Rigid Body Simulation
0 前言
声明:此篇博客仅用于个人学习记录之用,并非是分享代码。Hornor the Code
刚体动力学仿真的实现,方法来自Games103。
同时因为之前学习Jonh Crag的《机器人学》,感觉自己的动力学部分差的很多,所以也有很多动力学的知识来自于Cambridge David Tong: Lectures on Dynamics and Relativity, 这个讲义的相对论那边没怎么看。
参考了《Physically Based Modeling by David Baraff Pixar Animation Studios》 只用到了前面一章的内容 Unconstrained Rigid Body Dynamics。这也是给出的课后阅读材料,大致70页左右。
现在David Baraff 是斯坦福 cs448b 的 Course Speakers https://graphics.stanford.edu/courses/cs448b-00-winter/papers/phys_model.pdf 又有一本全面的大概300页的物理仿真的Lecture。
有关姿态更新的地方,王华民老师的课件里给出的是不包含torque-free-motion的角速度更新方程。torque-free-motion的核心就是,因为角动量守恒,在不受力矩的情况下,具有初始的角速度,因此刚体的姿态会发生变化,导致角速度也得变化。
碰撞响应的部分,并没有同PBM给出的回溯时间的方法,当有顶点侵入到物体内部,时间回溯到碰撞之时,重启ode-solver。因为刚体碰撞,也就是说,两个物体之间是有相对速度的,碰撞的时候,速度会发生较大的改变,可以说在那瞬间,速度并不是连续的。
本课程给出的碰撞响应,是通过计算冲量的方式,用一个简化方式。\(J = F \Delta{t} = Ma \Delta{t} = M \Delta{v}\)。
当让能够称之为等号的是 \(dv = adt\), 上式其实只能算近似 \(\Delta{v} \approx a \Delta{t}\)。
这就导致了位置一直是连续的,所以哪怕是侵入了墙体之后,兔子也不可能瞬间出来,反而会在里面待一会儿。
1 核心技术
1.1 Semi-implicit Euler
这个如何理解呢,关键就是对于每一帧的渲染。我们只有三个量
- \(\mathbf{v}^{[0]}\)
- \(\mathbf{x}^{[0]}\)
- \(\Delta{t}\)
也就是说,前一帧的位置和速度信息,以及一个时间差。
需要我们计算当前的位置与速度,并且渲染出来。
半隐式欧拉这玩意有1阶精度。但更稳定一点。
怎么说呢,就以课程代码给出的时间间隔t = 0.0015f, 那么就算是2阶精度 t^2 = 0.00000225。就以纯累加算,1秒60帧,一分钟3600帧,已经导致将近 0.0081的误差(似乎也不能么算)。
事实上,我试过只有torque-free-motion的仿真,5分钟直接爆炸,numerical instability。
1.2 刚体模拟
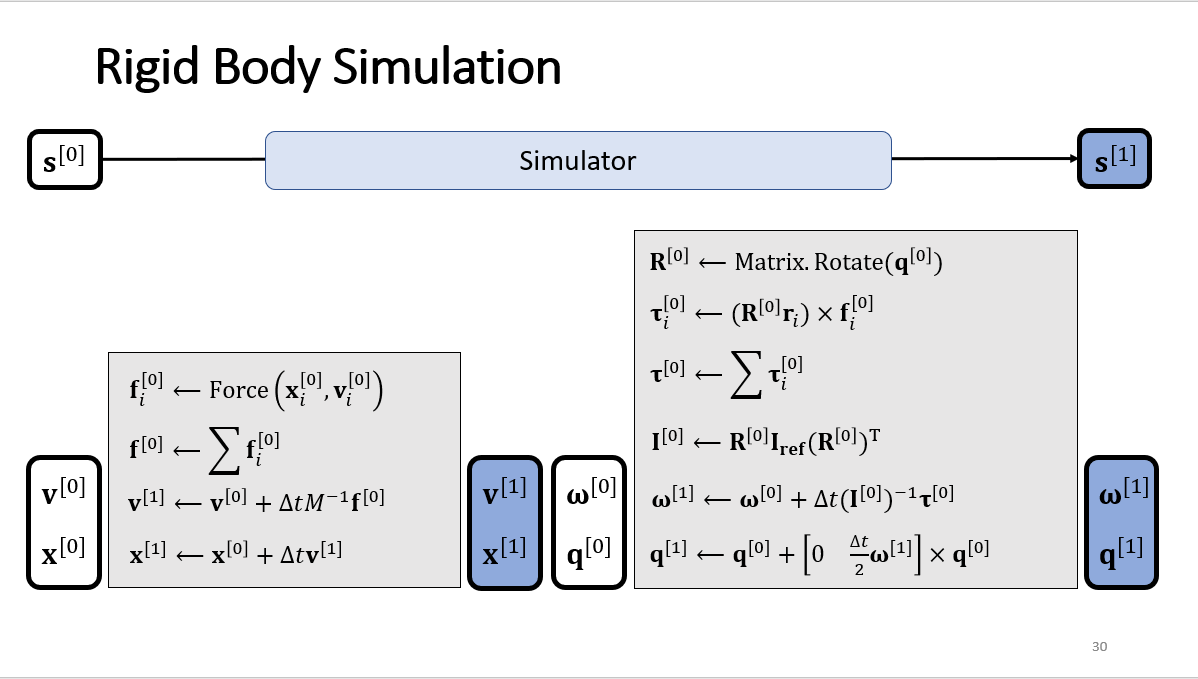
图片来源: Games103 lecture3 Rigid Body Dynamics
Inertia_tensor 的从 body 到 world 的变换可以看 PBM。这个tensor会随着姿态的变化而变化, body frame 的坐标系原点是质心。
- 2.10 The Inertia Tensor Page.13
角速度的更新不考虑torque-free-motion,这个可以看 PBM。
- C.2 Angular Accelerion Page.60 具体推导。
四元数的更新可以看 PBM。PBM中给出的四元数的乘法,说是为了与矩阵乘法类似,是左乘的过程。而Unity给出的是右乘。这是需要注意的点。
- 4 Quaternions vs. Rotation Matrices Page.20
- Appendix B Quaternion Derivations Page.58
ODE相关的知识可以去看 MIT的 Matrix Calculus 2023年10月23日 鸡汤来喽。里面关于导数的一些认识,特别有启发。
1.3 Collision
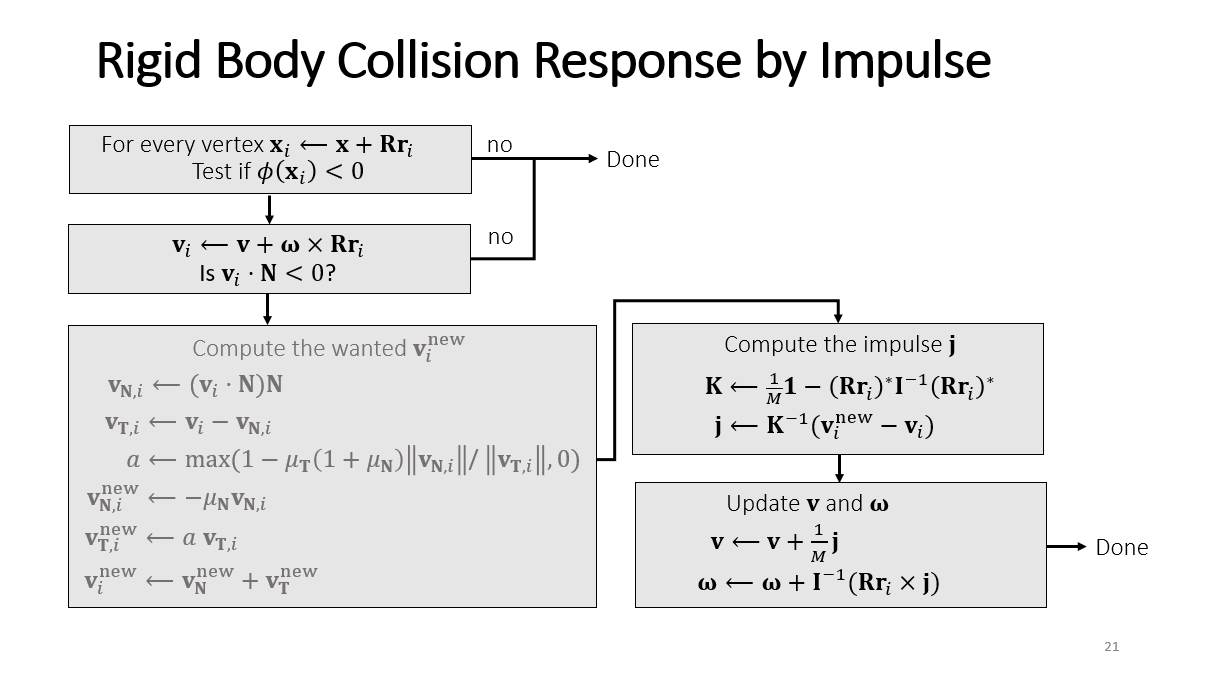
图片来源: Games103 lecture4 Rigid Body Contacts
𝑎 should be minimized while meeting Coulomb’s law, 𝑎是决定切向速度的改变量。最小是0,也就是说,一碰,切向的速度就成了0,因为比较大的摩擦力的缘故。
另外冲量的计算是遍历所有的顶点,找出其中处于碰撞的点,然后取平均值,基于平均的速度和位置,计算冲量。
2 实现
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class Rigid_Bunny : MonoBehaviour
{
bool launched = false;
float dt = 0.015f;
Vector3 v = new Vector3(0, 0, 0); // velocity
Vector3 w = new Vector3(0, 0, 0); // angular velocity
float mass; // mass
Matrix4x4 I_ref; // reference inertia
float linear_decay = 0.999f; // for velocity decay
float angular_decay = 0.98f;
float restitution = 0.5f; // for collision Mu_N
// Mine Var
Vector3 g = new Vector3(0, -9.8f, 0);
float Mu_T = 0.8f;
// Use this for initialization
void Start ()
{
Mesh mesh = GetComponent<MeshFilter>().mesh;
Vector3[] vertices = mesh.vertices;
float m=1;
mass=0;
for (int i=0; i<vertices.Length; i++)
{
mass += m;
float diag=m*vertices[i].sqrMagnitude;
I_ref[0, 0]+=diag;
I_ref[1, 1]+=diag;
I_ref[2, 2]+=diag;
I_ref[0, 0]-=m*vertices[i][0]*vertices[i][0];
I_ref[0, 1]-=m*vertices[i][0]*vertices[i][1];
I_ref[0, 2]-=m*vertices[i][0]*vertices[i][2];
I_ref[1, 0]-=m*vertices[i][1]*vertices[i][0];
I_ref[1, 1]-=m*vertices[i][1]*vertices[i][1];
I_ref[1, 2]-=m*vertices[i][1]*vertices[i][2];
I_ref[2, 0]-=m*vertices[i][2]*vertices[i][0];
I_ref[2, 1]-=m*vertices[i][2]*vertices[i][1];
I_ref[2, 2]-=m*vertices[i][2]*vertices[i][2];
}
I_ref [3, 3] = 1;
}
Matrix4x4 Get_Cross_Matrix(Vector3 a)
{
//Get the cross product matrix of vector a
Matrix4x4 A = Matrix4x4.zero;
A [0, 0] = 0;
A [0, 1] = -a [2];
A [0, 2] = a [1];
A [1, 0] = a [2];
A [1, 1] = 0;
A [1, 2] = -a [0];
A [2, 0] = -a [1];
A [2, 1] = a [0];
A [2, 2] = 0;
A [3, 3] = 1;
return A;
}
// In this function, update v and w by the impulse due to the collision with
//a plane <P, N>
void Collision_Impulse(Vector3 P, Vector3 N)
{
Mesh mesh = GetComponent<MeshFilter>().mesh;
Vector3[] vertices = mesh.vertices;
Vector3 x = transform.position;
Matrix4x4 R = Matrix4x4.Rotate(transform.rotation);
Matrix4x4 Inertia_tensor = R * I_ref * R.transpose;
Vector3 avg_pos = new Vector3(0, 0, 0);
Vector3 avg_vol = new Vector3(0, 0, 0);
bool isCllison = false;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < vertices.Length; i++)
{
Vector3 Rv_i = R.MultiplyVector(vertices[i]);
Vector3 world_vertice = x + Rv_i;
float SDF = Vector3.Dot(world_vertice - P, N);
if (SDF < 0.0f)
{
Vector3 world_volocity = v + Vector3.Cross(w, Rv_i);
float vSDF = Vector3.Dot(world_volocity, N);
if (vSDF < 0.0f)
{
count++;
avg_pos += vertices[i];
avg_vol += world_volocity;
isCllison = true;
}
}
}
if (isCllison)
{
avg_pos /= count;
avg_vol /= count;
Vector3 Rv_i = R.MultiplyVector(avg_pos);
// Compute the wanted v_new^i
Vector3 v_N = Vector3.Dot(avg_vol, N) * N;
Vector3 v_T = avg_vol - v_N;
float a = Mathf.Max(1 - (Mu_T * (1 + restitution) * v_N.magnitude / v_T.magnitude), 0.0f);
v_N = -restitution * v_N;
v_T = a * v_T;
Vector3 v_new = v_N + v_T;
float massinv = (1.0f / mass);
Matrix4x4 massinv_Indentity = new Matrix4x4(massinv * Matrix4x4.identity.GetColumn(0),
massinv * Matrix4x4.identity.GetColumn(1),
massinv * Matrix4x4.identity.GetColumn(2),
Matrix4x4.identity.GetColumn(3));
Matrix4x4 K = M_minus_M(massinv_Indentity,
Get_Cross_Matrix(Rv_i) * Inertia_tensor.inverse * Get_Cross_Matrix(Rv_i));
Vector3 j = K.inverse.MultiplyVector(v_new - avg_vol);
Debug.Log(K);
Debug.Log(j);
// update volocity
v = v + massinv * j;
w = w + Inertia_tensor.inverse.MultiplyVector(Vector3.Cross(Rv_i, j));
}
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update ()
{
//Game Control
if(Input.GetKey("r"))
{
transform.position = new Vector3 (0, 0.6f, 0);
restitution = 0.5f;
launched=false;
}
if(Input.GetKey("l"))
{
v = new Vector3 (5, 2, 0);
launched=true;
}
// Part I: Update velocities
float m = 1;
Vector3 f_i = new Vector3(0, 0, 0);
Vector3 toruqe_i = new Vector3(0, 0, 0);
Vector3 F = new Vector3(0, 0, 0);
Vector3 Torque = new Vector3(0, 0, 0);
Matrix4x4 R = Matrix4x4.Rotate(transform.rotation);
Matrix4x4 Inertia_tensor = R * I_ref * R.transpose;
Mesh mesh = GetComponent<MeshFilter>().mesh;
Vector3[] vertices = mesh.vertices;
for (int i = 0; i < vertices.Length; i++)
{
// Linear
f_i = m * g;
F += f_i;
// Rotation
toruqe_i = Vector3.Cross(R * vertices[i], f_i);
Torque += toruqe_i;
}
// or v = v + F / mass * dt - (1.0f - linear_decay) * v
v = v + F / mass * dt;
Vector3 L = Inertia_tensor.MultiplyVector(w);
// + Inertia_tensor.inverse.MultiplyVector(Vector3.Cross(L, w))*dt torque free motion
w = w + Inertia_tensor.inverse.MultiplyVector(Torque) *dt;
v = linear_decay * v;
w = angular_decay * w;
// Part II: Collision Impulse
// floor
Collision_Impulse(new Vector3(0, 0.01f, 0), new Vector3(0, 1, 0));
// wall
Collision_Impulse(new Vector3(2, 0, 0), new Vector3(-1, 0, 0));
// Part III: Update position & orientation
//Update linear status
Vector3 x = transform.position;
x = x + v * dt;
//Update angular status
Quaternion q = transform.rotation;
Vector3 w_update = 0.5f * dt * w;
Quaternion q_dt = new Quaternion(w_update[0], w_update[1], w_update[2], 0);
// Rotating by the product lhs * rhs is the same as applying the two rotations in sequence: lhs first and then rhs
q = Q_plus(q, q * q_dt);
// Part IV: Assign to the object
transform.position = x;
transform.rotation = q;
}
private Quaternion Q_plus(Quaternion lhs, Quaternion rhs)
{
Quaternion q = new Quaternion(lhs.x + rhs.x, lhs.y + rhs.y, lhs.z + rhs.z, lhs.w + rhs.w);
return q.normalized;
}
private Matrix4x4 M_minus_M(Matrix4x4 lhs, Matrix4x4 rhs)
{
Matrix4x4 A = Matrix4x4.zero;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
A[i, j] = lhs[i, j] - rhs[i, j];
}
}
// Metion here, if A[3,3] == 0 then the matrix is sigular, which doesn't have a inverse,
// however, in the singular case, the inverse is Matrix.zero;
A[3, 3] = 1;
return A;
}
}
X Ref
大模型时代,文字创作已死。2025年全面停更了,世界不需要知识分享。
如果我的工作对您有帮助,您想回馈一些东西,你可以考虑通过分享这篇文章来支持我。我非常感谢您的支持,真的。谢谢!
作者:Dba_sys (Jarmony)
转载以及引用请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/asmurmur/p/17938575
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用CC 署名-非商业使用-相同方式共享 许可协议。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号