ArcGIS三大文件格式解析
一、Shape数据
Shapefile是ArcView GIS 3.x的原生数据格式,属于简单要素类,用点、线、多边形存储要素的形状,却不能存储拓扑关系,具有简单、快速显示的优点。一个shapefile是由若干个文件组成的,空间信息和属性信息分离存储,所以称之为“基于文件”。
每个shapefile,都至少有这三个文件组成,其中:
*.shp 存储的是几何要素的的空间信息,也就是XY坐标
*.shx 存储的是有关*.shp存储的索引信息。它记录了在*.shp中,空间数据是如何存储的,XY坐标的输入点在哪里,有多少XY坐标对等信息
*.dbf 存储地理数据的属性信息的dBase表
这三个文件是一个shapefile的基本文件,shapefile还可以有其他一些文件,但所有这些文件都与该shapefile同名,并且存储在同一路径下。
其它较为常见的文件:
*.prj 如果shapefile定义了坐标系统,那么它的空间参考信息将会存储在*.prj文件中
*.shp.xml 这是对shapefile进行元数据浏览后生成的xml元数据文件
*.sbn和*.sbx 这两个存储的是shapefile的空间索引,它能加速空间数据的读取。这两个文件是在对数据进行操作、浏览或连接后才产生的,也可以通过 ArcToolbox >Data Management Tools >Indexes >Add spatial Index工具生成。
当使用ArcCatalog对shapefile进行创建、移动、删除或重命名等操作,或使用ArcMap对shapefile进行编辑时,ArcCatalog将自动维护数据的完整性,将所有文件同步改变。所以需要使用ArcCatalog管理shapefile。
虽然Shapefile无法存储拓扑关系,但它并不是普通用于显示的图形文件,作为地理数据,它自身有拓扑的。比如一个多边形要素类,shapefile会按顺时针方向为它的所有顶点排序,然后按顶点顺序两两连接成的边线向量,在向量右侧的为多边形的内部,在向量左侧的是多边形的外部。
由于1990年代地理信息的迅速发展以及ArcView GIS 3.x软件在世界范围内的推广,shapefile格式的数据使用非常广泛,数据来源也较多。很多软件都提供了向shapefile转换的接口(eg:MapInfo、MapGIS等)。ArcGIS支持对shapefile的编辑操作,也支持shapefile向第三代数据模型geodatabase的转换。下图为一个shp文件所相关的所有数据文件。
二、Coverage数据
Coverage是ArcInfo workstation的原生数据格式。之所以称之为“基于文件夹的存储”,是因为在windows资源管理器下,它的空间信息和属性信息是分别存放在两个文件夹里。Coverage是一个集合,它可以包含一个或多个要素类。
例如,在我的电脑E:\MyTest\example文件夹中,有3个coverage,它们在windows资源管理器下的状态如下图所示,所有信息都以文件夹的形式来存储。空间信息以二进制文件的形式存储在独立的文件夹中,文件夹名称即为该coverage名称,属性信息和拓扑数据则以INFO表的形式存储。Coverage将空间信息与属性信息结合起来,并存储要素间的拓扑关系。
coverage是一个非常成功的早期地理数据模型,二十多年来深受用户欢迎,很多早期的数据都是coverage格式的。ESRI不公开coverage的数据格式,但是提供了coverage格式转换的一个交换文件(interchange file,即E00),并公开数据格式,这样就方便了coverage数据与其他格式的数据之间的转换。但是ESRI为推广其第三代数据模型geodatabase,从ArcGIS 8.3版本开始,屏蔽了对coverage的编辑功能。如果需要使用coverage格式的数据,可以安装ArcInfo workstation,或者将coverage数据转换为其他可编辑的数据格式。
adf 为coverage格式,包括lab.adf、arc.adf、sec.adf、pal.adf、cnt.adf、tic.adf、lnk.adf、bnd.adf都记录了坐标信息,arx.adf、pax.adf为索引文件和pat.adf、aat.adf为属性文件
pat 点属性表,记录lable点的坐标信息
tic 控制点,用于配准地图的点
aux 保存栅格文件自身不能保存的辅助信息,包括彩色地图信息,直方图或表格,坐标系统,变换信息,投影信息
rrd 保存影像金字塔信息索引,加速显示和漫游
dat 属性信息
nit 属性表定义文件
dir 属性表路径管理文件,用于关联dat和nit
三、Geodatabase数据
Geodatabase作为ArcGIS的原生数据格式,体现了很多第三代地理数据模型的优势。随着IT技术的发展,普通的事务型数据的管理模式,早已从传统的基于文件的管理转向利用基于工业标准建立的关系型数据库进行管理,这种基于数据库的管理方式的优点是不言而喻的。那么带有空间信息的地理数据是否也可以利用这种非常成熟的数据库技术进行管理呢?于是ESRI推出了geodatabase数据模型,利用数据库技术高效安全地管理我们的地理数据。
Geodatabase可以分为两种,一种是基于Microsoft Access的personal geodatabase,另一种是基于oracle、SQL Server、Informix或者DB2的enterprise geodatabase,由于它需要中间件ArcSDE进行连接,所以enterprise geodatabase又称为ArcSDE geodatabase。由于Microsoft Access自身容量的限制,personal geodatabase的容量上限为2GB,这显然不能满足企业级的海量地理数据的存储需求。于是可以将geodatabase扩展为ArcSDE geodatabase,底层数据库可以使用oracle这样的大型关系数据库,能够存储近乎“无限”的海量数据(仅受硬盘大小的限制)。虽然底层使用的数据库各不相同,但是geodatabase给用户提供的是一个一致的操作环境。
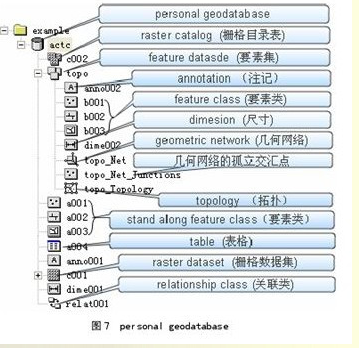
在geodatabase中,不仅可以存储类似shapefile的简单要素类,还可以存储类似coverage的要素集,并且支持一系列的行为规则对其空间信息和属性信息进行验证。表格、关联类、栅格、注记和尺寸都可以作为geodatabase对象存储。这些在perasonal geodatabase和ArcSDE geodatabase中都是一样的(栅格的存储有点小差异,但对用户来说都是一样的)。如图所示,是一个personal geodatabase。
对Personal geodatabase进行编辑,使用ArcView的license即可。不需要额外的软件就能直接连接。但是Personal geodatabase不支持多用户编辑,仅能满足小项目的要求。
而通过ArcSDE连接的ArcSDE geodatabase的编辑,则需要至少ArcEditor的license。ArcSDE geodatabase通过版本的机制,可支持多用户、长事务编辑。
在ArcToolbox >Conversion Tools > To Geodatabase中,有多种转换工具支持coverage、shapefile、CAD等矢量数据向geodatabase的转换。在personal geodatabase和ArcSDE geodatabase间只要复制、粘贴即可,无须转换。

adf - ARC/INFO coverage data file agf - Atlas GIS native binary geodataset file ain - attribute index file aih - attribute index file alg - ER Mapper algorithm apr - ArcView Project File (ODB format) avl - legend template file (ODB format) avp - palette file (ODB format) ave - Avenue script avx - ArcView extension file (ODB format) ai - Adobe Illlustrator picture file bat - DOS batch file bil - image file (band interleaved by line) bip - image file (band interleaved by pixel) blw - world file for bil image bmp - Windows bitmap image file bpw - world file for bip or bmp images bsq - image file (band sequential) bqw - world file for bsq image c - C programming language source code filename cat - UNIX hyperhelp supporting file cgm - Computer Graphics Metafile cls - geocoding classification file cnt - help file contents dat - generic data file extension dat - INFO attribute file db - Object Database File (also ODB) dbf - dBASE tabular data file dbf - Shapefile attribute table file dbg - problem debug log file dcp - default codepage file dct - geocoding dictionary file dec - UNIX hyperhelp supporting file def - defaults file (North Arrows, Layout Templates, etc) (ODB format) dem - Digital Elevation Model file dgn - Design drawing file (Intergraph) dir - INFO directory manager file dlg - Digital Line Graph file dll - Windows Dynamic Link Library file doc - MS-Word, MS-Wordpad document file dtd - UNIX hyperhelp supporting file dwg - Drawing file (AutoCAD) dxf - Drawing exchange file e00 - ARC/INFO export file ecw - ER Mapper Enhanced Compressed Wavelet eps - Encapsulated PostScript ers - ER Mapper raster file format exe - DOS/Windows executable file fbn - spatial index file for read-only datasets fbx - spatial index file for read-only datasets fls - Windows help supporting file ftg - UNIX help supporting file fts - UNIX help supporting file gen - ARC/INFO UnGenerate format gfw - world file for gif image gif - image file (CompuServe) hdr - header file (for ArcView extensions or TIF images) hlp - Windows help file htm - WWW file (hypertext markup, 3-character DOS version) html- WWW file (hypertext markup language, UNIX version) ico - Icon file idx - geocoding index for read-only datasets img - ERDAS Imagine image file ini - initialization file ixc - geocoding index for read-write coverages ixs - geocoding index for read-write shapefiles jpg - image file (Joint Photographic Experts Group) key - geocoding matching keys (ODB format) lin - ARC/INFO lineset symbol file lnk - Windows shortcut icon link file mat - geocoding matching parameters file mcp - image file (MacPaint) mid - MapInfo interchange format (always paired with "mif") mif - MapInfo interchange format (always paired with "mid") mrk - ARC/INFO markerset symbol file (not compatible w/ArcView) mxc - geocoding index for read-write coverages (ODB format) mxs - geocoding index for read-write shapefiles (ODB format) nit - INFO table definitions file ndx - fonts index file (UNIX only) nls - Codepage language files odb - Object Database ASCII file (ODB format) pat - geocoding pattern recognition file pdf - preferences definition file pif - Windows program information file (for DOS programs) pps - processing set codes prj - projections definition file ps - PostScript. file rlc - image file (run-length coding) rs - image file (raster snapshot | Sun rasterfile) sbn - spatial index for read-write shapefiles sbx - spatial index for read-write shapefiles shd - ARC/INFO shadeset symbol file shp - Shapefile (stores feature geometry) shx - Shapefile (stores file lookup index) stn - geocoding standardization file tab - lookup file tbl - geocoding support table tif - image file (Tag Image Format file) tfw - world file for tif image tmp - temporary file ttf - TrueType font file txt - text file (usually ASCII) xbm - image file (X Bitmap) wmf - image file (Windows Metafile) wld - world file for CAD datasets wri - Windows Write.exe file
没有整理与归纳的知识,一文不值!高度概括与梳理的知识,才是自己真正的知识与技能。 永远不要让自己的自由、好奇、充满创造力的想法被现实的框架所束缚,让创造力自由成长吧! 多花时间,关心他(她)人,正如别人所关心你的。理想的腾飞与实现,没有别人的支持与帮助,是万万不能的。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号