软引用使用
概述
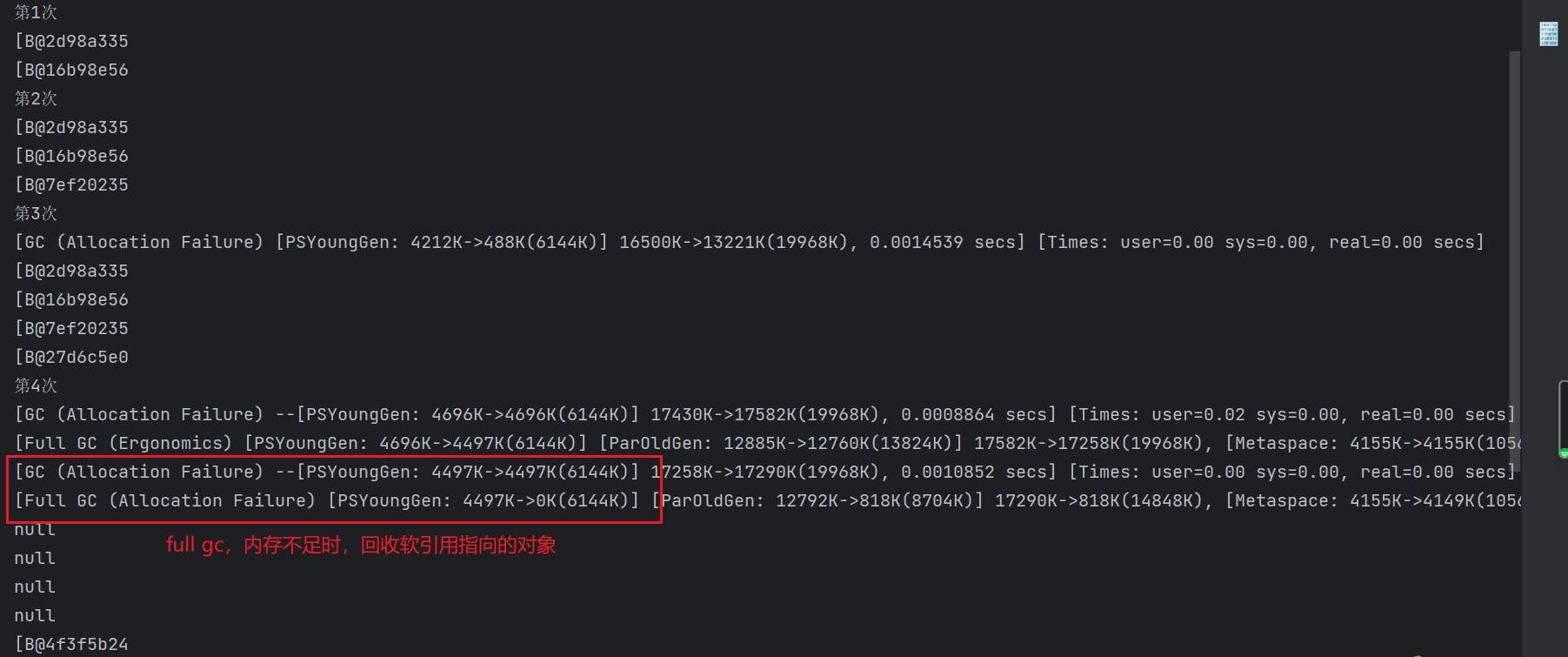
软引用:内存不足时,如果GC Root只有软引用,执行gc时会被回收
例子
/**
* @Author liufq
* @Date 2023/5/27
* @Desc 软引用使用,内存不足时,如果GC Root只有软引用,执行gc时会被回收
*
* 虚拟机参数:-Xmx20m -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc
*/
public class SoftReferenceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
t3();
}
public static void t1() {
List<byte[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
list.add(new byte[4 * 1024 * 1024]);
}
}
/**
* list -> SoftReference -> byte[]
*/
public static void t2() {
List<SoftReference<byte[]>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("第" + i + "次");
list.add(new SoftReference<>(new byte[4 * 1024 * 1024]));
list.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.get()));
}
}
/**
* 关联引用队列
* gc回收软引用指向的对象后,软引用被放入引用队列中,可以遍历队列对软引用做操作
*/
public static void t3() {
List<SoftReference<byte[]>> list = new ArrayList<>();
ReferenceQueue<byte[]> queue = new ReferenceQueue();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("第" + i + "次");
list.add(new SoftReference<>(new byte[4 * 1024 * 1024], queue));
list.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.get()));
}
//list中删除引用对象已经被回收的软引用
Reference<? extends byte[]> reference = queue.poll();
int i = 0;
while (reference != null) {
list.remove(reference);
reference = queue.poll();
i++;
}
//引用队列大小为4,最后一个不需要回收
System.out.println("引用队列大小:" + i);
//剩下最后一个
list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号