 return true; 29 } 30 } 31 return false; 32 } 33 public static void main(String[] args) { 34 TestRace tr = new TestRace(); 35 new Thread(tr,"乌龟").start(); 36 new Thread(tr,"兔子").start(); 37 38 } 39 }
3.实现Callable接口。重写call()方法(有返回,可throw异常)

1 public class TestCallable implements Callable{ 2 private int ticketNums=20; 3 public Object call() throws Exception { 4 while(true) { 5 if(ticketNums<0) { 6 break; 7 } 8 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->"+ticketNums--); 9 } 10 return null; 11 } 12 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { 13 TestCallable tc = new TestCallable(); 14 ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); 15 Future <Object> f1 = ser.submit(tc); 16 Future <Object> f2 = ser.submit(tc); 17 Future <Object> f3 = ser.submit(tc); 18 Object o1 = f1.get(); 19 Object o2 = f2.get(); 20 Object o3 = f3.get(); 21 ser.shutdownNow(); 22 } 23 }
静态代理设计模式:
以直接实现Runable接口为例
婚庆公司=Thread类(代理)
具体结婚的人=继承Runable接口的类
结婚=run()方法

1 public class TestStaticProxy { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 new WeddingCompany(new person()).marry(); 4 } 5 } 6 interface Marry{ 7 void marry(); 8 } 9 10 class person implements Marry{ 11 public void marry() { 12 System.out.println("结婚啦!"); 13 } 14 } 15 16 class WeddingCompany implements Marry{ 17 private Marry customer; 18 19 public WeddingCompany(Marry customer) { 20 super(); 21 this.customer = customer; 22 } 23 24 public void marry() { 25 ready(); 26 this.customer.marry(); 27 after(); 28 } 29 private void ready() { 30 System.out.println("准备婚礼"); 31 } 32 private void after() { 33 System.out.println("打扫现场"); 34 } 35 }
Lambda表达式:
用于简化线程的使用。
复习:外部类——>静态内部类——>局部内部类——>匿名内部类——>Lambda表达式
格式:接口名称 对象名称 = ()->{
方法内容(省略方法声明)
};
1.以下代码包含五种调用方法方式的比较:

1 public class TestLambda { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Like1 l1 = new Like1(); 4 l1.lambda();//调用外部类 5 Like2 l2 = new Like2(); 6 l2.lambda(); //调用静态内部类(存在于类中) 7 8 class Like3 implements ILike{ 9 public void lambda() { 10 System.out.println("局部内部类"); 11 } 12 } 13 Like3 l3 = new Like3();//调用局部内部类(存在于方法中) 14 l3.lambda(); 15 16 ILike l4 = new ILike(){ 17 public void lambda() { 18 System.out.println("匿名内部类"); 19 } 20 }; 21 l4.lambda(); 22 23 ILike l5 = ()->{ 24 System.out.println("lambda表达式"); 25 }; 26 l5.lambda();//调用lambda表达式 27 } 28 static class Like2 implements ILike{ 29 public void lambda() { 30 System.out.println("静态内部类"); 31 } 32 } 33 34 } 35 interface ILike{ 36 void lambda(); 37 } 38 class Like1 implements ILike{ 39 public void lambda() { 40 System.out.println("外部类"); 41 } 42 }
2.带参的Lambda表达式简化方式:
接口名称 对象名称 = 参数名称-> 方法内容;

1 public class TestLambdaWithParameters { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 ILove l1 = (int a)->{ 4 System.out.println("lamda表达式——>"+a); 5 }; 6 l1.lambda(1); 7 8 ILove l2 = a->{ //数据类型可以省略,若只有一个参数,括号也可省略 9 System.out.println("lamda表达式——>"+a); 10 }; 11 l2.lambda(2); 12 13 ILove l3 = a-> System.out.println("lamda表达式——>"+a);//若方法只有一行,花括号也可省略 14 l3.lambda(3); 15 } 16 17 } 18 interface ILove{ 19 void lambda(int a); 20 }
3.带返回值的Lambda表达式:
接口名称 对象名称 = (参数列表)->返回内容;(若方法内容不为空,则需要与返回内容一起放花括号中)

1 public class LambdaNoVoid { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 4 IInterest interst = (a,c)->a+c;//返回a+c 5 System.out.println(interst.lambda(10,20)); 6 } 7 } 8 interface IInterest{ 9 int lambda(int a,int b); 10 }
线程状态:
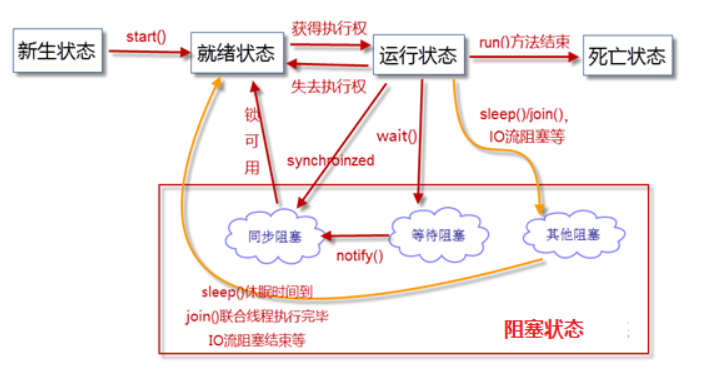
注意:1.当运行状态变成阻塞状态后,不能马上回到运行状态,必须先回到就绪状态等待。
2.线程一旦死亡,不可再变成其他状态。
终止线程的方式:
提供一个boolean型的终止变量,当这个变量置为false,则终止线程的运行。
具体写法:run()方法中写明,终止变量为false时才执行线程体。额外提供一个终止方法,方法内将终止变量置为false。main函数中给出调用终止方法的条件即可。这样在线程运行后,满足main函数指定的终止条件后,调用终止方法,终止变量则变为flag,run()方法就不再运行,线程终止。

1 public class BooleanStopThread implements Runnable{ 2 private boolean flag =true; 3 private String name; 4 public BooleanStopThread(String name) { 5 super(); 6 this.name = name; 7 } 8 @Override 9 public void run() { 10 int i=0; 11 while(flag) {//在线程体中说明,只有flag为真,才运行 12 System.out.println(name+"--->"+i++); 13 } 14 } 15 public void terminate() {//线程终止方法 16 this.flag=false; 17 } 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 BooleanStopThread bst = new BooleanStopThread("C罗"); 20 new Thread(bst).start(); 21 for(int i=0;i<99;i++) { 22 if(i==88) {//写明调用终止方法的条件 23 bst.terminate(); 24 System.out.println("Game over!"); 25 } 26 System.out.println("main-->"+i); 27 } 28 } 29 }
改变运行状态的线程的方法:
1.sleep():不释放资源,多用于倒计时或等待时间。运行状态——>阻塞状态

1 public class ThreadSleep { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 3 Date time = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()+10000);//创建当前时间的Date类对象 4 long ti = time.getTime();//获得当前时间毫秒数 5 while(true) { 6 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("mm:ss").format(time));//创建特定的格式。将Date对象time转换成该格式并打印 7 Thread.sleep(1000);//线程阻塞10秒 8 time = new Date(time.getTime()-1000); 9 if(ti-10000>time.getTime()) { 10 break; 11 } 12 } 13 } 14 }
2.yield():礼让线程,运行状态——>就绪状态

1 new Thread (()-> { 2 for(int i=0;i<100;i++) { 3 System.out.println("lambda"+i); 4 } 5 }).start(); 6 for(int i=0;i<100;i++) { 7 if(i%20==0) { 8 Thread.yield(); 9 } 10 System.out.println("main"+i); 11 }
3.join():是成员方法,只能通过thread的对象调用。写在哪个线程体中,哪个线程体被阻塞。直到其他线程都执行完,才能继续执行。

1 public class TestJoin { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 System.out.println("爸爸和儿子买烟的故事"); 4 Father f = new Father(); 5 f.start();//开始执行父亲线程体内容 6 7 } 8 9 } 10 class Father extends Thread{ 11 public void run(){ 12 System.out.println("想抽烟,让儿子去买"); 13 Son s = new Son(); 14 s.start(); //开始执行儿子线程体内容 15 try { 16 s.join();//父亲线程被阻塞,给其他线程(儿子)让路,只有儿子线程结束后,才能继续执行 17 System.out.println("接过烟,把零钱给儿子"); 18 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 19 System.out.println("孩子走丢了"); 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } 22 23 24 } 25 } 26 class Son extends Thread{ 27 public void run(){ 28 System.out.println("接过老爸的钱,出门"); 29 System.out.println("路边有个游戏厅,玩了10秒"); 30 for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { 31 System.out.println(i+"秒过去了...");//每循环一次(过1秒报一次时间) 32 try { 33 Thread.sleep(1000);//当前线程睡眠1s,重复10次,即10秒 34 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 } 38 System.out.println("去买烟,买完回家给老爸~"); 39 } 40 }
线程状态观察:
线程阻塞可能有4种原因:1.sleep()2.join()3.wait()4.IO中的read(),write()
其中1和2使线程变为wait(或timewait)阻塞状态。3和4使线程变为blocked阻塞状态。
观察线程状态:State 对象名称 = 线程名称.getState();
System.out.println(对象名称);
使阻塞的线程结束的方法:1.while条件写为(对象名称!=Thread.State.TERMINATED),即线程如果死亡就退出。
2.用activeCount()方法获取当前活跃线程数,若只剩下主线程,则判定break退出。
int num = Thread.activeCount();
System.out.println(num);
if(num==1) {
break;
}

1 public class StateObserver { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 3 Thread t =new Thread(()-> { 4 for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { 5 try { 6 Thread.sleep(100); 7 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 8 e.printStackTrace(); 9 } 10 } 11 }); 12 State state = t.getState(); 13 System.out.println(state); 14 15 t.start(); 16 state = t.getState(); 17 System.out.println(state); 18 /* 19 while(state!=Thread.State.TERMINATED) {//线程状态不为结束才运行 20 try { 21 Thread.sleep(200); 22 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } 25 state = t.getState(); 26 System.out.println(state); 27 }*/ 28 29 while(true) { 30 int num = Thread.activeCount(); 31 System.out.println(num); 32 if(num==1) { 33 break;//只剩下主线程,即该线程结束 34 } 35 try { 36 Thread.sleep(500); 37 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } 40 state = t.getState(); 41 System.out.println(state); 42 } 43 44 } 45 46 }
线程优先级:
线程的优先级代表进入就绪状态的线程被调度的概率,最高为10,最低为1,默认为5。
最高优先级:Thread.MAX_PRIORITY
最低优先级:Thread.MIN_PRIORITY
设置优先级:线程对象名.setPriority()
获得优先级:线程对象名.getPriority()

1 public class ThreadPriority { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getPriority());//默认线程优先级为5 4 MyPriority mp = new MyPriority(); 5 Thread t1 = new Thread(mp,"lamer"); 6 Thread t2 = new Thread(mp,"雅诗兰黛"); 7 Thread t3 = new Thread(mp,"倩碧"); 8 Thread t4 = new Thread(mp,"巴黎欧莱雅"); 9 Thread t5 = new Thread(mp,"相宜本草"); 10 Thread t6 = new Thread(mp,"大宝"); 11 12 t1.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); 13 t2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY-2); 14 t3.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY-4); 15 t4.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY-6); 16 t5.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY+2); 17 t6.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); 18 19 t1.start(); 20 t2.start(); 21 t3.start(); 22 t4.start(); 23 t5.start(); 24 t6.start(); 25 } 26 27 } 28 class MyPriority implements Runnable{ 29 30 public void run() { 31 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); 32 Thread.yield(); 33 34 } 35 36 }
守护线程:
线程分为用户线程和守护线程两种。java虚拟机一定会等待用户线程执行完毕。但是若一个线程被设置成守护线程,则java虚拟机则不会等待它执行完毕。
设置方法:线程对象名称.setDaemon(true);

1 public class TestDaemon { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 You you = new You(); 4 Thread t1 = new Thread(you); 5 t1.start(); 6 God god = new God(); 7 Thread t2 = new Thread(god); 8 t2.setDaemon(true); 9 t2.start(); 10 } 11 } 12 class You implements Runnable{ 13 14 @Override 15 public void run() { 16 for(int i=0;i<365*100;i++) { 17 System.out.println("happylife~"); 18 } 19 20 } 21 22 } 23 24 class God implements Runnable{ 25 26 @Override 27 public void run() { 28 for(int i=0;i<365*10000;i++) { 29 System.out.println("God bless you~"); 30 } 31 32 } 33 34 }
其他方法:
设置/获取代理线程名字:setName(),getName()
测试线程是否在线:代理线程对象名称.isAlive()
获取当前在线的线程:Thread.currentThread()

1 public class TestSetNameisAlive { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 3 MyInfo mi = new MyInfo("战斗机"); 4 Thread t = new Thread(mi); 5 t.setName("公鸡"); 6 t.start(); 7 System.out.println(t.isAlive()); 8 t.sleep(1000); 9 System.out.println(t.isAlive()); 10 11 } 12 13 } 14 class MyInfo implements Runnable{ 15 private String name; 16 17 18 public MyInfo(String name) { 19 super(); 20 this.name = name; 21 } 22 23 @Override 24 public void run() { 25 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->"+name); 26 27 } 28 }
三种典型不安全的线程案例:
1.12306抢票:

1 public class Test12306 implements Runnable{ 2 private int ticketNums=20; 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Test12306 t = new Test12306(); 6 7 new Thread(t,"小明").start(); 8 new Thread(t,"小兰").start(); 9 new Thread(t,"小芳").start(); 10 } 11 12 public void run() { 13 while(true) { 14 if(ticketNums<0) { 15 break; 16 } 17 try { 18 Thread.sleep(200); 19 } 20 catch (InterruptedException e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->"+ticketNums--); 24 } 25 26 } 27 }
2.两人同时取钱:

1 public class Unsafe { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Account account = new Account(100,"结婚礼金"); 4 Drawing you = new Drawing(account,80,"你"); 5 Drawing wife = new Drawing(account,90,"她"); 6 you.start(); 7 wife.start(); 8 } 9 10 11 } 12 class Account{ 13 int money; 14 String name; 15 public Account(int money, String name) { 16 super(); 17 this.money = money; 18 this.name = name; 19 } 20 21 } 22 23 class Drawing extends Thread{ 24 Account account; 25 int drawingmoney; 26 int packettotal; 27 public Drawing(Account account, int drawingmoney, String name) { 28 super(name); 29 this.account = account; 30 this.drawingmoney = drawingmoney; 31 } 32 @Override 33 public void run() { 34 if(account.money-drawingmoney<0) { 35 return; 36 } 37 try { 38 Thread.sleep(1000); 39 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 account.money-=drawingmoney; 43 packettotal+=drawingmoney; 44 System.out.println(this.getName()+"剩下的钱--->"+account.money); 45 System.out.println(this.getName()+"取的钱--->"+packettotal); 46 47 } 48 49 }
3.容器计数:

1 public class Unsafe2 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 4 for(int i=0;i<1000;i++) { 5 new Thread(()-> { 6 list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 7 }).start(); 8 } 9 System.out.println(list.size()); 10 } 11 }
synchronized关键字:
synchronized 方法:
通过在方法声明中加入 synchronized关键字来声明。
synchronized 方法控制对“对象的类成员变量”的访问:每个对象对应一把锁,每个 synchronized 方法都必须获得调用该方法的对象的锁方能执行,否则所属线程阻塞,方法一旦执行,就独占该锁,直到从该方法返回时才将锁释放,此后被阻塞的线程方能获得该锁,重新进入可执行状态。
缺陷:若将一个大的方法声明为synchronized 将会大大影响效率。
安全的12306抢票:

1 public class Safe12306{ 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 SafeTicket t = new SafeTicket(); 5 new Thread(t,"小明").start(); 6 new Thread(t,"小兰").start(); 7 new Thread(t,"小芳").start(); 8 } 9 } 10 class SafeTicket implements Runnable{ 11 private int ticketNums=20; 12 private boolean flag = true; 13 public void run() { 14 while(flag) { 15 try { 16 Thread.sleep(200); 17 } 18 catch (InterruptedException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 test(); 22 } 23 24 } 25 public synchronized void test(){ 26 if(ticketNums<0) { 27 flag=false; 28 return; 29 } 30 try { 31 Thread.sleep(200); 32 } 33 catch (InterruptedException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->"+ticketNums--); 37 } 38 }
synchronized块:
synchronized 块可以让我们精确地控制到具体的“成员变量”,缩小同步的范围,提高效率。
格式:synchronized(对象名称){ }
安全地取钱:

1 public class Unsafe { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Account account = new Account(200,"结婚礼金"); 4 Drawing you = new Drawing(account,80,"你"); 5 Drawing wife = new Drawing(account,90,"她"); 6 you.start(); 7 wife.start(); 8 } 9 10 11 } 12 class Account{ 13 int money; 14 String name; 15 public Account(int money, String name) { 16 super(); 17 this.money = money; 18 this.name = name; 19 } 20 21 } 22 23 class Drawing extends Thread{ 24 Account account; 25 int drawingmoney; 26 int packettotal; 27 public Drawing(Account account, int drawingmoney, String name) { 28 super(name); 29 this.account = account; 30 this.drawingmoney = drawingmoney; 31 } 32 @Override 33 public void run() { 34 test(); 35 36 } 37 public void test() { 38 synchronized(account) { 39 if(account.money-drawingmoney<0) { 40 return; 41 } 42 try { 43 Thread.sleep(1000); 44 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } 47 account.money-=drawingmoney; 48 packettotal+=drawingmoney; 49 System.out.println(this.getName()+"剩下的钱--->"+account.money); 50 System.out.println(this.getName()+"取的钱--->"+packettotal); 51 } 52 } 53 }
安全容器:

1 public class Unsafe2 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 4 for(int i=0;i<1000;i++) { 5 new Thread(()-> { 6 synchronized(list) { 7 list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 8 } 9 }).start(); 10 } 11 System.out.println(list.size()); 12 } 13 }
改进版12306:

1 public class Safe12306{ 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 SafeTicket t = new SafeTicket(); 5 new Thread(t,"小明").start(); 6 new Thread(t,"小兰").start(); 7 new Thread(t,"小芳").start(); 8 } 9 } 10 class SafeTicket implements Runnable{ 11 private int ticketNums=20; 12 private boolean flag = true; 13 public void run() { 14 while(flag) { 15 try { 16 Thread.sleep(200); 17 } 18 catch (InterruptedException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 test(); 22 } 23 24 } 25 public void test(){ 26 if(ticketNums<0) { 27 flag=false; 28 return; 29 }synchronized(this) { 30 if(ticketNums<0) { 31 flag=false; 32 return; 33 } 34 try { 35 Thread.sleep(200); 36 } 37 catch (InterruptedException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } 40 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->"+ticketNums--); 41 } 42 } 43 }
同步线程练习:
1.影院选座

1 public class TestCinema { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 List <Integer> available =new ArrayList<Integer>(); 4 available.add(1); 5 available.add(2); 6 available.add(3); 7 available.add(6); 8 available.add(7); 9 10 List <Integer> seats1 =new ArrayList<Integer>(); 11 seats1.add(1); 12 seats1.add(2); 13 List <Integer> seats2 =new ArrayList<Integer>(); 14 seats2.add(4); 15 seats2.add(5); 16 Cinema c = new Cinema(available,"happycinema"); 17 new Thread(new customer(c,seats1),"小明").start(); 18 new Thread(new customer(c,seats2),"小刚").start(); 19 } 20 } 21 class Cinema{ 22 List <Integer> available; 23 String name; 24 public Cinema(List <Integer> available, String name) { 25 super(); 26 this.available = available; 27 this.name = name; 28 } 29 public boolean bookTickects(List <Integer> seats) { 30 System.out.println("可用位置为:"+available); 31 List <Integer> copy =new ArrayList<Integer>(); 32 copy.addAll(available); 33 copy.removeAll(seats); 34 if(available.size()-copy.size()!=seats.size()) { 35 return false; 36 } 37 available=copy; 38 return true; 39 } 40 } 41 class customer implements Runnable{ 42 Cinema cinema; 43 List <Integer> seats; 44 public customer(Cinema cinema, List<Integer> seats) { 45 super(); 46 this.cinema = cinema; 47 this.seats = seats; 48 } 49 @Override 50 public void run() { 51 synchronized(cinema) { 52 boolean flag = cinema.bookTickects(seats); 53 if(flag) { 54 System.out.println("出票成功"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+seats); 55 }else { 56 System.out.println("出票失败"+Thread.currentThread().getName()); 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 61 }
2.买火车票(p218待看)
3.并发容器:
CopyOnWriteArrayList内部自带锁,可以直接替代ArrayList。

1 CopyOnWriteArrayList <String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>(); 2 for(int i=0;i<1000;i++) { 3 new Thread(()-> { 4 list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 5 try { 6 Thread.sleep(1000); 7 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 8 e.printStackTrace(); 9 } 10 }).start(); 11 } 12 System.out.println(list.size());
死锁:
“死锁”指的是:多个线程各自占有一些共享资源,并且互相等待其他线程占有的资源才能进行,而导致两个或者多个线程都在等待对方释放资源,都停止执行的情形。
因此, 某一个同步块需要同时拥有“两个以上对象的锁”时,就可能会发生“死锁”的问题。
死锁程序:

1 public class TestMakeUp { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 makeup girl1 =new makeup(0,"大丫"); 4 makeup girl2 =new makeup(1,"小丫"); 5 girl1.start(); 6 girl2.start(); 7 8 } 9 10 } 11 class lipstick{ 12 13 } 14 class mirror{ 15 16 } 17 class makeup extends Thread{ 18 int choice; 19 String girl; 20 static lipstick ls = new lipstick(); 21 static mirror mr = new mirror(); 22 23 public makeup(int choice, String girl) { 24 super(); 25 this.choice = choice; 26 this.girl = girl; 27 } 28 29 @Override 30 public void run() { 31 makeup(); 32 } 33 private void makeup(){ 34 if (choice==0) { 35 synchronized(ls){ 36 System.out.println(this.girl+"获得口红"); 37 try { 38 Thread.sleep(1000); 39 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 synchronized(mr){ 43 System.out.println(this.girl+"获得镜子"); 44 } 45 46 } 47 48 }else { 49 synchronized(mr){ 50 System.out.println(this.girl+"获得镜子"); 51 try { 52 Thread.sleep(1000); 53 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 54 e.printStackTrace(); 55 } 56 synchronized(ls){ 57 System.out.println(this.girl+"获得口红"); 58 } 59 60 } 61 62 } 63 } 64 65 }
解决方法:同一个代码块,不要同时持有两个对象锁。
解除死锁程序:

1 public class TestMakeUp { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 makeup girl1 =new makeup(0,"大丫"); 4 makeup girl2 =new makeup(1,"小丫"); 5 girl1.start(); 6 girl2.start(); 7 8 } 9 10 } 11 class lipstick{ 12 13 } 14 class mirror{ 15 16 } 17 class makeup extends Thread{ 18 int choice; 19 String girl; 20 static lipstick ls = new lipstick(); 21 static mirror mr = new mirror(); 22 23 public makeup(int choice, String girl) { 24 super(); 25 this.choice = choice; 26 this.girl = girl; 27 } 28 29 @Override 30 public void run() { 31 makeup(); 32 } 33 private void makeup(){ 34 if (choice==0) { 35 synchronized(ls){ 36 System.out.println(this.girl+"获得口红"); 37 try { 38 Thread.sleep(1000); 39 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 43 } 44 synchronized(mr){ 45 System.out.println(this.girl+"获得镜子"); 46 } 47 48 }else { 49 synchronized(mr){ 50 System.out.println(this.girl+"获得镜子"); 51 try { 52 Thread.sleep(1000); 53 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 54 e.printStackTrace(); 55 } 56 57 } 58 synchronized(ls){ 59 System.out.println(this.girl+"获得口红"); 60 } 61 62 } 63 } 64 65 }
并发协作:
生产者/消费者模式:
生产者指的是负责生产数据的模块(这里模块可能是:方法、对象、线程、进程)。
消费者指的是负责处理数据的模块(这里模块可能是:方法、对象、线程、进程)。
消费者不能直接使用生产者的数据,它们之间有个“缓冲区”。生产者将生产好的数据放入“缓冲区”,消费者从“缓冲区”拿要处理的数据。

有了缓冲区以后,生产者线程只需要往缓冲区里面放置数据,而不需要管消费者消费的情况;同样,消费者只需要从缓冲区拿数据处理即可,也不需要管生产者生产的情况。 这样,就从逻辑上实现了“生产者线程”和“消费者线程”的分离。
编程思路:
管程法:
4个类,分别为数据,缓存区,生产者,消费者。
数据类中包含数据的编号(索引)即可。
缓存区中,需要建立一个数据的数组。写2个同步方法,分别为取数据与放数据。放数据方法中,若数组为空,调用wait()阻塞使用该方法的线程,否则唤醒线程,放入数据。取数据方法中,若数组已满,调用wait()阻塞使用该方法的线程,否则唤醒线程,取出数据。
生产者,消费者类须继承Thread类,初始化缓冲区对象,并重写run()方法,在其中创建数据对象并分别调用缓冲区类中的取数据、放数据方法。
信号灯法:
无缓存区。数据类中定义一个布尔类对象,写2个同步方法(与管程法类似)。不同之处在于信号灯法利用布尔类对象来控制调用wait()与notyfy()方法。
定时调度:
通过Timer和Timetask,我们可以实现定时启动某个线程。
创建一个类继承TimerTask类,重写run()方法。
主程序中:
创建Timer类的对象:Timer 对象名称1 = new Timer();
TimerTask 对象名称2 = new 自建类名();
对象名称1.schedule(对象名称2, delay, period);
schedule()方法的使用非常灵活,可根据实际需求写参数。

1 public class TestTimerTask { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Timer t = new Timer(); 4 long delay = 1000; 5 long period = 1000; 6 TimerTask tt = new MyTask(); 7 t.schedule(tt, delay, period); 8 } 9 10 11 } 12 class MyTask extends TimerTask{ 13 public void run() { 14 for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { 15 System.out.println("休息时间到~"); 16 } 17 } 18 19 }
volatile关键字:
保证数据同步,即线程变量的可见性,可视作一个轻量级的synchronized。
线程对变量进行修改后,立即回写到主内存。
线程读取变量时,从主内存读。
如下程序中,若不加volatile关键字,则cpu读不到num值的改变,程序将进入死循环。

1 public class TestVolatile { 2 private volatile static int num = 0; 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 4 new Thread(()-> { 5 while(num==0) { 6 7 } 8 9 }).start(); 10 Thread.sleep(1000); 11 num=1; 12 } 13 }
可重入锁:
如果某个线程试图获取一个已经由它自己持有的锁时,这个请求会立刻成功,且这个锁的计数值加1。当线程退出同步代码块时,计数器减1,计数为0时,锁释放。
若使用普通锁,在第二次试图获得时,会造成死锁。
直接使用ReentrantLock即可。
CAS(Compare and Swap):
悲观锁:synchronized是独占锁(悲观锁),会导致其他所有需要锁的线程挂起,等待持有锁的线程释放锁。
乐观锁:每次不加锁而是假设没有冲突而去完成某项操作。如果因为冲突失败,就重试,知道成功为止。
实现方法:有三个值:当前内存值V,旧的预期值A,将更新的值B。获取当前内存值V,将其与预期值A比较,若相同,则V修改为B,返回true,否则返回false。
可用商品秒杀来理解:当前商品库存1。多个人抢该商品,预期值都是1。网速最快的人拍下时,当前内存值为1,与预期值相同,则秒杀成功,商品内存改为0。这样别的人再拍,实际内存(0)就与预期值(1)不相同了,秒杀失败。
核心代码:Atomiclnteger 库存对象名称 = new Atomiclnteger(库存数)
Integer 剩余量对象名称 = 库存对象名称.decrementAndGet()相减同时获取






