Cloth Simulation with Root Finding and Optimization
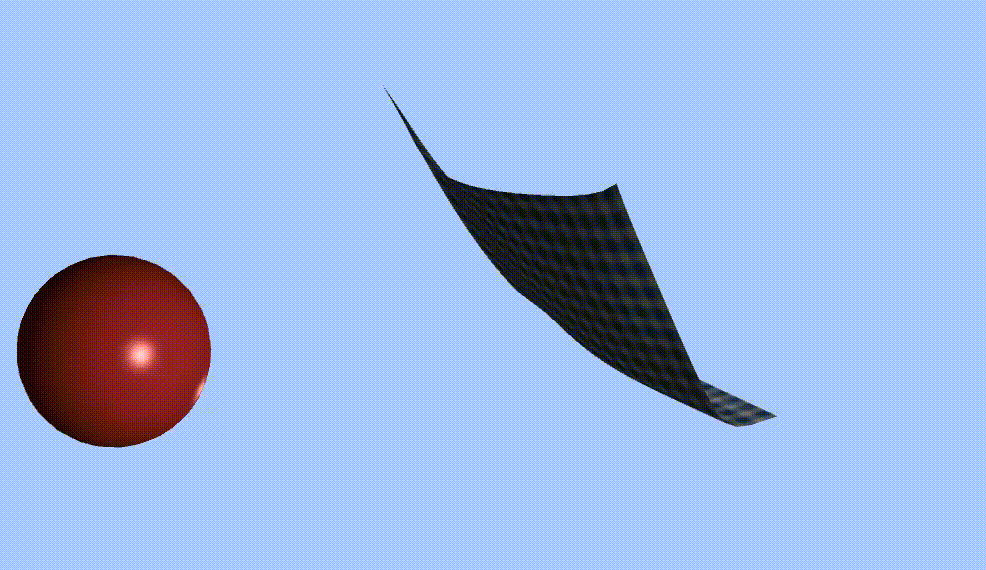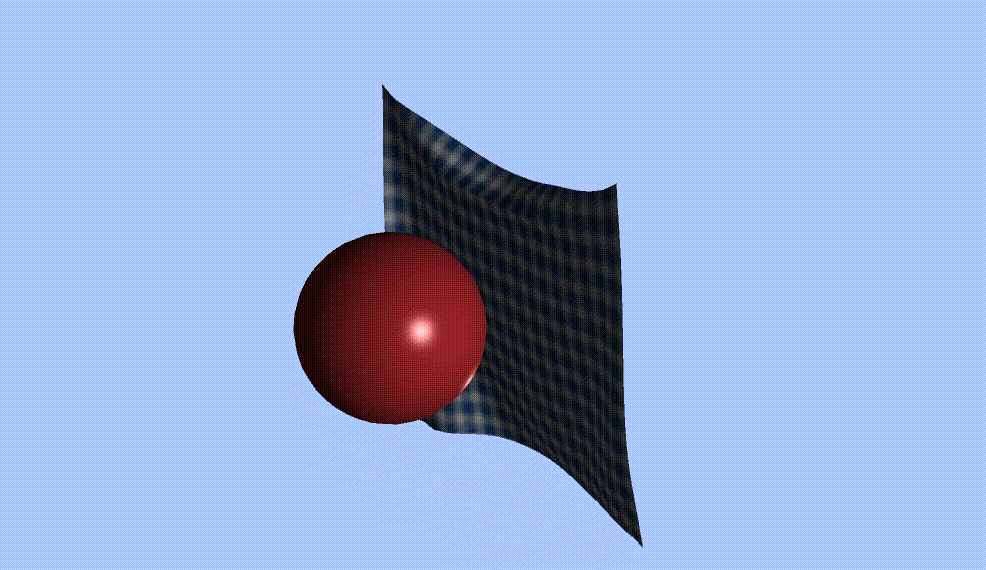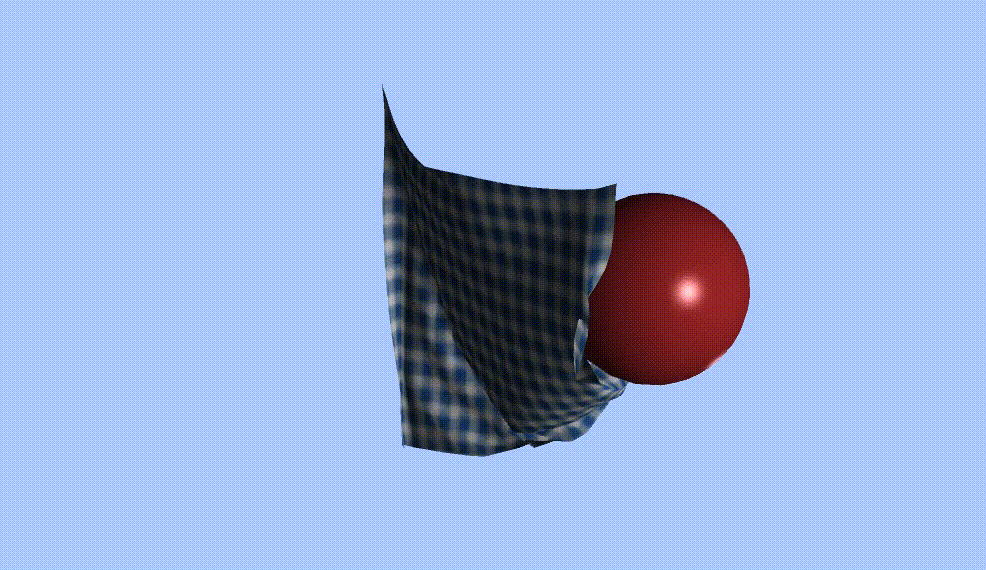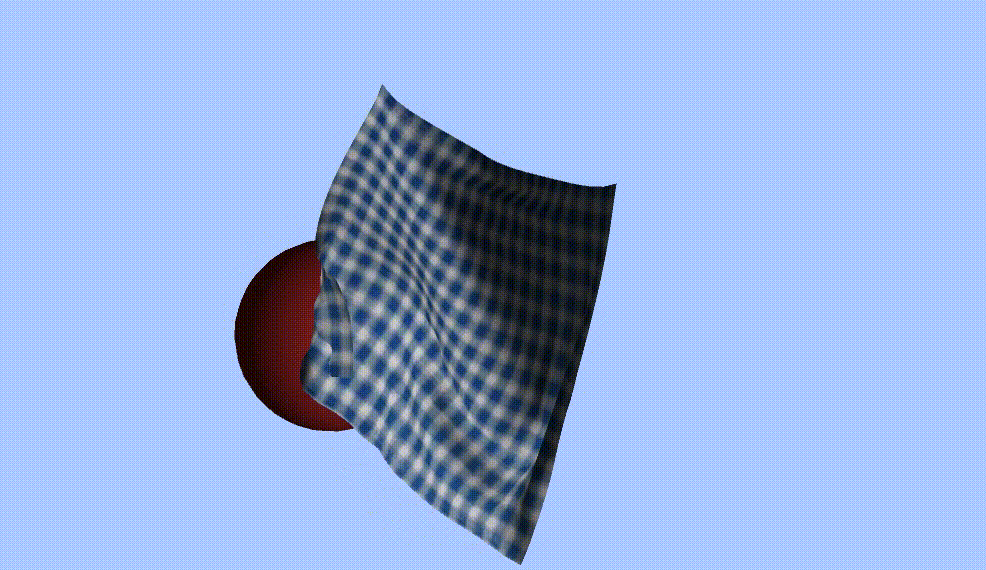
0 前言
声明:此篇博客仅用于个人学习记录之用,并非是分享代码。Hornor the Code
我只能说,衣料模拟的技术深度比3D刚体模拟的技术深太多了。这次的实验参考了许多资料,包括
- 《University of Tennessee MES301 Fall, 2023》
- 《Root finding and optimization: Scientific Computing for Physicists 2017》
- 《Physics-based animation lecture 5: OH NO! It's More Finite Elements》 这个老师讲课用一个小猫,特逗
- 当然主要还是 Games103王华民老师的《Intro to Physics-Based Animation!》
里面用到的一些技术,在有限元里也有应用。
另外还有不基于物理的衣料模拟 《Position Based Dynamics》, 这个是05年左右开始出现的技术。详细的内容可以看PBA 2014: Position Based Dynamics by Ladislav Kavan,因为不基于物理,这里不再涉及。
1 Implicit Method
进行一些简单的变换。
这里,我们只是认为力是位置的函数,所以可以写成。
这就需要解一个非线性方程,其中力并非是线性的。
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system (or a non-linear system) is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input.
In mathematics, a linear map (or linear function)is one which satisfies both of the following properties:
上面的式子其实是求出了隐式积分的原函数,上式求导就是隐式积分本身。
所以一个求解非线性方程,或者是求解非线性方程根的模式就可以变成优化问题,而且是非线性优化。
1.1 Root-finding
The solution of nonlinear algebraic equations is frequently called root-finding, since our goal is to find the value of
1.2 Optimization
Optimization means finding a maximum or minimum.
In mathematical terms, optimization means finding where the derivative is zero.
University of Tennessee MES301
Root finding and optimization: Scientific Computing for Physicists 2017
1.3 Insight
我们看到,这两个东西很像,基本就是解方程。所以有时候我们可以将其进行转化。
就是导数和积分的关系。
Physics-based animation lecture 5: OH NO! It's More Finite Elements
2 Newton-Raphson Method
Given a current
We then solve:
Specifically to simulation, we have:
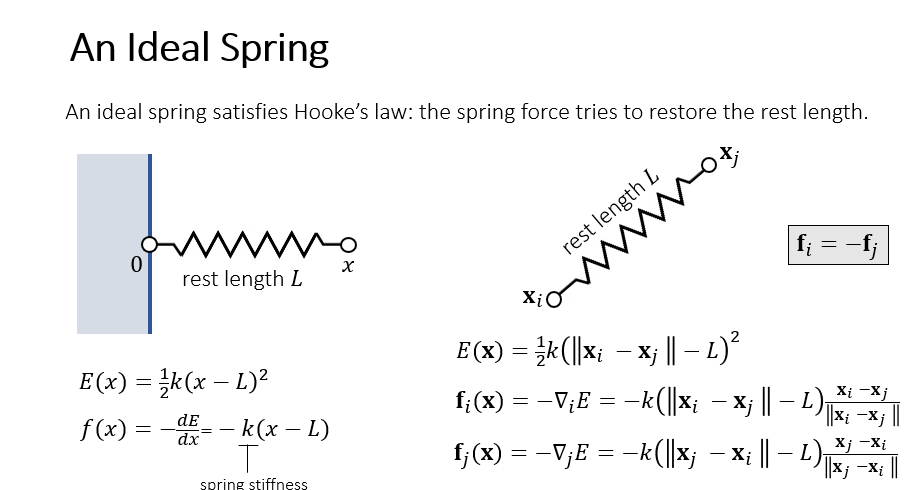
3 Mass-Spring System
3.1 Matrix calculus
3.2 A Spring with Two Ends
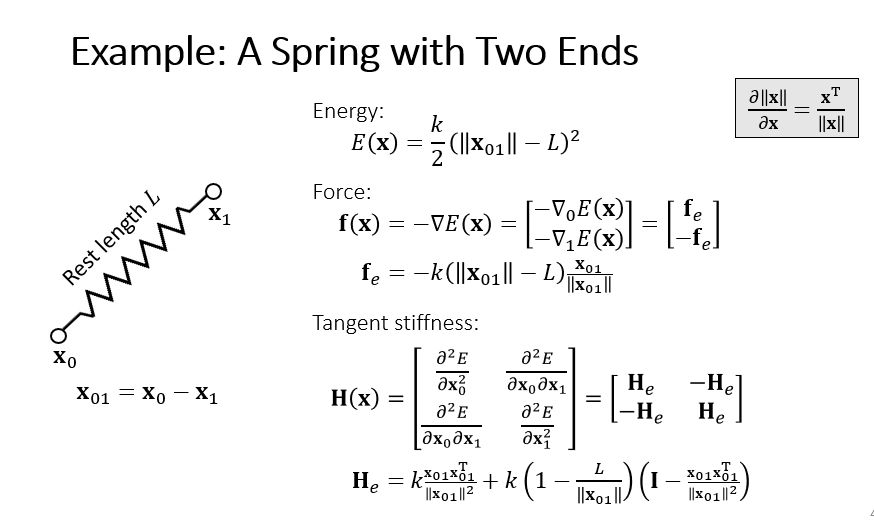
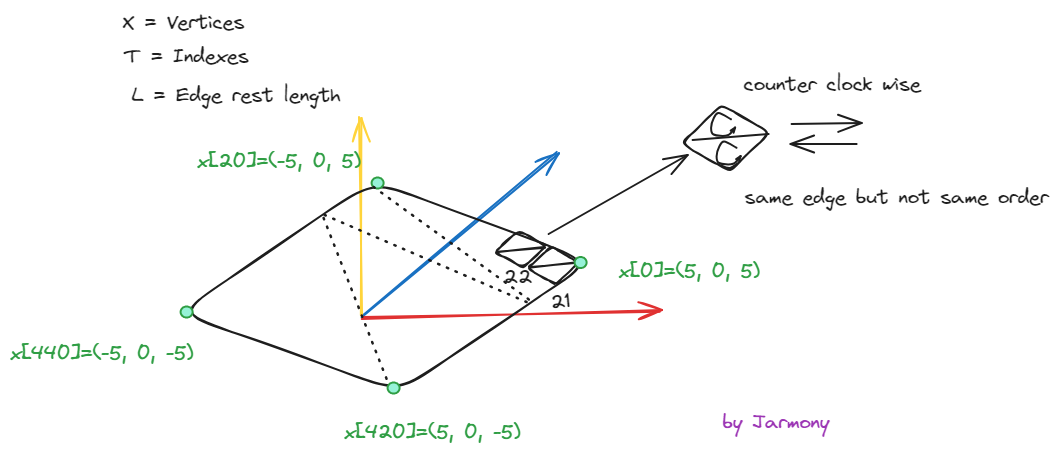
4 Explaination of Init Code with 3D Image
4.1 Initialize
void Start()
{
Mesh mesh = GetComponent<MeshFilter> ().mesh;
//Resize the mesh.
int n=21;
Vector3[] X = new Vector3[n*n];
Vector2[] UV = new Vector2[n*n];
int[] triangles = new int[(n-1)*(n-1)*6];
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
X[j*n+i] =new Vector3(5-10.0f*i/(n-1), 0, 5-10.0f*j/(n-1));
UV[j*n+i]=new Vector3(i/(n-1.0f), j/(n-1.0f));
}
int t=0;
for(int j=0; j<n-1; j++)
for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++)
{
triangles[t*6+0]=j*n+i;
triangles[t*6+1]=j*n+i+1;
triangles[t*6+2]=(j+1)*n+i+1;
triangles[t*6+3]=j*n+i;
triangles[t*6+4]=(j+1)*n+i+1;
triangles[t*6+5]=(j+1)*n+i;
t++;
}
mesh.vertices=X;
mesh.triangles=triangles;
mesh.uv = UV;
mesh.RecalculateNormals ();
Debug.Log("triangles.Length " + triangles.Length);
//Construct the original E
int[] _E = new int[triangles.Length*2];
Debug.Log("_E.Length " + _E.Length);
for (int i=0; i<triangles.Length; i+=3)
{
_E[i*2+0]=triangles[i+0];
_E[i*2+1]=triangles[i+1];
_E[i*2+2]=triangles[i+1];
_E[i*2+3]=triangles[i+2];
_E[i*2+4]=triangles[i+2];
_E[i*2+5]=triangles[i+0];
}
//Reorder the original edge list
for (int i=0; i<_E.Length; i+=2)
if(_E[i] > _E[i + 1])
Swap(ref _E[i], ref _E[i+1]);
//Sort the original edge list using quicksort
// One edge have two end point, this quicksort method sort all of them at the same time
// the order is from small to big with the pattern of
// [start end] [start end] [start end]
//Debug.Log("_E.Length/2-1 " + (_E.Length / 2 - 1) );
Quick_Sort(ref _E, 0, _E.Length/2-1);
// short-circuit evaluation: or(if first condition is true then skip other) and(if first condition is false then skip other)
int e_number = 0;
for (int i=0; i<_E.Length; i+=2)
if (i == 0 || _E [i + 0] != _E [i - 2] || _E [i + 1] != _E [i - 1])
e_number++;
E = new int[e_number * 2];
for (int i=0, e=0; i<_E.Length; i+=2)
if (i == 0 || _E [i + 0] != _E [i - 2] || _E [i + 1] != _E [i - 1])
{
E[e*2+0]=_E [i + 0];
E[e*2+1]=_E [i + 1];
e++;
}
// [0-9] 10/2=5 <5=4 4*2+1=9
// [0-10] 11/2=5 <5=4 4*2+1=9
// asert(E.length % 2 == 0) this should always be true, becuase we use one dim array to store the Edges. One edge takes two places in this array.
L = new float[E.Length/2];
for (int e=0; e<E.Length/2; e++)
{
int v0 = E[e*2+0];
int v1 = E[e*2+1];
L[e]=(X[v0]-X[v1]).magnitude;
}
V = new Vector3[X.Length];
for (int i=0; i<V.Length; i++)
V[i] = new Vector3 (0, 0, 0);
}
4.2 Index
int t=0;
// Because of 21 points have 20 gaps, this index will iterate 400 squares and split them two triangels
// per square.
for(int j=0; j<n-1; j++)
for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++)
{
triangles[t*6+0]=j*n+i;
triangles[t*6+1]=j*n+i+1;
triangles[t*6+2]=(j+1)*n+i+1;
triangles[t*6+3]=j*n+i;
triangles[t*6+4]=(j+1)*n+i+1;
triangles[t*6+5]=(j+1)*n+i;
t++;
}
这里的 triangles 其实就是 三角形顶点的Index(下标)。
State: j=0, i=0, t=0.
t[0] = 0
t[1] = 1
t[2] = 22
t[3] = 0
t[4] = 22
t[5] = 21
/*********/
State: j=0, i=1, t=1.
t[6] = 1
t[7] = 2
t[8] = 23
t[9] = 1
t[10] = 23
t[11] = 22
4.3 Edge
//Construct the original E
int[] _E = new int[triangles.Length*2];
Debug.Log("_E.Length " + _E.Length);
for (int i=0; i<triangles.Length; i+=3)
{
_E[i*2+0]=triangles[i+0];
_E[i*2+1]=triangles[i+1];
_E[i*2+2]=triangles[i+1];
_E[i*2+3]=triangles[i+2];
_E[i*2+4]=triangles[i+2];
_E[i*2+5]=triangles[i+0];
}
//Reorder the original edge list
for (int i=0; i<_E.Length; i+=2)
if(_E[i] > _E[i + 1])
Swap(ref _E[i], ref _E[i+1]);
因为这里使用一维数组进行边的存储,那么从一条边到另一条边的步长是2。
State: i=0.
_E[0] = t[0]:0
_E[1] = t[1]:1
_E[2] = t[1]:1
_E[3] = t[2]:22
_E[4] = t[2]:22
_E[5] = t[0]:0
/*********/
State: i=3.
_E[6]= t[3]:0
_E[7] = t[4]:22
_E[8] = t[4]:22
_E[9] = t[5]:21
_E[10] = t[5]:21
_E[11] = t[3]:0
4.4 Sort Edge
//Reorder the original edge list
for (int i=0; i<_E.Length; i+=2)
if(_E[i] > _E[i + 1])
Swap(ref _E[i], ref _E[i+1]);
初始的时候,一条边有两种表达方式。我们将其都按从小的顶点到大的顶点进行重新排序,一条边就只有一种表达方式。
Quick_Sort(ref _E, 0, _E.Length/2-1);
void Quick_Sort(ref int[] a, int l, int r)
{
int j;
if(l<r)
{
j=Quick_Sort_Partition(ref a, l, r);
Quick_Sort (ref a, l, j-1);
Quick_Sort (ref a, j+1, r);
}
}
int Quick_Sort_Partition(ref int[] a, int l, int r)
{
int pivot_0, pivot_1, i, j;
pivot_0 = a [l * 2 + 0];
pivot_1 = a [l * 2 + 1];
i = l;
j = r + 1;
//Debug.Log("i: " + i + " j:" + j);
while (true)
{
do ++i; while( i<=r && (a[i*2]<pivot_0 || a[i*2]==pivot_0 && a[i*2+1]<=pivot_1));
do --j; while( a[j*2]>pivot_0 || a[j*2]==pivot_0 && a[j*2+1]> pivot_1);
if(i>=j) break;
Swap(ref a[i*2], ref a[j*2]);
Swap(ref a[i*2+1], ref a[j*2+1]);
}
Swap (ref a [l * 2 + 0], ref a [j * 2 + 0]);
Swap (ref a [l * 2 + 1], ref a [j * 2 + 1]);
return j;
}
void Swap(ref int a, ref int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
这里的quick sort是以两个数为一次比较的依据,好像是这两个数打包(其实就是一条边)进行比较,平常就是一次比较只关心一个数。
5 Update
// Update is called once per frame
void Update ()
{
Mesh mesh = GetComponent<MeshFilter> ().mesh;
Vector3[] X = mesh.vertices;
Vector3[] last_X = new Vector3[X.Length];
Vector3[] X_hat = new Vector3[X.Length];
Vector3[] G = new Vector3[X.Length];
//Initial Setup.
for (int i = 0; i < X.Length; i++)
{
if (i == 0 || i == 20) continue;
V[i] = V[i] * damping;
X_hat[i] = X[i] + V[i] * t;
last_X[i] = X[i];
// Guess X[i] init state
X[i] = X_hat[i];
}
float invSquareDt = 1 / (t * t);
// Hessian Matrix is complicated to construct
// So we use some fake inverse, due to the mass is same for all vertices, we put this out of the loop.
float fakeInv = 1 / (invSquareDt * mass + 4.0f * spring_k);
for (int k=0; k<32; k++)
{
Get_Gradient(X, X_hat, t, G);
//Update X by gradient.
for (int i = 0; i < X.Length; i++)
{
if (i == 0 || i == 20) continue;
X[i] = X[i] - fakeInv * G[i];
}
}
float invTime = 1.0f / t;
for (int i = 0; i < X.Length; i++)
{
if (i == 0 || i == 20) continue;
V[i] = invTime * (X[i] - last_X[i]);
}
//Finishing.
mesh.vertices = X;
Collision_Handling ();
mesh.RecalculateNormals ();
}
因为要进行优化,位置迭代,来找到最小值。所以需要一个迭代的初始位置,设置为X_init = X[i] + V[i] * t。也可以不设置,不进行变化。
6 Get_Gradient
void Get_Gradient(Vector3[] X, Vector3[] X_hat, float t, Vector3[] G)
{
//Momentum and Gravity.
float invSquareDt = 1 / (t * t);
for (int i = 0; i < X.Length; i++)
{
G[i] = invSquareDt * mass * (X[i] - X_hat[i]) - mass * gravity;
}
//Spring Force.
Vector3 spForceDir = Vector3.zero;
Vector3 spForce = Vector3.zero;
for (int e = 0; e < E.Length / 2; e++)
{
int vi = E[e * 2 + 0];
int vj = E[e * 2 + 1];
spForceDir = X[vi] - X[vj];
spForce = spring_k * (1.0f - L[e] / spForceDir.magnitude) * spForceDir;
G[vi] = G[vi] + spForce;
G[vj] = G[vj] - spForce;
}
}
6.1 first derivative
由于上式的特性,我们需要两次遍历来得到梯度一阶导的数值。
- 逐顶点
- 逐边计算弹簧弹力
当然无论是逐顶点还是逐边,导数都是位置的函数。
最后给每一个顶点的梯度加上重力,当然根据 g 需要加负号。
6.2 second derivative
In reality, there are two roadblocks:
1)The Hessian matrix is complicated to construct;
2) the linear solver is difficult to implement on Unity.
Instead, we choose a much simpler method by considering the Hessian as a diagonal matrix. This
yields a simple update to every vertex as:
Games103 Huamin Wang Lab2
7 Collision_Handling
void Collision_Handling()
{
Mesh mesh = GetComponent<MeshFilter> ().mesh;
Vector3[] X = mesh.vertices;
//Handle colllision.
Vector3 ballPos = GameObject.Find("Sphere").transform.position;
float radius = 2.7f;
for (int i = 0; i < X.Length; i++)
{
if (i == 0 || i == 20) continue;
if (SDF(X[i], ballPos))
{
V[i] = V[i] + 1.0f / t * (ballPos + radius * (X[i] - ballPos).normalized - X[i]);
X[i] = ballPos + radius * (X[i] - ballPos).normalized;
}
}
}
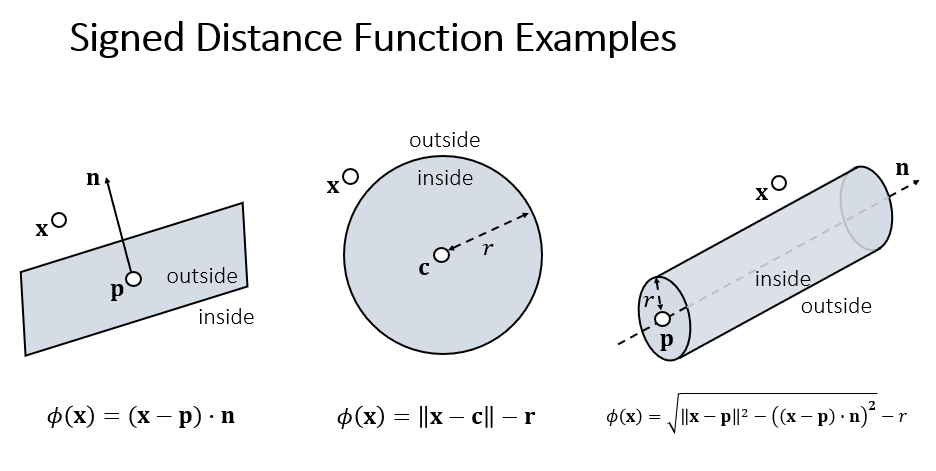
bool SDF(Vector3 v, Vector3 center, float radius = 2.7f)
{
float sdf = (v - center).magnitude - radius;
return sdf > 0.0f ? false : true;
}
Once a colliding vertex is found, apply impulse-based method as follows:
大模型时代,文字创作已死。2025年全面停更了,世界不需要知识分享。
如果我的工作对您有帮助,您想回馈一些东西,你可以考虑通过分享这篇文章来支持我。我非常感谢您的支持,真的。谢谢!
作者:Dba_sys (Jarmony)
转载以及引用请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/asmurmur/p/17955603
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用CC 署名-非商业使用-相同方式共享 许可协议。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律