实验2
验证性实验部分
①函数声明和函数定义各自的作用及二者的区别
函数声明一定要放在主函数之前,因为系统要先识别才能调用,函数定义则是对函数的解释,是函数算法的说明,可以放在主函数后面。
②什么是形参?什么是实参?函数参数和返回值在函数中起到什么作用?
函数定义时写的参数叫做形参,这个只是告诉你函数需要这些参数才能运行,这些参数只是给你看的,没有分配内存,没有具体的值。
函数调用时写的参数叫做实参,这些参数要有意义,即分配了内存,有具体的值。
③函数参数传递过程中,值传递和引用传递区别
值传递仅仅传递的是值。
引用传递,传递的是内存地址,修改后会改变内存地址对应储存的值。
编程实验部分
1
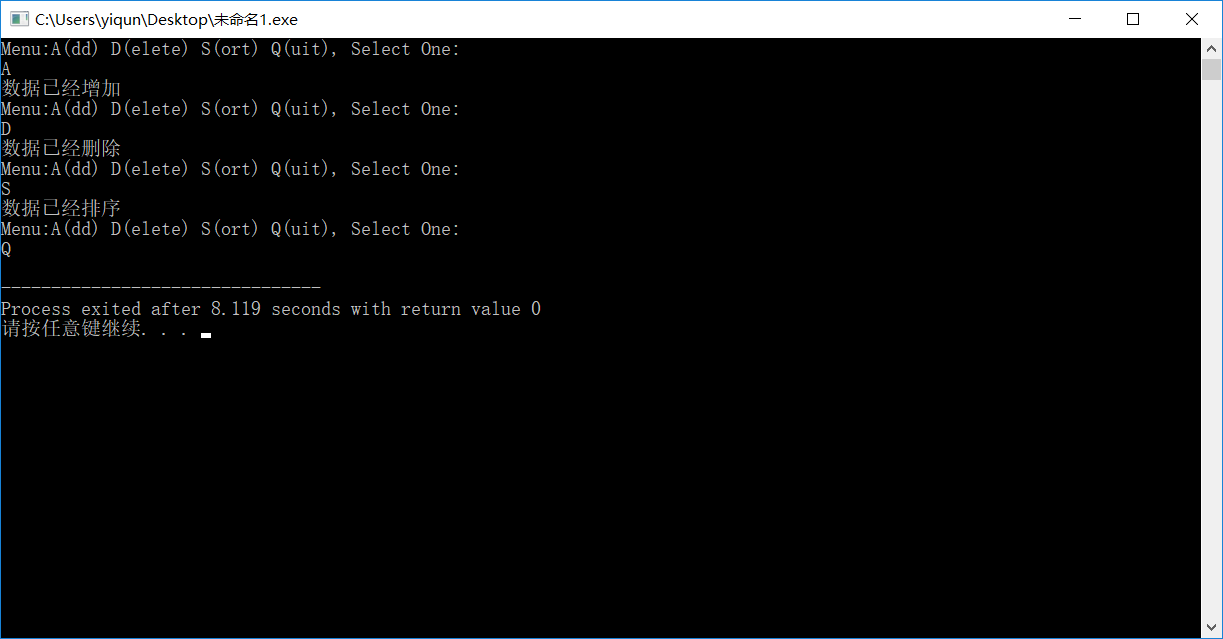
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "Menu: A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:" << endl; while (true){ char t;cin >> t; if (t == 'A') { cout << "数据已经增加。" << endl; continue; } else if (t == 'D') { cout << "数据已经删除。" << endl; continue; } else if (t == 'S') { cout << "数据已经排序。" << endl; continue; } if (t =='Q') break; return 0; } }
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { while(true) { cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit), Select One:"<<endl; char t; cin>>t; switch(t) { case 'A':cout<<"数据已经增加"<<endl;break; case 'D':cout<<"数据已经删除"<<endl;break; case 'S':cout<<"数据已经排序"<<endl;break; case 'Q':return 0; } } }
2
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main(){ int a,i=2,j; while (i<=100) { a=1,j=2; while (j<=i) { if (i%j == 0) { a++; }j++; } if (a==2){ cout << i << " "; } i++; } return 0; }
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int i, j, a; for (i = 2; i <=100; i++) { a = 1; for (j = 2; j <= i; j++){ if (i%j == 0) { a++; } } if (a == 2) { cout << i << " "; } }return 0; }
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int i=2, j, a; do { a = 1, j = 2; for (j = 2; j <= i; j++) { if (i%j == 0) { a++; } } if (a == 2) { cout << i << " "; } i++; } while (i <= 100); return 0; }

3
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int i,n=65;//n为要猜的数,可修改n的值 cout << "猜这个数:"; cin >> i; while (true) { if (i != n) { if (i < n) cout << "猜小了" << endl; else cout << "猜大了" << endl; } else { cout << "猜对了"; break; } cin >> i; } return 0; }
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int i, n = 65;//n为要猜的数,可修改n的值 cout << "猜这个数:"; cin >> i; do { if (i != n) { if (i < n) cout << "猜小了" << endl; else cout << "猜大了" << endl; } else { cout << "猜对了"; break; } cin >> i; } while (true); return 0; }

4
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int i,j,k,s=0; for(i=0;i<5;i++) for(j=i+1;j<5;j++) for(k=j+1;k<5;k++) if(i!=k&&j!=k&&i!=j) s+=1; cout<<s<<endl; return 0; }