C#线程学习笔记七:Task详细用法
一、Task类简介
Task类是在.NET Framework 4.0中提供的新功能,主要用于异步操作的控制。它比Thread和ThreadPool提供了更为强大的功能,并且更方便使用。
Task和Task<TResult>类:前者接收的是Action委托类型;后者接收的是Func<TResult>委托类型。
任务Task和线程Thread的区别:
1)任务是架构在线程之上。也就是说任务最终还是要抛给线程去执行,它们都是在同一命名空间System.Threading下。
2)任务跟线程并不是一对一的关系。比如说开启10个任务并不一定会开启10个线程,因为使用Task开启新任务时,是从线程池中调用线程,这点与ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem类似。
二、Task的创建
1)创建方式1:调用构造函数

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 工作者线程:使用任务实现异步 ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(1000, 1000); PrintMessage("Main thread start."); //调用构造函数创建Task对象 Task<int> task = new Task<int>(n => AsyncMethod((int)n), 10); //启动任务 task.Start(); //等待任务完成 task.Wait(); Console.WriteLine("The method result is: " + task.Result); Console.ReadLine(); #endregion } /// <summary> /// 打印线程池信息 /// </summary> /// <param name="data"></param> private static void PrintMessage(string data) { //获得线程池中可用的工作者线程数量及I/O线程数量 ThreadPool.GetAvailableThreads(out int workThreadNumber, out int ioThreadNumber); Console.WriteLine("{0}\n CurrentThreadId is:{1}\n CurrentThread is background:{2}\n WorkerThreadNumber is:{3}\n IOThreadNumbers is:{4}\n", data, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsBackground.ToString(), workThreadNumber.ToString(), ioThreadNumber.ToString()); } /// <summary> /// 异步方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="n"></param> /// <returns></returns> private static int AsyncMethod(int n) { Thread.Sleep(1000); PrintMessage("Asynchoronous method."); int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { //运算溢出检查 checked { sum += i; } } return sum; } }
2)创建方式2:任务工厂

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 工作者线程:使用任务工厂实现异步 ////无参无返回值 //ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(1000, 1000); //Task.Factory.StartNew(() => PrintMessage("Main thread.")); //Console.Read(); //有参有返回值 ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(1000, 1000); PrintMessage("Main thread start."); var task = Task.Factory.StartNew(n => AsyncMethod((int)n), 10); //等待任务完成 task.Wait(); Console.WriteLine("The method result is: " + task.Result); Console.ReadLine(); #endregion } /// <summary> /// 打印线程池信息 /// </summary> /// <param name="data"></param> private static void PrintMessage(string data) { //获得线程池中可用的工作者线程数量及I/O线程数量 ThreadPool.GetAvailableThreads(out int workThreadNumber, out int ioThreadNumber); Console.WriteLine("{0}\n CurrentThreadId is:{1}\n CurrentThread is background:{2}\n WorkerThreadNumber is:{3}\n IOThreadNumbers is:{4}\n", data, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsBackground.ToString(), workThreadNumber.ToString(), ioThreadNumber.ToString()); } /// <summary> /// 异步方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="n"></param> /// <returns></returns> private static int AsyncMethod(int n) { Thread.Sleep(1000); PrintMessage("Asynchoronous method."); int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { //运算溢出检查 checked { sum += i; } } return sum; } }
3)创建方式3:Run方法

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 工作者线程:使用Task.Run实现异步 ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(1000, 1000); PrintMessage("Main thread start."); var task = Task.Run(() => AsyncMethod(10)); //等待任务完成 task.Wait(); Console.WriteLine("The method result is: " + task.Result); Console.ReadLine(); #endregion } /// <summary> /// 打印线程池信息 /// </summary> /// <param name="data"></param> private static void PrintMessage(string data) { //获得线程池中可用的工作者线程数量及I/O线程数量 ThreadPool.GetAvailableThreads(out int workThreadNumber, out int ioThreadNumber); Console.WriteLine("{0}\n CurrentThreadId is:{1}\n CurrentThread is background:{2}\n WorkerThreadNumber is:{3}\n IOThreadNumbers is:{4}\n", data, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsBackground.ToString(), workThreadNumber.ToString(), ioThreadNumber.ToString()); } /// <summary> /// 异步方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="n"></param> /// <returns></returns> private static int AsyncMethod(int n) { Thread.Sleep(1000); PrintMessage("Asynchoronous method."); int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { //运算溢出检查 checked { sum += i; } } return sum; } }
三、Task的简略生命周期
• 可通过Status属性获取。
| 状态 | 说明 |
| Created | 表示默认初始化任务,但是工厂及Run创建方式会直接跳过。 |
| WaitingToRun | 表示等待任务调度器分配线程给任务执行。 |
| RanToCompletion | 表示任务执行完毕。 |
四、Task的控制
| 方法名 | 说明 |
| Task.Wait | 如task1.Wait();就是等待task1任务的执行,执行完成后状态变为Completed。 |
| Task.WaitAll | 等待所有的任务执行完毕。 |
| Task.WaitAny | 等待任意一个任务完成后就继续向下执行。 |
| Task.ContinueWith | 上一个任务执行完成后自动启动下一个任务,实现任务的按序进行。 |
| CancellationTokenSource | 通过其token来取消一个Task。 |
4.1、组合任务

class Program { public static void Main() { #region 工作者线程:Task组合任务 //创建一个任务 Task<int> task = new Task<int>(() => { int sum = 0; Console.WriteLine("使用任务实现异步。"); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { sum += i; } return sum; }); //任务启动并安排到任务队列等待执行(System.Threading.Tasks.TaskScheduler) task.Start(); //任务完成时执行处理 Task cwt = task.ContinueWith(t => { Console.WriteLine("任务的执行结果:{0}", t.Result.ToString()); }); task.Wait(); cwt.Wait(); Console.ReadLine(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:
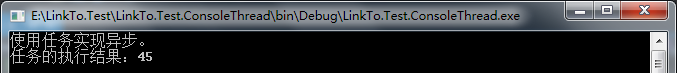
4.2、串行任务

class Program { public static void Main() { #region 工作者线程:Task串行任务 //堆栈 ConcurrentStack<int> stack = new ConcurrentStack<int>(); //t1最早串行 var t1 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { stack.Push(1); stack.Push(2); }); //t2、t3并行执行 var t2 = t1.ContinueWith(t => { stack.TryPop(out int result); Console.WriteLine("Task t2 result={0},thread id is {1}.", result, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); }); var t3 = t1.ContinueWith(t => { stack.TryPop(out int result); Console.WriteLine("Task t3 result={0},thread id is {1}.", result, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); }); //等待t2、t3执行完毕 Task.WaitAll(t2, t3); //t4串行执行 var t4 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { Console.WriteLine("The stack count={0},thread id is {1}.", stack.Count, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); }); t4.Wait(); Console.ReadLine(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:
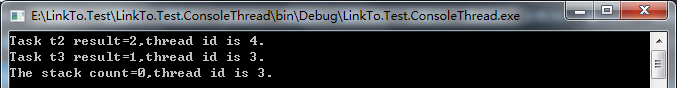
4.3、子任务

class Program { public static void Main() { #region 工作者线程:Task子任务 Task<string[]> parent = new Task<string[]>(state => { Console.WriteLine(state); string[] result = new string[2]; //创建并启动子任务 new Task(() => { result[0] = "子任务1。"; }, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent).Start(); new Task(() => { result[1] = "子任务2。"; }, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent).Start(); return result; }, "我是父任务,我创建了2个子任务,它们执行完后我才会结束执行。"); //任务完成时执行处理 parent.ContinueWith(t => { Array.ForEach(t.Result, r => Console.WriteLine(r)); }); //启动父任务 parent.Start(); parent.Wait(); Console.ReadLine(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:
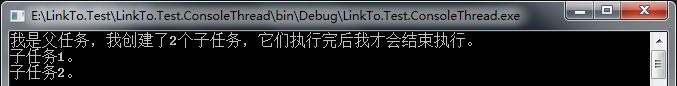
4.4、动态并行任务

/// <summary> /// 结点类 /// </summary> class Node { public Node Left { get; set; } public Node Right { get; set; } public string Text { get; set; } } class Program { public static void Main() { #region 工作者线程:Task动态并行任务 Node root = GetNode(); DisplayTree(root); Console.ReadLine(); #endregion } /// <summary> /// GetNode方法 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> static Node GetNode() { Node root = new Node { Left = new Node { Left = new Node { Text = "L-L" }, Right = new Node { Text = "L-R" }, Text = "L" }, Right = new Node { Left = new Node { Text = "R-L" }, Right = new Node { Text = "R-R" }, Text = "R" }, Text = "Root" }; return root; } /// <summary> /// DisplayTree方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="root"></param> static void DisplayTree(Node root) { var task = Task.Factory.StartNew ( () => DisplayNode(root), CancellationToken.None, TaskCreationOptions.None, TaskScheduler.Default ); task.Wait(); } /// <summary> /// DisplayNode方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="current"></param> static void DisplayNode(Node current) { if (current.Left != null) { Task.Factory.StartNew ( () => DisplayNode(current.Left), CancellationToken.None, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent, TaskScheduler.Default ); } if (current.Right != null) { Task.Factory.StartNew ( () => DisplayNode(current.Right), CancellationToken.None, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent, TaskScheduler.Default ); Console.WriteLine("The current node text={0},thread id is {1}.", current.Text, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); } } }
运行结果如下:

4.5、取消任务

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 取消任务 ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(1000, 1000); PrintMessage("Main thread start."); CancellationTokenSource cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); //调用构造函数创建Task对象,将一个CancellationToken传给Task构造器从而使Task和CancellationToken关联起来。 Task<int> task = new Task<int>(n => AsyncMethod(cts.Token, (int)n), 10); //启动任务 task.Start(); //延迟取消任务 Thread.Sleep(3000); //取消任务 cts.Cancel(); Console.WriteLine("The method result is: " + task.Result); Console.ReadLine(); #endregion } /// <summary> /// 打印线程池信息 /// </summary> /// <param name="data"></param> private static void PrintMessage(string data) { //获得线程池中可用的工作者线程数量及I/O线程数量 ThreadPool.GetAvailableThreads(out int workThreadNumber, out int ioThreadNumber); Console.WriteLine("{0}\n CurrentThreadId is:{1}\n CurrentThread is background:{2}\n WorkerThreadNumber is:{3}\n IOThreadNumbers is:{4}\n", data, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsBackground.ToString(), workThreadNumber.ToString(), ioThreadNumber.ToString()); } /// <summary> /// 异步方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="ct"></param> /// <param name="n"></param> /// <returns></returns> private static int AsyncMethod(CancellationToken ct, int n) { Thread.Sleep(1000); PrintMessage("Asynchoronous method."); int sum = 0; try { for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { //当CancellationTokenSource对象调用Cancel方法时,就会引起OperationCanceledException异常, //通过调用CancellationToken的ThrowIfCancellationRequested方法来定时检查操作是否已经取消, //这个方法和CancellationToken的IsCancellationRequested属性类似。 ct.ThrowIfCancellationRequested(); Thread.Sleep(500); //运算溢出检查 checked { sum += i; } } } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine("Exception is:" + e.GetType().Name); Console.WriteLine("Operation is canceled."); } return sum; } }
运行结果如下:
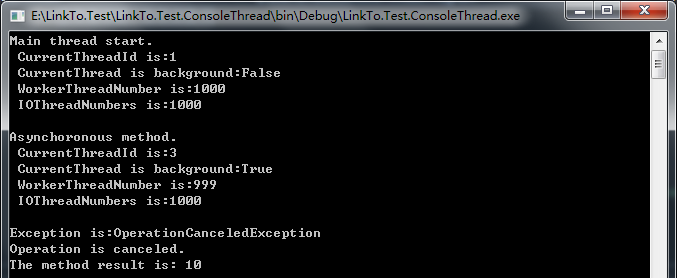
4.6、处理单个任务中的异常

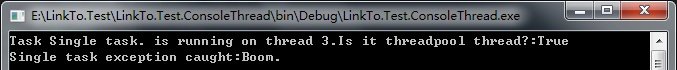
class Program { public static void Main() { #region 工作者线程:处理单个任务中的异常 try { Task<int> task = Task.Run(() => SingleTaskExceptionMethod("Single task.", 2)); int result = task.GetAwaiter().GetResult(); Console.WriteLine("Result:{0}", result); } catch (Exception ex) { Console.WriteLine("Single task exception caught:{0}", ex.Message); } Console.ReadLine(); #endregion } /// <summary> /// SingleTaskException方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="name"></param> /// <param name="seconds"></param> /// <returns></returns> static int SingleTaskExceptionMethod(string name, int seconds) { Console.WriteLine("Task {0} is running on thread {1}.Is it threadpool thread?:{2}", name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds)); throw new Exception("Boom."); } }
运行结果如下:
4.7、处理多个任务中的异常

class Program { public static void Main() { #region 工作者线程:处理多个任务中的异常 try { var t1 = new Task<int>(() => MultipleTaskExceptionMethod("Multiple task 1", 3)); var t2 = new Task<int>(() => MultipleTaskExceptionMethod("Multiple task 2", 2)); var complexTask = Task.WhenAll(t1, t2); var exceptionHandler = complexTask.ContinueWith ( t => Console.WriteLine("Result:{0}", t.Result), TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnFaulted ); t1.Start(); t2.Start(); Task.WaitAll(t1, t2); Console.ReadLine(); } catch (AggregateException ex) { ex.Handle ( exception => { Console.WriteLine(exception.Message); return true; } ); } #endregion } /// <summary> /// MultipleTaskException方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="name"></param> /// <param name="seconds"></param> /// <returns></returns> static int MultipleTaskExceptionMethod(string name, int seconds) { Console.WriteLine("Task {0} is running on thread id {1}. Is it threadpool thread?:{2}", name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds)); throw new Exception(string.Format("Task {0} Boom.", name)); } }
运行结果如下:

4.8、Task.FromResult的应用

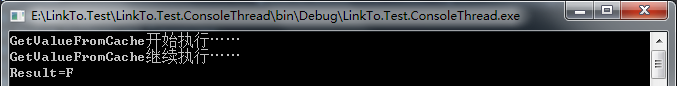
class Program { //字典 private static readonly IDictionary<string, string> cache = new Dictionary<string, string>() { {"0001","A"}, {"0002","B"}, {"0003","C"}, {"0004","D"}, {"0005","E"}, {"0006","F"}, }; public static void Main() { #region 工作者线程:Task.FromResult的应用 Task<string> task = GetValueFromCacheMethod("0006"); Console.WriteLine("Result={0}", task.Result.ToString()); Console.ReadLine(); #endregion } /// <summary> /// GetValueFromCache方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="key"></param> /// <returns></returns> private static Task<string> GetValueFromCacheMethod(string key) { Console.WriteLine("GetValueFromCache开始执行……"); string result = string.Empty; Thread.Sleep(3000); Console.WriteLine("GetValueFromCache继续执行……"); if (cache.TryGetValue(key, out result)) { return Task.FromResult(result); } return Task.FromResult(""); } }
运行结果如下:
4.9、使用IProgress实现异步编程的进程通知
IProgress<in T>只提供了一个方法void Report(T value),通过Report方法把一个T类型的值报告给IProgress,然后IProgress<in T>的实现类Progress<in T>的构造函数接收类型为Action<T>的形参,通过这个委托让进度显示在UI界面中。

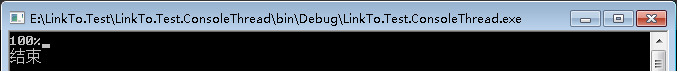
class Program { public static void Main() { #region 工作者线程:使用IProgress实现异步编程的进程通知 Task task = Display(); task.Wait(); Console.ReadLine(); #endregion } /// <summary> /// DoProcessing方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="progress"></param> static void DoProcessing(IProgress<int> progress) { for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { Thread.Sleep(100); if (progress != null) { progress.Report(i); } } } /// <summary> /// Display方法 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> static async Task Display() { //当前线程 var progress = new Progress<int> ( percent => { Console.Clear(); Console.Write("{0}%", percent); } ); //线程池线程 await Task.Run(() => DoProcessing(progress)); Console.WriteLine(""); Console.WriteLine("结束"); } }
运行结果如下:
4.10、Factory.FromAsync的应用
• 简APM模式(委托)转换为任务
• BeginXXX和EndXXX
1)带回调方式:

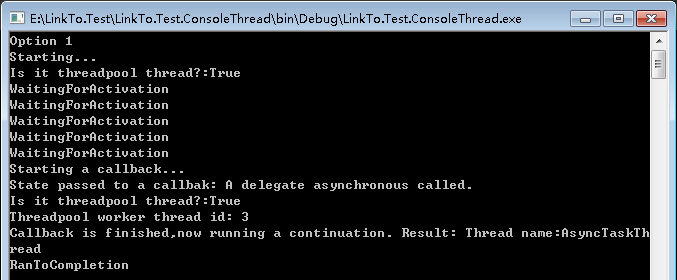
class Program { //使用委托实现异步,是使用了异步编程模型APM。 private delegate string AsynchronousTask(string threadName); public static void Main() { #region 工作者线程:带回调方式的Factory.FromAsync的应用 AsynchronousTask d = TestMethod; Console.WriteLine("Option 1"); Task<string> task = Task<string>.Factory.FromAsync(d.BeginInvoke("AsyncTaskThread", Callback, "A delegate asynchronous called."), d.EndInvoke); task.ContinueWith(t => Console.WriteLine("Callback is finished,now running a continuation. Result: {0}",t.Result)); while (!task.IsCompleted) { Console.WriteLine(task.Status); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.5)); } Console.WriteLine(task.Status); Console.ReadLine(); #endregion } /// <summary> /// FromAsync方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="threadName"></param> /// <returns></returns> private static string FromAsyncMethod(string threadName) { Console.WriteLine("Starting..."); Console.WriteLine("Is it threadpool thread?:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); Thread.CurrentThread.Name = threadName; return string.Format("Thread name:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.Name); } /// <summary> /// Callback方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="ar"></param> private static void Callback(IAsyncResult ar) { Console.WriteLine("Starting a callback..."); Console.WriteLine("State passed to a callbak: {0}", ar.AsyncState); Console.WriteLine("Is it threadpool thread?:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); Console.WriteLine("Threadpool worker thread id: {0}",Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); } }
运行结果如下:
2)不带回调方式:

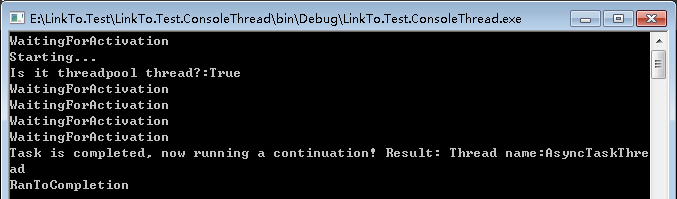
class Program { //使用委托实现异步,是使用了异步编程模型APM。 private delegate string AsynchronousTask(string threadName); public static void Main() { #region 工作者线程:不带回调方式的Factory.FromAsync的应用 AsynchronousTask d = FromAsyncMethod; Task<string> task = Task<string>.Factory.FromAsync(d.BeginInvoke, d.EndInvoke, "AsyncTaskThread", "A delegate asynchronous called."); task.ContinueWith(t => Console.WriteLine("Task is completed, now running a continuation! Result: {0}",t.Result)); while (!task.IsCompleted) { Console.WriteLine(task.Status); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.5)); } Console.WriteLine(task.Status); Console.ReadLine(); #endregion } /// <summary> /// FromAsync方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="threadName"></param> /// <returns></returns> private static string FromAsyncMethod(string threadName) { Console.WriteLine("Starting..."); Console.WriteLine("Is it threadpool thread?:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); Thread.CurrentThread.Name = threadName; return string.Format("Thread name:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.Name); } }
运行结果如下:
参考自:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号