KestrelServer详解[1]:注册监听终结点(Endpoint)
具有跨平台能力的KestrelServer是最重要的服务器类型。针对KestrelServer的设置均体现在KestrelServerOptions配置选项上,注册的终结点是它承载的最重要的配置选项。这里所谓的终结点(Endpoint)与“路由”介绍的终结点不是一回事,这里表示的就是服务器在监听请求时绑定的网络地址,对应着一个System.Net.Endpoint对象。我们知道ASP.NET Core应用承载API也提供了注册监听地址的方法,其本质其实也是为了注册终结点,那么两种注册方式如何取舍呢?本文提供的示例演示已经同步到《ASP.NET Core 6框架揭秘-实例演示版》)
一、UseKestrel扩展方法
二、两种终结点的取舍
三、终结点配置
四、针对HTTPS的设置
五、限制约束
六、其他设置
一、UseKestrel扩展方法
IWebHostBuilder接口如下三个UseKestrel扩展方法重载会帮助我们完成KestrelServer的注册并对KestrelServerOptions配置选项作相应设置,我们先来看看如何利用它们来注册终结点。
public static class WebHostBuilderKestrelExtensions { public static IWebHostBuilder UseKestrel(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder); public static IWebHostBuilder UseKestrel(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder,Action<KestrelServerOptions> options); public static IWebHostBuilder UseKestrel(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder, Action<WebHostBuilderContext, KestrelServerOptions> configureOptions); }
注册到KestrelServer上的终结点体现为如下这个Endpoint对象。Endpoint是对网络地址的抽象,它们在大部分下体现为“IP地址+端口”或者“域名+端口”,对应的类型分别为IPEndPoint和DnsEndPoint。UnixDomainSocketEndPoint表示基于Unix Domain Socket/IPC Socket的终结点,它旨在实现同一台机器上多个进程之间的通信(IPC)。FileHandleEndPoint表示指向某个文件句柄(比如TCP或者Pipe类型的文件句柄)的终结点。
public abstract class EndPoint { public virtual AddressFamily AddressFamily { get; } public virtual EndPoint Create(SocketAddress socketAddress); public virtual SocketAddress Serialize(); } public class IPEndPoint : EndPoint public class DnsEndPoint : EndPoint public sealed class UnixDomainSocketEndPoint : EndPoint public class FileHandleEndPoint : EndPoint
终结点注册利用如下这个ListenOptions配置选项来描述。该类型实现的IConnectionBuilder和IMultiplexedConnectionBuilder接口涉及针对连接的构建,我们将在后面讨论这个话题。注册的终结点体现为该配置选项的EndPoint属性,如果是一个IPEndPoint对象,该对象也会体现在IPEndPoint属性上。如果终结点类型为UnixDomainSocketEndPoint和FileHandleEndPoint,我们可以利用配置选项的SocketPath和FileHandle得到对应的Socket路径和文件句柄。
public class ListenOptions : IConnectionBuilder, IMultiplexedConnectionBuilder { public EndPoint EndPoint { get; } public IPEndPoint IPEndPoint { get; } public string SocketPath { get; } public ulong FileHandle { get; } public HttpProtocols Protocols { get; set; } public bool DisableAltSvcHeader { get; set; } public IServiceProvider ApplicationServices { get; } public KestrelServerOptions KestrelServerOptions { get; } ... }
同一个终结点可以同时支持HTTP 1.x、HTTP 2 和HTTP 3三种协议,具体设置体现在Protocols属性上,该属性返回如下这个HttpProtocols枚举。由于枚举项Http3和Http1AndHttp2AndHttp3上面标注了RequiresPreviewFeaturesAttribute特性,如果需要采用HTTP 3协议,项目文件中必须添加“<EnablePreviewFeatures>true</EnablePreviewFeatures>”属性。如果HTTP3终结点同时支持HTTP 1.X和HTTP 2,针对HTTP 1.X和HTTP 2的请求的响应一般会添加一个alt-svc (Alternative Service)报头指示可以升级到HTTP 3,我们可以设置DisableAltSvcHeader属性关闭此特性。该属性默认值为Http1AndHttp2。
[Flags] public enum HttpProtocols { None = 0, Http1 = 1, Http2 = 2, Http1AndHttp2 = 3, [RequiresPreviewFeatures] Http3 = 4, [RequiresPreviewFeatures] Http1AndHttp2AndHttp3 = 7 }
KestrelServerOptions的ListenOptions属性返回的ListenOptions列表代表所有注册的终结点,它由CodeBackedListenOptions和ConfigurationBackedListenOptions属性合并而成,这两个属性分别表示通过代码和配置注册的终结点。基于“代码”的终结点注册由如下所示的一系列Listen和以“Listen”为前缀的方法来完成。除了这些注册单个终结点的方法, ConfigureEndpointDefaults方法为注册的所有终结点提供基础设置。
public class KestrelServerOptions { internal List<ListenOptions> CodeBackedListenOptions { get; } internal List<ListenOptions> ConfigurationBackedListenOptions { get; } internal IEnumerable<ListenOptions> ListenOptions { get; } public void Listen(EndPoint endPoint); public void Listen(IPEndPoint endPoint); public void Listen(EndPoint endPoint, Action<ListenOptions> configure); public void Listen(IPAddress address, int port); public void Listen(IPEndPoint endPoint, Action<ListenOptions> configure); public void Listen(IPAddress address, int port, Action<ListenOptions> configure); public void ListenAnyIP(int port); public void ListenAnyIP(int port, Action<ListenOptions> configure); public void ListenHandle(ulong handle); public void ListenHandle(ulong handle, Action<ListenOptions> configure); public void ListenLocalhost(int port); public void ListenLocalhost(int port, Action<ListenOptions> configure); public void ListenUnixSocket(string socketPath); public void ListenUnixSocket(string socketPath, Action<ListenOptions> configure); public void ConfigureEndpointDefaults(Action<ListenOptions> configureOptions) ... }
二、两种终结点的取舍
我们知道监听地址不仅可以添加到WebApplication对象的Urls属性中,WebApplication类型用来启动应用的RunAsync和Run方法也提供了可缺省的参数url来指定监听地址。从如下的代码片段可以看出,这三种方式提供的监听地址都被添加到了IServerAddressesFeature特性的Addresses属性中。
public sealed class WebApplication : IHost { private readonly IHost _host; public ICollection<string> Urls => _host.Services.GetRequiredService<IServer>().Features .Get<IServerAddressesFeature>()?.Addresses
?? throw new InvalidOperationException("IServerAddressesFeature could not be found."); public Task RunAsync(string? url = null) { Listen(url); return ((IHost)this).RunAsync(); } public void Run(string? url = null) { Listen(url); ((IHost)this).Run(); } private void Listen(string? url) { if (url != null) { var addresses = ServerFeatures.Get<IServerAddressesFeature>()?.Addresses?? throw new InvalidOperationException("No valid IServerAddressesFeature is found"); addresses.Clear(); addresses.Add(url); } } }
如果KestrelServerOptions配置选项不能提供注册的终结点,那么KestrelServer就会使用IServerAddressesFeature特性提供的地址来创建对应的终结点,否则就会根据它的PreferHostingUrls属性来进行取舍。如果IServerAddressesFeature特性的PreferHostingUrls属性返回True,它提供的地址会被选择,否则就使用直接注册到KestrelServerOptions配置选项的终结点。针对监听地址的注册和PreferHostingUrls的设置可以利用IWebHostBuilder接口如下两个扩展方法来完成。从给出的代码片段可以看出这两个方法会将提供的设置存储配置上,配置项名称分别为“urls”和“preferHostingUrls”,对应着WebHostDefaults定义的两个静态只读字段ServerUrlsKey和PreferHostingUrlsKey。既然这两个设置来源于配置,我们自然可以利用命令行参数、环境变量或者直接修改对应配置项的方式来指定它们。
public static class HostingAbstractionsWebHostBuilderExtensions { public static IWebHostBuilder UseUrls(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder, params string[] urls) => hostBuilder.UseSetting(WebHostDefaults.ServerUrlsKey, string.Join(';', urls)); public static IWebHostBuilder PreferHostingUrls(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder, bool preferHostingUrls) => hostBuilder.UseSetting(WebHostDefaults.PreferHostingUrlsKey, preferHostingUrls ? "true" : "false"); }
如果服务器的特性集合提供的IServerAddressesFeature特性包含监听地址,以配置方式设置的监听地址和针对PreferHostingUrls的设置将会被忽略,这一个特性体现在GenericWebHostService的StartAsync方法中。如下面的代码片段所示,该方法会从服务器中提取IServerAddressesFeature特性,只有该特性不能提供监听地址的情况下,利用配置注册的监听地址和针对PreferHostingUrls的设置才会应用到该特性中。
internal sealed class GenericWebHostService : IHostedService { public async Task StartAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken) { ... var serverAddressesFeature = Server.Features.Get<IServerAddressesFeature>(); var addresses = serverAddressesFeature?.Addresses; if (addresses != null && !addresses.IsReadOnly && addresses.Count == 0) { var text = Configuration[WebHostDefaults.ServerUrlsKey]; if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(text)) { serverAddressesFeature.PreferHostingUrls = WebHostUtilities.ParseBool(Configuration, WebHostDefaults.PreferHostingUrlsKey); string[] array = text.Split(';', StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); foreach (string item in array) { addresses.Add(item); } } } } }
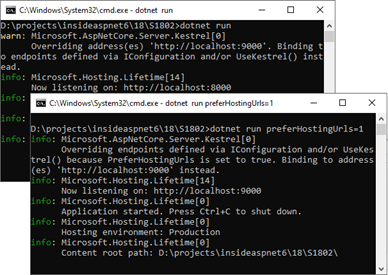
下面的演示程序通过调用IWebHostBuilder接口的UseKestrel扩展方法注册了一个采用8000端口的本地终结点,通过调用UseUrls扩展方法注册了一个采用9000端口的监听地址。
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.WebHost
.UseKestrel(kestrel => kestrel.ListenLocalhost(8000))
.UseUrls("http://localhost:9000");
var app = builder.Build();
app.Run();
我们以命令行的方式两次启动了该程序。默认情况下应用会选择调用UseKestrel扩展方法注册的终结点。如果指定了命令行参数“preferHostingUrls=1”,那么最终使用的都是将是调用UseUrls扩展方法注册的监听地址。由于两种情况都涉及到放弃某种设置,所以输出了相应的日志。
三、终结点配置
KestrelServerOptions承载的很多设置都可以利用配置来提供。由于该配置选项类型的定义与配置的结构存在差异, KestrelServerOptions配置选项无法直接使用对应的IConfiguration对象进行绑定,所以KestrelServerOptions类型定义如下三个Configure方法。后面两个方法提供了承载配置内容的IConfiguration对象,最后一个重载还提供了reloadOnChange参数来决定是否自动加载更新后的配置。第一个重载提供的其实是一个空的IConfiguration对象。
public class KestrelServerOptions { public KestrelConfigurationLoader Configure(); public KestrelConfigurationLoader Configure(IConfiguration config); public KestrelConfigurationLoader Configure(IConfiguration config, bool reloadOnChange) }
三个Configure方法都返回KestrelConfigurationLoader对象,后者是对当前KestrelServerOptions配置选项和指定IConfiguration对象的封装。KestrelConfigurationLoader的Load方法会读取配置的内容并将其应用到KestrelServerOptions配置选项上,该类型还提供了一系列注册各类终结点的方法。
public class KestrelConfigurationLoader { public KestrelServerOptions Options { get; } public IConfiguration Configuration { get; } public KestrelConfigurationLoader Endpoint(string name, Action<EndpointConfiguration> configureOptions); public KestrelConfigurationLoader Endpoint(IPAddress address, int port); public KestrelConfigurationLoader Endpoint(IPAddress address, int port, Action<ListenOptions> configure); public KestrelConfigurationLoader Endpoint(IPEndPoint endPoint); public KestrelConfigurationLoader Endpoint(IPEndPoint endPoint, Action<ListenOptions> configure); public KestrelConfigurationLoader LocalhostEndpoint(int port); public KestrelConfigurationLoader LocalhostEndpoint(int port, Action<ListenOptions> configure); public KestrelConfigurationLoader AnyIPEndpoint(int port); public KestrelConfigurationLoader AnyIPEndpoint(int port, Action<ListenOptions> configure); public KestrelConfigurationLoader UnixSocketEndpoint(string socketPath); public KestrelConfigurationLoader UnixSocketEndpoint(string socketPath, Action<ListenOptions> configure); public KestrelConfigurationLoader HandleEndpoint(ulong handle); public KestrelConfigurationLoader HandleEndpoint(ulong handle, Action<ListenOptions> configure); public void Load(); }
ASP.NET Core应用在启动时会调用IHostBuilder接口如下这个ConfigureWebHostDefaults扩展方法进行初始化设置,该方法会从当前配置中提取出“Kestrel”配置节,并将其作为参数调用Configure方法将配置内容应用到KestrelServerOptions配置选项上。由于reloadOnChange参数被设置成了True,所以更新后的配置会自动被重新加载。
public static class GenericHostBuilderExtensions { public static IHostBuilder ConfigureWebHostDefaults(this IHostBuilder builder, Action<IWebHostBuilder> configure) => builder.ConfigureWebHost(webHostBuilder => { WebHost.ConfigureWebDefaults(webHostBuilder); configure(webHostBuilder); }); } public static class WebHost { internal static void ConfigureWebDefaults(IWebHostBuilder builder) { ... builder.UseKestrel((builderContext, options) => { options.Configure(builderContext.Configuration.GetSection("Kestrel"), reloadOnChange: true); }) ... } }
如下的代码片段展现了针对终结点的配置。我们在“Kestrel:Endpoints”配置了两个分别命名为“endpoint1”和“endpoint2”终结点,它们采用的监听地址分别为“http://localhost:9000”和“https://localhost:9001”。KestrelServerOptions绝大部分配置选项都可以定义在配置文件中,具体的配置定义方法可以参阅官方文档。
{
"Kestrel": {
"Endpoints": {
"endpoint1": {
"Url": "http://localhost:9000"
},
"endpoint2": {
"Url": "https://localhost:9001"
}
}
}
}
四、针对HTTPS的设置
较之普通的终结点,HTTPS(SSL/TLS)终结点需要提供额外的设置,这些设置大都体现在如下这个HttpsConnectionAdapterOptions配置选项上。KestrelServerOptions的ConfigureHttpsDefaults方法为所有HTTPS终结点提供了默认的设置。
public class HttpsConnectionAdapterOptions { public X509Certificate2? ServerCertificate { get; set; } public Func<ConnectionContext?, string?, X509Certificate2?>? ServerCertificateSelector { get; set; } public TimeSpan HandshakeTimeout { get; set; } public SslProtocols SslProtocols { get; set; } public Action<ConnectionContext, SslServerAuthenticationOptions>? OnAuthenticate { get; set; } public ClientCertificateMode ClientCertificateMode { get; set; } public Func<X509Certificate2, X509Chain?, SslPolicyErrors, bool>? ClientCertificateValidation { get; set; } public bool CheckCertificateRevocation { get; set; } public void AllowAnyClientCertificate() { get; set; } } public static class KestrelServerOptions { public void ConfigureHttpsDefaults(Action<HttpsConnectionAdapterOptions> configureOptions); ... }
表示服务端证书的X509Certificate2对象可以直接设置到ServerCertificate属性上,我们也可以在ServerCertificateSelector属性上设置一个根据当前连结动态选择证书的委托。SslProtocols属性用来设置采用的协议(SSL或者TLS),对应的类型为如下这个SslProtocols枚举。HandshakeTimeout属性用来设置TLS/SSL“握手”的超时时间,默认为10秒。
[Flags] public enum SslProtocols { None = 0x0, [Obsolete("SslProtocols.Ssl2 has been deprecated and is not supported.")] Ssl2 = 0xC, [Obsolete("SslProtocols.Ssl3 has been deprecated and is not supported.")] Ssl3 = 0x30, Tls = 0xC0, [Obsolete("SslProtocols.Default has been deprecated and is not supported.")] Default = 0xF0, Tls11 = 0x300, Tls12 = 0xC00, Tls13 = 0x3000 }
HTTPS主要解决的是服务端的认证和传输安全问题,所以服务端的认证信息需要在前期“协商”阶段利用建立的安全通道传递给客户端,具体的认证信息是如下这个SslServerAuthenticationOptions配置选项格式化后的结果。HttpsConnectionAdapterOptions的OnAuthenticate属性提供的委托可以帮助我们对这个配置选项进行设置,所以绝大部分HTTPS相关的设置都可以利用该属性来完成。
public class SslServerAuthenticationOptions { public bool AllowRenegotiation { get; set; } public bool ClientCertificateRequired { get; set; } public List<SslApplicationProtocol>? ApplicationProtocols { get; set; } public RemoteCertificateValidationCallback? RemoteCertificateValidationCallback { get; set; } public ServerCertificateSelectionCallback? ServerCertificateSelectionCallback { get; set; } public X509Certificate? ServerCertificate { get; set; } public SslStreamCertificateContext? ServerCertificateContext { get; set; } public SslProtocols EnabledSslProtocols { get; set; } public X509RevocationMode CertificateRevocationCheckMode { get; set; } public EncryptionPolicy EncryptionPolicy { get; set; } public CipherSuitesPolicy? CipherSuitesPolicy { get; set; } }
HTTPS不仅仅能够帮助客户端来验证服务端的身份,还能帮助服务端来对客户端身份进行验证。服务端验证利用服务端证书来完成,与之类似,服务端要识别客户端的身份,同样需要客户端提供证书。我们可以利用HttpsConnectionAdapterOptions的ClientCertificateMode属性来决定是否要求客户端提供证书,该属性类型为如下这个ClientCertificateMode枚举。针对客户端认证的验证可以利用ClientCertificateValidation属性设置的委托来完成。
public enum ClientCertificateMode { NoCertificate, AllowCertificate, RequireCertificate, DelayCertificate }
由权威机构(Certificate Authority)颁发的证书可能会由于某种原因被撤销,我们有两种途径来确定某张证书是否处于被撤销的状态:证书颁发机构可以采用标准的OCSP(Online Certificate Status Protocol)协议提供用于确定证书状态的API,也可以直接提供一份撤销的证书清单(CRL:Certificate Revocation List)。HttpsConnectionAdapterOptions的CheckCertificateRevocation属性用来决定是否需要对证书的撤销状态进行验证。如果不需要对客户端证书作任何验证,我们可以调用HttpsConnectionAdapterOptions的AllowAnyClientCertificate方法。
当我们将某个终结点注册到KestrelServer上并生成对应ListenOptions配置选项后,我们可以调用后者的UseHttps扩展方法(注册终结点的很多方法都提供一个Action<ListenOptions>参数)完成针对HTTPS的设置,我们有如下这一系列UseHttps重载可供选择。对于证书的设置,我们可以直接指定一个X509Certificate2对象,也可以指定证书文件的路径(一般还需要提供读取证书的密码),还可以指定证书的存储(Certificate Store)。我们可以利用部分方法重载提供的委托对HttpsConnectionAdapterOptions配置选项进行设置。部分方法重载还提供了一个ServerOptionsSelectionCallback委托直接返回SslServerAuthenticationOptions配置选项。
public static class ListenOptionsHttpsExtensions { public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, string fileName); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, string fileName, string? password); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, string fileName, string? password, Action<HttpsConnectionAdapterOptions> configureOptions); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, StoreName storeName, string subject); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, StoreName storeName, string subject, bool allowInvalid); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, StoreName storeName, string subject, bool allowInvalid, StoreLocation location); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, StoreName storeName, string subject, bool allowInvalid, StoreLocation location, Action<HttpsConnectionAdapterOptions> configureOptions); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, X509Certificate2 serverCertificate); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, X509Certificate2 serverCertificate, Action<HttpsConnectionAdapterOptions> configureOptions); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, Action<HttpsConnectionAdapterOptions> configureOptions); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, HttpsConnectionAdapterOptions httpsOptions); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, ServerOptionsSelectionCallback serverOptionsSelectionCallback, object state); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, ServerOptionsSelectionCallback serverOptionsSelectionCallback, object state, TimeSpan handshakeTimeout); public static ListenOptions UseHttps(this ListenOptions listenOptions, TlsHandshakeCallbackOptions callbackOptions); } public delegate ValueTask<SslServerAuthenticationOptions> ServerOptionsSelectionCallback(SslStream stream, SslClientHelloInfo clientHelloInfo, object? state, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
除了调用上述这些方法来为注册的终结点提供HTTPS相关的设置外,这些设置也可以按照如下的方式放在终结点的配置中。
{
"Kestrel": {
"Endpoints": {
"MyHttpsEndpoint": {
"Url": "https://localhost:5001",
"ClientCertificateMode": "AllowCertificate",
"Certificate": {
"Path": "c:\\certificates\\foobar.pfx>",
"Password": "password"
}
}
}
}
}
五、限制约束
为了确保KestrelServer稳定可靠地运行,需要根据需要为它设置相应的限制和约束,这些设置体现在KestrelServerOptions配置选项Limits属性返回的KestrelServerLimits对象上。
public class KestrelServerOptions { public KestrelServerLimits Limits { get; } = new KestrelServerLimits(); } public class KestrelServerLimits { public long? MaxConcurrentConnections { get; set; } public long? MaxConcurrentUpgradedConnections { get; set; } public TimeSpan KeepAliveTimeout { get; set; } public int MaxRequestHeaderCount { get; set; } public long? MaxRequestBufferSize { get; set; } public int MaxRequestHeadersTotalSize { get; set; } public int MaxRequestLineSize { get; set; } public long? MaxRequestBodySize { get; set; } public TimeSpan RequestHeadersTimeout { get; set; } public MinDataRate MinRequestBodyDataRate { get; set; } public long? MaxResponseBufferSize { get; set; } public MinDataRate MinResponseDataRate { get; set; } public Http2Limits Http2 { get; } public Http3Limits Http3 { get; } }
KestrelServerLimits利用其丰富的属性对连接、请求和响应进行了相应的限制。KestrelServer提供了针对HTTP 2和HTTP3的支持,针对性的限制设置体现在KestrelServerLimits类型的Http2和Http3属性上。下表对定义在KestrelServerLimits类型中的这些属性所体现的限制约束进行了简单说明。
属性 | 含 义 |
MaxConcurrentConnections | 最大并发连接。如果设置为Null(默认值),意味着不作限制。 |
MaxConcurrentUpgradedConnections | 可升级连接(比如从HTTP升级到WebSocket)的最大并发数。如果设置为Null(默认值),意味着不作限制。 |
KeepAliveTimeout | 连接保持活动状态的超时时间,默认值为130秒。 |
MaxRequestHeaderCount | 请求携带的最大报头数量,默认值为100。 |
MaxRequestBufferSize | 请求缓冲区最大容量,默认值为1,048,576字节(1M)。 |
MaxRequestHeadersTotalSize | 请求携带报头总字节数,默认值为 32,768字节(32K)。 |
MaxRequestLineSize | 对于HTTP 1.X来说就是请求的首行(Request Line)最大字节数。对于HTTP 2/3来说就是 :method, :scheme, :authority, and :path这些报头的总字节数。默认值为8,192 字节(8K)。 |
MaxRequestBodySize | 请求主体最大字节数,默认值为30,000,000 字节(约28.6M)。如果设置为Null,意味着不作限制。 |
RequestHeadersTimeout | 接收请求报头的超时时间,默认为30秒。 |
MinRequestBodyDataRate | 请求主体内容最低传输率。 |
MaxResponseBufferSize | 响应缓冲区最大容量,默认值为65,536(1M)。 |
MinResponseDataRate | 响应最低传输率。 |
KestrelServerLimits的MinRequestBodyDataRate和MinResponseDataRate属性返回的最低传输率体现为如下这个MinDataRate对象。如果没有达到设定的传输率,当前连接就会被重置。MinDataRate对象除了提供表示传输率的BytesPerSecond属性外,还提供了一个表示“宽限时间”的GracePeriod属性。并非传输率下降到设定的阈值的那一刻就重置连接,只要在指定的时段内传输率上升到阈值以上也没有问题。MinRequestBodyDataRate和MinResponseDataRate属性的默认值均为“240 bytes/second(5 seconds)”。
public class MinDataRate { public double BytesPerSecond { get; } public TimeSpan GracePeriod { get; } public MinDataRate(double bytesPerSecond, TimeSpan gracePeriod); }
HTTP 1.X建立在TCP之上,客户端和服务端之间的交互依赖预先创建的TCP连接。虽然HTTP 1.1引入的流水线技术允许客户端可以随时向服务端发送请求,而无需等待接收到上一个请求的响应,但是响应依然只能按照请求的接收顺序返回的。真正意义上的“并发”请求只能利用多个连接来完成,但是针对同一个域名支持的TCP连接的数量又是有限的。这个问题在HTTP 2得到了一定程度的解决。
与采用文本编码的HTTP 1.X相比, HTTP 2采用更加高效的二进制编码。帧(Frame)成为了基本通信单元,单个请求和响应可以分解成多个帧进行发送。客户端和服务端之间额消息交换在一个支持双向通信的信道(Channel)中完成,该信道被称为“流(Stream)”。每一个流具有一个唯一标识,同一个TCP连接可以承载成百上千的流。每个帧携带着所属流的标识,所以它可以随时被“乱序”发送,接收端可以利用流的标识进行重组,所以HTTP 2在同一个TCP连接上实现了“多路复用”。
使用同一个连接发送的请求和响应都存在很多重复的报头,为了减少报头内容占据的带宽,HTTP 2会采用一种名为HPACK的压缩算法对报头文本进行编码。HPACK会在发送和接收端维护一个索引表来存储编码的文本,报头内容在发送前会被替换成在该表的索引,接收端这利用此索引在本地压缩表中找到原始的内容。
public class Http2Limits { public int MaxStreamsPerConnection { get; set; } public int HeaderTableSize { get; set; } public int MaxFrameSize { get; set; } public int MaxRequestHeaderFieldSize { get; set; } public int InitialConnectionWindowSize { get; set; } public int InitialStreamWindowSize { get; set; } public TimeSpan KeepAlivePingDelay { get; set; } public TimeSpan KeepAlivePingTimeout { get; set; } }
于HTTP 2相关限制和约束的设置体现在KestrelServerLimits的Http2属性上,该属性返回如上所示的Http2Limits对象。下表对定义在Http2Limits类型中的这些属性所体现的限制约束进行了简单说明。
属性 | 含 义 |
MaxStreamsPerConnection | 连接能够承载的流数量,默认值为100。 |
HeaderTableSize | HPACK报头压缩表的容量,默认值为4096。 |
MaxFrameSize | 帧的最大字节数,有效值在[214~224 – 1]区间范围内,默认值为214(16384)。 |
MaxRequestHeaderFieldSize | 最大请求报头(含报头名称)的最大字节数,默认值为214(16384)。 |
InitialConnectionWindowSize | 连接的初始化请求主体缓存区的大小,有效值在[65535~231]区间范围内,默认为131072。 |
InitialStreamWindowSize | 流的初始化请求主体缓存区的大小,有效值在[65535~231]区间范围内,默认为98304。 |
KeepAlivePingDelay | 如果服务端在该属性设定的时间跨度内没有接收到来自客户端的有效帧,它会主动发送Ping请求确定客户端的是否保持活动状态,默认值为1秒。 |
KeepAlivePingTimeout | 发送Ping请求的超时时间,如果客户端在该时限内一直处于为活动状态,当前连接将被关闭,默认值为20秒。 |
由于HTTP 2的多路复用是在同一个TCP连接上实现的,这样的实现并不“纯粹”,因为它不可能解决由于TCP的“拥塞控制”机制导致的“队头阻塞(Header-Of-Line Blocking)”问题。如果希望在得到并发支持的前提下还能在低延时上有更好的作为,就不得不抛弃TCP。目前被正式确定为HTTP 3的QUIC(Quick UDP Internet Connection)就将TCP替换成了UDP。如果KestrelServer支持HTTP 3,我们可以利用KestrelServerLimits的Http3属性返回的Http3Limits对象都限制约束进行针对性设置。Http3Limits只包含如下这个表示最大请求报头字节数的MaxRequestHeaderFieldSize属性,它的默认值为16384。
public class Http3Limits { public int MaxRequestHeaderFieldSize { get; set;} }
六、其他设置
除了注册的终结点和基于通信的限制约束,KestrelServerOptions配置选项还利用如下的属性承载着其他的设置。
public class KestrelServerOptions { public bool AddServerHeader { get; set; } public bool AllowResponseHeaderCompression { get; set; } public bool AllowSynchronousIO { get; set; } public bool AllowAlternateSchemes { get; set; } public bool DisableStringReuse { get; set; } public Func<string, Encoding> RequestHeaderEncodingSelector { get; set; } public Func<string, Encoding> ResponseHeaderEncodingSelector { get; set; } }
下表对定义在KestrelServerOptions类型中的上述这些属性进行了简单的说明。
属性 | 含 义 |
AddServerHeader | 是否会在回复的响应中自动添加“Server: Kestrel”报头,默认值为True。 |
AllowResponseHeaderCompression | 是否允许对响应报头进行HPACK压缩,默认值为True。 |
AllowSynchronousIO | 是否允许对请求和响应进行同步IO操作,默认值为False,意味这个默认情况下以同步方式读取请求和写入响应都会抛出异常。 |
AllowAlternateSchemes | 是否允许为“:scheme”字段(针对HTTP 2和HTTP 3)提供一个与当前传输不匹配的值(“http”或者“https”),默认值为False。如果将这个属性设置为True,意味着HttpRequest.Scheme属性可能与采用的传输类型不匹配。 |
DisableStringReuse | 创建的字符串是否可以在多个请求中复用。 |
RequestHeaderEncodingSelector | 用于设置某个请求报头采用的编码方式,默认为Utf8Encoding。 |
ResponseHeaderEncodingSelector | 用于设置某个响应报头采用的编码方式,默认为ASCIIEncoding。 |


 具有跨平台能力的KestrelServer是最重要的服务器类型。针对KestrelServer的设置均体现在KestrelServerOptions配置选项上,注册的终结点是它承载的最重要的配置选项。这里所谓的终结点(Endpoint)与“路由”介绍的终结点不是一回事,这里表示的就是服务器在监听请求时绑定的网络地址,对应着一个System.Net.Endpoint对象。
具有跨平台能力的KestrelServer是最重要的服务器类型。针对KestrelServer的设置均体现在KestrelServerOptions配置选项上,注册的终结点是它承载的最重要的配置选项。这里所谓的终结点(Endpoint)与“路由”介绍的终结点不是一回事,这里表示的就是服务器在监听请求时绑定的网络地址,对应着一个System.Net.Endpoint对象。


 蒋金楠,网名Artech,大内老A,知名IT博主, 微软多领域MVP,畅销IT图书作者。
蒋金楠,网名Artech,大内老A,知名IT博主, 微软多领域MVP,畅销IT图书作者。








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)
2012-03-28 ASP.NET路由系统实现原理:HttpHandler的动态映射