java 字符流 字节流
java对文本文档进行操作(拷贝、显示)出现乱码一般来说,可以从两个方面入手。
1、文本文件本身的编码格式。
2、java代码中处理文本文件的编码格式。
这里要注意的一点是,我们可以看出copyFileByByte方法和copyFileByChar1方法都是没有办法设置目的文件的编码格式的,并且处理不好都可能出现乱码,但是需要明确一点的是,copyFileByByte方法拷贝的文件即便出现乱码也可以通过另存为其他格式来调整消除乱码,同样的操作在copyFileByChar1方法拷贝生成的源文件是不能消除乱码的。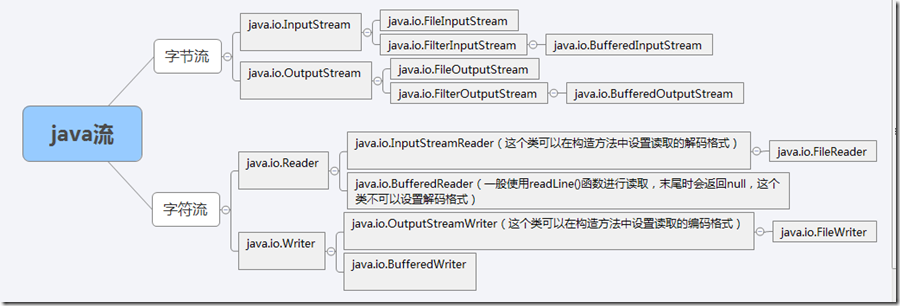
假设我们以字节流格式来读取一份utf-8编码格式的txt文档:
package com.audi; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; public class ReadFile { File fileName = new File("C:/Users/Mike/Desktop/为什么使用接口.txt"); public void readFileByByte() { InputStream inputStream =null; try { inputStream = new FileInputStream(fileName); byte[] temp = new byte[2048]; StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(); //非线程安全,不过这里是单线程,无所谓线程安全与否 int length = 0; while (-1!=(length=inputStream.read(temp))) { // 注意下面的代码使用utf-8作为编码格式 buf.append(new String(temp,0,length,"utf-8")); } System.out.println(buf.toString()); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("文件C:/Users/Mike/Desktop/为什么使用接口.txt不存在"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (inputStream!=null) { inputStream.close(); } } catch (Exception e2) { e2.printStackTrace(); } } } public void readFileByChar() { } }
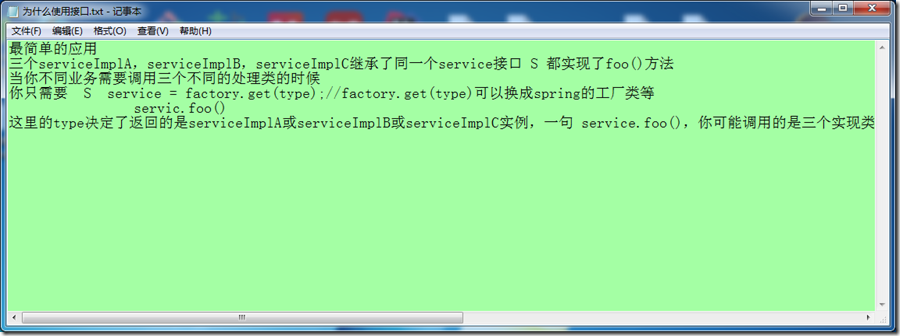
文本文件本来的内容为:
测试代码如下:
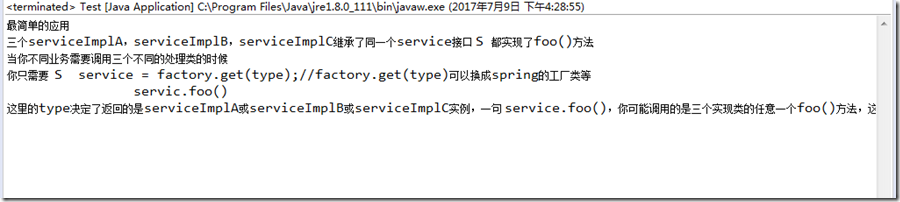
package com.audi; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ReadFile readFile = new ReadFile(); readFile.readFileByByte(); } }
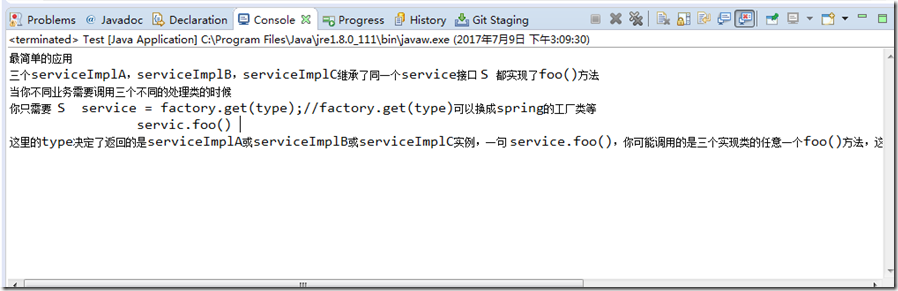
运行程序读取文本文件得到的控制台输出:
可以看出中文没有乱码,一切正常,如果我们在在上面的代码中不设置解码格式,运行程序,依然正常,这是为什么?
这是因为我的java文件的默认编码格式就是utf-8,所以java代码在编译的时候默认就取了这个格式作为解码格式。
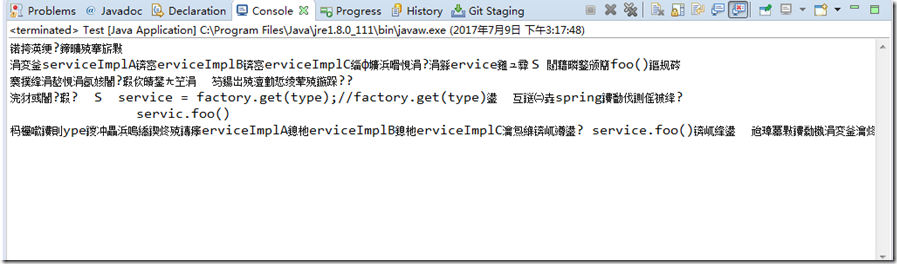
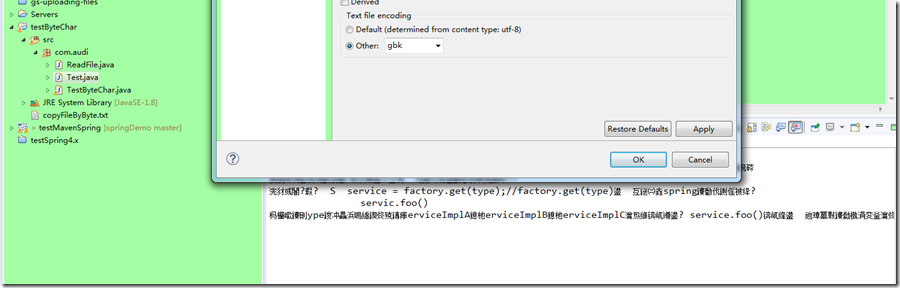
如果换成GBK,那么一样会出现乱码:
那么如果我们要使用字节流拷贝一份文本文件呢?
java代码如下:
public void copyFileByByte() { InputStream inputStream = null; OutputStream outputStream = null; File destName = new File("copyFileByByte.txt"); try { inputStream = new FileInputStream(fileName); outputStream = new FileOutputStream(destName); int length =0; byte[] temp = new byte[2048]; while (-1!=(length=inputStream.read(temp))) { outputStream.write(temp, 0, length); } outputStream.flush(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (inputStream!=null) { inputStream.close(); } if (outputStream!=null) { outputStream.close(); } } catch (Exception e2) { e2.printStackTrace(); } } }
测试代码如下:
package com.audi; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ReadFile readFile = new ReadFile(); // readFile.readFileByByte(); readFile.copyFileByByte(); } }
我的实际测试结果是,拷贝后的文件的编码格式是由源文件格式决定的,它会和源文件的格式保持一致。一般不会出现乱码。
下面是使用字符流来操作文本文件。
public void readFileByChar() { Reader reader = null; try { reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName)); int length =0; char[] temp = new char[2048]; StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(); while (-1!=(length=reader.read(temp))) { buf.append(new String(temp, 0, length)); } System.out.println(buf.toString()); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("文件C:/Users/Mike/Desktop/为什么使用接口.txt不存在"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
上面的代码和字节流读取文件不同的是:
1、缓冲数组改成了char[]类型
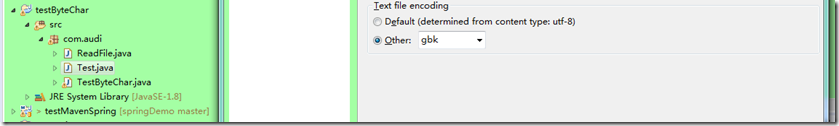
2、new string构造函数中不能再设定格式,这将会导致它直接使用测试的java文件格式来解码读取的字符流。如下图所示,因为我的txt文档也是utf-8格式的,所以不会出现乱码错误。
测试代码:
package com.audi; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ReadFile readFile = new ReadFile(); // readFile.readFileByByte(); // readFile.copyFileByByte(); readFile.readFileByChar(); } }
实际运行效果;
如果把测试java文件的编码格式改为gbk,那么就会出现乱码
下面以字符流方式拷贝文件,同样无法手动设置文件的编码格式:
public void copyFileByChar1() { FileReader fReader = null; FileWriter fWriter = null; File destName = new File("copyFileByChar1.txt"); try { fReader = new FileReader(fileName); fWriter = new FileWriter(destName); int length =0; char[] temp = new char[2048]; while (-1!=(length=fReader.read(temp))) { fWriter.write(temp,0,length); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("文件C:/Users/Mike/Desktop/为什么使用接口.txt不存在"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (fReader!=null) { fReader.close(); } if (fWriter!=null) { fWriter.close(); } System.out.println("copy succeed"); } catch (Exception e2) { e2.printStackTrace(); } } }
测试代码,拷贝后文件的格式依然会和测试代码的java文件的编码格式保持一致。
package com.audi; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ReadFile readFile = new ReadFile(); // readFile.readFileByByte(); // readFile.copyFileByByte(); // readFile.readFileByChar(); readFile.copyFileByChar1(); } }
这里要注意的一点是,我们可以看出copyFileByByte方法和copyFileByChar1方法都是没有办法设置目的文件的编码格式的,并且处理不好都可能出现乱码,但是需要明确一点的是,copyFileByByte方法拷贝的文件即便出现乱码也可以通过另存为其他格式来调整消除乱码,同样的操作在copyFileByChar1方法拷贝生成的源文件是不能消除乱码的。
下面介绍另外一种方法来拷贝文件,使用的是InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter:
public void copyFileByChar2() { InputStreamReader inputStreamReader =null; OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = null; File destName = new File("copyFileByChar2.txt"); try { /*其实只有InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter才可以设置编码格式 * * */ inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(new java.io.FileInputStream(fileName),"utf-8"); outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(new java.io.FileOutputStream(destName),"utf-8"); int length =0; char[] temp = new char[2048]; while (-1!=(length=inputStreamReader.read(temp))) { outputStreamWriter.write(temp,0,length); } } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { outputStreamWriter.flush(); if (inputStreamReader!=null) { inputStreamReader.close(); } if (outputStreamWriter!=null) { outputStreamWriter.close(); } } catch (Exception e2) { e2.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("拷贝结束了"); } }
这个时候拷贝文件的格式完全可控,再也不会依赖测试文件的格式了。
此时,设置源文件UTF-8格式,测试java文件GBK格式:
运行测试代码:
package com.audi; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ReadFile readFile = new ReadFile(); // readFile.readFileByByte(); readFile.copyFileByByte(); // readFile.readFileByChar(); readFile.copyFileByChar1(); readFile.copyFileByChar2(); } }
拷贝后的文件,没有出现乱码:
最后,其实我们上面一直在强调都是针对文本文件的操作,那如果是非文本文件呢?
非文本文件☞什么?
严格来说,文件只有两种类型:文本文件(也叫ASCII文件)和二进制文件。
ASCII码: 00110101 00110110 00110111 00111000
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
十进制码: 5 6 7 8 共占用4个字节。
二进制文件是按二进制的编码方式来存放文件的。 例如, 数5678(五千六百七十八,十进制)的存储形式为:
00010110 00101110(二进制)只占二个字节。
非文本文件我们只能通过字节流来操作,因为字节流虽然也不能设置编解码格式,但是它是一个一个字节读取的,源文件是什么样,拷贝出的文件也是什么样,特定的解码器再去解码就可以了。
字符流就不一样了,它会根据设定的编解码格式的不同,一次读取两个或者三个字节来进行编解码,这样很可能会损坏源文件的编码方式,导致拷贝的文件出错。