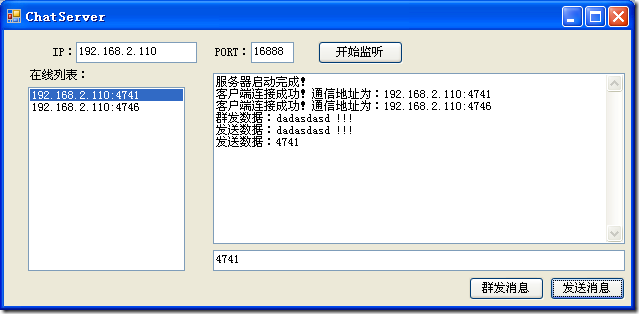
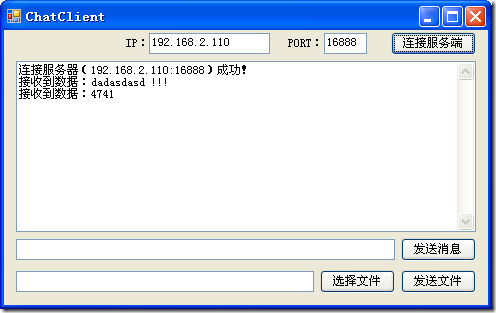
Socket 通信(基础原理、实时聊天系统雏形)
什么是 Socket?
Socket 英文直译为“孔或插座”,也称为套接字。用于描述 IP 地址和端口号,是一种进程间的通信机制。你可以理解为 IP 地址确定了网内的唯一计算机,而端口号则指定了将消息发送给哪一个应用程序(大多应用程序启动时会主动绑定一个端口,如果不主动绑定,操作系统自动为其分配一个端口)。
什么是端口?
一台主机一般运行了多个软件并同时提供一些服务。每种服务都会打开一个 Socket,并绑定到一个端口号上,不同端口对应于不同的应用程序。例如 http 使用 80 端口;ftp 使用 21 端口;smtp 使用 23 端口。
Socket 的类型
- Stream:一种流式 Socket,针对于面向连接的 TCP 服务应用,安全,但效率低。(本文重点)
- Datagram:数据报式的 Socket,针对于无连接的 UDP 服务应用,不安全(丢失、顺序混乱,往往在接收端要分析完整性、重排、或要求重发),但效率高。
Socket 程序一般应用模式及运行流程
- 服务器端会启动一个 Socket,开始监听端口,监听客户端的连接信息,我们称之为 Watch Socket。
- 客户端 Socket 连接服务器端的监听 Socket,一旦成功连接,服务器端会立刻创建一个新的 Socket 负责与客户端进行通信,之后,客户端将不再与 Watch Socket 通信。
- Watch Socket 继续监听可能会来自其他客户端的连接。
上述过程就像是实现了一次三方会谈。服务器端的 Socket 至少会有 2 个。一个是 Watch Socket,每成功接收到一个客户端的连接,便在服务器端创建一个通信 Socket。客户端 Socket 指定要连接的服务器端地址和端口,创建一个 Socket 对象来初始化一个到服务器的 TCP 连接。
通信的雏形
下面就看一个最简单的 Socket 示例,实现了网络聊天通信的雏形。
服务器端:
public partial class ChatServer : Form
{
public ChatServer()
{
InitializeComponent();
ListBox.CheckForIllegalCrossThreadCalls = false;
}
/// <summary>
/// 监听 Socket 运行的线程
/// </summary>
Thread threadWatch = null;
/// <summary>
/// 监听 Socket
/// </summary>
Socket socketWatch = null;
/// <summary>
/// 服务器端通信套接字集合
/// 必须在每次客户端连接成功之后,保存新建的通讯套接字,这样才能和后续的所有客户端通信
/// </summary>
Dictionary<string, Socket> dictCommunication = new Dictionary<string, Socket>();
/// <summary>
/// 通信线程的集合,用来接收客户端发送的信息
/// </summary>
Dictionary<string, Thread> dictThread = new Dictionary<string, Thread>();
private void btnBeginListen_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 创建服务器端监听 Socket (IP4寻址协议,流式连接,TCP协议传输数据)
socketWatch = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
// 监听套接字绑定指定端口
IPAddress address = IPAddress.Parse(txtIP.Text.Trim());
IPEndPoint endPoint = new IPEndPoint(address, int.Parse(txtPort.Text.Trim()));
socketWatch.Bind(endPoint);
// 将监听套接字置于侦听状态,并设置连接队列的最大长度
socketWatch.Listen(20);
// 启动监听线程开始监听客户端请求
threadWatch = new Thread(Watch);
threadWatch.IsBackground = true;
threadWatch.Start();
ShowMsg("服务器启动完成!");
}
Socket socketCommunication = null;
private void Watch()
{
while (true)
{
// Accept() 会创建新的通信 Socket,且会阻断当前线程,因此应置于非主线程上使用
// Accept() 与线程上接受的委托类型不符,因此需另建一方法做桥接
socketCommunication = socketWatch.Accept();
// 将新建的通信套接字存入集合中,以便服务器随时可以向指定客户端发送消息
// 如不置于集合中,每次 new 出的通信线程都是一个新的套接字,那么原套接字将失去引用
dictCommunication.Add(socketCommunication.RemoteEndPoint.ToString(), socketCommunication);
lbSocketOnline.Items.Add(socketCommunication.RemoteEndPoint.ToString());
// Receive 也是一个阻塞方法,不能直接运行在 Watch 中,否则监听线程会阻塞
// 另外,将每一个通信线程存入集合,方便今后的管理(如关闭、或挂起)
Thread thread = new Thread(() =>
{
while (true)
{
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 2];
int length = socketCommunication.Receive(bytes);
string msg = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes, 0, length);
ShowMsg("接收到来自" + socketCommunication.RemoteEndPoint.ToString() + "的数据:" + msg);
}
});
thread.IsBackground = true;
thread.Start();
dictThread.Add(socketCommunication.RemoteEndPoint.ToString(), thread);
ShowMsg("客户端连接成功!通信地址为:" + socketCommunication.RemoteEndPoint.ToString());
}
}
delegate void ShowMsgCallback(string msg);
private void ShowMsg(string msg)
{
if (this.InvokeRequired) // 也可以启动时修改控件的 CheckForIllegalCrossThreadCalls 属性
{
this.Invoke(new ShowMsgCallback(ShowMsg), new object[] { msg });
}
else
{
this.txtMsg.AppendText(msg + "\r\n");
}
}
private void btnSendMsg_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (lbSocketOnline.Text.Length == 0)
MessageBox.Show("至少选择一个客户端才能发送消息!");
else
{
// Send() 只接受字节数组
string msg = txtSendMsg.Text.Trim();
dictCommunication[lbSocketOnline.Text].Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(msg));
ShowMsg("发送数据:" + msg);
}
}
private void btnSendToAll_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string msg = txtSendMsg.Text.Trim();
foreach (var socket in dictCommunication.Values)
{
socket.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(msg));
}
ShowMsg("群发数据:" + msg);
}
}
客户端:
public partial class ChatClient : Form
{
public ChatClient()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
/// <summary>
/// 此线程用来接收服务器发送的数据
/// </summary>
Thread threadRecive = null;
Socket socketClient = null;
private void btnConnect_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 客户端创建通讯套接字并连接服务器、开始接收服务器传来的数据
socketClient = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
socketClient.Connect(IPAddress.Parse(txtIP.Text.Trim()), int.Parse(txtPort.Text.Trim()));
ShowMsg(string.Format("连接服务器({0}:{1})成功!", txtIP.Text.Trim(), txtPort.Text.Trim()));
threadRecive = new Thread(new ThreadStart(() =>
{
while (true)
{
// Receive 方法从套接字中接收数据,并存入接收缓冲区
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 2];
int length = socketClient.Receive(bytes);
string msg = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes, 0, length);
ShowMsg("接收到数据:" + msg);
}
}));
threadRecive.IsBackground = true;
threadRecive.Start();
}
delegate void ShowMsgCallback(string msg);
private void ShowMsg(string msg)
{
if (this.InvokeRequired) // 也可以启动时修改控件的 CheckForIllegalCrossThreadCalls 属性
{
this.Invoke(new ShowMsgCallback(ShowMsg), new object[] { msg });
}
else
{
this.txtMsg.AppendText(msg + "\r\n");
}
}
private void btnSend_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string msg = txtSendMsg.Text.Trim();
socketClient.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(msg));
ShowMsg("发送数据:" + msg);
}
}
现在所有客户都能和服务器进行通信,服务器也能和所有客户进行通信。那么,客户端之间互相通信呢?
显然,在客户端界面也应创建在线列表,每次有人登录后,服务器端除了刷新自身在线列表外,还需将新客户端的套接字信息发送给其他在线客户端,以便它们更新自己的在线列表。
客户端发送消息给服务器,服务器转发此消息给另一个客户端。当然,这个消息需要进行一些处理,至少要包含目标套接字和发送内容。
更为完善的是,服务器必须定时按制定的规则检测列表中套接字通信的有效性,通过发送响应信号,并接收客户端应答信号以确认客户端的连接性是真实的(否则,需剔除无效客户端)。
客户端上传文件
客户端:
private void btnChooseFile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog ofd = new OpenFileDialog();
if (ofd.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
txtFilePath.Text = ofd.FileName;
}
}
private void btnSendFile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (FileStream fs = new FileStream(txtFilePath.Text, FileMode.Open))
{
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 2];
// 假设第一个字节为标志位:0 表示传送文件
// 方式一:整体向后偏移 1 个字节;但这样有潜在缺点,
// 有时在通信时会非常准确的按照约定的字节长度来传递,
// 那么这种偏移方案显然是不可靠的
// bytes[0] = 0;
// int length = fs.Read(bytes, 1, bytes.Length);
// 方式二:创建多出 1 个字节的数组发送
int length = fs.Read(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);
byte[] newBytes = new byte[length + 1];
newBytes[0] = 0;
// BlockCopy() 会比你自己写for循环赋值更为简单合适
Buffer.BlockCopy(bytes, 0, newBytes, 1, length);
socketClient.Send(newBytes);
}
}
服务器端(Receive 方法中修改成这样):
Thread thread = new Thread(() =>
{
while (true)
{
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 2];
int length = socketCommunication.Receive(bytes);
if (bytes[0] == 0) // File
{
SaveFileDialog sfd = new SaveFileDialog();
if (sfd.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
using (FileStream fs = new FileStream(sfd.FileName, FileMode.Create))
{
fs.Write(bytes, 1, length - 1);
fs.Flush();
ShowMsg("文件保存成功,路径为:" + sfd.FileName);
}
}
}
else // Msg
{
string msg = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes, 0, length);
ShowMsg("接收到来自" + socketCommunication.RemoteEndPoint.ToString() + "的数据:" + msg);
}
}
});
异常捕捉
Socket 通信属于网络通信程序,会有许多的意外,必须进行异常处理以便程序不会被轻易的击垮。不管是客户端还是服务器端,只要和网络交互的环节(Connect、Accept、Send、Receive 等)都要做异常处理。
本例中对服务器端 Receive 方法环节做了一些异常处理,并移除了相应的资源,例如下面:
try
{
length = socketCommunication.Receive(bytes);
}
catch (SocketException ex)
{
ShowMsg("出现异常:" + ex.Message);
string key = socketCommunication.RemoteEndPoint.ToString();
lbSocketOnline.Items.Remove(key);
dictCommunication.Remove(key);
dictThread.Remove(key);
break;
}
系统界面截图