SprintBoot 启动任务系统
简介:
有一些特殊的任务需要在系统启动时执行,例如配置文件的加载,数据库初始化等操作,如果没有使用SpringBoot,这些问题可以在Listener中解决。SpringBoot提供了两种解决方案:CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner,这两个差别主要体现在参数上。
1.CommandLineRunner
SpringBoot项目在启动时会遍历所有的CommandLineRunner的实现类并调用其中的run方法,如果整个系统中有多个CommandLineRunner的实现类,可以使用@Order("数字")去解决先后调用顺序,数字越小越先调用。
测试:
@Component @Order(1) public class MyCommandLineRunner1 implements CommandLineRunner { @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { System.out.println("Runner1>>>"+Arrays.toString(args)); } } @Component @Order(2) public class MyCommandLineRunner2 implements CommandLineRunner { @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { System.out.println("Runner2>>>"+Arrays.toString(args)); } }
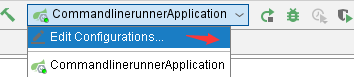
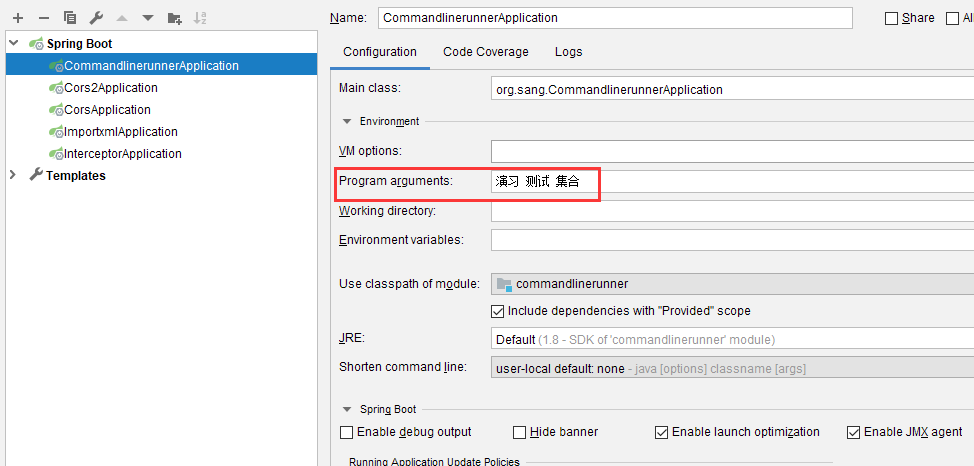
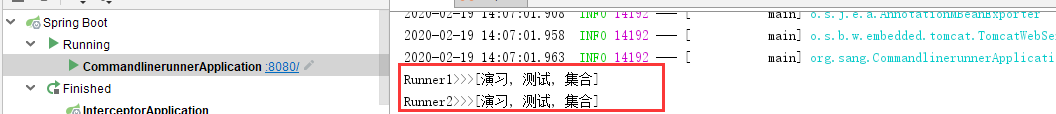
系统启动时传入参数,@Order("1")先于@Order("2")
2.ApplicationRunner
用法和CommandLineRunnner基本一致,区别在于run方法的参数上。
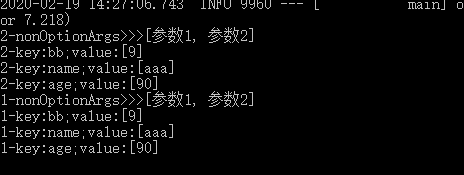
@Component @Order(2) public class MyApplicationRunner1 implements ApplicationRunner { @Override public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { //获取main方法中接受的参数 List<String> nonOptionArgs = args.getNonOptionArgs(); System.out.println("1-nonOptionArgs>>>" + nonOptionArgs); //获取项目启动命令行中的参数key Set<String> optionNames = args.getOptionNames(); for (String optionName : optionNames) { System.out.println("1-key:" + optionName + ";value:" + //对应的value args.getOptionValues(optionName)); } } } @Component @Order(1) public class MyApplicationRunner2 implements ApplicationRunner { @Override public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { List<String> nonOptionArgs = args.getNonOptionArgs(); System.out.println("2-nonOptionArgs>>>" + nonOptionArgs); Set<String> optionNames = args.getOptionNames(); for (String optionName : optionNames) { System.out.println("2-key:" + optionName + ";value:" + args.getOptionValues(optionName)); } } }
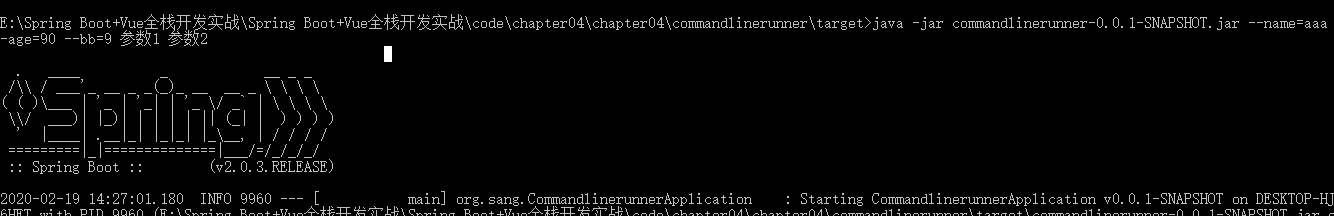
进入项目所在文件:mvn package

进入target文件夹下,发现我们打包的jar,传入参数
posted on 2020-03-17 13:28 atomgame的记事本 阅读(223) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号