带返回值的递归,构建和克隆数据结构
一.克隆链表
public class GraphCloneTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] l = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,6}; ListNode build = build(l, 0); LinkListUtil.displayList(build); } private static ListNode build(int[] nums,int pos){ if(pos>=nums.length){ return null; } ListNode newNode = new ListNode(nums[pos]); newNode.setNext(build(nums,pos+1)); return newNode; } }
输出:1->2->3->4->5->6->
过程分析
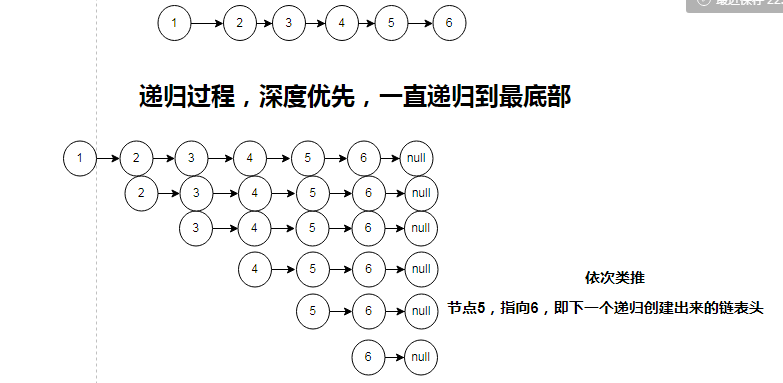
二.克隆二叉树
题源
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/375/
/** * Definition of TreeNode: * public class TreeNode { * public int val; * public TreeNode left, right; * public TreeNode(int val) { * this.val = val; * this.left = this.right = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { /** * @param root: The root of binary tree * @return: root of new tree */ public TreeNode cloneTree(TreeNode root) { // write your code here if(root==null){ return null; } TreeNode node = new TreeNode(root.val); node.left = cloneTree(root.left); node.right = cloneTree(root.right); return node; } }
过程分析,比如克隆下面二叉树
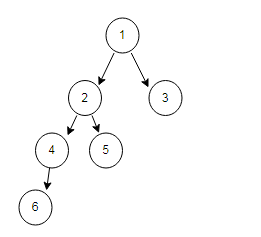
同链表类似,代码也类似二叉树的前序遍历
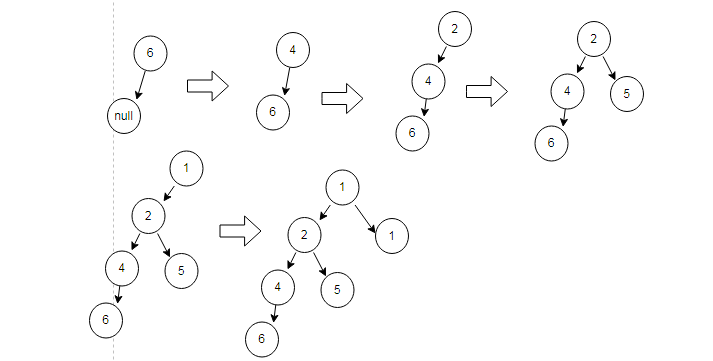
三.克隆图
题源:
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/clone-graph/
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() { val = 0; neighbors = new ArrayList<Node>(); } public Node(int _val) { val = _val; neighbors = new ArrayList<Node>(); } public Node(int _val, ArrayList<Node> _neighbors) { val = _val; neighbors = _neighbors; } } */ class Solution { public Node cloneGraph(Node node) { return dfs(node,new HashMap<Node,Node>()); } Node dfs(Node node,Map<Node,Node> visited){ if(node==null){ return null; } if(visited.containsKey(node)){ return visited.get(node); } Node newNode = new Node(node.val); visited.put(node,newNode); for(int i=0;i<node.neighbors.size();i++){ newNode.neighbors.add(dfs(node.neighbors.get(i),visited)); } return newNode; } }
过程和复制二叉树类似,需要注意的是,图有环,所以还需要一个hashmap来存储访问过的节点
和图dfs遍历的代码也类似,注意递归的返回值和指向。
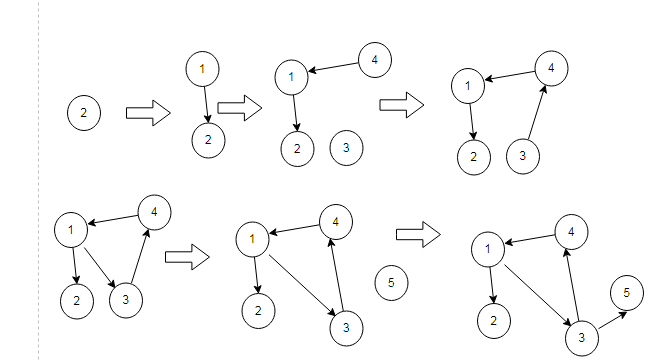
例如复制下面的图
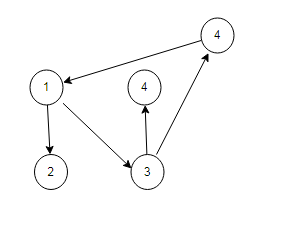
过程如下



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号