ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal
概述
ThreadLocal类用来提供线程内部的局部变量(线程本地变量)。这种变量在多线程环境下访问(通过get或set方法访问)时能保证各个线程里的变量相对独立于其他线程内的变量。ThreadLocal为变量在每个线程中都创建了一个副本,那么每个线程可以访问自己内部的副本变量。ThreadLocal实例通常来说都是private static类型的,用于关联线程和线程的上下文。
ThreadLocal
常用方法
public T get() { }
public void set(T value) { }
public void remove() { }
protected T initialValue() { }
get()方法是用来获取ThreadLocal在当前线程中保存的变量副本,set()用来设置当前线程中变量的副本,remove()用来移除当前线程中变量的副本,initialValue()是一个protected方法,一般是用来在使用时进行重写的。
get方法
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap,每个线程有一个ThreadLocalMap用于存储ThreadLocal键值对。
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
Thread.java
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap是一个基于数组的map
static class ThreadLocalMap {
/**
* The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using
* its main ref field as the key (which is always a
* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()
* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the
* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to
* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.
*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
/**
* The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two.
*/
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
/**
* The table, resized as necessary.
* table.length MUST always be a power of two.
*/
private Entry[] table;
/**
* The number of entries in the table.
*/
private int size = 0;
}
ThreadLocalMap源码有两个知识点:
- ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal的静态内部类。public class不能使用static修饰,只有内部类才可以使用static修饰。静态内部类与普通内部类的区别:静态内部类只能访问外部类的static变量,创建普通内部类的对象需要先创建外部类,静态内部类可以直接创建。
- WeakReference弱引用,如果一个对象只存在弱引用在gc时会被回收。
弱引用的简单使用
public class Student {
private String name;
Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
super.finalize();
System.out.println("回收Student对象");
}
}
public class Teacher extends WeakReference<Student> {
/**
* Creates a new weak reference that refers to the given object. The new
* reference is not registered with any queue.
*
* @param referent object the new weak reference will refer to
*/
public Teacher(Student referent) {
super(referent);
}
}
public class WeakReferenceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//不能这样写,这个是强引用,栈上强引用指向对象
//Student student = new Student("小红");
//Teacher teacher = new Teacher(student);
Teacher teacher = new Teacher(new Student("小红"));
System.out.println("Student:" + teacher.get());
//启动参数可以加上gc日志-XX:+PrintGCDetails,确保gc触发
System.gc();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("gc完成");
System.out.println("Student:" + teacher.get());
}
}
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap.Entry中的弱引用使用,Entry中的key为弱引用,value为ThreadLocal绑定的值。栈上的强引用断开后(=null),只存在key指向的弱引用,可以被gc回收,回收后key=null,而后如果调用ThreadLocalMap的getEntry函数或者set函数(线程的ThreadLocalMap还可能存在其他的键值,使用其他entry时调用getEntry可以清除掉key为null的value),这样value就会被回收了。
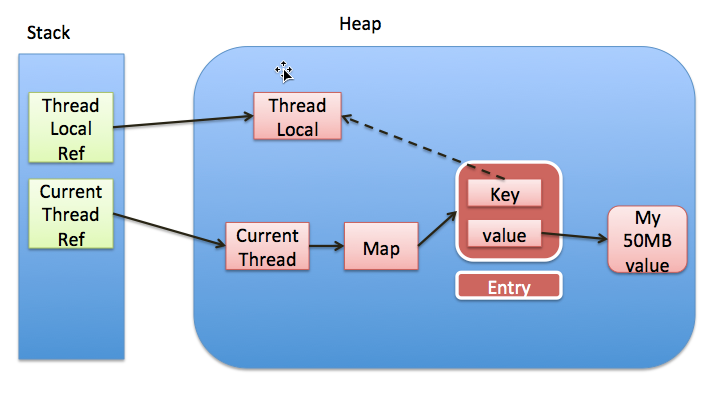
ThreadLocalMap主要方法
Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key){}
void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {}
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);返回此线程threadLocal对应的value。
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
要注意的点:getEntry()和set()都会调用getEntryAfterMiss(),循环了此线程的ThreadLocalMap中所有的键值,key为null的,即弱引用被gc的,调用expungeStaleEntry()。即使用其他threadLocal时,会清除ThreadLocalMap所有的key为null的entry。
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key)
return e;
if (k == null)
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
expungeStaleEntry(),擦除老旧的entry,即key已经被回收的entry。e.value = null;value引用指向null,gc时回收。
设计思路依赖一个前提条件,要调用ThreadLocalMap的getEntry函数或者set函数。这当然是不可能任何情况都成立的,所以很多情况下需要使用者手动调用ThreadLocal的remove函数,手动删除不再需要的ThreadLocal,防止内存泄露。所以JDK建议将ThreadLocal变量定义成private static的,这样的话ThreadLocal的生命周期就更长,由于一直存在ThreadLocal的强引用,所以ThreadLocal也就不会被回收,也就能保证任何时候都能根据ThreadLocal的弱引用访问到Entry的value值,然后remove它,防止内存泄露。
remove(), e.clear()设置key=null,调用expungeStaleEntry()擦除key为null的entry;
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear();
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}
public void clear() {
this.referent = null;
}
ThreadLocal应用场景
总结一下:
1)实际的通过ThreadLocal创建的副本是存储在每个线程自己的threadLocals中的;
2)threadLocals的ThreadLocalMap的键为ThreadLocal对象,因为每个线程中可有多个threadLocal变量。
3)在进行get之前,必须先set,否则会报空指针异常;
如果想在get之前不需要调用set就能正常访问的话,必须重写initialValue()方法。
如果没有先set的话,即在map中查找不到对应的存储,则会通过调用setInitialValue方法返回i,而在setInitialValue方法中,有一个语句是T value = initialValue(), 而默认情况下,initialValue方法返回的是null。
最常见的ThreadLocal使用场景为 用来解决 数据库连接、Session管理等。
数据库连接
知识点:匿名内部类常见用于接口的实现,实际上继承类也是可以的。
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> connectionHolder
= new ThreadLocal<Connection>() {
public Connection initialValue() {
return DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL);
}
};
public static Connection getConnection() {
return connectionHolder.get();
}
session管理
private static final ThreadLocal threadSession = new ThreadLocal();
public static Session getSession() throws InfrastructureException {
Session s = (Session) threadSession.get();
try {
if (s == null) {
s = getSessionFactory().openSession();
threadSession.set(s);
}
} catch (HibernateException ex) {
throw new InfrastructureException(ex);
}
return s;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号