操作系统导论习题解答(8. Multi-level Feedback)
0. 文件地址
1. MLFQ: Basic Rules
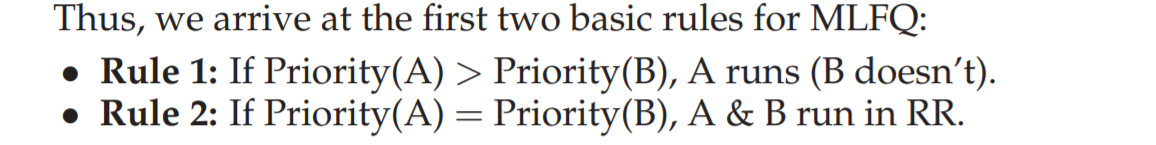

2. Attempt #1: How To Change Priority

2.1 Example 1: A Single Long-Running Job
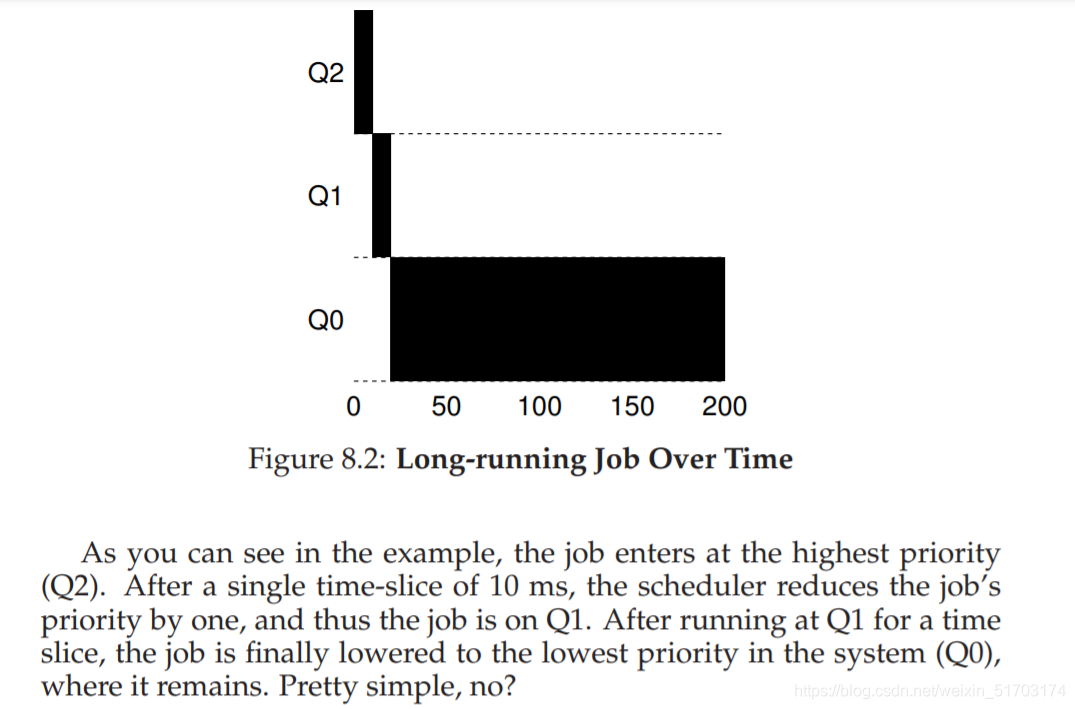
2.2 Example 2: Along Came A Short Job
In this example, there are two jobs: A, which is a long-running CPU-intensive job, and B, which is a short-running interactive job. Assume A has been running for some time, and then B arrives. What will happen? Will MLFQ approximate SJF for B?
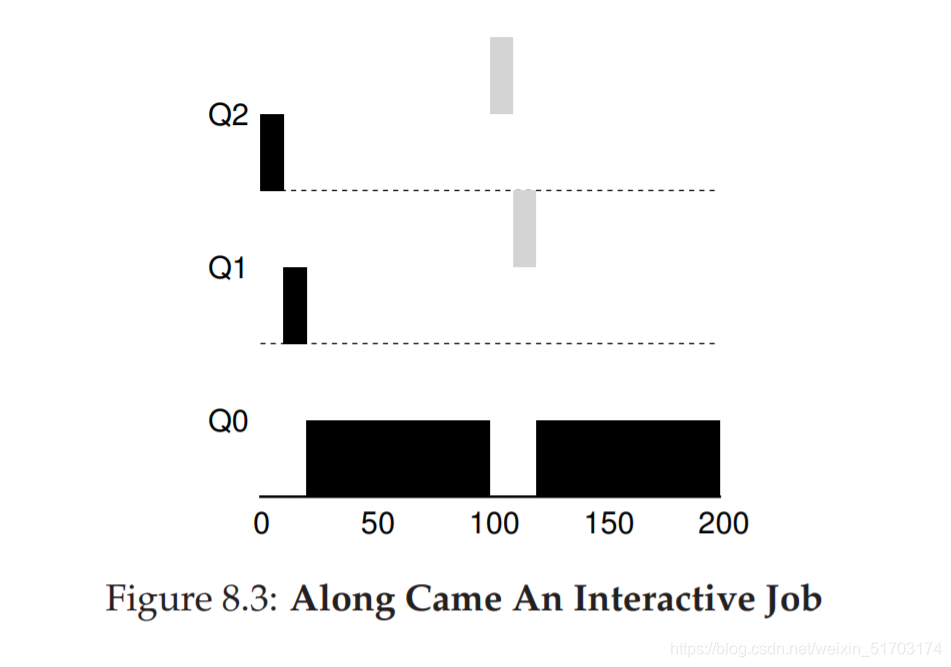
A (shown in black) is running along in the lowest-priority queue (as would any long-running CPU intensive jobs); B (shown in gray) arrives at time T = 100, and thus is inserted into the highest queue; as its run-time is short (only 20 ms), B completes before reaching the bottom queue, in two time slices; then A resumes running (at low priority).
2.3 Example 3: What About I/O?

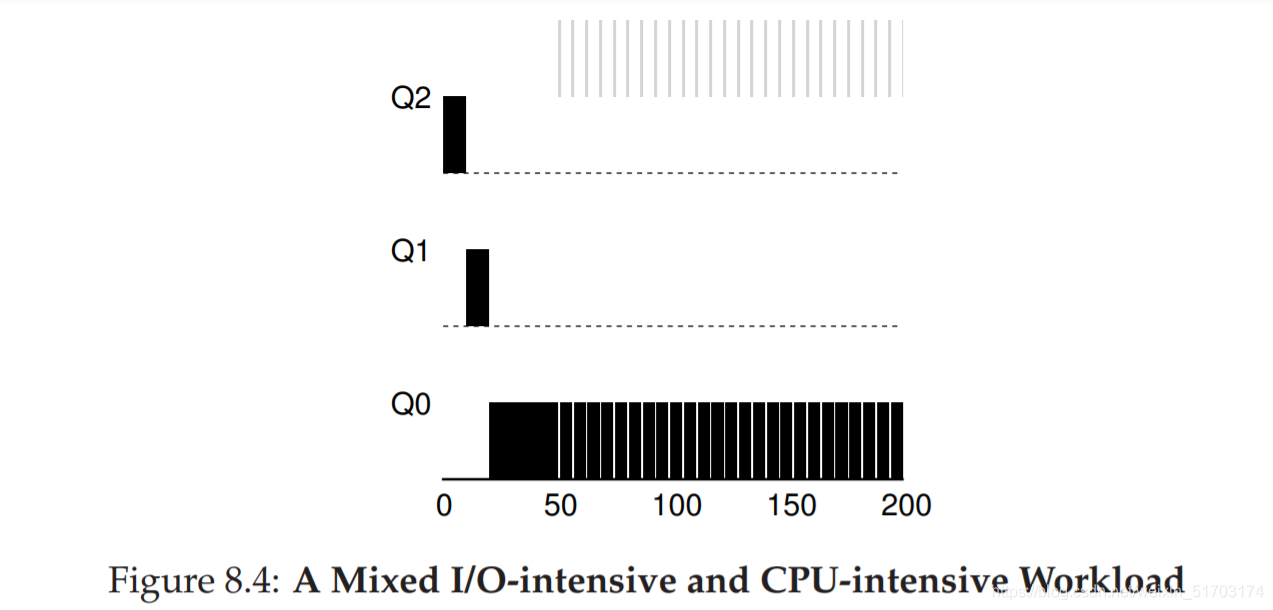
2.4 Problems With Our Current MLFQ
- starvation: if there are “too many” interactive jobs in the system, they will combine to consume all CPU time, and thus long-running jobs will never receive any CPU time (they starve).
- game the scheduler: Gaming the scheduler generally refers to the idea of doing something sneaky to trick the scheduler into giving you more than your fair share of the resource.
- a program may change its behavior over time: what was CPU-bound may transition to a phase of interactivity.
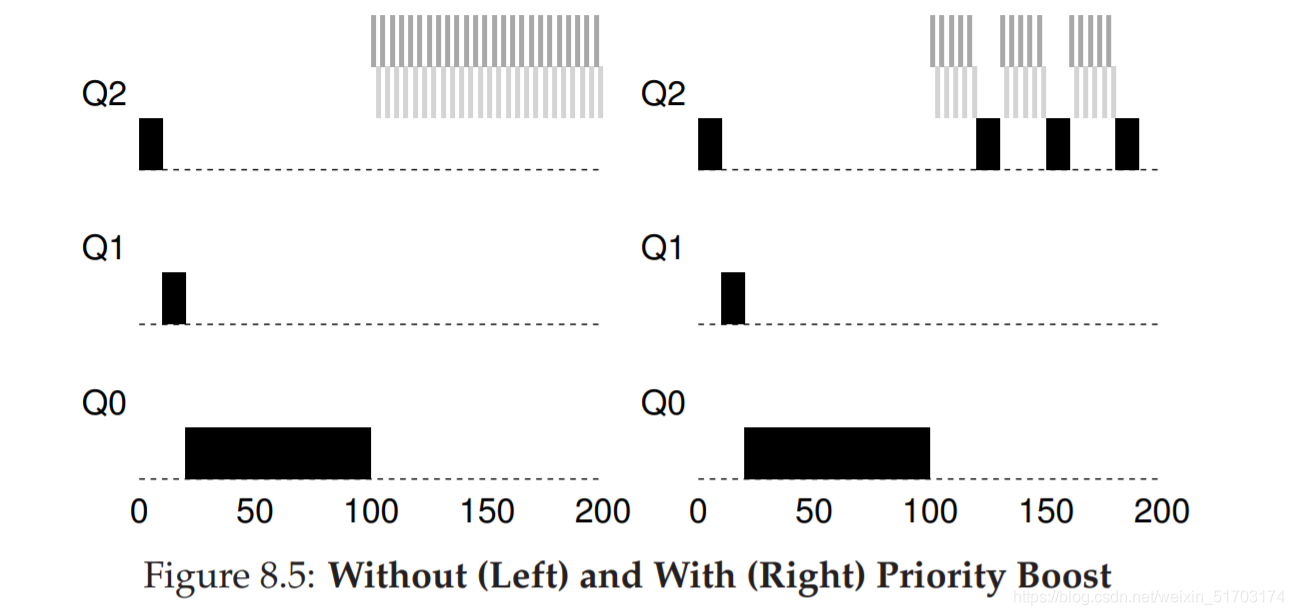
3. Attempt #2: The Priority Boost
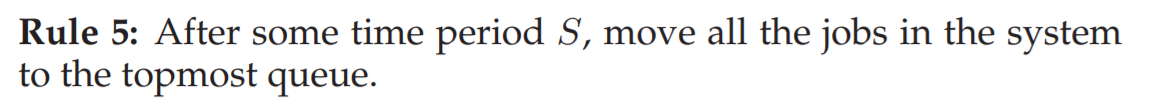


4. Attempt #3: Better Accounting
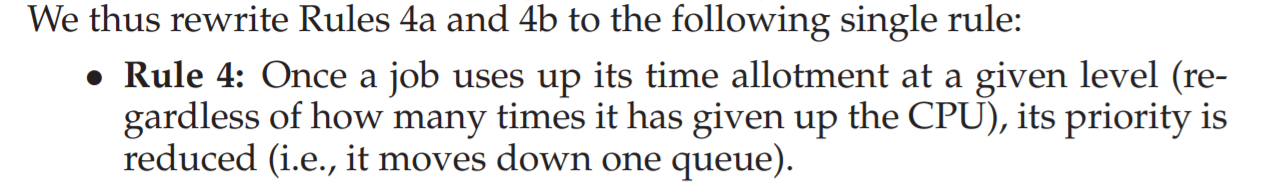

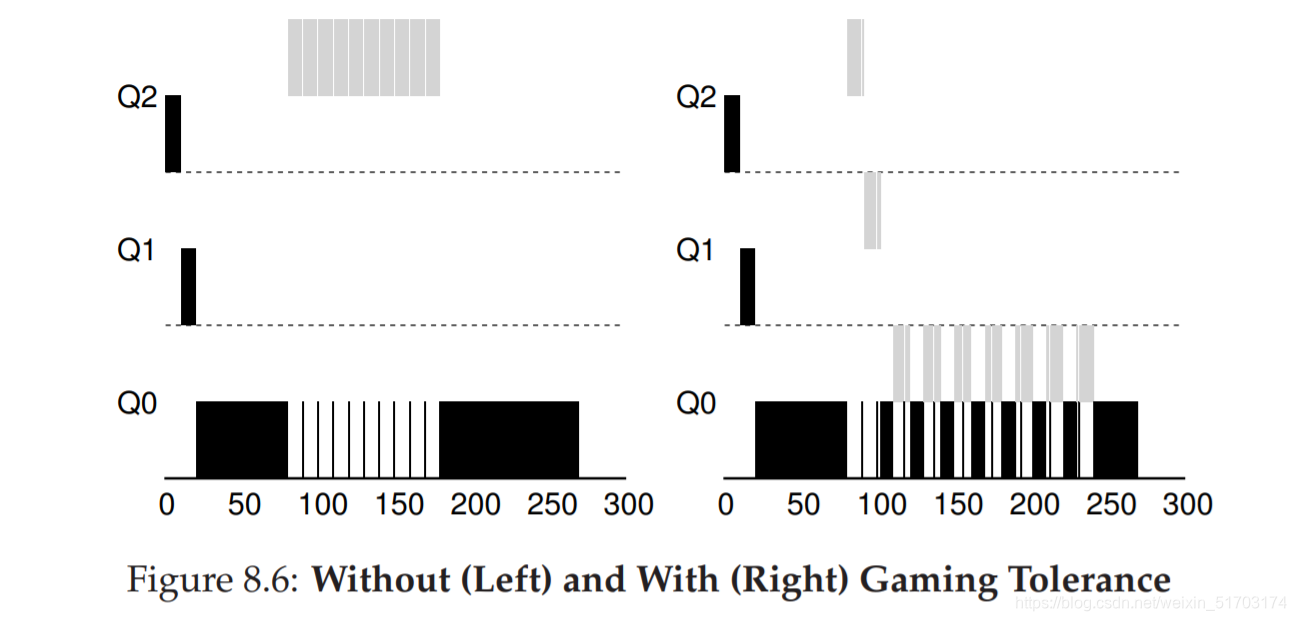
5. Tuning MLFQ And Other Issues

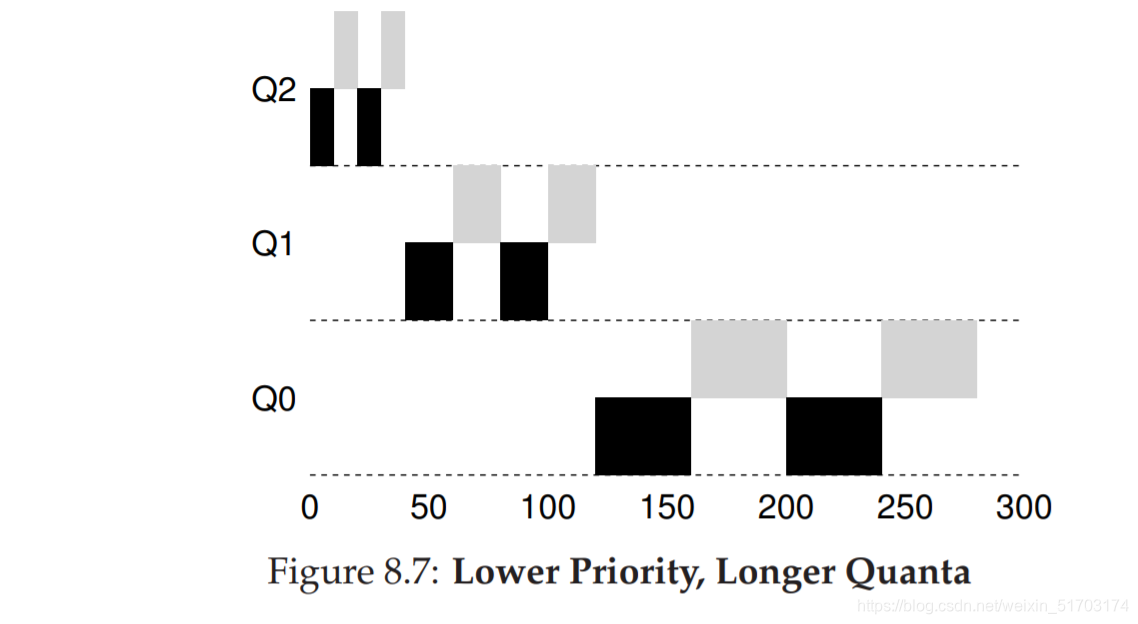
6. Summary

7. Homework (Simulation)

Question & Answer
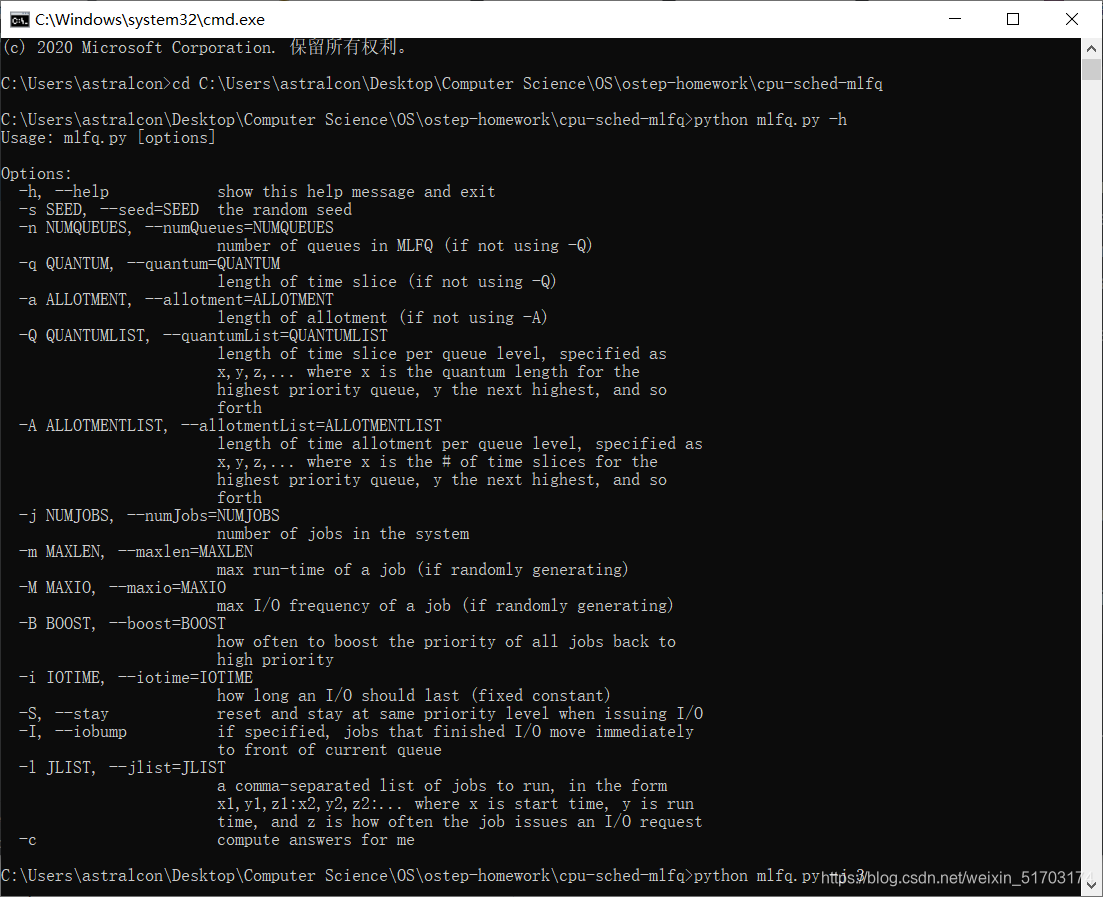
1. Run a few randomly-generated problems with just two jobs and two queues; compute the MLFQ execution trace for each. Make your life easier by limiting the length of each job and turning off I/Os.
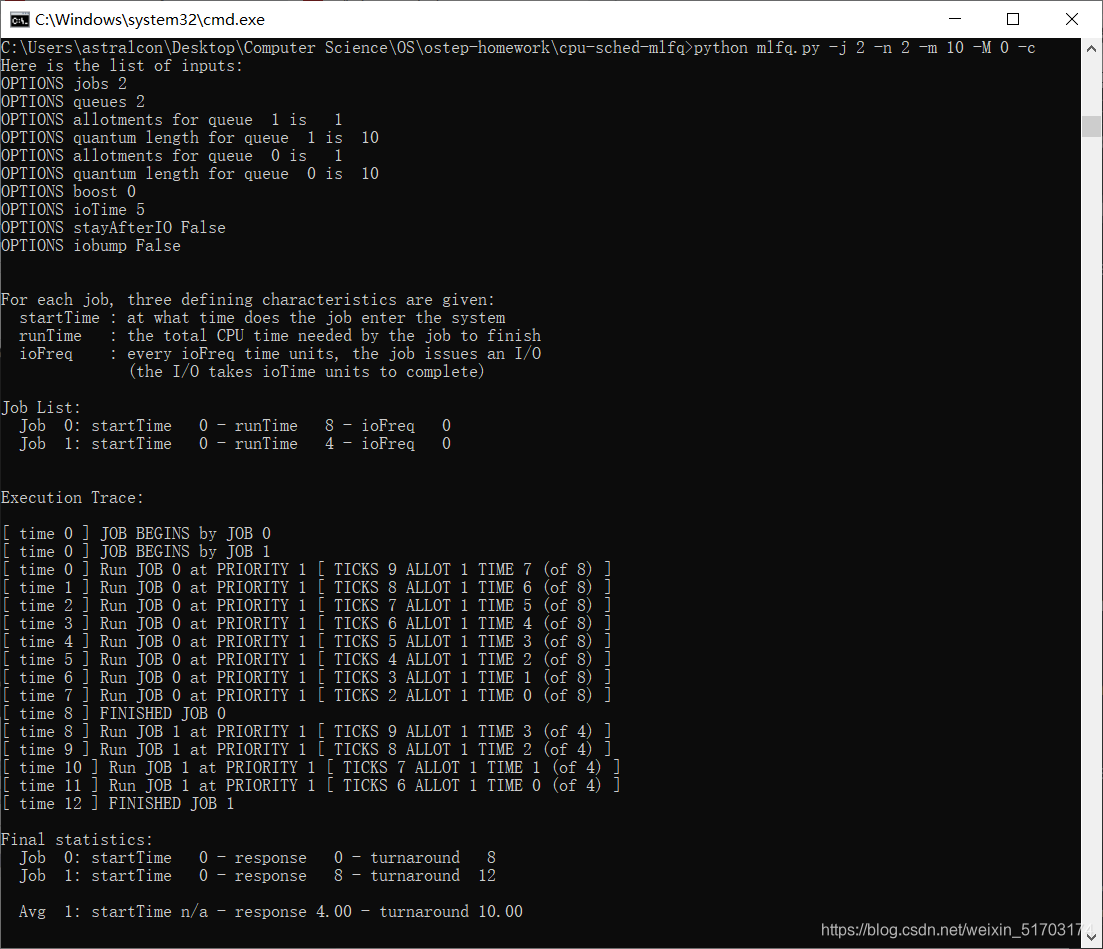
2. How would you run the scheduler to reproduce each of the examples in the chapter?
3. How would you configure the scheduler parameters to behave just like a round-robin scheduler?
in order to reflect RR scheduling, this parameter should have the following points:
1. Multiple jobs
2. One queue
3. There are the time slice
// x >= 2,y > 0
python mlfq.py -n 1 -j x -q y
4. Craft a workload with two jobs and scheduler parameters so that one job takes advantage of the older Rules 4a and 4b (turned on with the -S flag) to game the scheduler and obtain 99% of the CPU over a particular time interval.
to be continue....
5. Given a system with a quantum length of 10 ms in its highest queue, how often would you have to boost jobs back to the highest priority level (with the -B flag) in order to guarantee that a single long running (and potentially-starving) job gets at least 5% of the CPU?
T(boost) <= T(time slice) / 0.05 = 10ms / 0.05 = 200ms
6. One question that arises in scheduling is which end of a queue to add a job that just finished I/O; the -I flag changes this behavior for this scheduling simulator. Play around with some workloads and see if you can see the effect of this flag.
to be continue....




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端